Abstract
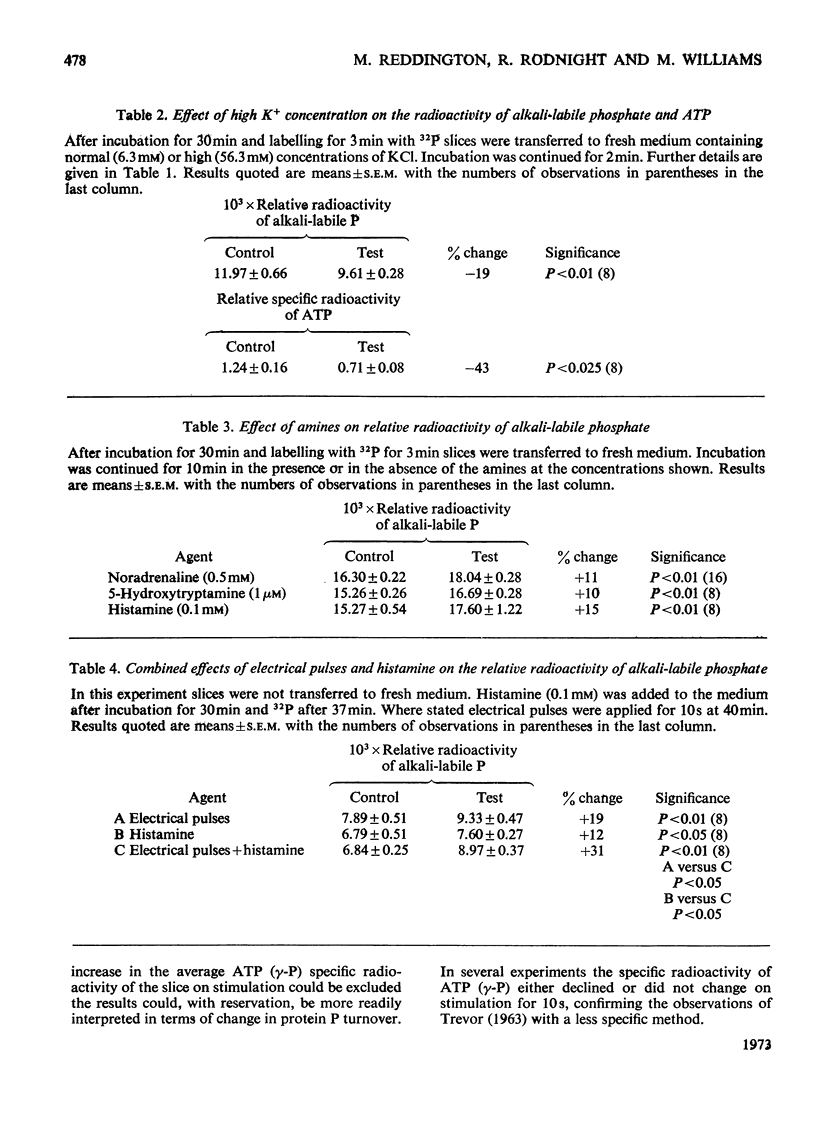
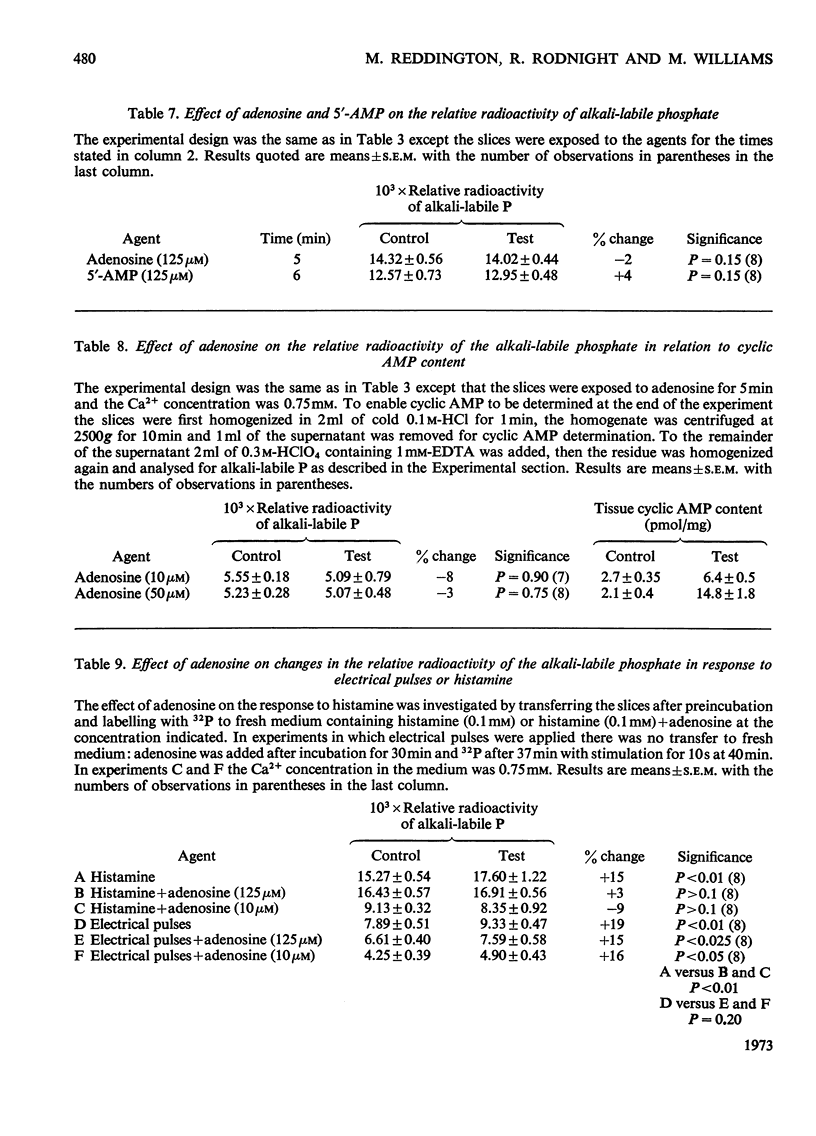
1. The effect of various agents on the turnover of protein-bound phosphorus in respiring slices of cerebral cortex was studied. 2. Confirming previous work turnover was increased by the application of electrical pulses for 10s to the tissue. 3. Turnover was also increased by exposure of the slices for 10min to noradrenaline (0.5mm), 5-hydroxytryptamine (1μm) and histamine (0.1mm). 4. When slices were stimulated by electrical pulses in the presence of histamine the increase in turnover was the sum of the responses given by each agent above, suggesting that different phosphorylating systems were involved. 5. Tetrodotoxin (0.5μm) blocked the increased turnover due to electrical pulses, but not that due to histamine. Tetrodotoxin also prevented the increase in tissue cyclic AMP content caused by the application of electrical pulses. 6. Phosphoprotein turnover was not affected by adenosine, despite the increase in tissue cyclic AMP content given by this agent. 7. Adenosine blocked the phosphoprotein response to histamine, but did not affect the response to electrical pulses. 8. The results are discussed in relation to the hypothesis that the stimulation of protein phosphorus turnover by electrical pulses is secondary to the release of cyclic AMP in the tissue.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blankenship J. E. Action of tetrodotoxin on spinal motoneurons of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Mar;31(2):186–194. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloedel J., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release at the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):49–50. doi: 10.1038/212049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin M., Rivkin I., Mamrak F., Samaniego S. G., Hess S. M. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors as mediators of accumulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in specific areas of guinea pig brain. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3037–3041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Perkins J. P. Regulation of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate concentration in cultured human astrocytoma cells by catecholamines and histamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2757–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colomo F., Erulkar S. D. Miniature synaptic potentials at frog spinal neurones in the presence of tertodotoxin. J Physiol. 1968 Nov;199(1):205–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., SASAOKA T., HOSOYA Y. Effects of tetrodotoxin on the neuromuscular junction. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Jun 25;9(2):143–152. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALD P. J. The incorporation of phosphate into cerebral phosphoportein promoted by electrical impulses. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):659–663. doi: 10.1042/bj0660659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Maeno H., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of endogenous protein of rat brain by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7731–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Rodnight R. Protein-bound phosphorylserine in acid hydrolysates of brain tissue. The determination of ( 32 P)phosphorylserine by ion-exchange chromatography and electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj1210597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W., McIlwain H. The effect of electrical stimulation upon the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in isolated cerebral tissue. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. Studies on adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in rabbit cerebral cortex. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Rall T. W. The influence of chemical agents on the accumulation of adenosine 3',5'-Phosphate in slices of rabbit cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;4(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):997–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):8–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. I., Chase T. N. Neurohumoral mechanisms in the brain slice. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1970;8:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Harvery J. A., Rodriguez G. Tetrodotoxin on the sodium and other ions of cerebral tissues, excited electrically and with glutamate. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):363–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Metabolism of ( 14 C)adenine and derivatives by cerebral tissues, superfused and electrically stimulated. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):965–973. doi: 10.1042/bj1260965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumphrey A. M. Incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate into brain-slice phospholipids and their precursors. Effects of electrical stimulation. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;112(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1120061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Hamprecht B., Daly J. W. Accumulation of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in clonal glial cells: labeling of intracellular adenine nucleotides with radioactive adenine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Creveling C. R., Daly J. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in brain slices: stimulation by batrachotoxin, ouabain, veratridine, and potassium ions. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;6(2):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Daly J. Formation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate from adenosine in brain slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Tanaka S., Kodama T. Adenosine kinase of mammalian brain: partial purification and its role for the uptake of adenosine. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):687–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THRELFALL C. J. An analytical procedure for the acid-soluble phosphorus compounds in rat-skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):694–699. doi: 10.1042/bj0650694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVOR A. J., RODNIGHT R. THE SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF CEREBRAL PHOSPHOPROTEINS SENSITIVE TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:889–896. doi: 10.1042/bj0950889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Rodnight R., Carrera D. Determination of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in cerebral tissues by saturation analysis. Assessment of a method using a binding protein from ox muscle. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):113–121. doi: 10.1042/bj1290113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Rodnight R. Protein kinase activity in membrane preparations from ox brain. Stimulation of intrinsic activity by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1320483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Rodnight R. Stimulation by cyclic AMP of intrinsic protein kinase activity in ox brain membrane preparations. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):187–188. doi: 10.1038/225187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Rodnight R. Turnover of protein-bound phosphorylserine in membrane preparations from ox brain catalysed by intrinsic kinase and phosphatase activity. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):393–406. doi: 10.1042/bj1240393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


