Abstract
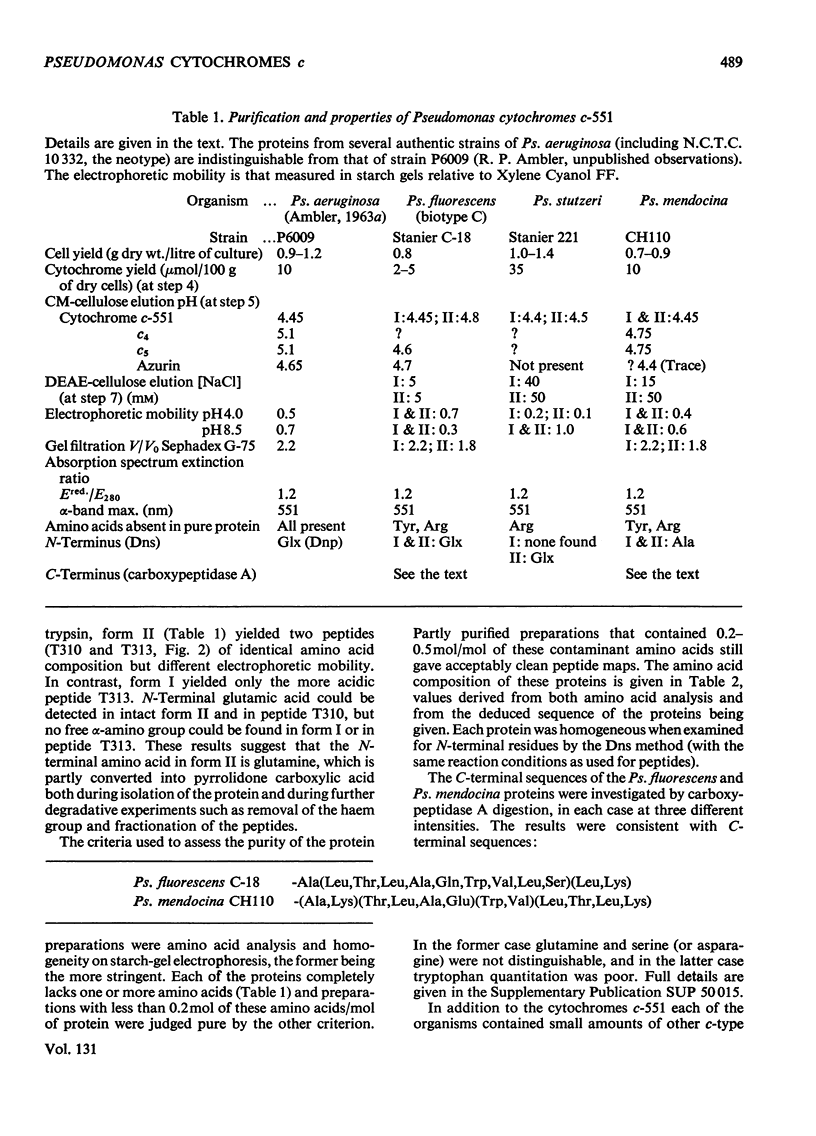
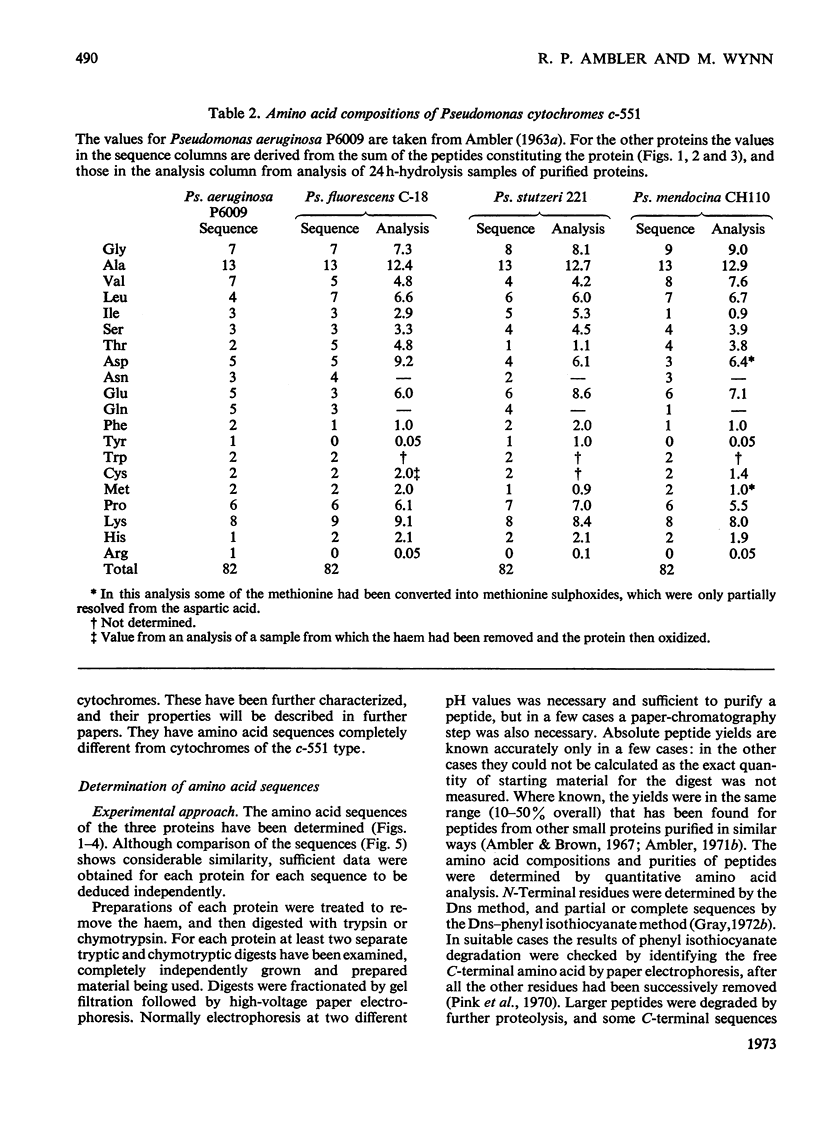
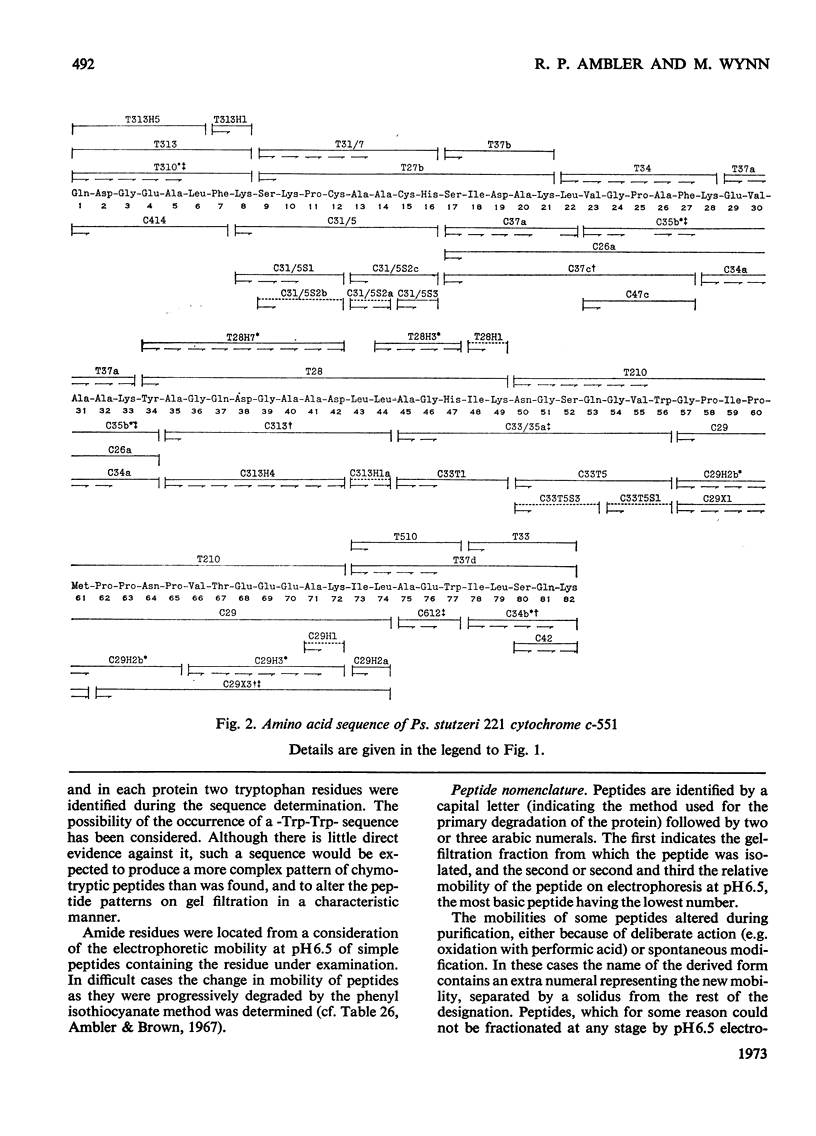
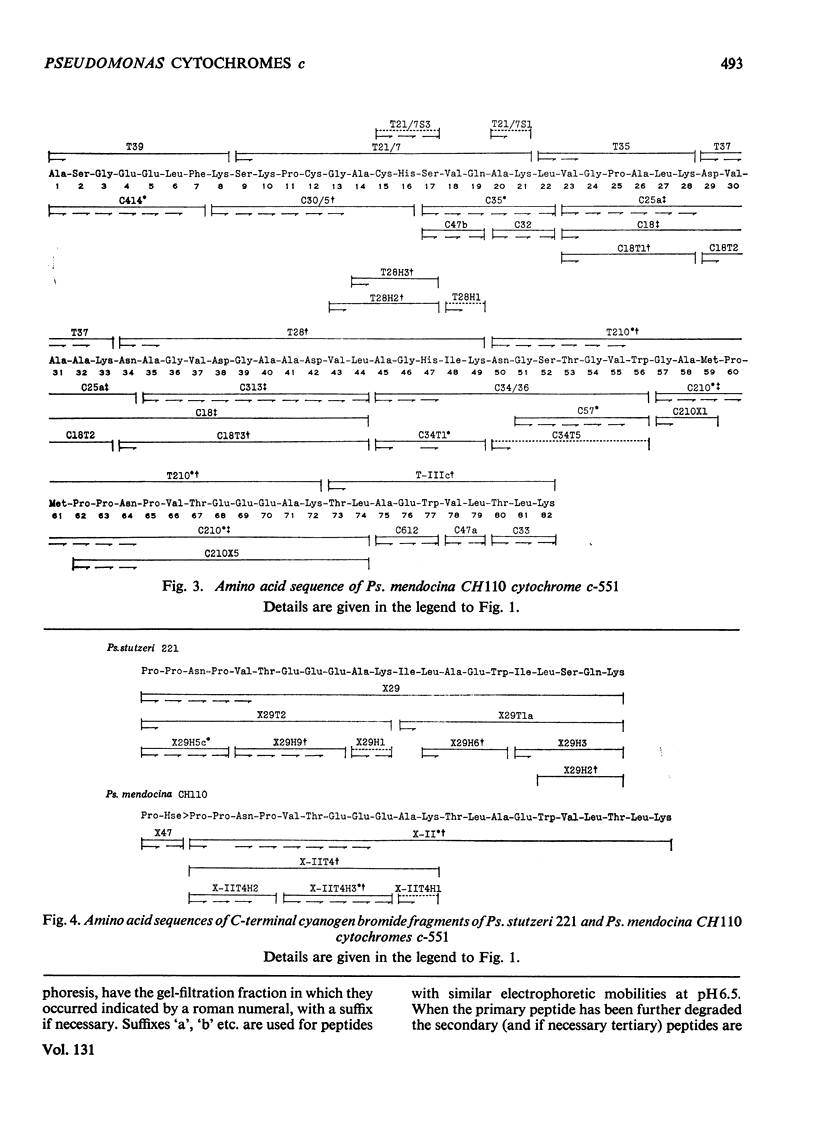
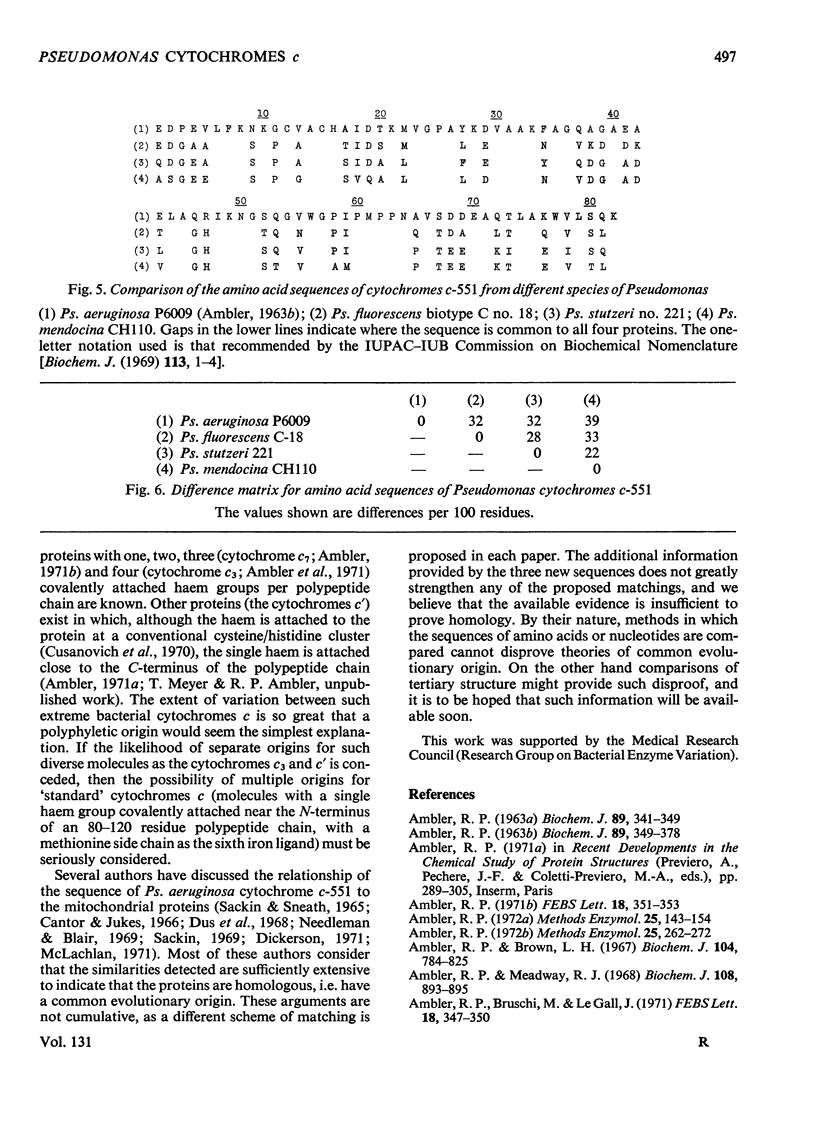
The amino acid sequences of the cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas have been determined. Each resembles the protein from Pseudomonas strain P6009 (now known to be Pseudomonas aeruginosa, not Pseudomonas fluorescens) in containing 82 amino acids in a single peptide chain, with a haem group covalently attached to cysteine residues 12 and 15. In all four sequences 43 residues are identical. Although by bacteriological criteria the organisms are closely related, the differences between pairs of sequences range from 22% to 39%. These values should be compared with the differences in the sequence of mitochondrial cytochrome c between mammals and amphibians (about 18%) or between mammals and insects (about 33%). Detailed evidence for the amino acid sequences of the proteins has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50015 at the National Lending Library for Science and Technology, Boston Spa, Yorks. LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies can be obtained on the terms indicated in Biochem. J. (1973), 131, 5.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMBLER R. P. THE PURIFICATION AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:341–349. doi: 10.1042/bj0890341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Brown L. H. The amino acid sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens azurin. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):784–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1040784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Bruschi M., Le Gall J. The amino acid sequence of cytochrome c(3) from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (strain el agheila Z, NCIB 8380). FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80483-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Meadway R. J. The use of thermolysin in amino acid sequence determination. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):893–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1080893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The amino acid sequence of cytochrome c-551.5 (Cytochrome c(7)) from the green photosynthetic bacterium Chloropseudomonas ethylica. FEBS Lett. 1971 Nov 1;18(2):351–353. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80484-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKER S. A., BOURNE E. J., STACEY M., WARD R. B. Some paper-chromatographic studies with Aspergillus niger '152' transfructosylase. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):60–62. doi: 10.1042/bj0690060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Jukes T. H. The repetition of homologous sequences in the polypetide chains of certain cytochromes and globins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):177–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusanovich M. A., Tedro S. M., Kamen M. D. Pseudomonas denitrificans cytochrome cc'. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):557–570. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Glazer A. N., Smith E. L. Presence and location of an unusual amino acid, epsilon-N-trimethyllysine, in cytochrome c of wheat germ and Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1385–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Sequence and structure homologies in bacterial and mammalian-type cytochromes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structure and history of an ancient protein. Sci Am. 1972 Apr;226(4):58–passim. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0472-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dus K., Sletten K., Kamen M. D. Cytochrome c2 of Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Complete amino acid sequence and phylogenetic relationships. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5507–5518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Hettinger T. P., Harbury H. A. Pseudomonas cytochrome c. II. Effect of modification of the methionine residues. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):713–720. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON P. B. AMINO-ACIDS ON HANDS. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:284–285. doi: 10.1038/205284b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIO T., HIGASHI T., SASAGAWA M., KUSAI K., NAKAI M., OKUNUKI K. Preparation of crystalline Pseudomonas cvtochrome c-551 and its general properties. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77:194–201. doi: 10.1042/bj0770194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio T., Kamen M. D. Bacterial cytochromes. II. Functional aspects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:399–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIGSBERG W., HILL R. J. The structure of human hemoglobin. III. The sequence of amino acids in the tryptic peptides of the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2547–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen M. D., Horio T. Bacterial cytochromes. I. Structural aspects. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:673–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Shidara S. Components of cytochrome system and purification and some properties of c-type cytochromes of a denitrifying bacterium, Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Biochem. 1969 Mar;65(3):351–360. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Blair T. T. Homology of Pseudomonas cytochrome c-551 with eukaryotic c-cytochromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1227–1233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Solánes R. E., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: the properties of the Pseudomonas stutzeri group. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):215–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink J. R., Buttery S. H., De Vries G. M., Milstein C. Human immunoglobulin subclasses. Partial amino acid sequence of the constant region of a gamma 4 chain. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):33–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1170033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHODES M. E. The characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens with the aid of an electronic computer. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jul;25:331–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels and its application to studies of serum proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:65–113. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60609-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Hartley B. S. Amino-acid sequence of porcine pancreatic elastase and its homologies with other serine proteinases. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):802–806. doi: 10.1038/225802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. W., Notton B. A., Richardson M., Boulter D. The amino acid sequence of cytochrome c from Abutilon theophrasti Medic. and Gossypium barbadense L. (cotton). Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):787–791. doi: 10.1042/bj1240787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN NIEL C. B., ALLEN M. B. A note on Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Bacteriol. 1952 Sep;64(3):413–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.3.413-422.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEY S. G., WATSON J. Trypsin-catalysed transpeptidations. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):529–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0570529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


