Abstract
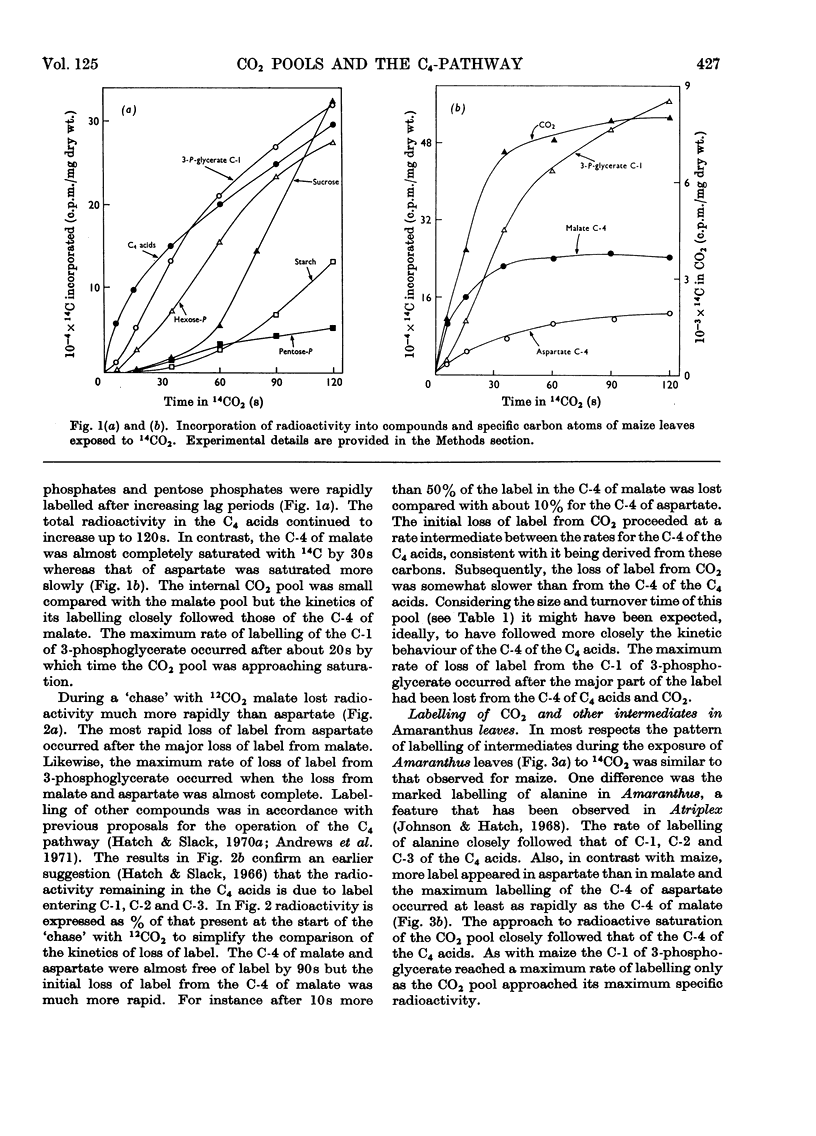
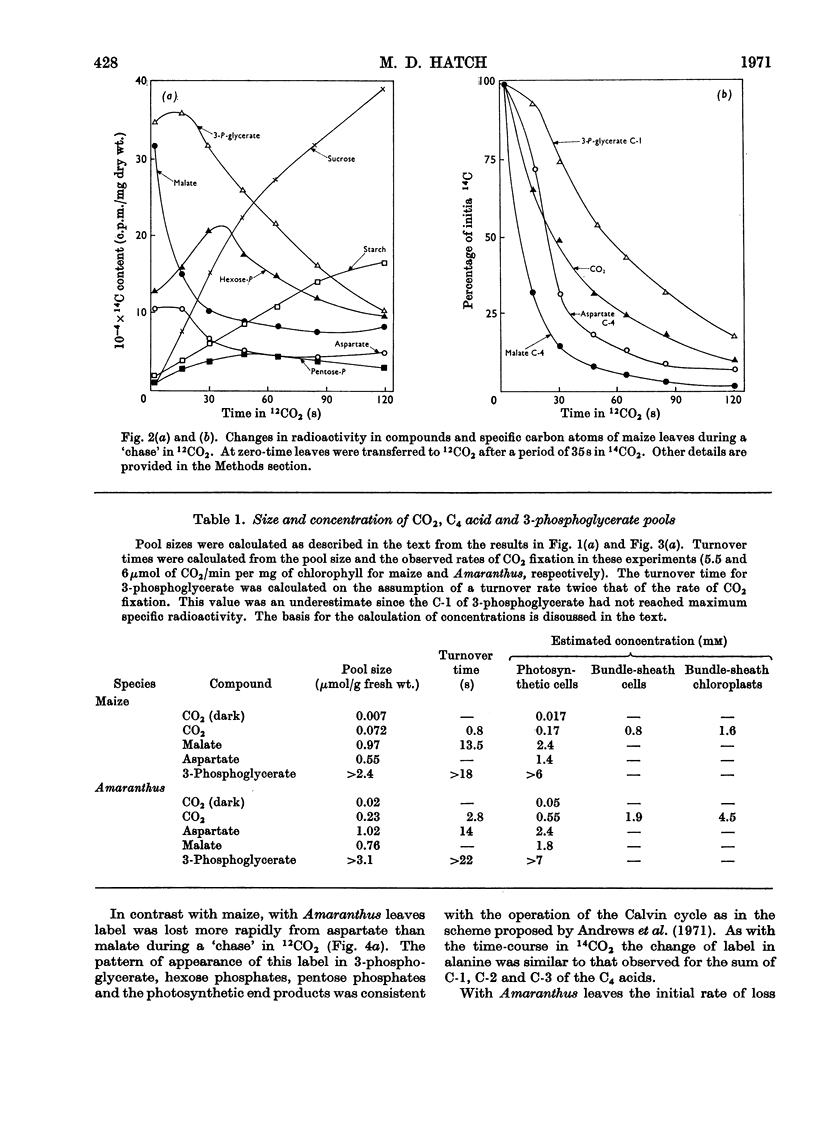
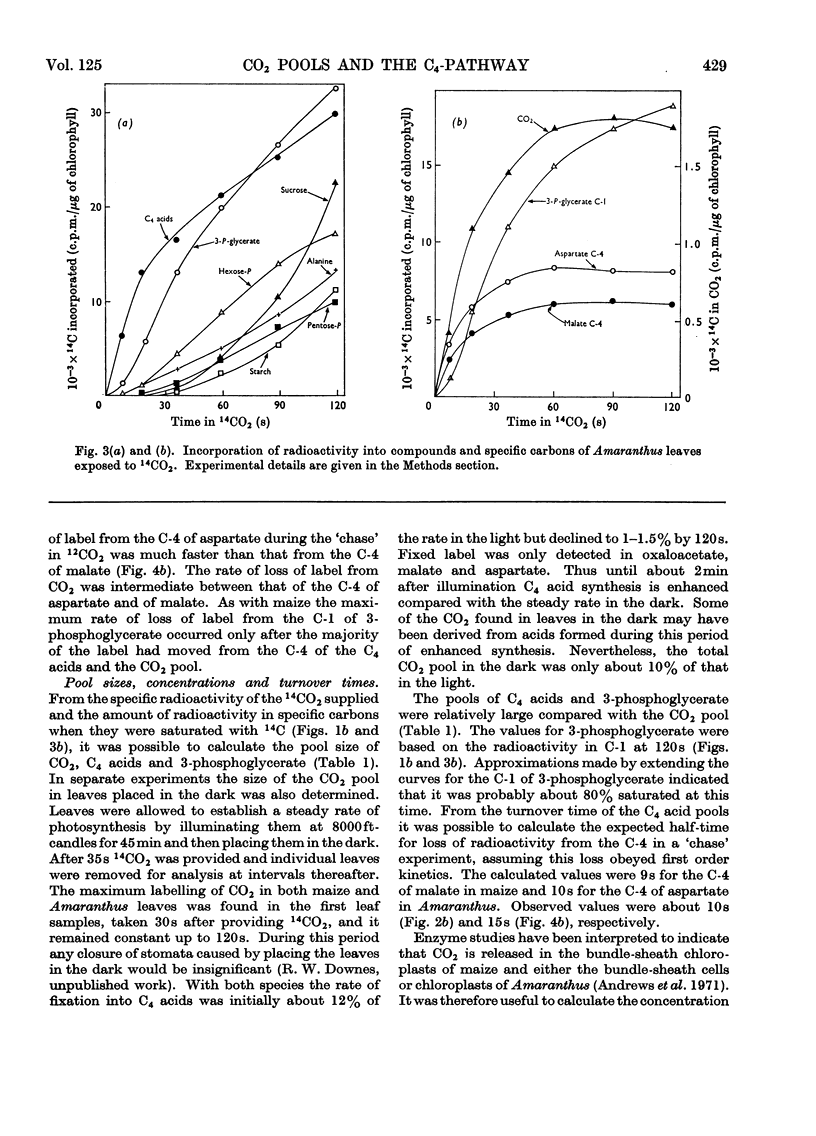
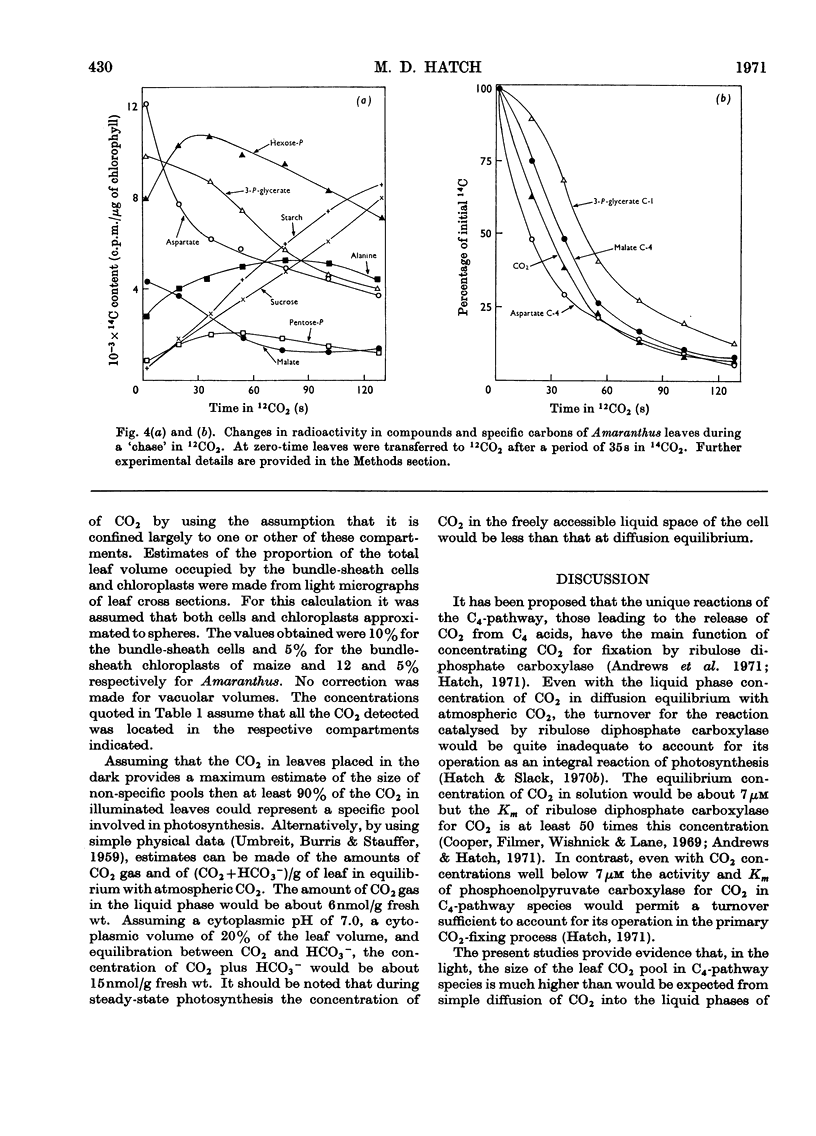
1. Leaves were exposed to 14CO2 under steady-state conditions for photosynthesis. The kinetics of entry or loss of label in pools of CO2 and other compounds was examined during the period of the pulse and a `chase' with 12CO2. 2. With maize the kinetics of labelling of the major CO2 pool and of depletion of label during a `chase' was consistent with this pool being derived from the C-4 of malate and being the precursor of the C-1 of 3-phosphoglycerate. 3. Similar results were obtained for Amaranthus leaves except that the C-4 of aspartate rather than malate was apparently the primary source of CO2. 4. The size and turnover time of the CO2 and C4 acid pools was calculated. These results provided the basis for estimating the concentration of CO2 in the bundle-sheath cells or chloroplasts assuming the pool was largely restricted to one or other of these compartments. 5. These findings are considered in relation to current schemes for the C4-pathway and the operation of a CO2 concentrating mechanism to serve ribulose diphosphate carboxylase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. Better services for the mentally handicapped. Nurs Mirror Midwives J. 1971 Oct 22;133(17):9–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. M., Brown R. H., Black C. C. Photosynthetic CO(2) Fixation Products and Activities of Enzymes Related to Photosynthesis in Bermudagrass and Other Plants. Plant Physiol. 1971 Feb;47(2):199–203. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Filmer D. The active species of "CO2" utilized by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. E., Lee S. S., Chen T. M., Black C. C. Carboxylation reactions and photosynthesis of carbon compounds in isolated mesophyll and bundle sheath cells of Digitaria sanguinalis (L.) Scop. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. A new enzyme for the interconversion of pyruvate and phosphopyruvate and its role in the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1060141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. Photosynthesis by sugar-cane leaves. A new carboxylation reaction and the pathway of sugar formation. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):103–111. doi: 10.1042/bj1010103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. S., Hatch M. D. Properties and regulation of leaf nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-malate dehydrogenase and 'malic' enzyme in plants with the C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):273–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1190273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. S., Hatch M. D. The C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Identification of intermediates and products and quantitative evidence for the route of carbon flow. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):127–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1140127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortschak H. P., Hartt C. E., Burr G. O. Carbon Dioxide Fixation in Sugarcane Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1965 Mar;40(2):209–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C. R., Hatch M. D. Comparative studies on the activity of carboxylases and other enzymes in relation to the new pathway of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation in tropical grasses. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):660–665. doi: 10.1042/bj1030660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C. R., Hatch M. D., Goodchild D. J. Distribution of enzymes in mesophyll and parenchyma-sheath chloroplasts of maize leaves in relation to the C4-dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):489–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1140489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


