Abstract
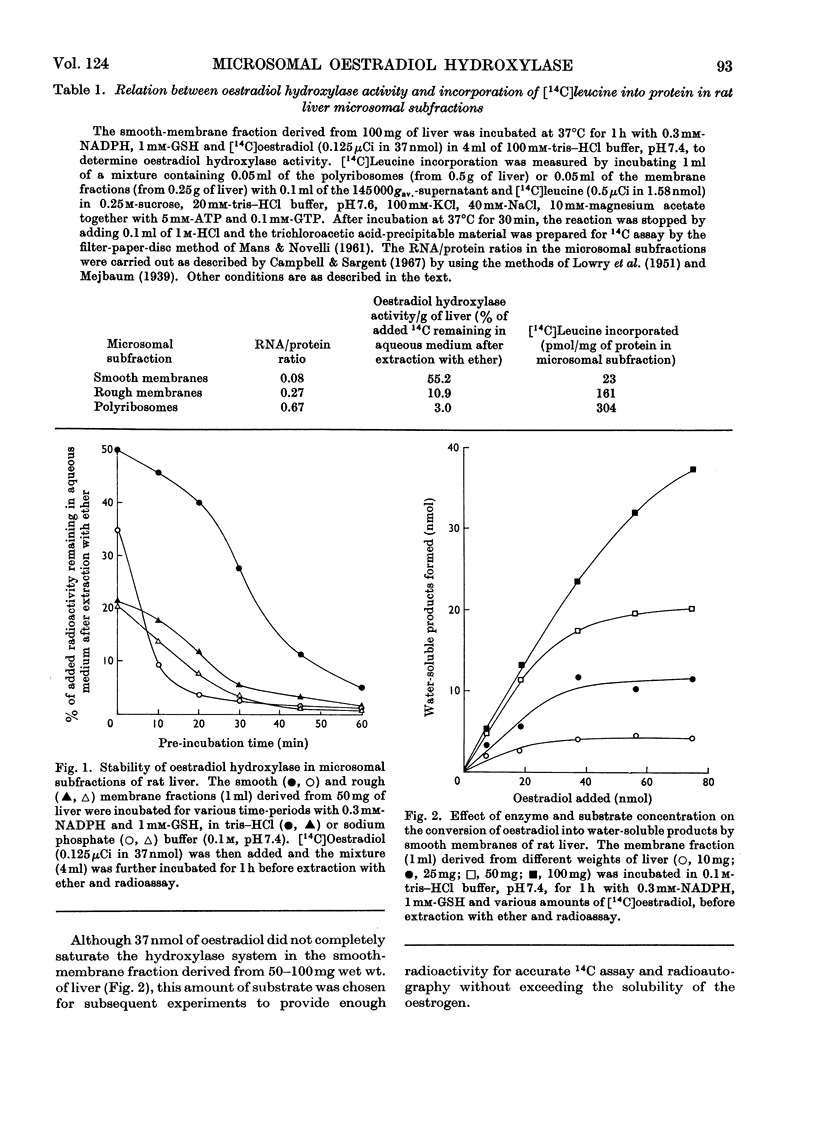
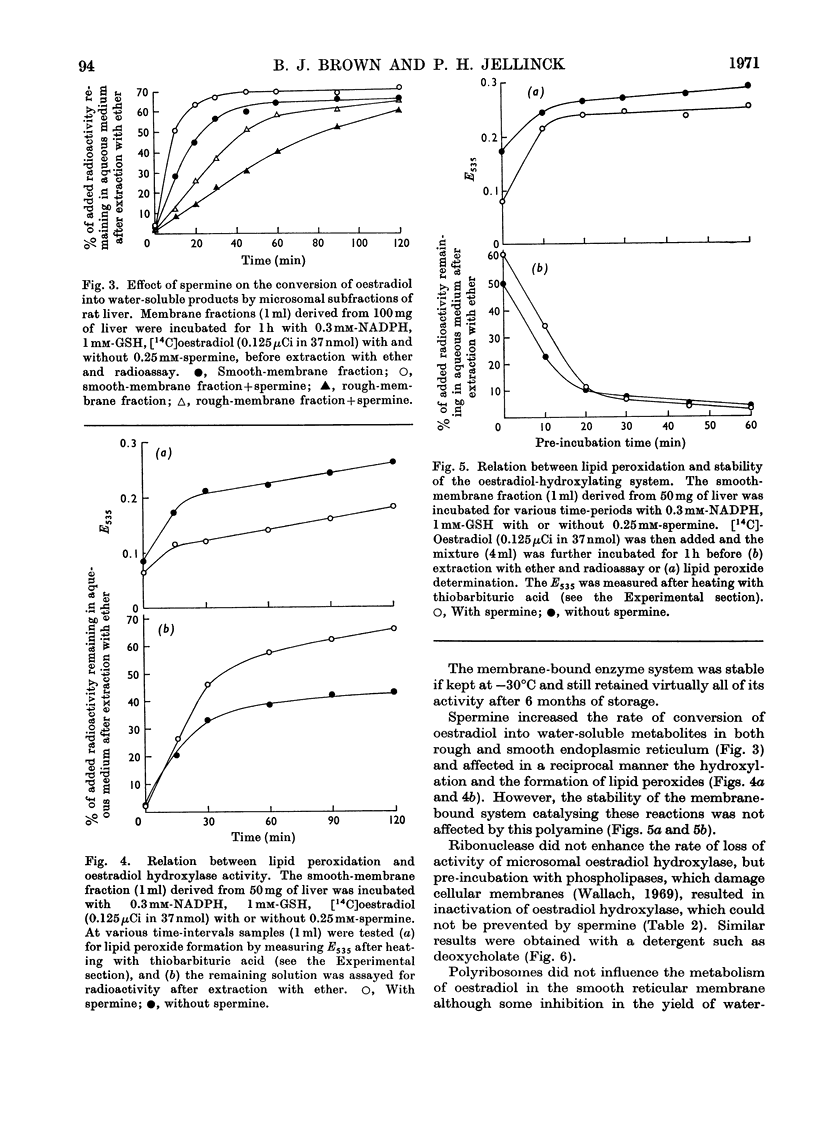
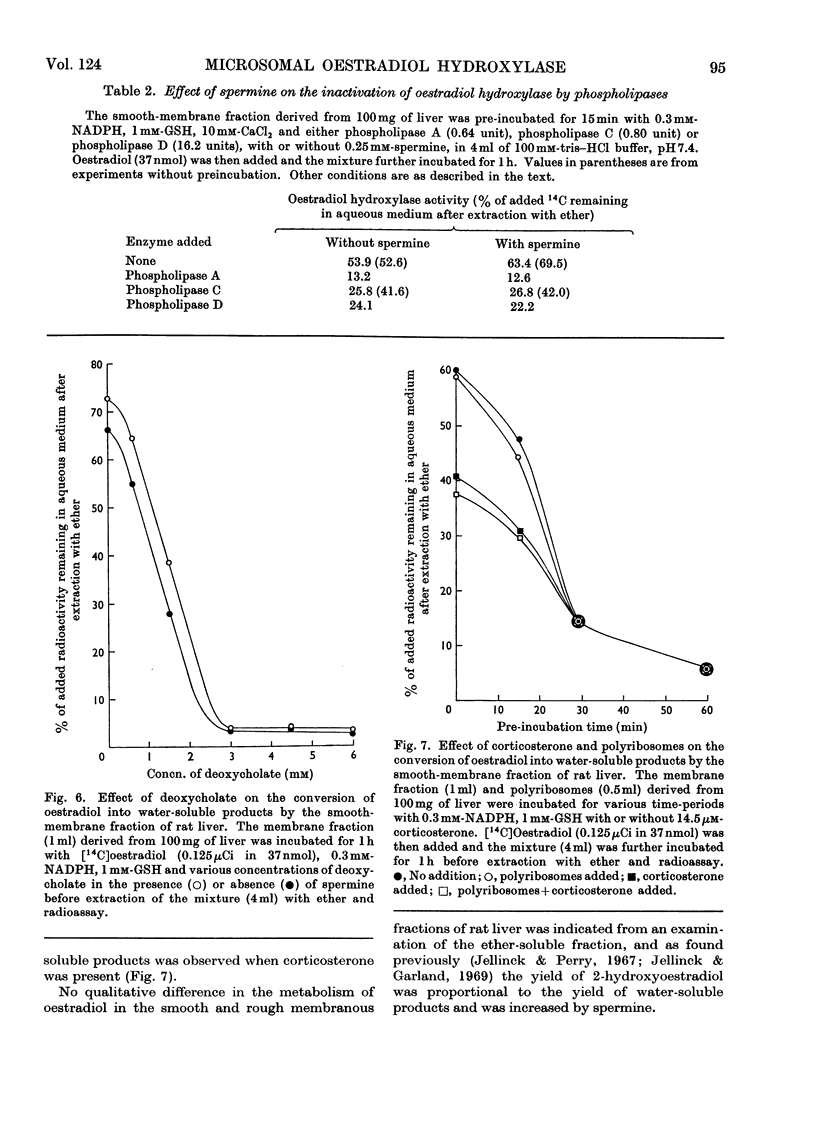
1. Oestradiol hydroxylase activity, as measured by the formation of water-soluble products, was significantly higher in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver than in the rough membrane. 2. The isolated membrane fractions retained their activity for at least 6 months if stored at −30°C and were more stable in tris–HCl than in sodium phosphate buffer. 3. The stability of the oestradiol-hydroxylating system was inversely related to lipid peroxidation and was decreased by phospholipases and deoxycholate, which damage the reticular membranes. Ribonuclease had no effect on this system. 4. Added polyribosomes did not influence the metabolism of oestradiol in the smooth membranes but some inhibition in the yield of water-soluble metabolites was produced by corticosterone. 5. The effect of spermine on microsomal hydroxylation was investigated. It is proposed that this polyamine acts either by direct activation of the enzyme complex or by inhibition of the lipid peroxidase pathway in a linked system rather than by stabilization of the reticular membranes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H., Bont W. S., de Vries M., Benedetti E. L. Isolation and properties of polyribosomes and fragments of the endoplasmic reticulum from rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):177–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1030177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINGOLD D. S., DAVIS B. D. Paradoxical effect of streptomycin, kanamycin and neomycin on Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:787–789. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90861-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillette J. R. Biochemistry of drug oxidation and reduction by enzymes in hepatic endoplasmic reticulum. Adv Pharmacol. 1966;4:219–261. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram T. E., Rogers L. A., Fouts J. R. Further studies on the metabolism of drugs by subfractions of hepatic microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Mar;155(3):479–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman J. L., Gram T. E., Gigon P. L., Gillette J. R. The distribution of the components of mixed-function oxidase between the rough and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of liver cells. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):407–412. doi: 10.1042/bj1100407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Rabin B. R., Williams D. J. Role of steroid hormones in the interaction of polysomes with endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):371–372. doi: 10.1038/224371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Cox J. Effect of spermine on the kinetics of estradiol hydroxylation by rat liver microsomes. Experientia. 1970 Oct 15;26(10):1066–1066. doi: 10.1007/BF02112675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Garland M. Endocrine control of the metabolism of oestradiol by rat liver microsomes. J Endocrinol. 1969 Sep;45(1):75–81. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0450075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Lewis J., Boston F. Further evidence for the formation of an estrogen-peptide conjugate by rat liver in vitro. Steroids. 1967 Sep;10(3):329–346. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(67)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Perry G. Effect of polyamines on the metabolism of [16-14C]estradiol by rat-liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinck P. H., Woo J. Changes in oestrogen metabolism induced in rat liver microsomes by subcutaneous pellets of oestrone and testosterone. J Endocrinol. 1967 Sep;39(1):99–104. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAZIER C., JELLINCK P. H. INHIBITION OF C-ESTRONE METABOLISM IN RAT LIVER MICROSOMES BY 2-HYDROXYESTROGENS AND RELATED COMPOUNDS. Can J Biochem. 1965 Feb;43:281–290. doi: 10.1139/o65-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann W. D., Breuer H. Stoffwechsel von Ostrogenen in der Rattenleber vor und nach Kastration sowie nach Verabreichung verschiedener Steroidhormone. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Feb;350(2):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL F. L., DAVIES R. E. The isolation and estimation of the steroid oestrogens in placental tissue. Biochem J. 1954 Apr;56(4):690–698. doi: 10.1042/bj0560690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Brown B. J. Protein synthesis by cerebral cortex polysomes: characterization of the system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):387–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90595-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks F., Hecker E. Stoffwechsel und Wirkungsmechanismus de Ostrogene. X. Beziehungen zwischen Ostrogenstoffwechsel und Lipidperoxydation in Rattenlebermikrosomen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 May;349(5):523–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina A., Telaranta T. Association of polyamines and RNA in isolated subcellular particles from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 29;138(1):200–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEKEVITZ P., PALADE G. E. Cytochemical study on the pancreas of the guinea pig. VII. Effects of spermine on ribosomes. J Cell Biol. 1962 May;13:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.13.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel H. W., Lu A. Y., Heidema J., Coon M. J. Phosphatidylcholine requirement in the enzymatic reduction of hemoprotein P-450 and in fatty acid, hydrocarbon, and drug hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4851–4854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBUR K. M., BERNHEIM F., SHAPIRO O. W. The thiobarbituric acid reagent as a test for the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by various agents. Arch Biochem. 1949 Dec;24(2):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. J., Rabin B. R. The effects of aflatoxin B(1) and steroid hormones on polysome binding to microsomal membranes as measured by the activity of an enzyme catalysing disulphide interchange. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. D. Lipid peroxide formation in microsomes. General considerations. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):315–324. doi: 10.1042/bj1130315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. D. Lipid peroxide formation in microsomes. Relationship of hydroxylation to lipid peroxide formation. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):333–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1130333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. D. Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj0990667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


