Abstract
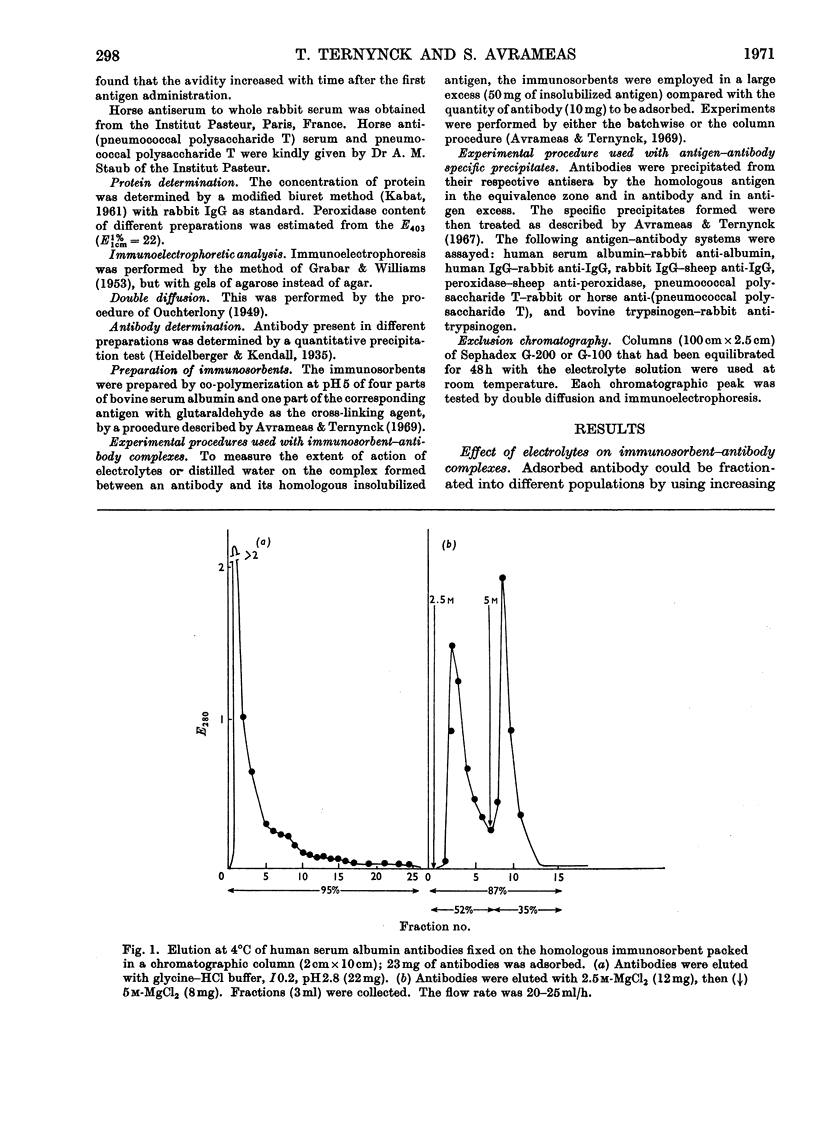
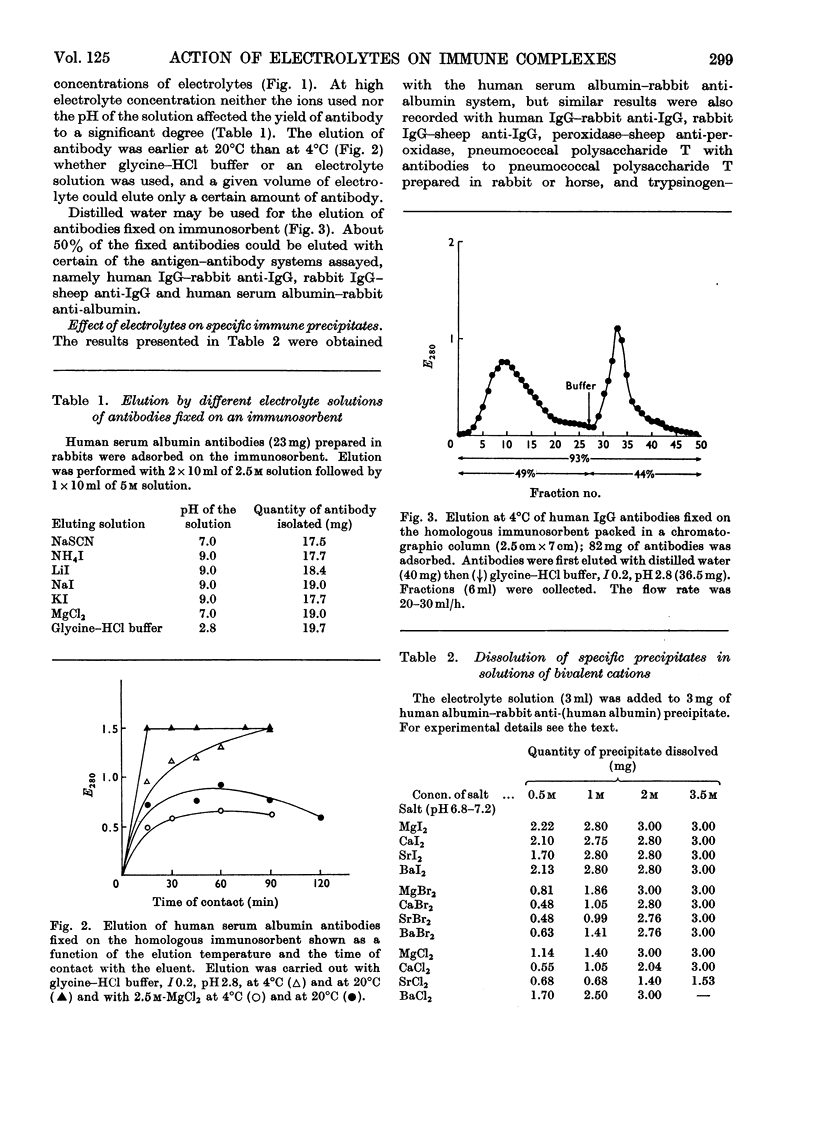
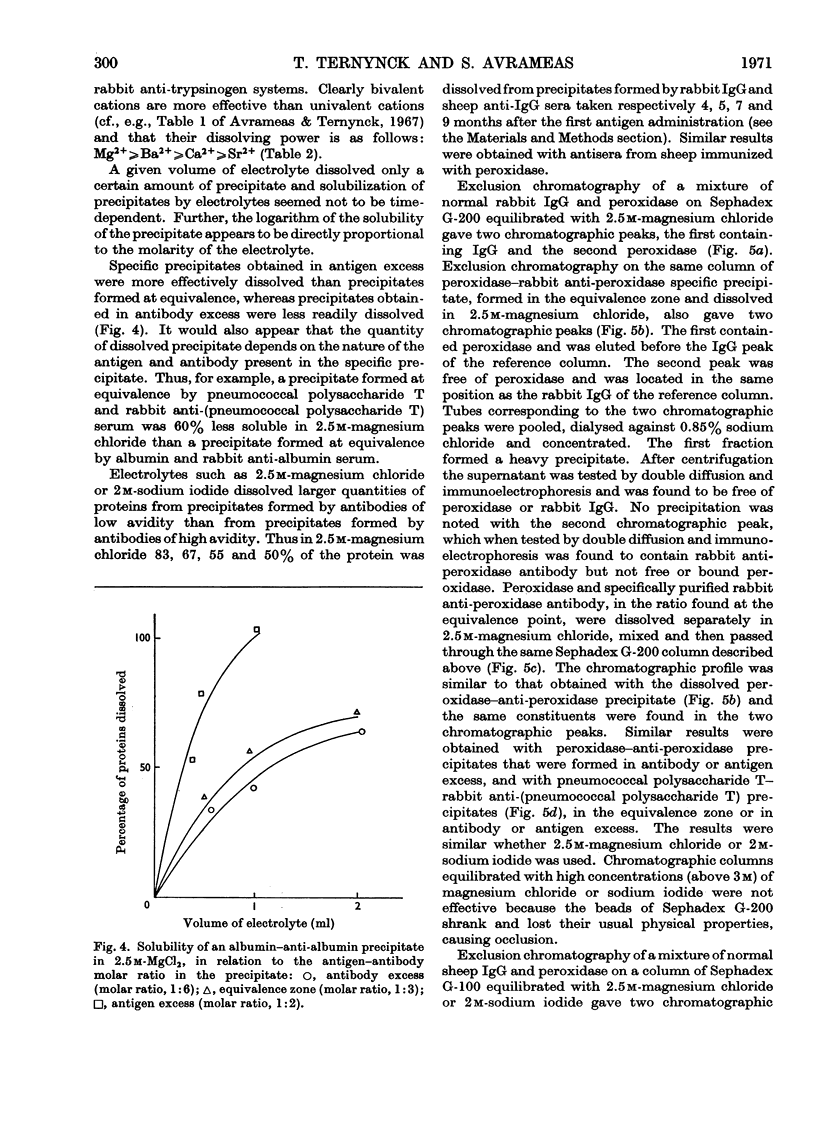
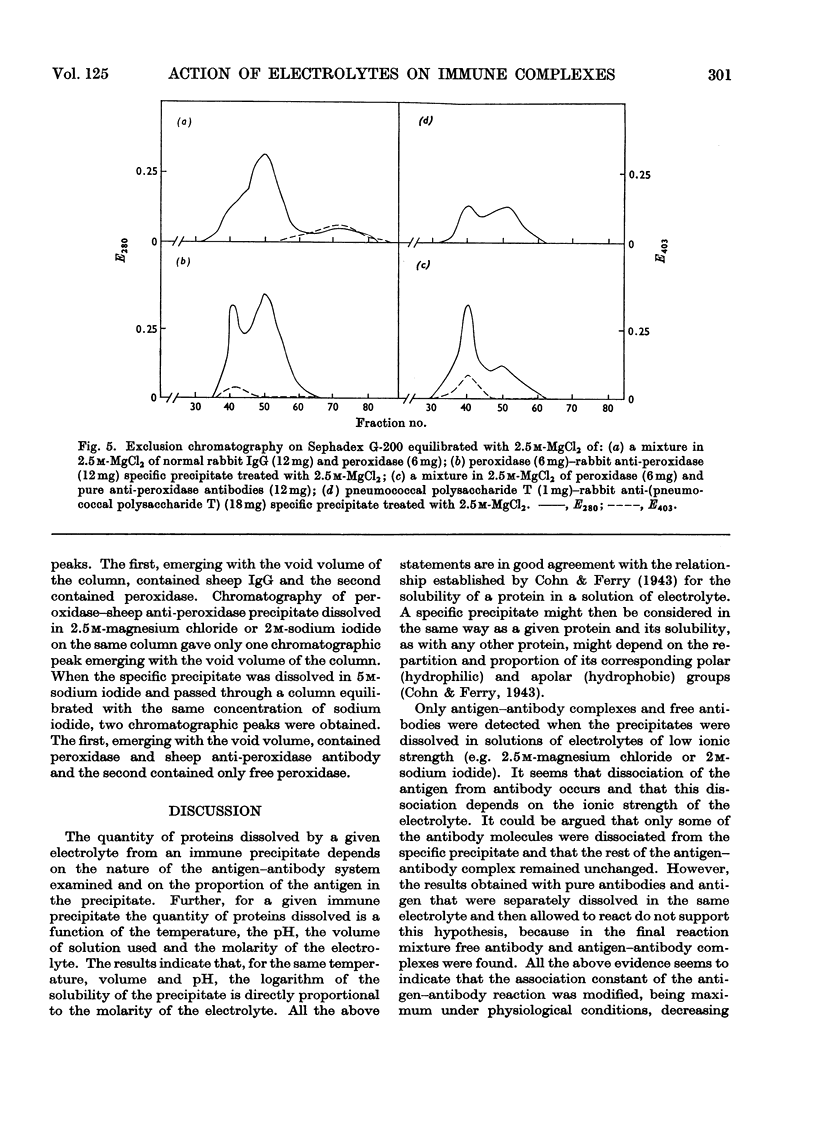
Specific immune precipitates dissolve in concentrated solutions of alkali-metal halides, and of alkaline-earth-metal halides and thiocyanates. The quantity of protein dissolved depends on the nature of the antigen–antibody system, on the proportion of the antigen in the precipitate, and on the avidity of the antibody. The extent of solubilization is a function of the temperature, of the volume of solution used and of the concentration of the ions in the solution, and also depends on the nature of these ions. The dissolving power of bivalent cations is greater than that of monovalent ones, and is as follows: Mg2+[unk]Ba2+[unk]Ca2+[unk]Sr2+. Antigen–antibody complexes and free antibodies, but no free antigen, are detected in supernatants of specific precipitates dissolved in solutions of electrolytes of low ionic strength. Antigen–antibody complexes, free antibodies and also free antigen are detected in supernatants of specific precipitates dissolved in solutions of electrolytes of high ionic strength. Comparable results are obtained when the electrolyte solutions are studied for their effect on the bonds formed between an antibody and its corresponding immunosorbent. Moreover, in the latter case, 50% of the fixed antibodies could be recovered by elution with distilled water.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Taudou B., Ternynck T. Specificity of antibodies synthetized by immunocytes as detected by immunoenzyme techniques. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(2):161–170. doi: 10.1159/000230403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandliker W. B., Alonso R., de Saussure V. A., Kierszenbaum F., Levison S. A., Schapiro H. C. The effect of chaotropic ions on the dissociation of antigen-antibody complexes. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1460–1467. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABAR P., WILLIAMS C. A. Méthode permettant l'étude conjuguée des proprietés électrophorétiques et immunochimiques d'un mélange de protéines; application au sérum sanguin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLECZKOWSKI A. A STUDY OF THE EFFECTS OF SALT AND OF PH ON PRECIPITATION OF ANTIGEN--ANTIBODY COMPOUNDS. Immunology. 1965 Feb;8:170–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT W. J., BOYER P. D. Interaction of protein antigens and antibodies. I. Inhibition studies with the egg albumin-antiegg albumin system. J Immunol. 1952 Sep;69(3):247–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


