Abstract
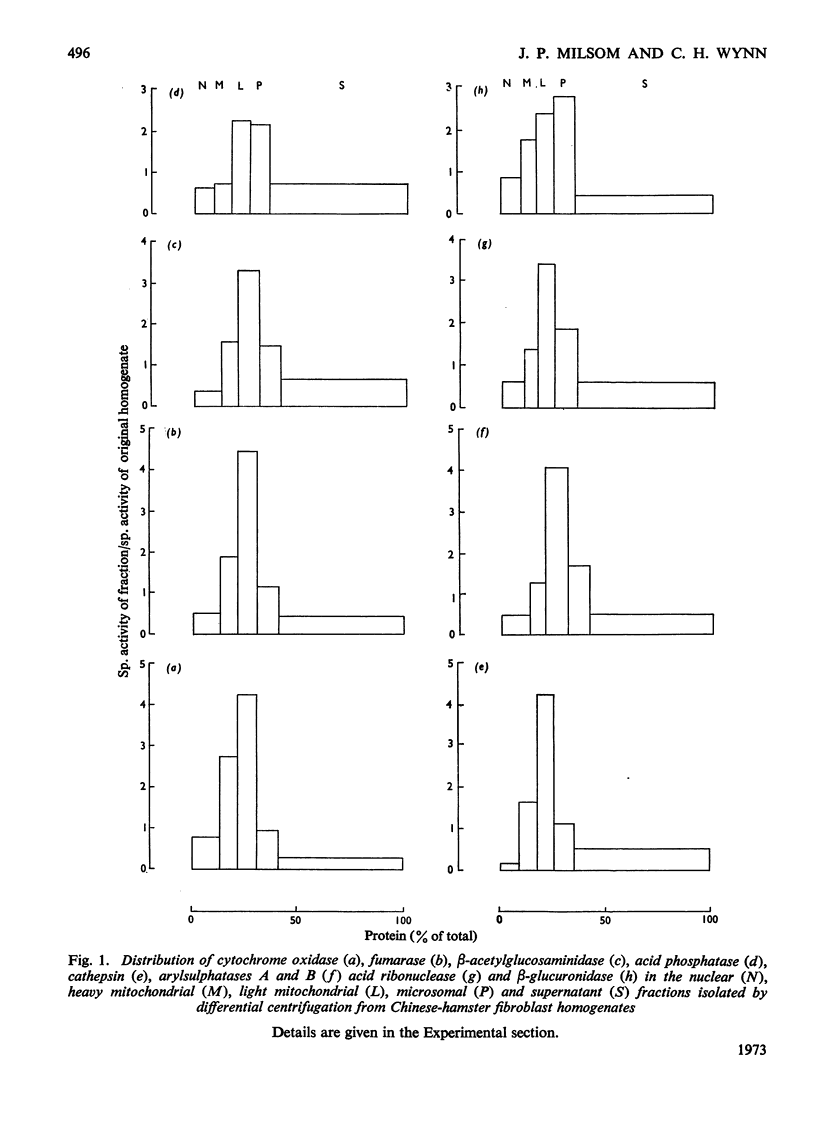
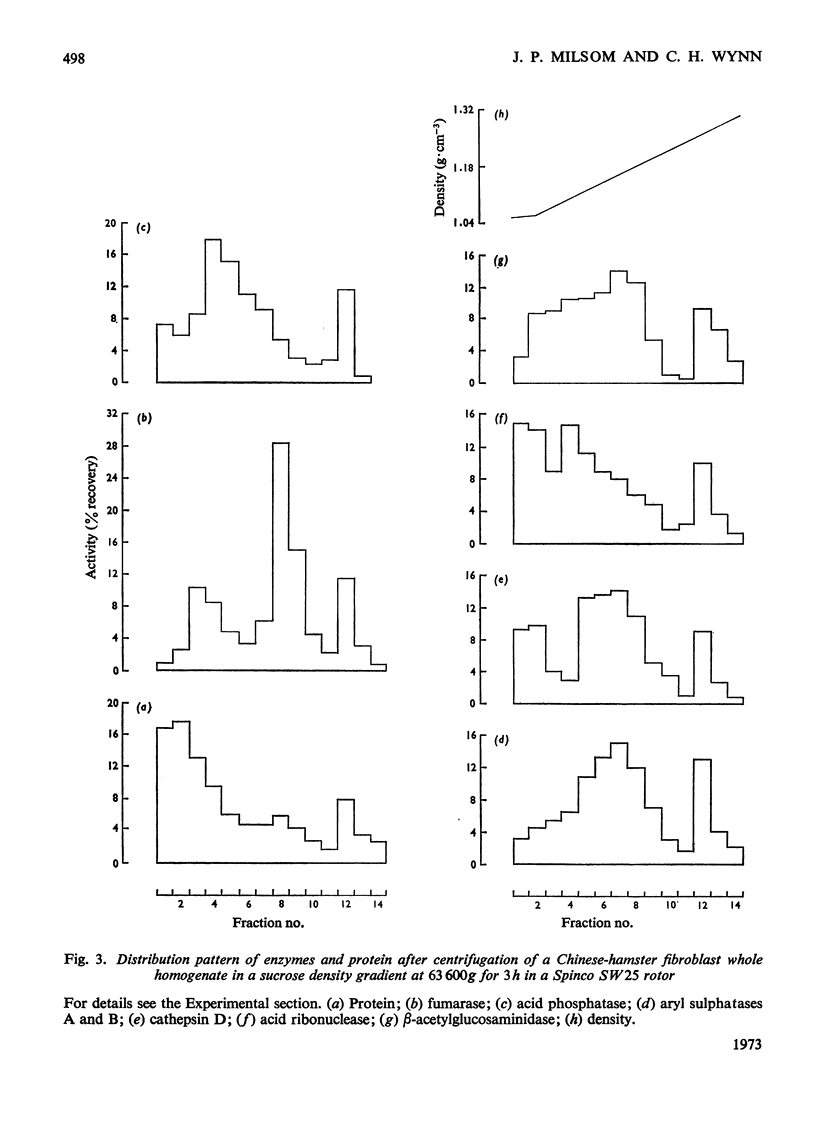
1. Chinese-hamster ovary fibroblasts were cultured to provide a homogeneous cell population. Homogenates obtained from these cells were fractionated by centrifugation techniques and the resulting fractions were analysed for protein and for enzymes representative of certain subcellular particles. 2. Unlike those in rat liver homogenates, the mitochondrial and lysosomal populations proved impossible to separate by differential centrifugation owing to the similarity of their sedimentation properties. Their resolution was possible by using isopycnic centrifugation in a continuous sucrose density gradient. 3. The mitochondrial population equilibrated at a density of 1.17g·cm−3 as in rat liver homogenates. However, the lysosomal population equilibrated at a lower rather than a higher density position than the mitochondria and the probable reasons for this are discussed. 4. The lysosomal population subdivided into two groups characterized by differences in acid hydrolase content and equilibrium densities. The fraction with a density of 1.15g·cm−3 contained the majority of arylsulphatases A and B, of cathepsin and of β-acetylglucosaminidase activities, whereas that with a density of 1.09g·cm−3 contained the majority of the acid phosphatase and acid ribonuclease activities. The probable division of the lysosomal population of a single cell into a number of distinguishable subgroups is suggested.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPELMANS F., WATTIAUX R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 5. The association of acid phosphatase with a special class of cytoplasmic granules in rat liver. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):438–445. doi: 10.1042/bj0590438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayad S. R., Bonsall R. W., Hunt S. A simple method for the production of accurate linear gradients using a contant-speed peristalic pump. Anal Biochem. 1968 Mar;22(3):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAUDHUIN P., BERLEUR A. N., DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R. Tissue fractionation studies. VIII. Cellular localization of bound enzymes. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):608–612. doi: 10.1042/bj0630608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUFAY H., BENDALL D. S., BAUDHUIN P., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 12. Intracellular distribution of some dehydrogenases, alkaline deoxyribonuclease and iron in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:623–628. doi: 10.1042/bj0730623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cathepsin D. Purification of isoenzymes from human and chicken liver. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1170601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Lysosomal acid proteinase of rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1040601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., Finkenstaedt J. T., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. I. The measurement of hydrolytic activities in whole homogenates. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):325–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. II. Intracellular distribution of acid hydrolases. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):339–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. III. Influence of various treatments of the animals on the distribution of acid hydrolases. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):349–364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., WIENER E. THE PARTICULATE HYDROLASES OF MACROPHAGES. I. COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY, ISOLATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:991–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R., BAUDHUIN P. Distribution of enzymes between subcellular fractions in animal tissues. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1962;24:291–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470124888.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B., THOMAS J. Studies on sulphatases. IX. The arylsulphatases of mammalian liver. Biochem J. 1955 Jan;59(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0590029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANETTO R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 4. Comparative study of the binding of acid phosphatase, beta-glucuronidase and cathepsin by rat-liver particles. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):433–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0590433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. CLONAL GROWTH OF MAMMALIAN CELLS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:288–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNRO T. R., DANIEL M. R., DINGLE J. T. LYSOSOMES IN CHINESE HAMSTER FIBROBLASTS IN CULTURE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Sep;35:515–530. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Spectrophotometric measurements of the enzymatic formation of fumaric and cis-aconitic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY A. B. The sulphatase of ox liver. I. The complex nature of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):12–15. doi: 10.1042/bj0530012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Y. E., Cerny E. A. Studies on rat liver ribonucleases. 3. Further studies on heterogeneity of liver lysosomes--intracellular localization of acid ribonuclease and acid phosphatase in rats of various ages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagni N., De Bernard B. Lysosomal enzyme activity in rat and beef skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 12;170(1):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G., Jacques P. Studies on bone enzymes. Distribution of acid hydrolases, alkaline phenylphosphatase, cytochrome oxidase and catalase in subcellular fraction of bone tissue homogenates. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):389–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0970389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. Studies on bone enzymes. The activation and release of latent acid hydrolases and catalase in bone-tissue homogenates. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj0970393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


