Abstract
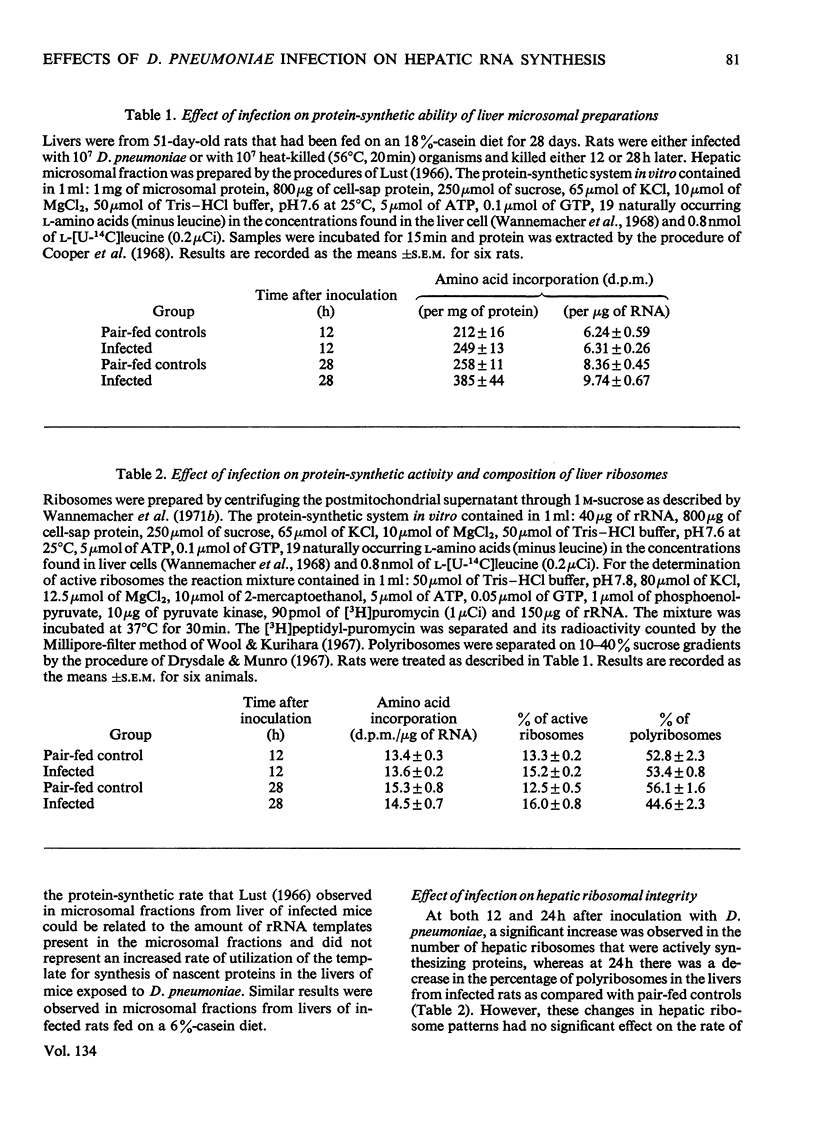
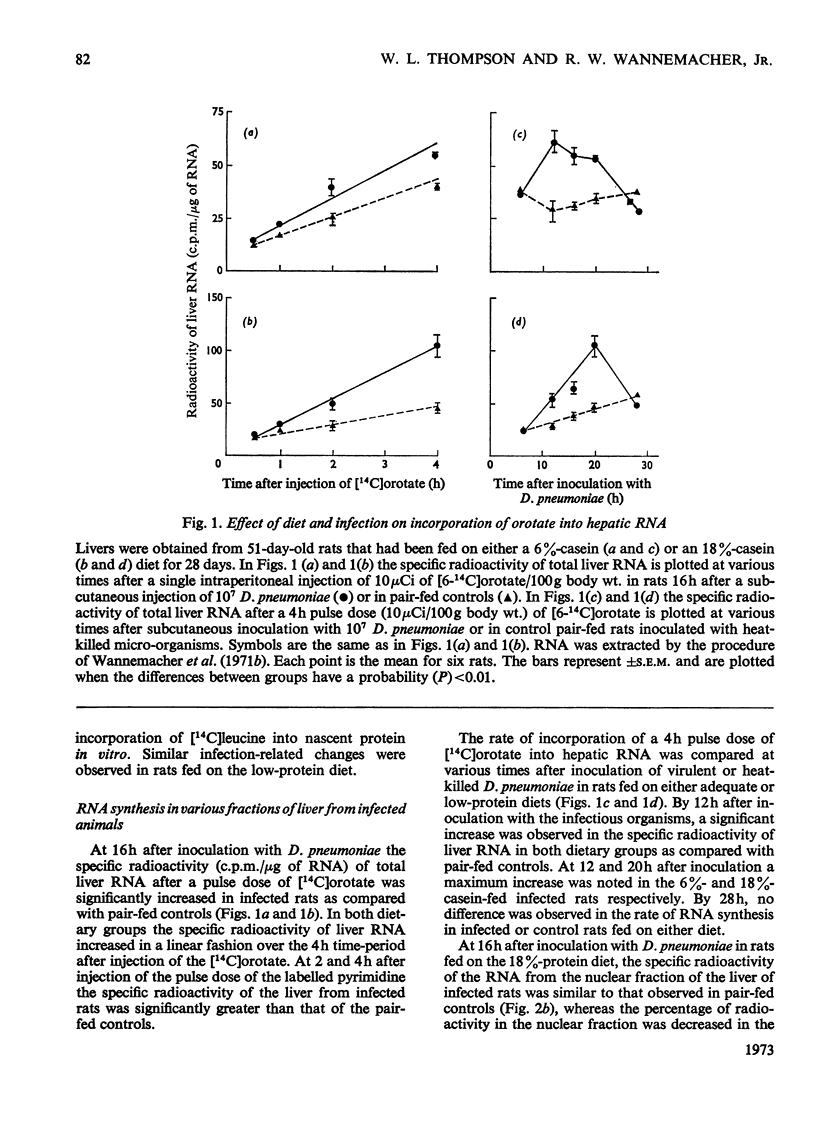
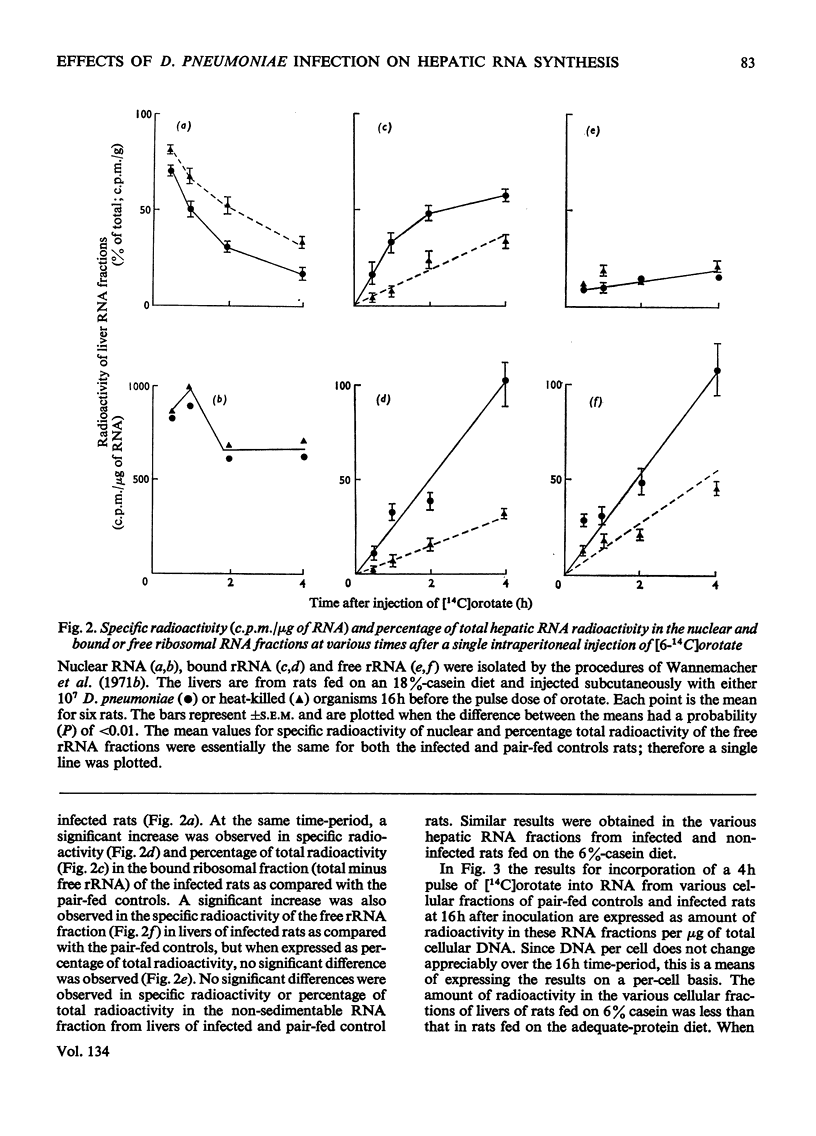
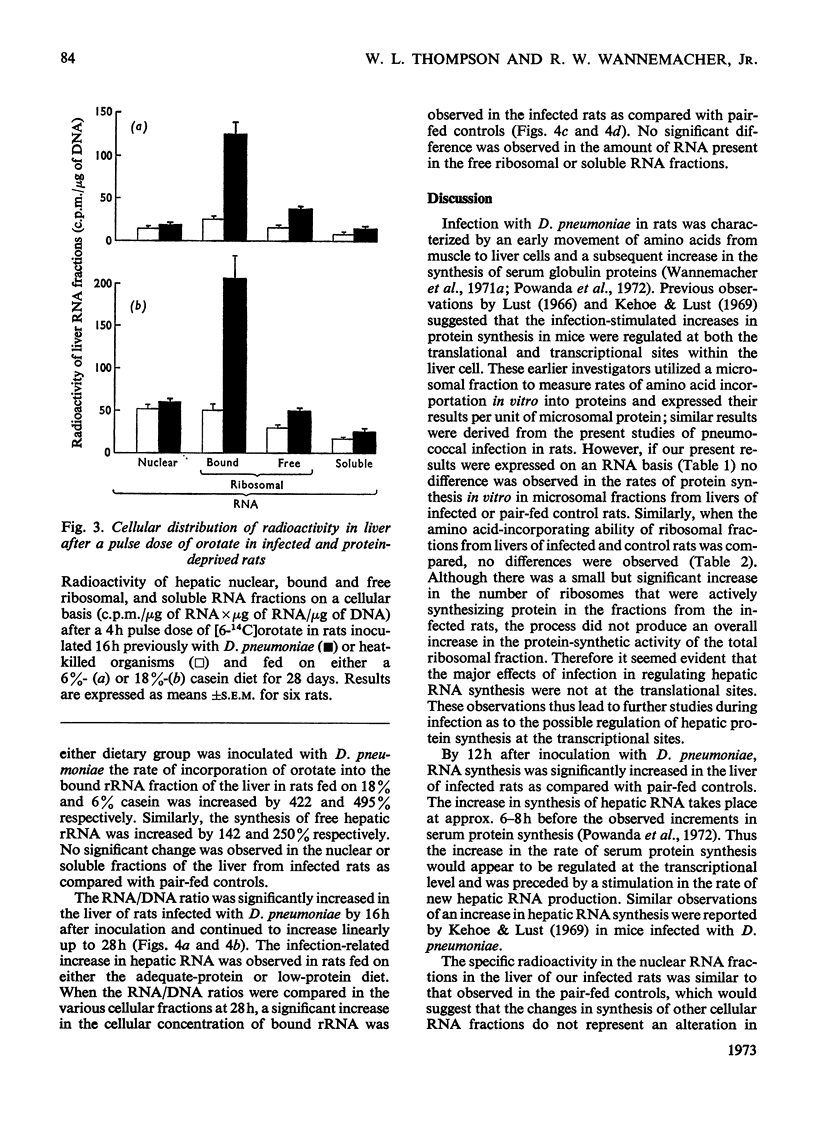
Rats infected with virulent Diplococcus pneumoniae developed a significant increase in the rate of incorporation of labelled orotate into hepatic RNA when compared with pair-fed controls inoculated with heat-killed organisms. The finding was readily detected in rats raised on either a low-protein diet (6% casein) or a diet containing adequate amounts of protein (18% casein). The increase in hepatic RNA synthesis was observed by 12h and was maximal by 16–20h after inoculation with the D. pneumoniae. Most of the infection-related increase in RNA synthesis was associated with the bound ribosomal RNA fraction of the liver. A small but less significant increase was observed in the synthesis of free ribosomal RNA. The increased synthesis of RNA in the liver of infected rats resulted in a marked elevation of the liver RNA/DNA ratio, the major increase being observed in concentration of bound ribosomal RNA fraction. When followed sequentially, the infection-related increase in synthesis of hepatic RNA was preceded by a flux of amino acids into liver and was followed by elevated synthesis rates of serum globulin proteins. These findings suggest that the infectious process was able to regulate hepatic RNA synthesis by altering the rate of transcription of new RNA. This mechanism was stimulated even in rats that had been severely depleted of body protein and amino acids by feeding them on a low-protein diet. The infection-related stimulation of liver RNA and protein synthesis thus appeared to take place at the expense of other body proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON J. B., WANNEMACHER R. W., Jr, BANKS W. L., Jr, WUNNER W. H. THE MAGNITUDE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF THE PROTEIN RESERVES IN RATS FED AT VARIOUS LEVELS OF NITROGEN. J Nutr. 1964 Dec;84:383–388. doi: 10.1093/jn/84.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. K., Muramatsu K., Wannemacher R. W., Jr An in vitro amino acid incorporating system for liver, brain and skeletal muscle ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 20;169(1):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Polysome profiles obtained from mammalian tissues by an improved procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 30;138(3):616–618. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90562-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Williams C. A. In vitro synthesis of different categories of specific protein by membrane-bound and free ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1370–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. J., Drysdale J. W., Munro H. N. Preferential synthesis of ferritin and albumin by different populations of liver polysomes. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):584–585. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. M., Lust G. Studies of the host response to infectious disease: alterations of RNA metabolism in mouse tissues. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):411–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G. Effect of infection on protein and nucleic acid synthesis in mammalian organs and tissues. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powanda M. C., Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Cockerell G. L. Nitrogen metabolism and protein synthesis during pneumococcal sepsis in rats. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):266–271. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.266-271.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport M. I., Lust G., Beisel W. R. Host enzyme induction of bacterial infection. Arch Intern Med. 1968 Jan;121(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Beisel W. R. Endocrine influences on altered hepatic tyrosine transaminase activity during pneumococcal septicemia in the rat. Endocrinology. 1968 Nov;83(5):965–974. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-5-965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Cooper W. K., Yatvin M. B. The regulation of protein synthesis in the liver of rats. Mechanisms of dietary amino acid control in the immature animal. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):615–623. doi: 10.1042/bj1070615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Banks W. L., Jr, Wunner W. H. Use of a single tissue extract to determine cellular protein and nucleic acid concentrations and rate of amino acid incorporation. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):320–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Powanda M. C., Pekarek R. S., Beisel W. R. Tissue amino acid flux after exposure of rats to Diplococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.556-562.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr Ribosomal RNA synthesis and function as influenced by amino acid supply and stress. Proc Nutr Soc. 1972 Dec;31(3):281–290. doi: 10.1079/pns19720052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Wannemacher C. F., Yatvin M. B. Amino acid regulation of synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in the liver of rats. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):385–392. doi: 10.1042/bj1240385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Kurihara K. Determination of the number of active muscle ribosomes: effect of diabetes and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2401–2407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


