Abstract
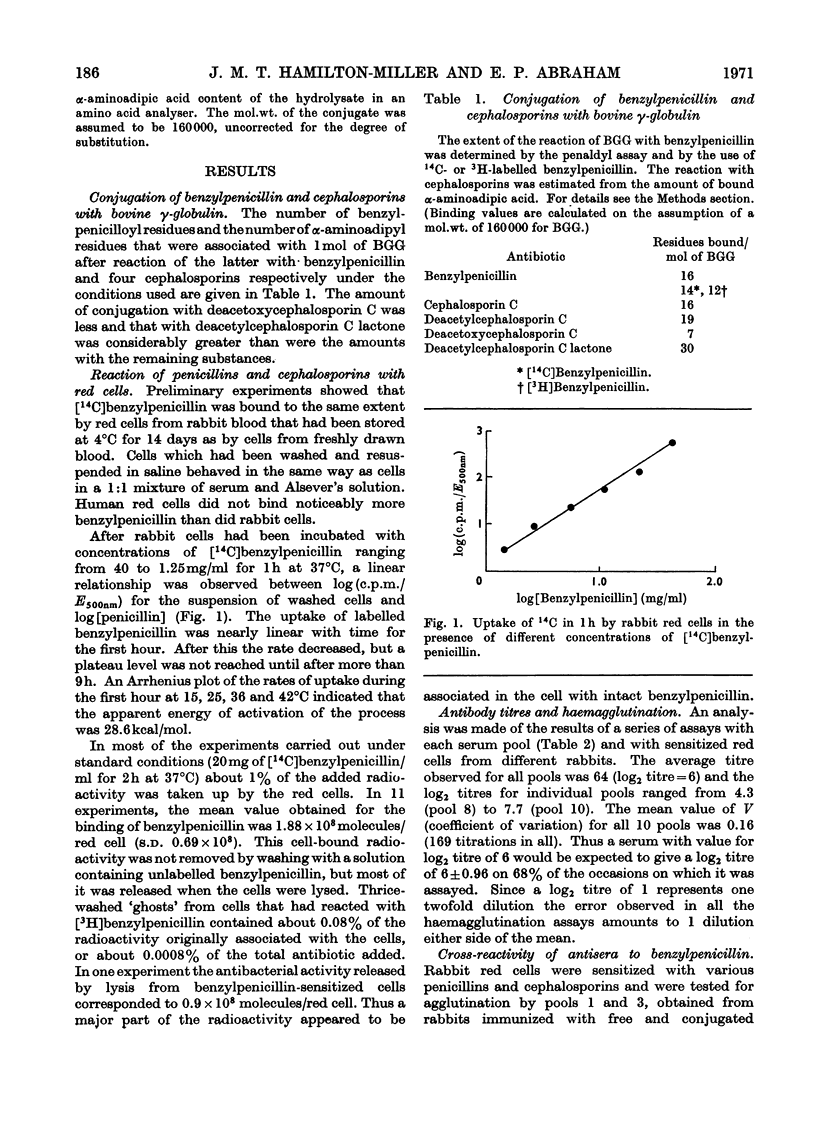
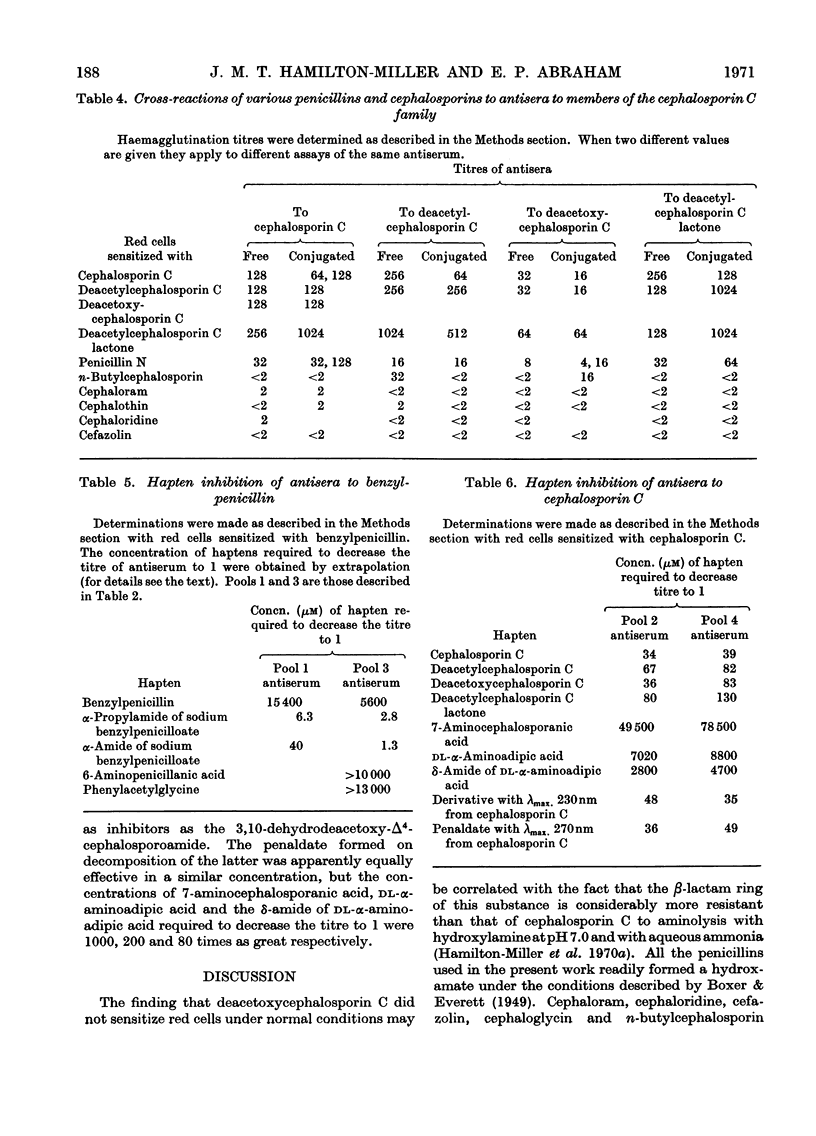
1. Antisera have been produced in rabbits to benzylpenicillin and four members of the cephalosporin C family and to conjugates of these substances with bovine γ-globulin. 2. Deacetoxycephalosporin C reacted less readily and deacetylcephalosporin C lactone more readily with bovine γ-globulin than did benzylpenicillin, cephalosporin C or deacetylcephalosporin C. 3. Antisera to free or conjugated benzylpenicillin agglutinated red cells sensitized with a variety of penicillins, but only reacted to a significant extent with cells sensitized with the cephalosporins tested when the latter contained an N-phenylacetyl or chemically related side chain. 4. Antisera to members of the cephalosporin C family agglutinated cells sensitized with these cephalosporins or with penicillin N, but did not react with cephalosporins whose side chains were chemically unrelated to α-aminoadipic acid. 5. Members of the cephalosporin C family and products of hydrolysis of cephalosporin C behaved as hapten inhibitors of antisera to cephalosporin C, but 7-aminocephalosporanic acid was relatively ineffective. 6. These findings are discussed in relation to differences in the chemical properties of penicillins and cephalosporins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. Purification and some properties of cephalosporin N, a new penicillin. Biochem J. 1954 Sep;58(1):94–102. doi: 10.1042/bj0580094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. Synthesis of D-delta-amino-delta-carboxyvalerylglycine (a degradation product of cephalosporin N) and of DL-delta-amino-delta-carboxyvaleramide. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):266–268. doi: 10.1042/bj0580266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. The structure of cephalesporin C. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:377–393. doi: 10.1042/bj0790377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDRISS M. W., SMITH J. W., STEINMAN H. G. COMMON ANTIGENIC DETERMINANTS OF PENICILLIN G, CEPHALOTHIN AND 6-AMINOPENICILLANIC ACID IN RABBITS. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:696–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor F. R., Dewdney J. M., Weston R. D., Wheeler A. W. The immunogenicity of cephalosporin derivatives and their cross-reaction with penicillin. Immunology. 1966 Jan;10(1):21–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WECK A. L. PENICILLIN ALLERGY: ITS DETECTION BY AN IMPROVED HAEMAGGLUTINATION TECHNIQUE. Nature. 1964 Jun 6;202:975–977. doi: 10.1038/202975a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG R. J., FLICK J. A. The detection of antibodies in hayfever sera by means of hemagglutination. J Immunol. 1956 Oct;77(4):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTHORPE A. J., TOVEY J. E., PARKE J. A., MONCKTON J. C. Pregnancy diagnosis by a one-stage passive haemagglutination inhibition method. Br Med J. 1963 Apr 20;1(5337):1049–1054. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5337.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P. Common antigenic determinants of penicillin G, ampicillin and the cephalosporins demonstrated in men. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(5):428–438. doi: 10.1159/000230058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Newton G. G., Abraham E. P. Products of aminolysis and enzymic hydrolysis of the cephalosporins. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):371–384. doi: 10.1042/bj1160371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Richards E., Abraham E. P. Changes in proton-magnetic-resonance spectra during aminolysis and enzymic hydrolysis of cephalosporins. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):385–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1160385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE B. B., OVARY Z. Studies on the mechanism of the formation of the penicillin antigen. III. The N-(D-alpha-benzylpenicilloyl) group as an antigenic determinant responsible for hypersensitivity to penicillin G. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:875–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEY A. B., HARRIS J. P., BRINKLEY M., LILES B., JACK J. A., CAHAN A. Circulating antibody directed against penicillin. Science. 1958 May 9;127(3306):1118–1119. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3306.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Levytska V. Hapten-specific insoluble immunoabsorbents prepared from hide powder (collagen). J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):647–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. W., DEWECK A. L., KERN M., EISEN H. N. The preparation and some properties of penicillenic acid derivatives relevant to penicillin hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:803–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ R. H., VAUGHAN J. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RESPONSIVENESS OF MAN TO PENICILLIN. JAMA. 1963 Dec 28;186:1151–1157. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63710130002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Jago M., Abraham E. P. Cephalosporinase and penicillinase activities of a beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):739–752. doi: 10.1042/bj0960739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C. H., de Weck A. L. Chemische Aspekte der Penicillin-Allergie: Die direkte Penicilloylierung von epsilon-Aminogruppen durch Penicilline bei pH 7,4. Helv Chim Acta. 1966 Jul 11;49(5):1695–1706. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19660490532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Atsumi T., Horiuchi Y., Mashimo K. Immunological cross-reactivities of cephalothin and its related compounds with benzylpenicillin (penicillin G). Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):419–420. doi: 10.1038/212419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


