Abstract
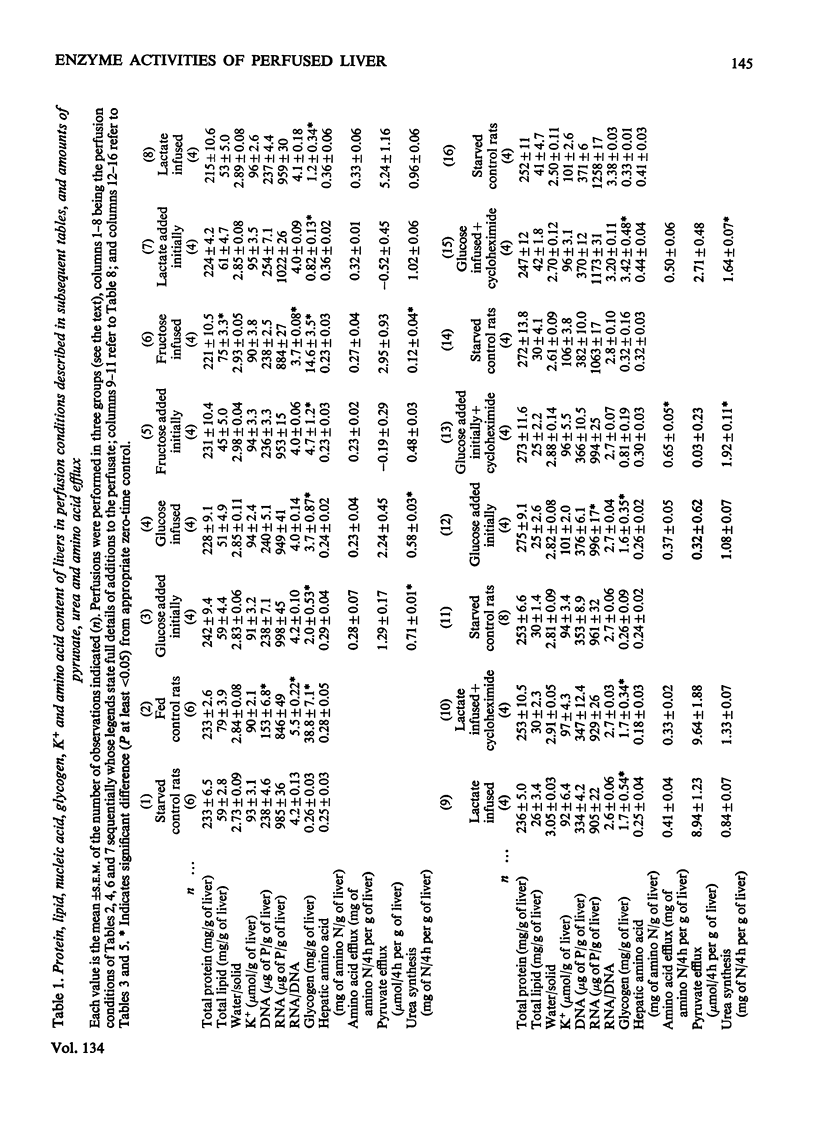
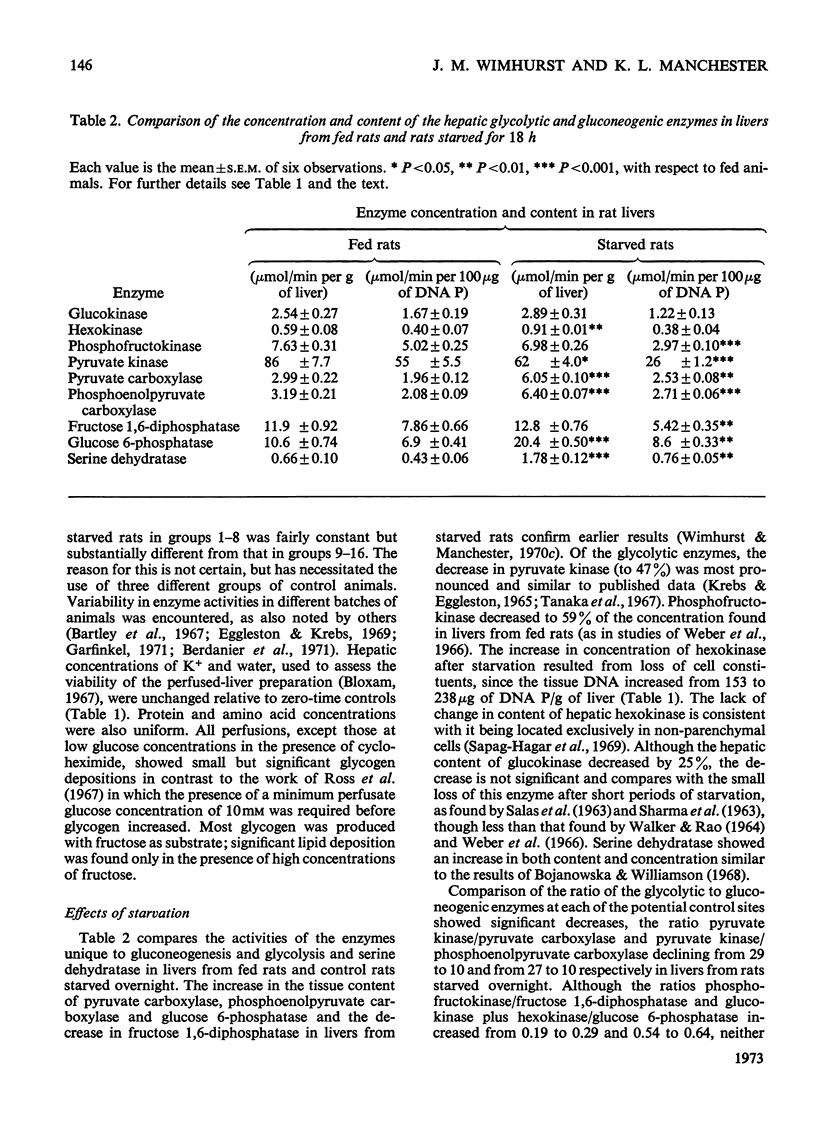
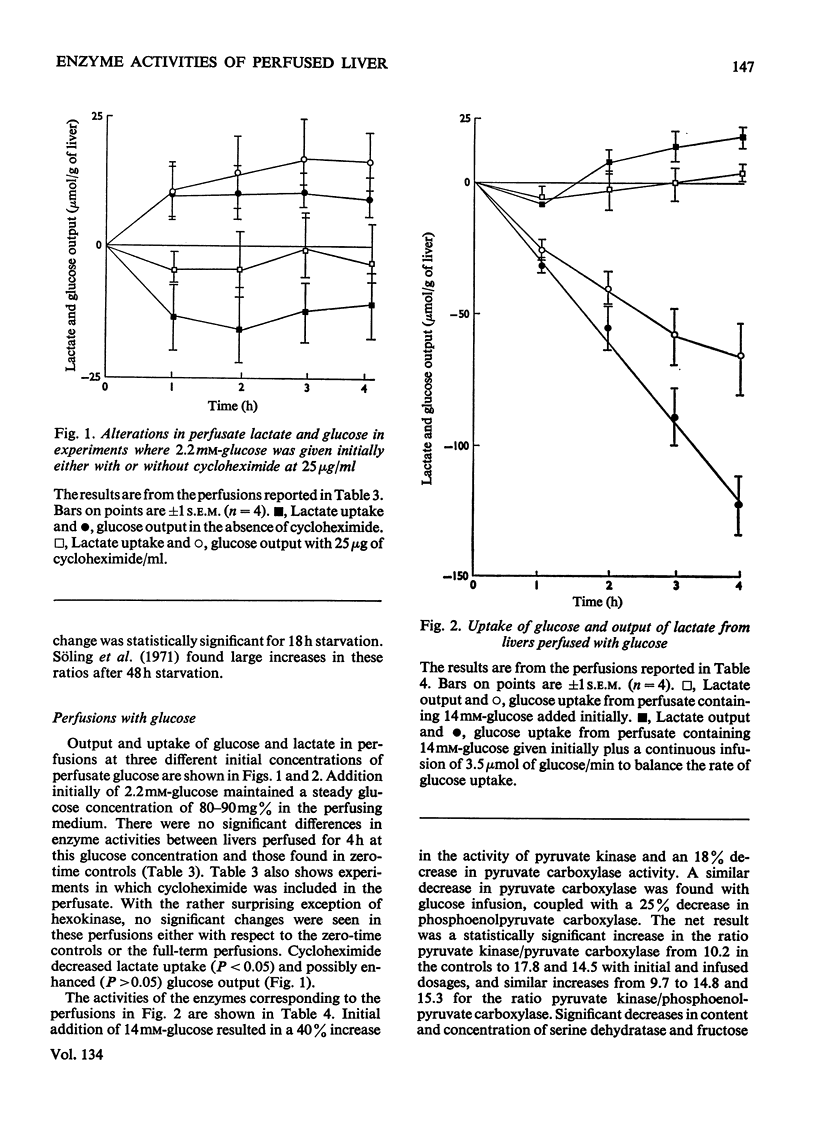
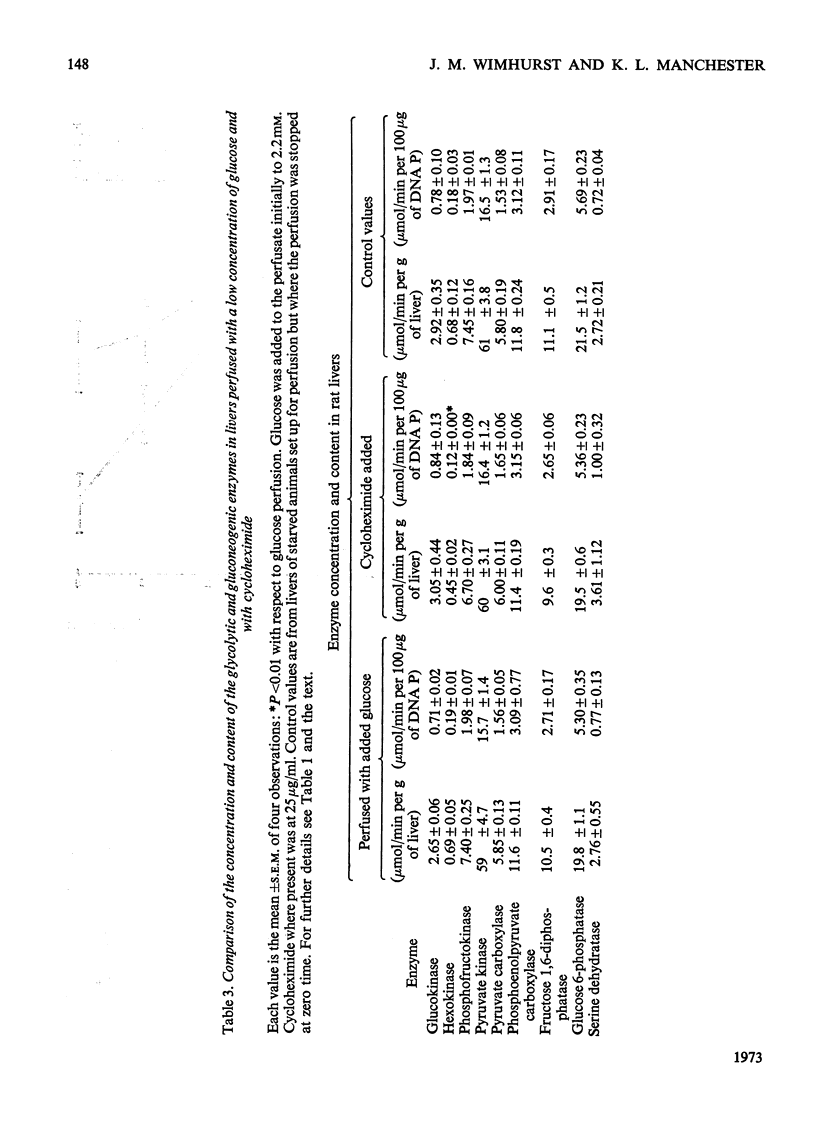
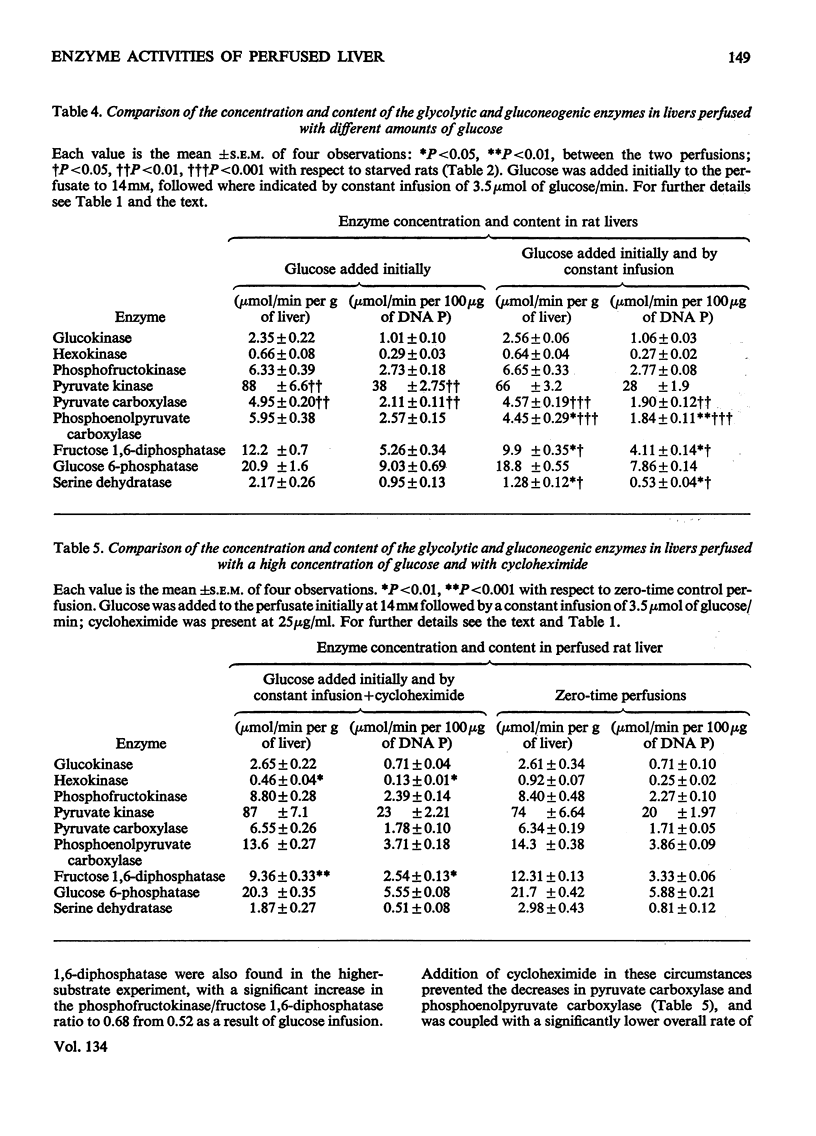
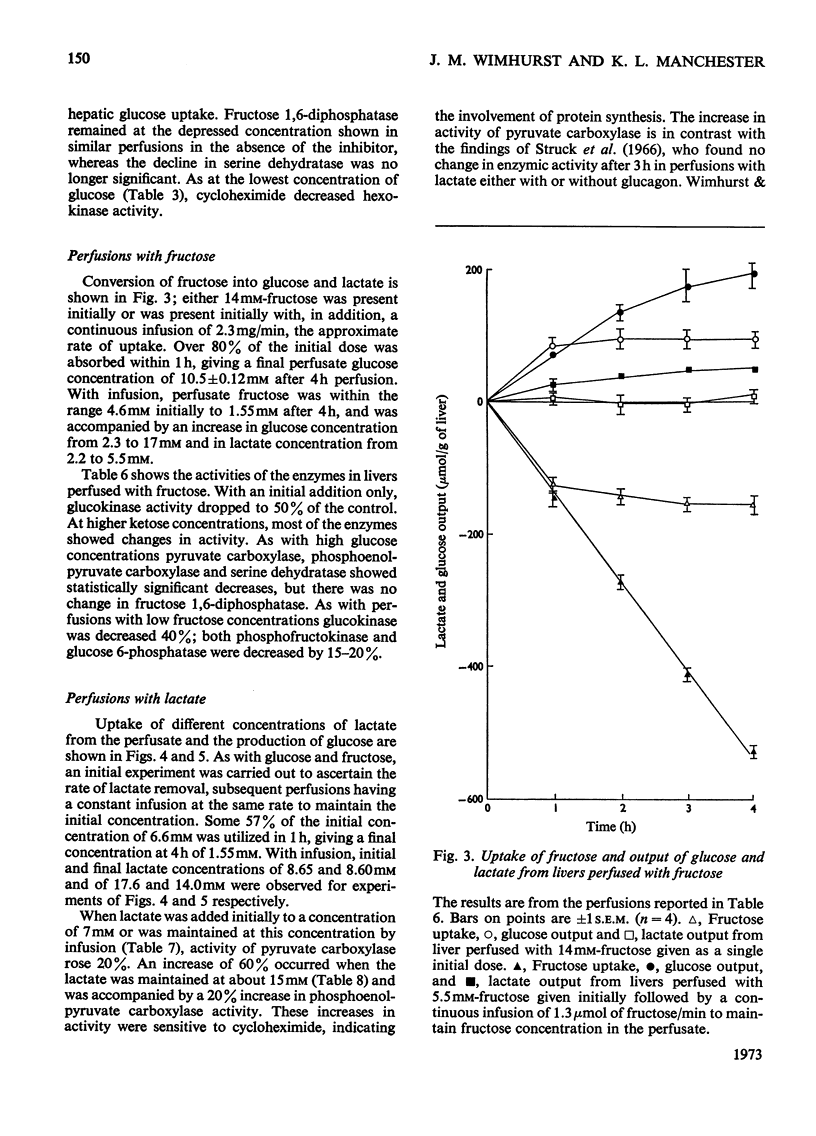
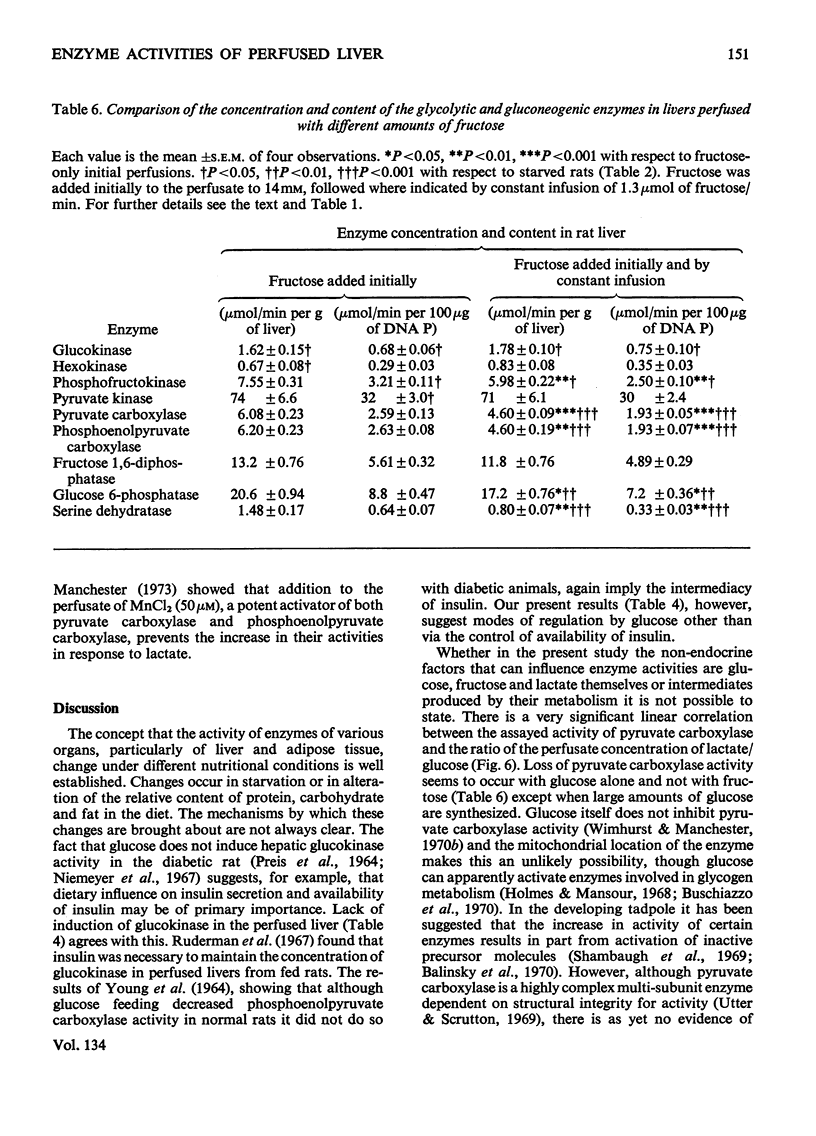
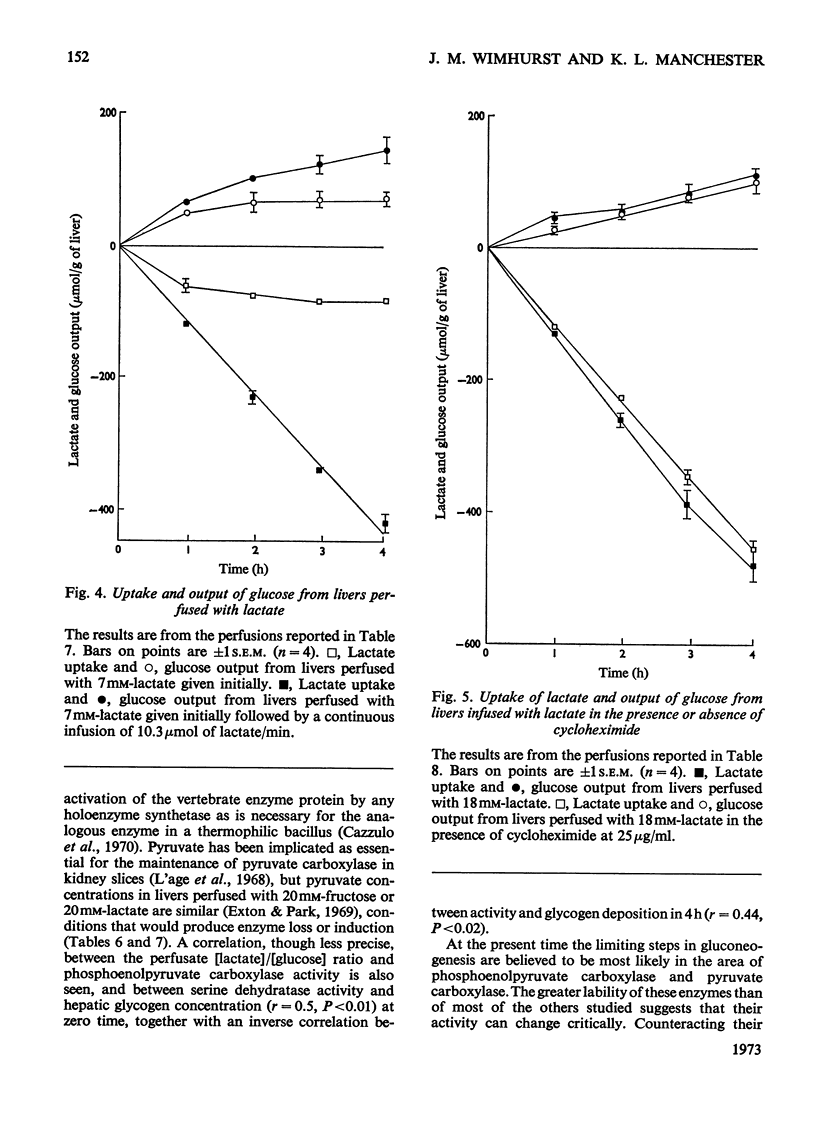
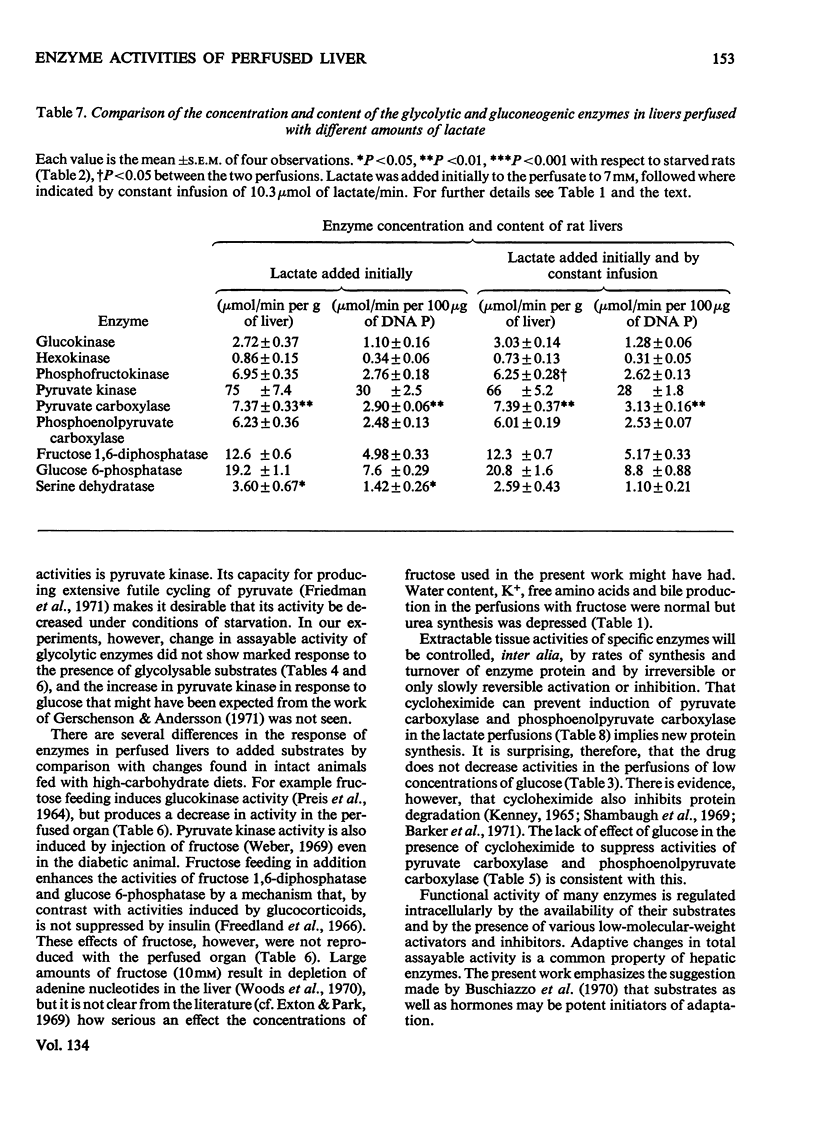
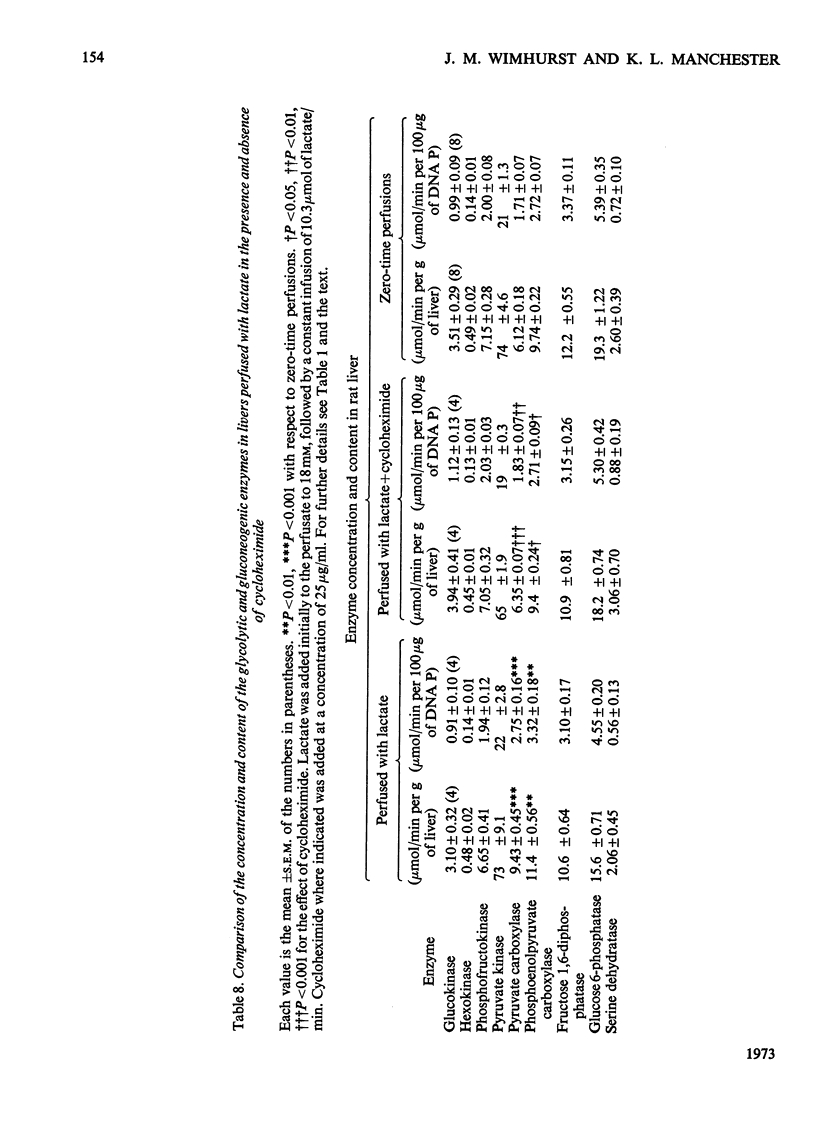
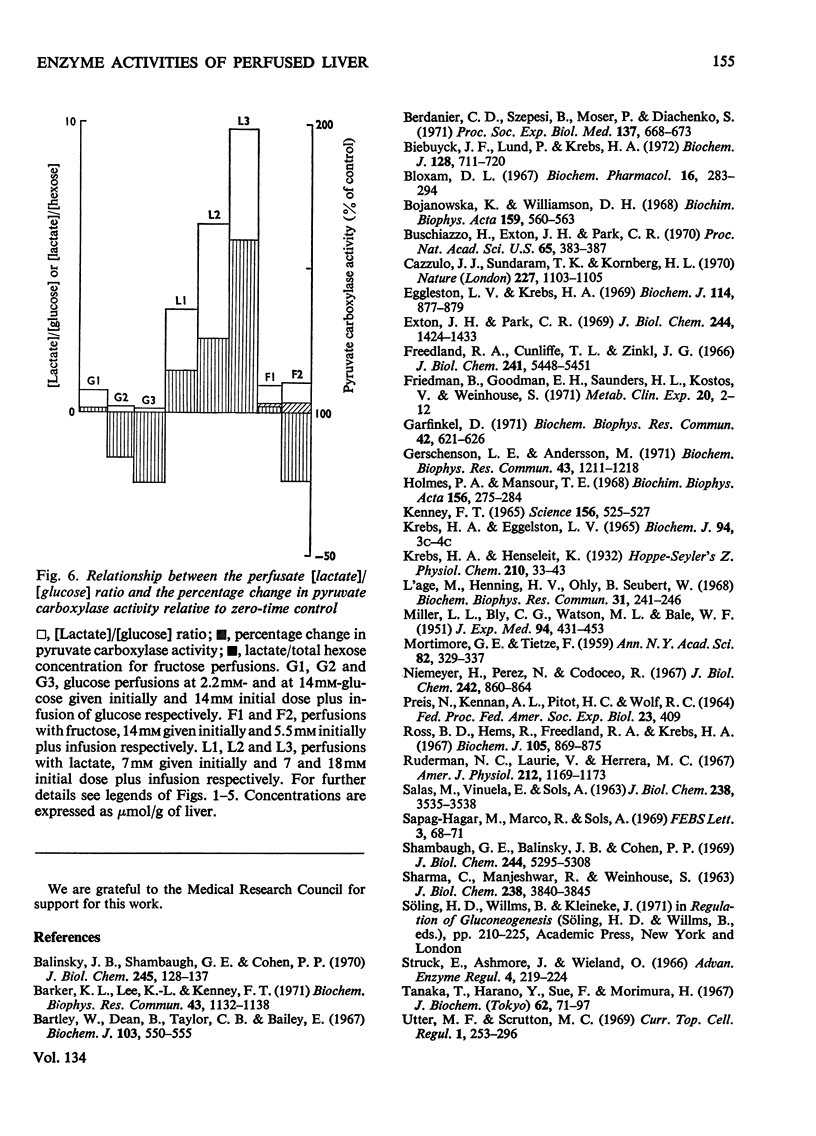
1. Measurements were made of the activities of the four key enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis, pyruvate carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.1), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (EC 4.1.1.32), fructose 1,6-diphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11) and glucose 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.9), of serine dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.13) and of the four enzymes unique to glycolysis, glucokinase (EC 2.7.1.2), hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1), phosphofructokinase (EC 2.7.1.11) and pyruvate kinase (EC 2.7.1.40), in livers from starved rats perfused with glucose, fructose or lactate. Changes in perfusate concentrations of glucose, fructose, lactate, pyruvate, urea and amino acid were monitored for each perfusion. 2. Addition of 15mm-glucose at the start of perfusion decreased the activity of pyruvate carboxylase. Constant infusion of glucose to maintain the concentration also decreased the activities of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, fructose 1,6-diphosphatase and serine dehydratase. Addition of 2.2mm-glucose initially to give a perfusate sugar concentration similar to the blood sugar concentration of starved animals had no effect on the activities of the enzymes compared with zero-time controls. 3. Addition of 15mm-fructose initially decreased glucokinase activity. Constant infusion of fructose decreased activities of glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose 6-phosphatase and serine dehydratase. 4. Addition of 7mm-lactate initially elevated the activity of pyruvate carboxylase, as also did constant infusion; maintenance of a perfusate lactate concentration of 18mm induced both pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activities. 5. Addition of cycloheximide had no effect on the activities of the enzymes after 4h of perfusion at either low or high concentrations of glucose or at high lactate concentration. Cycloheximide also prevented the loss or induction of pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activities with high substrate concentrations. 6. Significant amounts of glycogen were deposited in all perfusions, except for those containing cycloheximide at the lowest glucose concentration. Lipid was found to increase only in the experiments with high fructose concentrations. 7. Perfusion with either fructose or glucose decreased the rates of ureogenesis; addition of cycloheximide increased urea efflux from the liver.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balinsky J. B., Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Cohen P. P. Glutamate dehydrogenase biosynthesis in amphibian liver preparations. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):128–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker K. L., Lee K. L., Kenney F. T. Turnover of tyrosine transaminase in cultured hepatoma cells after inhibition of protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90580-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley W., Dean B., Taylor C. B., Bailey E. The effect on some enzymes of rat tissue of diets low in fat content. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):550–555. doi: 10.1042/bj1030550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebuyck J. F., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The effects of halothane (2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane) on glycolysis and biosynthetic processes of the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):711–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1280711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloxam D. L. Effects of various anaesthetics on the metabolism and general condition of the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Feb;16(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanowska K., Williamson D. H. Serine dehydratase activity in livers of phlorrhizin-treated rats and the hepatic serine plus threonine concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 9;159(3):560–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo H., Exton J. H., Park C. R. Effects of glucose on glycogen synthetase, phosphorylase, and glycogen deposition in the perfused rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Sundaram T. K., Kornberg H. L. Mechanism of pyruvate carboxylase formation from the apo-enzyme and biotin in a thermophilic bacillus. Nature. 1970 Sep 12;227(5263):1103–1105. doi: 10.1038/2271103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. Strain differences in the activities of rat liver enzymes. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):877–879. doi: 10.1042/bj1140877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. 3. Effects of L-lactate, pyruvate, fructose, glucagon, epinephrine, and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on gluconeogenic intermediates in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1424–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedland R. A., Cunliffe T. L., Zinkl J. G. The effect of insulin on enzyme adaptations to diets and hormones. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5448–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Goodman E. H., Jr, Saunders H. L., Kostos V., Weinhouse S. Estimation of pyruvate recycling during gluconeogenesis in perfused rat liver. Metabolism. 1971 Jan;20(1):2–12. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. Resolution by computer simulation of contradictory experimental findings as to the effect on gluconeogenesis of oleate addition in perfused rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenson L. E., Andersson M. Regulation of the pyruvate kinase of an established rat liver cell line (RLC) in culture by insulin, glucose and serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 18;43(6):1211–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes P. A., Mansour T. E. Glucose as a regulator of glycogen phosphorylase in rat diaphragm. II. Effect of glucose and related compounds on phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney F. T. Turnover of rat liver tyrosine transaminase: stabilization after inhibition of protein synthesis. Science. 1967 Apr 28;156(3774):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'age M., Henning H. V., Ohly B., Seubert W. On the role of insulin in the control of gluconeogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 19;31(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BLY C. G., WATSON M. L., BALE W. F. The dominant role of the liver in plasma protein synthesis; a direct study of the isolated perfused rat liver with the aid of lysine-epsilon-C14. J Exp Med. 1951 Nov;94(5):431–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F. Studies on the mechanism of capture and degradation of insulin-1131 by the cyclically perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer H., Pérez N., Codoceo R. Liver glucokinase induction in acute and chronic insulin insufficiency in rats. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):860–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. D., Hems R., Freedland R. A., Krebs H. A. Carbohydrate metabolism of the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):869–875. doi: 10.1042/bj1050869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Lauris V., Herrera M. G. Insulin preservation of glucokinase activity in isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1169–1173. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALAS M., VINUELA E., SOLS A. INSULIN-DEPENDENT SYNTHESIS OF LIVER GLUCOKINASE IN THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3535–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARMA C., MANJESHWAR R., WEINHOUSE S. EFFECTS OF DIET AND INSULIN ON GLUCOSE-ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE PHOSPHOTRANSFERASES OF RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:3840–3845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapag-Hagar M., Marco R., Sols A. Distribution of hexokinase and glucokinase between parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells of rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1969 Apr;3(1):68–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Balinsky J. B., Cohen P. P. Synthesis of carbamyl phosphate synthetase in amphibian liver in vitro. The effect of thyroxine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5295–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck E., Ashmore J., Wieland O. Effects of glucagon and long chain fatty acids on glucose production by isolated perfused rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:219–224. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Harano Y., Sue F., Morimura H. Crystallization, characterization and metabolic regulation of two types of pyruvate kinase isolated from rat tissues. J Biochem. 1967 Jul;62(1):71–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veneziale C. M., Walter P., Kneer N., Lardy H. A. Influence of L-tryptophan and its metabolites on gluconeogenesis in the isolated, perfused liver. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2129–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. G., Rao S. The role of glucokinase in the phosphorylation of glucose by rat liver. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):360–368. doi: 10.1042/bj0900360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G. Regulation of pyruvate kinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1969;7:15–40. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(69)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Singhal R. L., Stamm N. B., Lea M. A., Fisher E. A. Synchronous behavior pattern of key glycolytic enzymes: glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:59–81. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. A comparison of the effects of diabetes induced with either alloxan or streptozotocin and of starvation on the activities in rat liver of the key enzymes of gluconeogenesis. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):95–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1200095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. Comparison of ability of Mg and Mn to activate the key enzymes of glycolysis. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 1;27(2):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. Some aspects of the kinetics of rat liver pyruvate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):79–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1200079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. Suppression of pyruvate carboxylase by glucose in the perfused rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1970 May 25;8(2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods H. F., Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. The cause of hepatic accumulation of fructose 1-phosphate on fructose loading. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):501–510. doi: 10.1042/bj1190501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG J. W., SHRAGO E., LARDY H. A. METABOLIC CONTROL OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN LIPOGENESIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1687–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


