Abstract
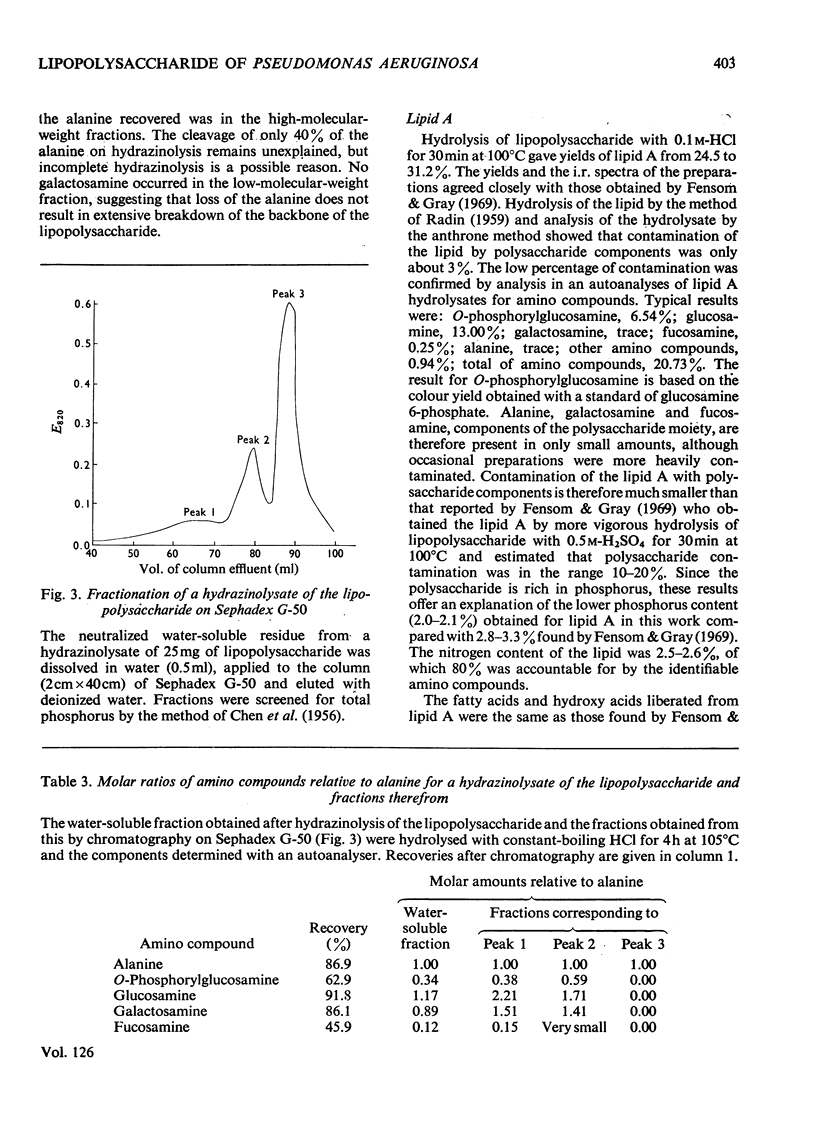
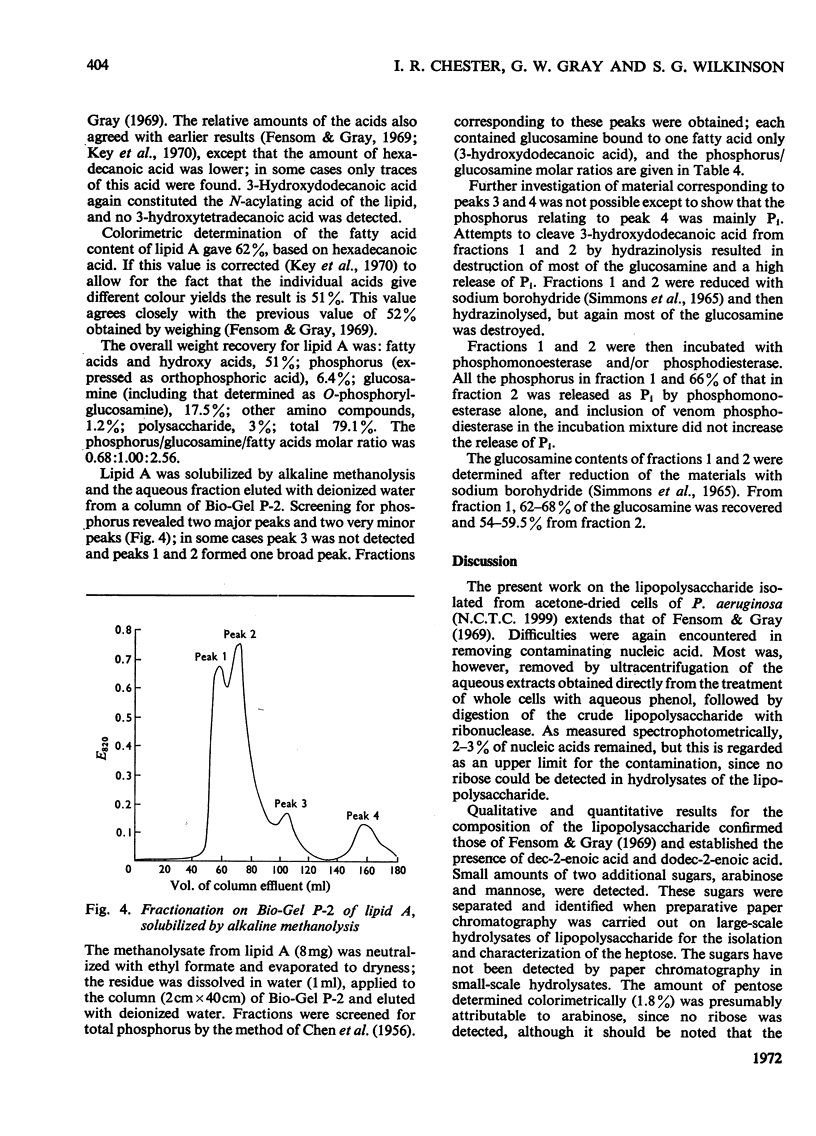
1. Qualitative and quantitative analytical results for the lipopolysaccharide from acetone-dried cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (N.C.T.C. 1999) are presented and possible contamination of the material with nucleic acid was further examined. 2. Additional sugars detected (only in large-scale hydrolysates) were mannose and arabinose; traces of spermidine and putrescine were also found. 3. The heptose component is l-glycero-d-mannoheptose. 4. The thiobarbituric acid-positive component is a 3-deoxy-2-octulonic acid, of which only 35–40% links lipid A to the polysaccharide. This linkage is not broken by hydrolysis with acetic acid up to 0.08m. 5. Liberation of lipid A required hydrolysis with 0.1m-hydrochloric acid, which substantially degraded the polysaccharide moiety. 6. Fractions obtained from the degraded polysaccharide by high-voltage electrophoresis were examined; in these, the alanine/galactosamine molar ratio is approx. 1. 7. Hydrazinolysis of whole lipopolysaccharide showed that at least 40% of the alanine is in amide linkage, possibly with galactosamine. 8. Lipid A, solubilized by alkaline methanolysis was fractionated; most of the phosphorus of the higher-molecular-weight fractions was released as Pi by a phosphomonoesterase. 9. Hydrazinolysis of lipid A destroyed approx. 80% of the glucosamine, and glycosidically linked glucosamine oligosaccharides could not be isolated.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Quadling C., Perry M. B. D-glycero-D-manno-heptose as a component of lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Dec;13(12):1605–1613. doi: 10.1139/m67-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Singh P. P. Structural features of lipid A preparations isolated from Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Singh P. P. The chemical constitution of lipid A from Serratia marcescens. Can J Biochem. 1970 Jan;48(1):55–62. doi: 10.1139/o70-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Singh P. P. The linkage between the D-glucosamine units of lipid A isolated from the lipopolysaccharide of Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 28;187(3):457–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., ROARK E. L-FUCOSAMINE AND 4-OXO-NORLEUCINE AS CONSTITUENTS IN MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES OF CERTAIN ENTERIC BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 May 2;202:493–494. doi: 10.1038/202493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON A. J., CARTER H. E. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE LIPID A COMPONENT OF THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:411–418. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdian G., Dröge W., Kotelko K., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Vorkommen zweier Heptosen in Lipopolysacchariden enterobakterieller Zellwände: L-Glycero-und D-Glycero-D-mannoheptose. Biochem Z. 1966 Mar 28;344(2):197–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A. The identification of aldoheptose sugars. Biochem J. 1957 Oct;67(2):253–256. doi: 10.1042/bj0670253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Release of ethanolamine pyrophosphate during mild acid hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):400–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood D. C. The distribution of 2-keto-3-deoxy-octonic acid in bacterial walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):373–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Gray G. W. The chemical composition of the lipopolyacarideof Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1140185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Meadow P. M. Evidence for two regions in the polysaccharide moiety of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghalambor M. A., Levine E. M., Heath E. C. The biosynthesis of cell wall lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli. 3. The isolation and characterization of 3-deoxyoctulosonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3207–3215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella R mutants. 6. Investigations on the structure of the lipid A component. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jan;7(3):370–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANESSIAN S., HASKELL T. H. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGEN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2758–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITAYA K., UI M. COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS IN BIOLOGICAL FLUIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. The purification and chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1200559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamkin W. M., Ward D. N., Walborg E. F., Jr Quantitative determination of neutral monosaccharide residues in glycoproteins and glycopeptides by thin-layer densitometry. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lato M., Brunelli B., Ciuffini G., Mezzetti T. Bidimensional thin-layer chromatography of carbohydrates on silica gel impregnated with boric acid. J Chromatogr. 1968 Mar 26;34(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O. Recent results on the biochemistry of the cell wall lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1970 Sep;9(9):649–663. doi: 10.1002/anie.197006491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Partridge S. M. Studies in immunochemistry: The fractionation and nature of antigenic material isolated from Bact. dysenteriae (Shiga). Biochem J. 1940 Feb;34(2):169–191. doi: 10.1042/bj0340169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Cundy K. R., Neale N. L., Nowotny A. M., Radvany R., Thomas S. P., Tripodi D. J. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. IV. Fractionation of the components. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):586–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A. Heterogeneity of endotoxic bacterial lipopolysaccharides revealed by ion-exchange column chromatography. Nature. 1966 Apr 16;210(5033):278–280. doi: 10.1038/210278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'NEILL G. J., TODD J. P. Extraction of nucleic acid-free lipopolysaccharides from gram-negative bacteria. Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:344–345. doi: 10.1038/190344b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribi E., Anacker R. L., Brown R., Haskins W. T., Malmgren B., Milner K. C., Rudbach J. A. Reaction of endotoxin and surfactants. I. Physical and biological properties of endotoxin treated with sodium deoxycholate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1493–1509. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1493-1509.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. A., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. The immunochemistry of Salmonella chemotype VI O-antigens. The structure of oligosaccharides from Salmonella group G (o 13,22) lipopolysaccharides. Biochem J. 1965 Dec;97(3):807–814. doi: 10.1042/bj0970807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Knox K. W., Work E. Chemical and biological properties of an extracellular lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli grown under lysine-limiting conditions. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):53–61. doi: 10.1042/bj0990053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


