Abstract
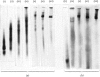
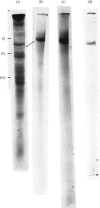
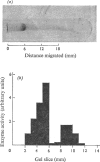
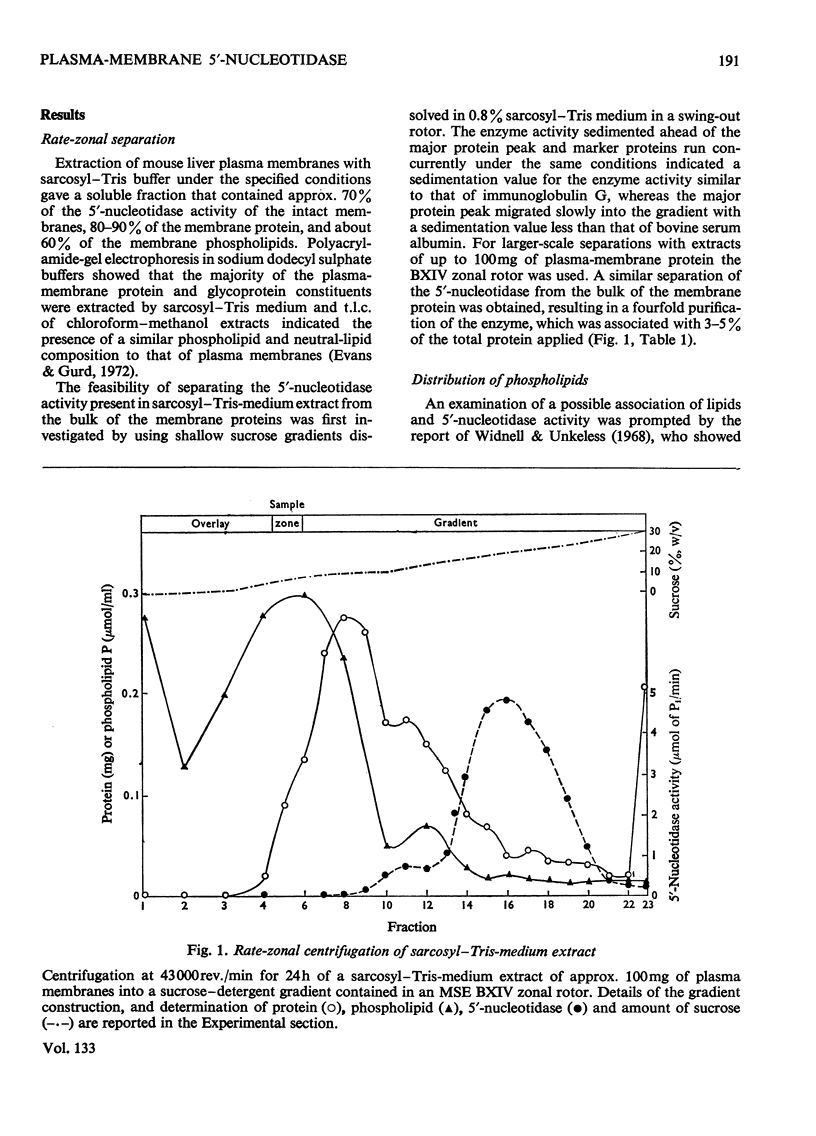
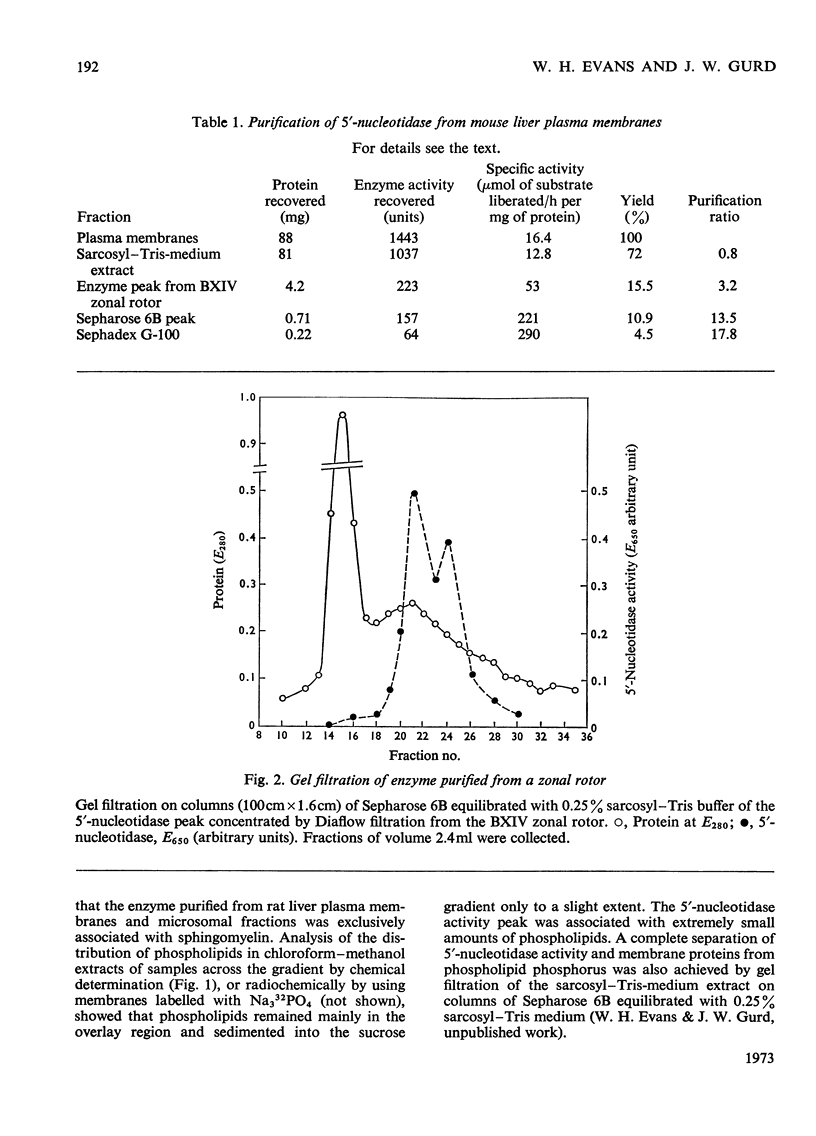
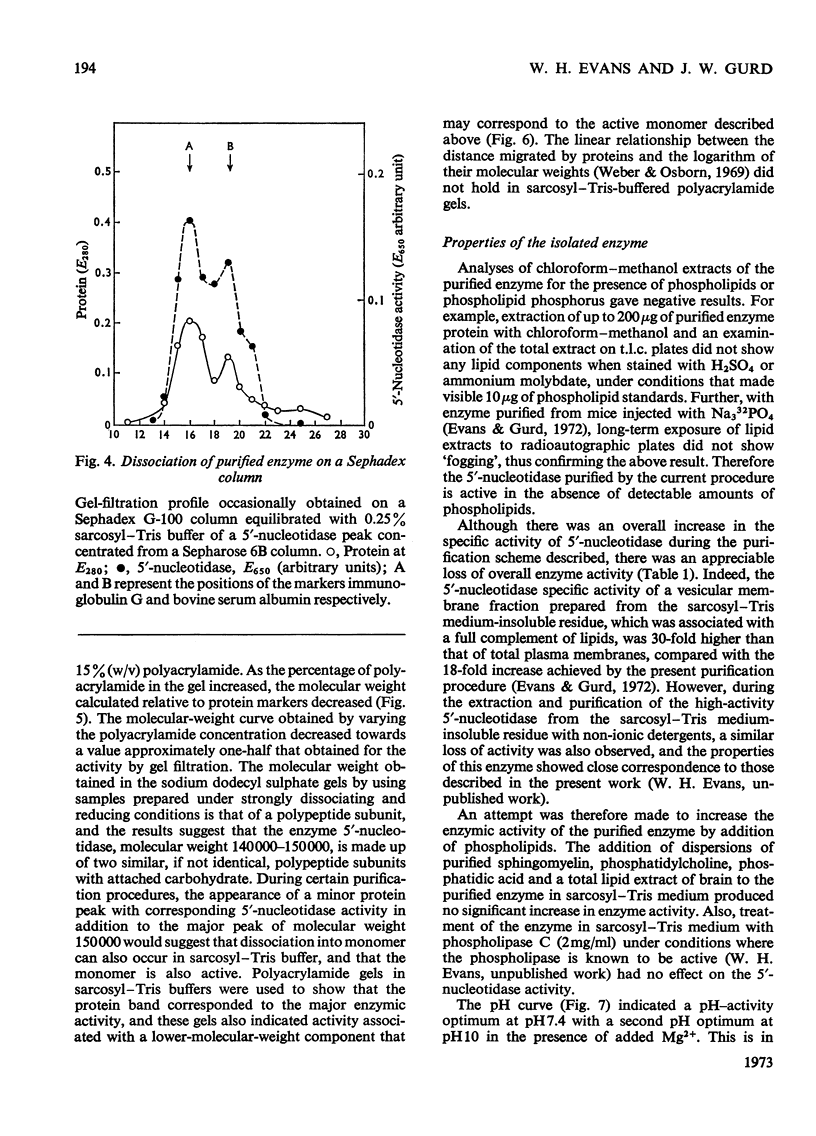
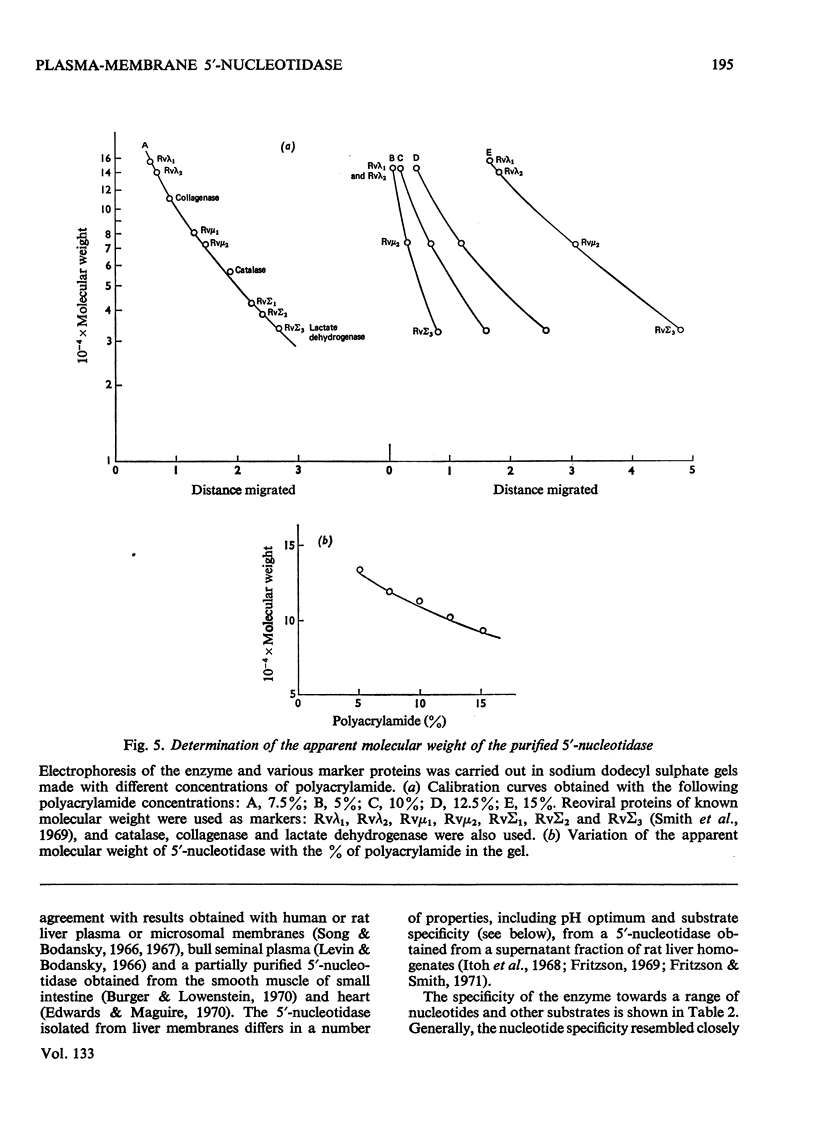
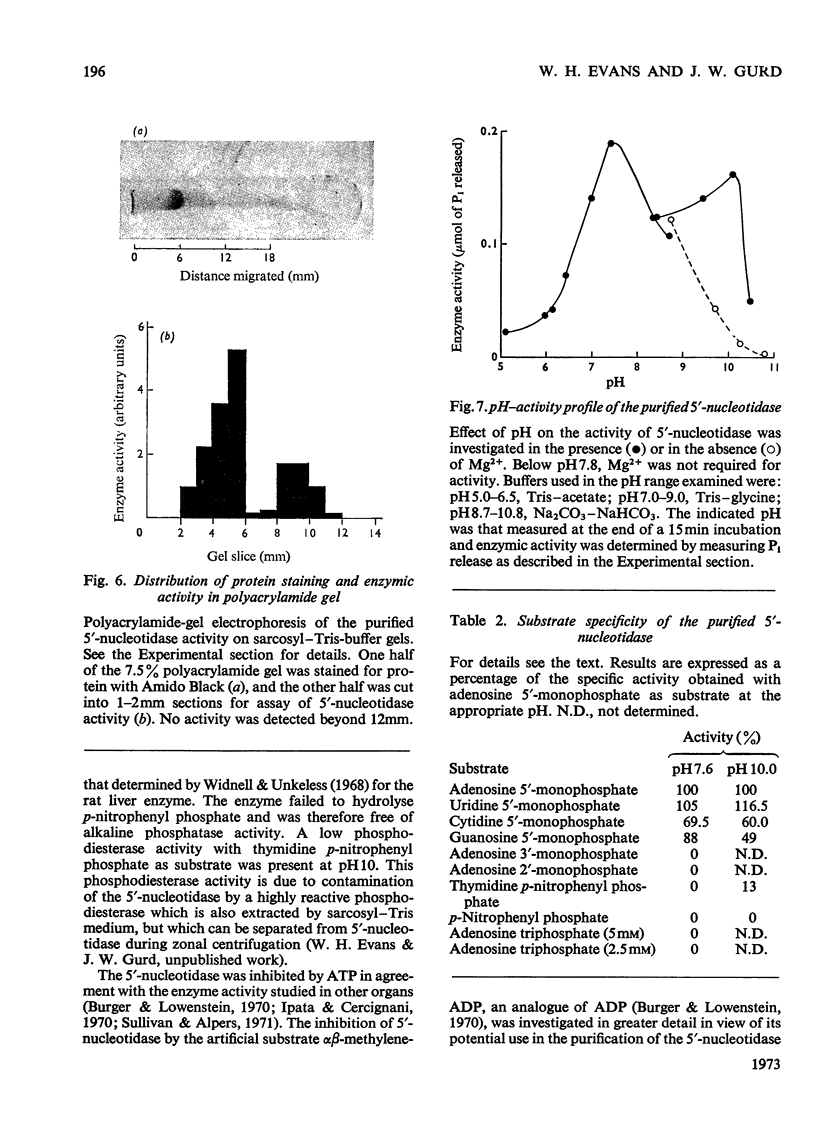
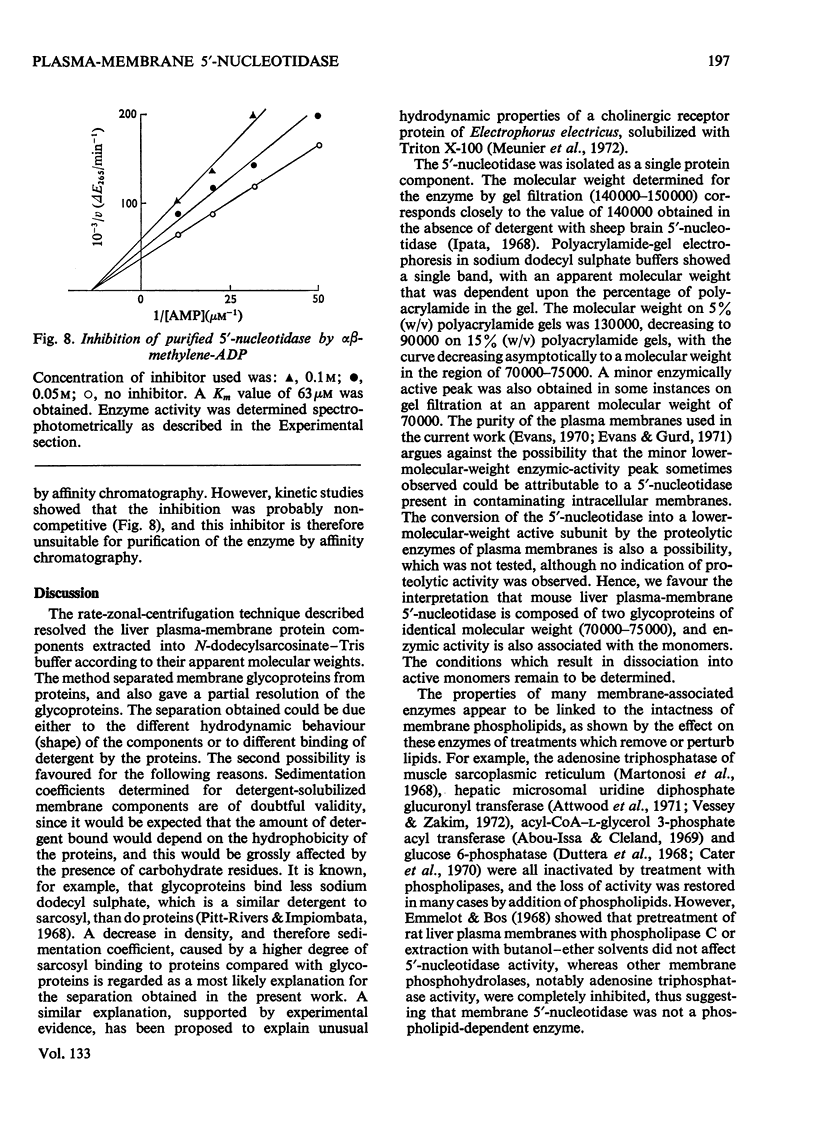
1. Extraction of a mouse liver plasma-membrane fraction with a detergent buffer, N-dodecylsarcosinate–Tris buffer (sarcosyl–Tris buffer), solubilized 90% of the protein and 70% of the 5′-nucleotidase activity. 2. The proteins of the sarcosyl–Tris buffer extract were fractionated by a rate-zonal centrifugation in a sucrose–detergent gradient. The major protein peak sedimented ahead of phospholipids, which mainly remained in the overlay. Glycoproteins were separated ahead of the protein peak. 3. The 5′-nucleotidase activity peak was associated with 5% of the protein applied to the gradient, and contained relatively few protein bands. 4. The 5′-nucleotidase was purified further by gel filtration on Sepharose and Sephadex columns equilibrated with sarcosyl–Tris buffer, to give a single glycoprotein band on sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The purified enzyme was lipid-free. 5. Electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels in sarcosyl–Tris buffers showed that the enzymic activity was coincident with the protein band. 6. The molecular weight suggested for the enzyme activity by gel filtration or centrifugation in sucrose gradients was 140000–150000. Sometimes, a minor enzyme peak of lower molecular weight was obtained. 7. Polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulphate indicated that as the polyacrylamide concentration was increased from 5 to 15%, the apparent molecular weight of the enzyme decreased from 130000 to 90000. 8. The evidence that 5′-nucleotidase is composed of two active and similar, if not identical, glycoprotein subunits and the role of detergent in effecting the separation of membrane proteins and glycoproteins are discussed. 9. Substrate requirements, pH optima and the nature of inhibition by an analogue of adenosine diphosphate are reported.
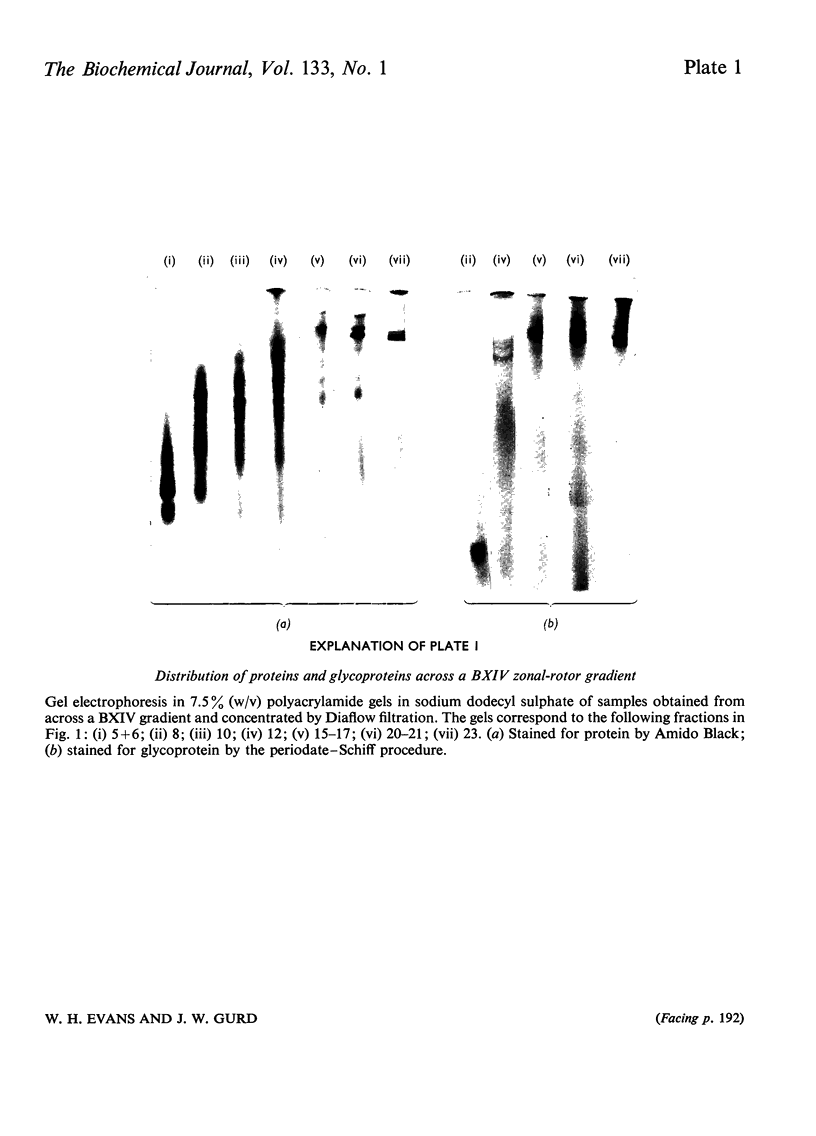
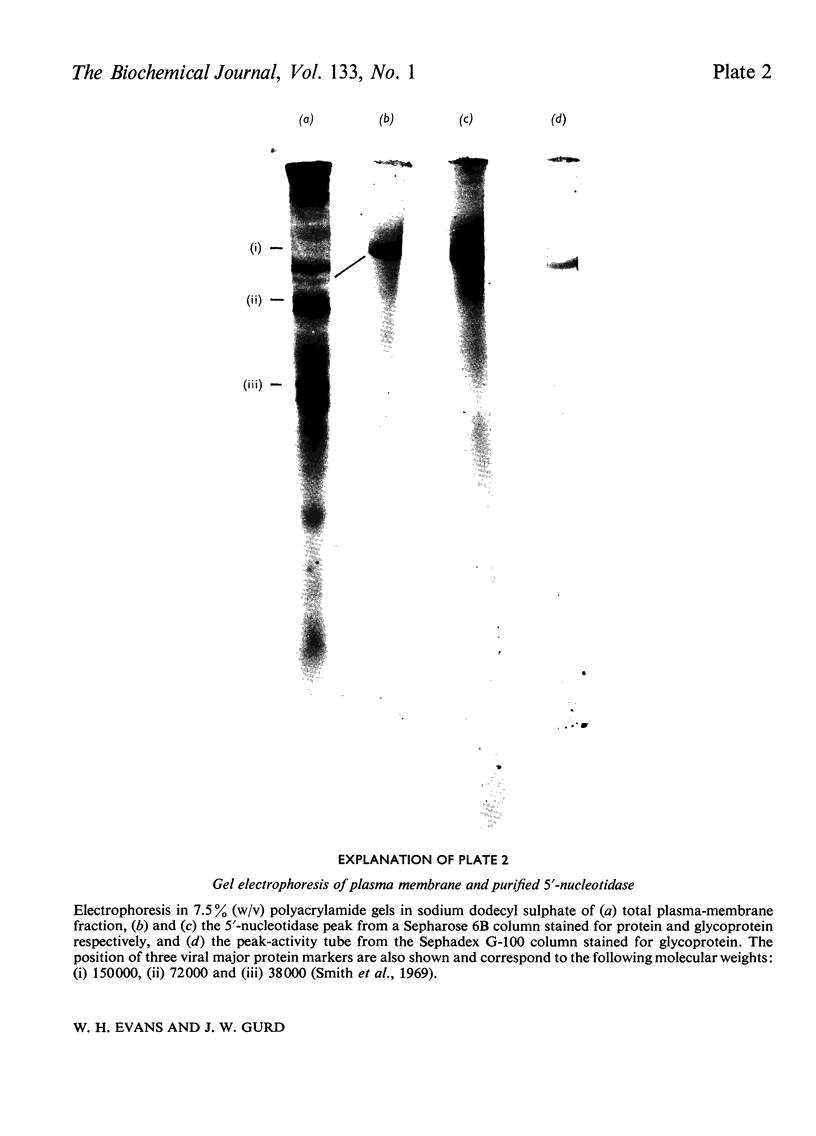
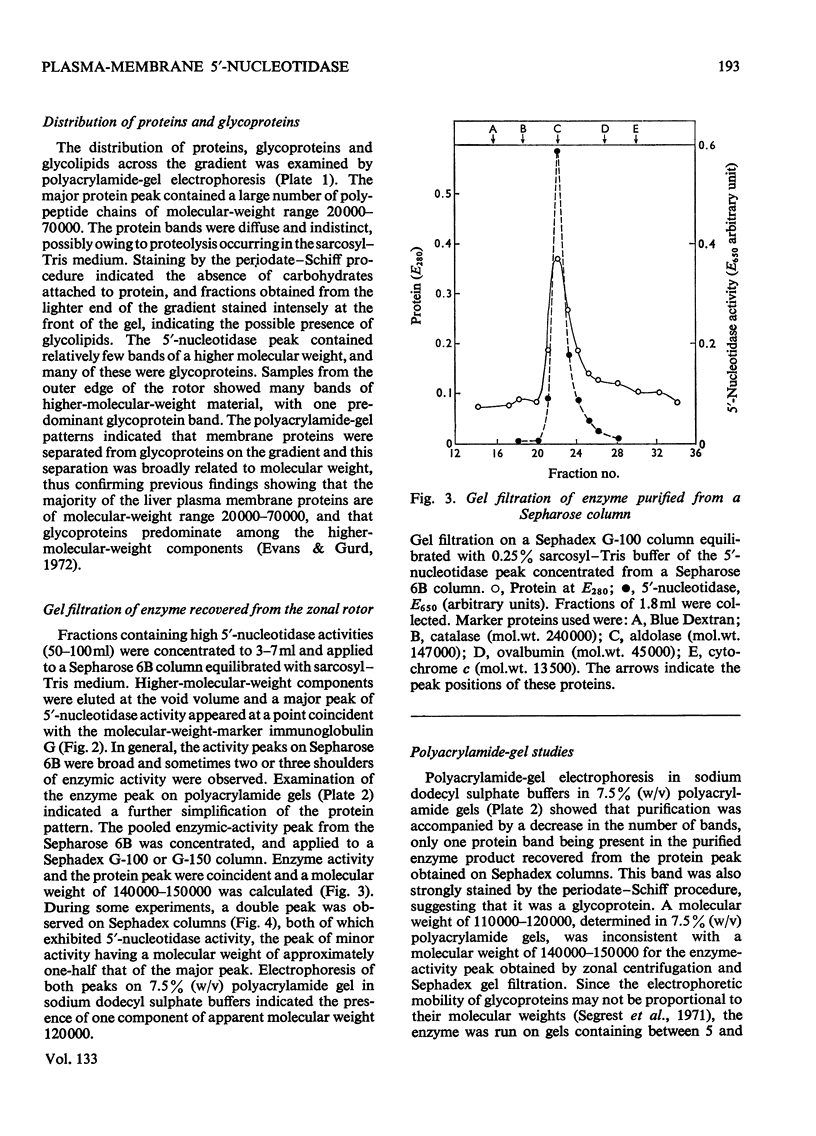
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Issa H. M., Cleland W. W. Studies on the microsomal acylation of L-glycerol-3-phosphate. II. The specificity and properties of the rat liver enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 10;176(4):692–698. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Crumpton M. J. Solubilization of pig lymphocyte plasma membrane and fractionation of some of the components. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):967–975. doi: 10.1042/bj1230967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood D., Graham A. B., Wood G. C. The phospholipid-dependence of uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase. Reactivation of phospholipase A-inactivated enzyme by phospholipids and detergents. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):875–882. doi: 10.1042/bj1230875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M., Lowenstein J. M. Preparation and properties of 5'-nucleotidase from smooth muscle of small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6274–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cater B. R., Poulter J., Hallinan T. The quantitative dependence of glucose-6-phosphohydrolase upon phospholipids: Effects of phospholipase C at 50 degrees and 370 degrees. FEBS Lett. 1970 Oct;10(5):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duttera S. M., Byrne W. L., Ganoza M. C. Studies on the phospholipid requirement of glucose 6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2216–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. J., Maguire M. H. Purification and properties of rat heart 5'-nucleotidase. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;6(6):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelot P., Bos C. J. Studies on plasma membranes. V. On the lipid dependence of some phosphohydrolases of isolated rat-liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):341–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. Fractionation of liver plasma membranes prepared by zonal centrifugation. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):833–842. doi: 10.1042/bj1160833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Gurd J. W. Biosynthesis of liver membranes. Incorporation of ( 3 H)leucine into proteins and of ( 14 C)glucosamine into proteins and lipids of liver microsomal and plasma-membrane fractions. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):615–624. doi: 10.1042/bj1250615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Gurd J. W. Preparation and properties of nexuses and lipid-enriched vesicles from mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):691–700. doi: 10.1042/bj1280691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzson P. Nucleotidase activities in the soluble fraction of rat liver homogenate. Partial purification and properties of a 5'-nucleotidase with pH optimum 6.3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 27;178(3):534–541. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzson P., Smith I. A new nucleotidase of rat liver with activity toward 3'-and 5'-nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 14;235(1):128–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. Membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:731–752. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Evans W. H., Perkins H. R. Chemical characterization of the proteins and glycoproteins of mouse liver plasma membranes solubilized by sequential extraction with aqueous and organic solvents. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):459–466. doi: 10.1042/bj1260459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Evans W. H., Perkins H. R. The distribution of surface antigens during fractionation of mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):271–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1300271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Isolation of glycoproteins from pig lymphocyte plasma membrane using Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. M., Keenan T. W. Preparation and properties of 5'-nucleotidases from bovine milk fat globule membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):246–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipata P. L. A coupled optical enzyme assay for 5'-nucleotidase. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipata P. L., Cercignani G. The effect of pH on the allosteric properties of sheep brain 5'-nucleotidase. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 2;7(2):129–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipata P. L. Sheep brain 5'-nucleotidase. Some enzymic properties and allosteric inhibition by nucleoside triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):507–515. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito R., Mitsui A., Tsushima K. Properties of 5'-nucleotidase from hepatic tissue of higher animals. J Biochem. 1968 Feb;63(2):165–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S. J., Bodansky O. The double pH optimum of 5'-nucleotidase of bull seminal plasma. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Donley J., Halpin R. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. 3. The role of phospholipids in the adenosine triphosphatase activity and Ca++ transport. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Olsen R. W., Changeux J. P. Studies on the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus. Effect of detergents on some hydrodynamic properties of the receptor protein in solution. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Hawthorne J. N. The site of diphosphoinositide synthesis in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippot J. Study of human red blood cell membrane using sodium deoxycholate. I. Mechanism of the solubilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankland W. The equilibrium and structure of lecithin-cholate mixed micelles. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Apr;4(2):109–130. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Bodansky O. Subcellular localization and properties of 5'-nucleotidase in the rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):694–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Nisselbaum J. S., Tandler B., Bodansky O. Partial solubilization of protein and 5'-nucleotidase from microsomal membranes of the rat liver by ultrasonic irradiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 1;150(2):300–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G., Sandri G., Panfili E., De Bernard B., Gazzotti P., Vasington F. D., Carafoli E. Isolation of a soluble Ca 2+ binding glycoprotein from ox liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):808–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. M., Alpers J. B. In vitro regulation of rat heart 5'-nucleotidase by adenine nucleotides and magnesium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3057–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey D. A., Zakim D. Regulation of microsomal enzymes by phospholipids. V. Kinetic studies of hepatic uridine diphosphate-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3023–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C. Cytochemical localization of 5'-nucleotidase in subcellular fractions isolated from rat liver. I. The origin of 5'-nucleotidase activity in microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):542–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Unkeless J. C. Partial purification of a lipoprotein with 5'-nucleotidase activity from membranes of rat liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1050–1057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]