Abstract
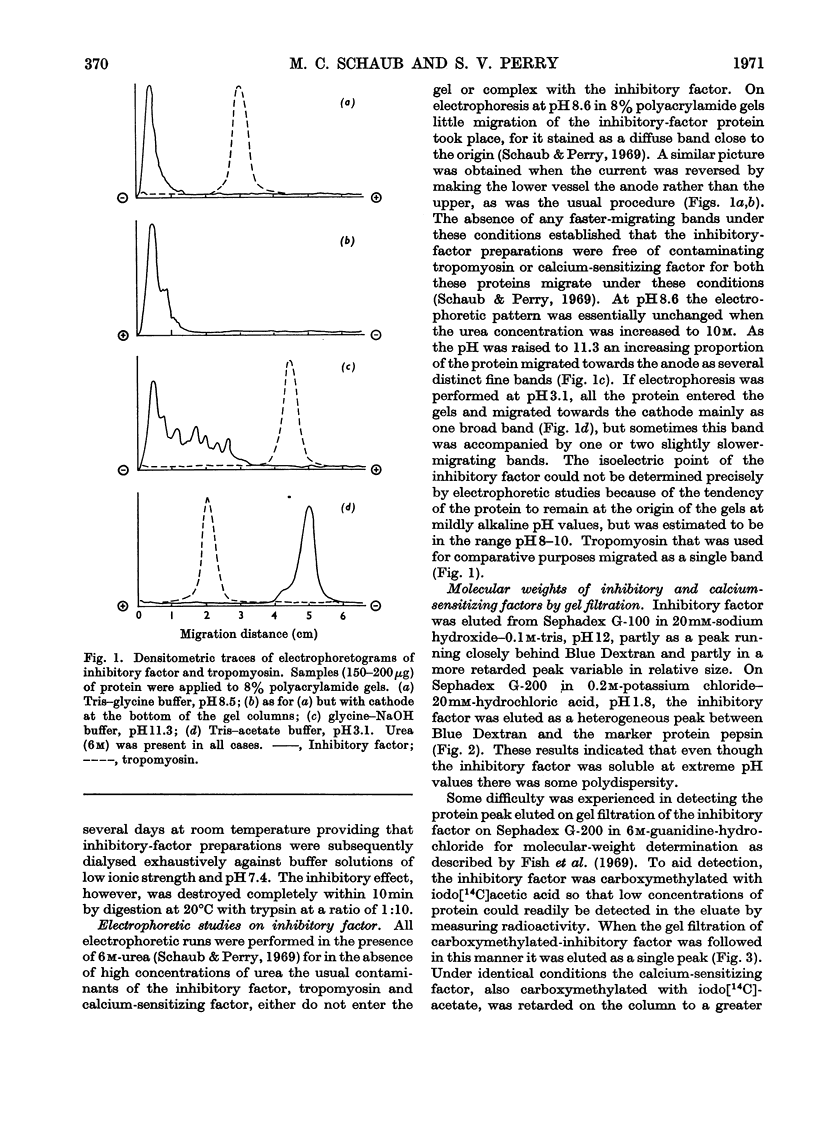
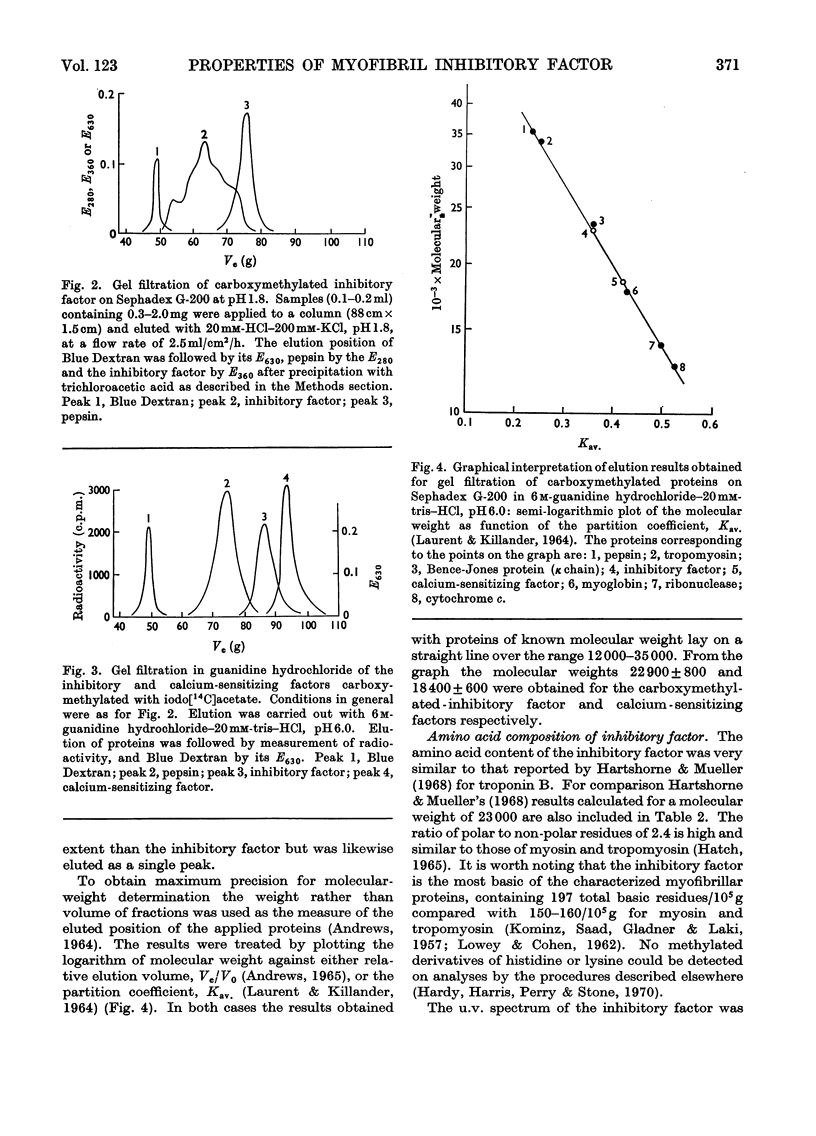
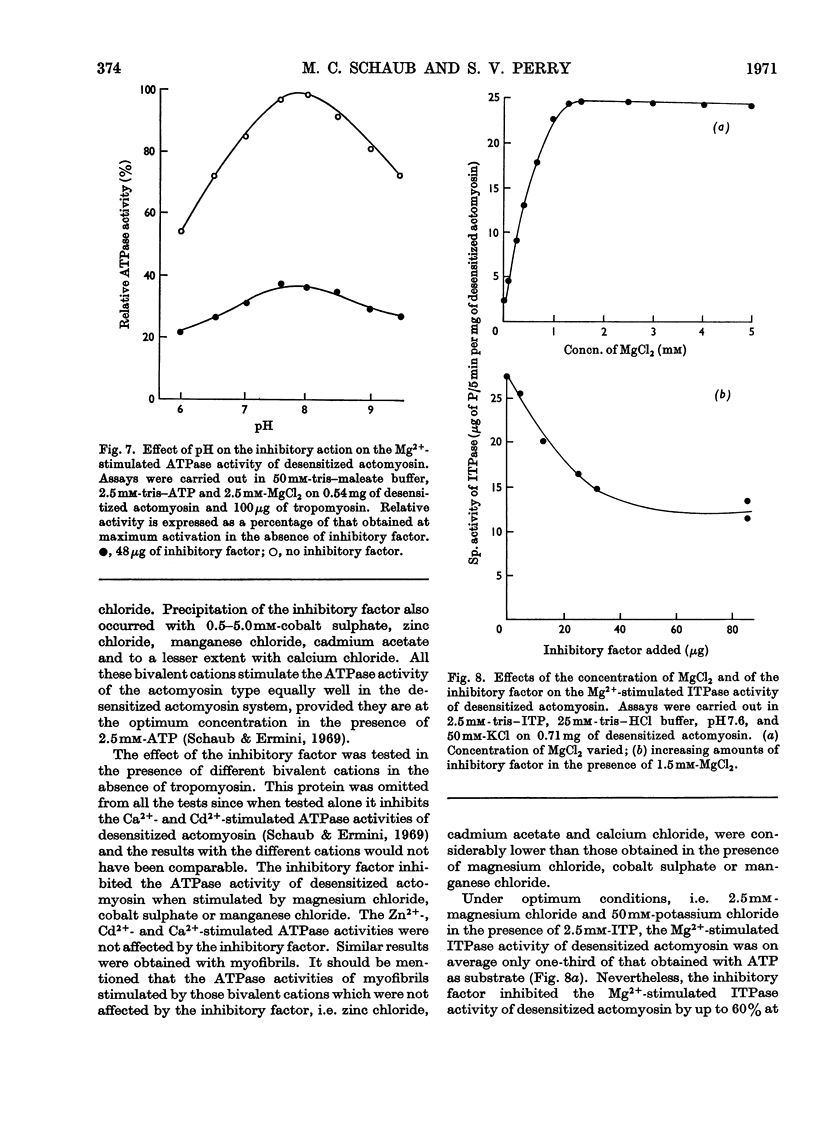
1. Gel-filtration results indicate that the major component of inhibitory-factor preparations isolated by dissociation of the troponin complex consisted of a protein of subunit weight 23000 daltons. By the same procedure a molecular weight of 18000 was obtained for the calcium-sensitizing factor. 2. The inhibitory factor is specific for the actomyosin type of ATPase and ITPase. It is effective on desensitized actomyosin, natural actomyosin and intact myofibrils. 3. For inhibition, the actomyosin ATPase must be stimulated by Mg2+, Ca2+ or Mn2+. The Co2+-, Cd2+- or Zn2+-stimulated ATPases are not affected. 4. Biological activity is stable to treatment with dissociating agents, heat, pH11, pH1 and carboxymethylation. 5. Increasing amounts of actin, but not myosin or tropomyosin, progressively neutralize the inhibitory activity when added to desensitized actomyosin or myofibrils.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY K. End-group assay in some proteins of the keratin-myosin group. Biochem J. 1951 Jun;49(1):23–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0490023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey K. Tropomyosin: a new asymmetric protein component of the muscle fibril. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj0430271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., WILKINSON J. M. AMINO ACID COMPOSITIONS OF HUMAN AND RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULINS AND OF THE FRAGMENTS PRODUCED BY REDUCTION. Biochem J. 1963 Aug;88:228–234. doi: 10.1042/bj0880228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F. Proteins in denaturing solvents: gel exclusion studies. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):906–907. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Mann K. G., Tanford C. The estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel filtration in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4989–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELBACH W. Die Wechselwirkung verschiedener Nukleosidtriphosphate mit Aktomyosin in Gelzustand. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 May;20(2):355–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The sequence of the amino acid residues in performic acid-oxidized ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:633–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. F., Harris C. I., Perry S. V., Stone D. Occurrence and formation of the N epsilon-methyl-lysines in myosin and the myofibrillar proteins. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):653–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1200653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J. Interactions of desensitized actomyosin with tropomyosin, troponin A, troponin B, and polyanions. J Gen Physiol. 1970 May;55(5):585–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H. Fractionation of troponin into two distinct proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90610-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Perry S. V., Davies V. A factor inhibiting the adenosine triphosphatase activity and the superprecipitation of actomyosin. Nature. 1966 Mar 26;209(5030):1352–1353. doi: 10.1038/2091352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Perry S. V., Schaub M. C. A protein factor inhibiting the magnesium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of desensitized actomyosin. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):907–913. doi: 10.1042/bj1040907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Theiner M., Mueller H. Studies on troponin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch F. T. Correlation of amino-acid composition with certain characteristics of proteins. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):777–779. doi: 10.1038/206777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOMINZ D. R., SAAD F., GLADNER J. A., LAKI K. Mammalian tropomyosins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jul;70(1):16–28. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBEATER L., PERRY S. V. The effect of actin on the magnesium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of heavy meromyosin. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:233–239. doi: 10.1042/bj0870233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWEY S., COHEN C. Studies on the structure of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1962 Apr;4:293–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E. Amino acid sequence of chymotryptic peptides from horse heart cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2161–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELAMED M. D., GREEN N. M. AVIDIN. 2. PURIFICATION AND COMPOSITION. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:591–599. doi: 10.1042/bj0890591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F., Metzger H. Characterization of a human macroglobulin. II. Distribution of the disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4740–4745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V., CORSI A. Extraction of proteins other than myosin from the isolated rabbit myofibril. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):5–12. doi: 10.1042/bj0680005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V., ZYDOWO M. The nature of the extra protein fraction from myofibrils of striated muscle. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):220–228. doi: 10.1042/bj0710220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V. The structure and interactions of myosin. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:325–381. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRAM E., MOORE S., BIGWOOD E. J. Chromatographic determination of cystine as cysteic acid. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):33–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0570033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ A., BACHELARD H. S., McIL WAIN H. The sodium-stimulated adenosine-triphosphatase activity and other properties of cerebral microsomal fractions and subfractions. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:626–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0840626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Ermini M. Effect of bivalent cations on the adenosine triphosphatase of actomyosin and its modification by tropomyosin and troponin. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):777–783. doi: 10.1042/bj1110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Hartshorne D. J., Perry S. V. The adeonosine-triphosphatase activity of desensitized actomyosin. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):263–269. doi: 10.1042/bj1040263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Perry S. V. The relaxing protein system of striated muscle. Resolution of the troponin complex into inhibitory and calcium ion-sensitizing factors and their relationship to tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1042/bj1150993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. C. Effects of salts of monovalent ions on the adenosine triphosphatase activities of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1142–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. Parallel response of myofibrillar contraction and relaxation to four different nucleoside triphophates. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):781–791. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. Parallel response of myofibrillar contraction and relaxation to four different nucleoside triphophates. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):781–791. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods E. F. Comparative physicochemical studies on vertebrate tropomyosins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4336–4344. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods E. F. Molecular weight and subunit structure of tropomyosin B. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2859–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods E. F. The dissociation of tropomyosin by urea. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):581–584. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


