Abstract
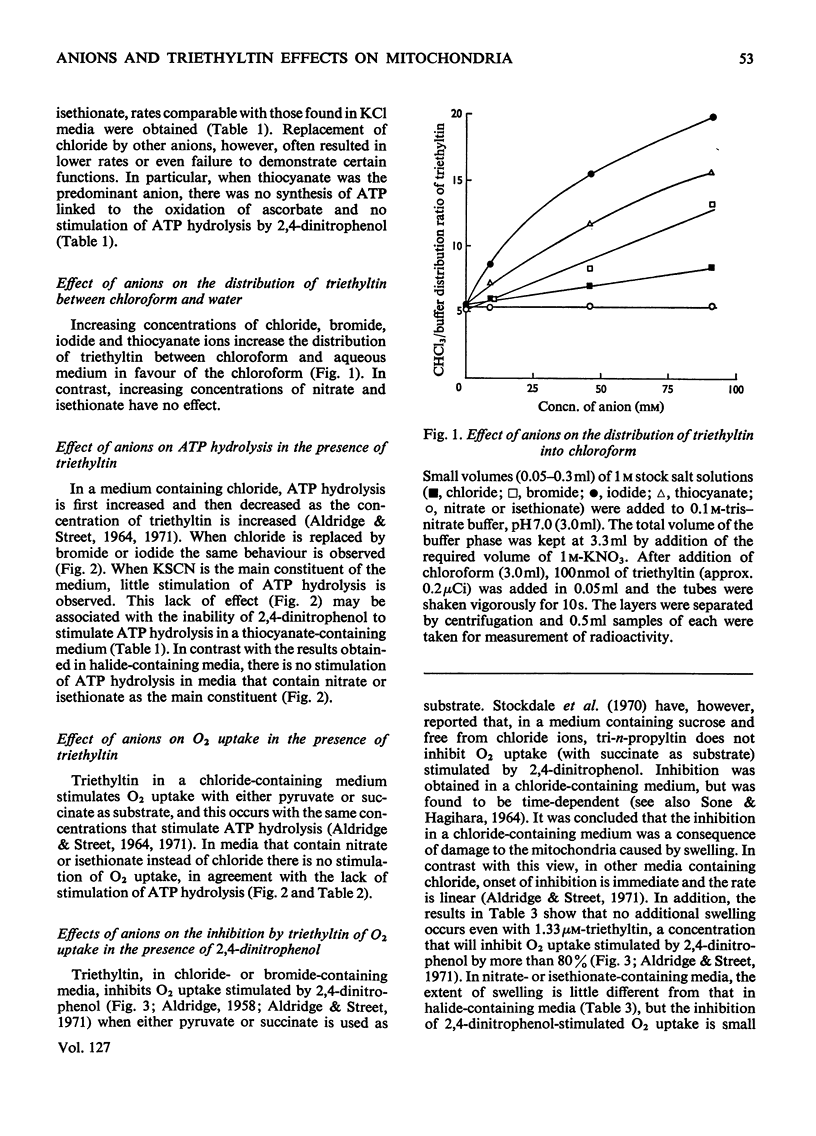
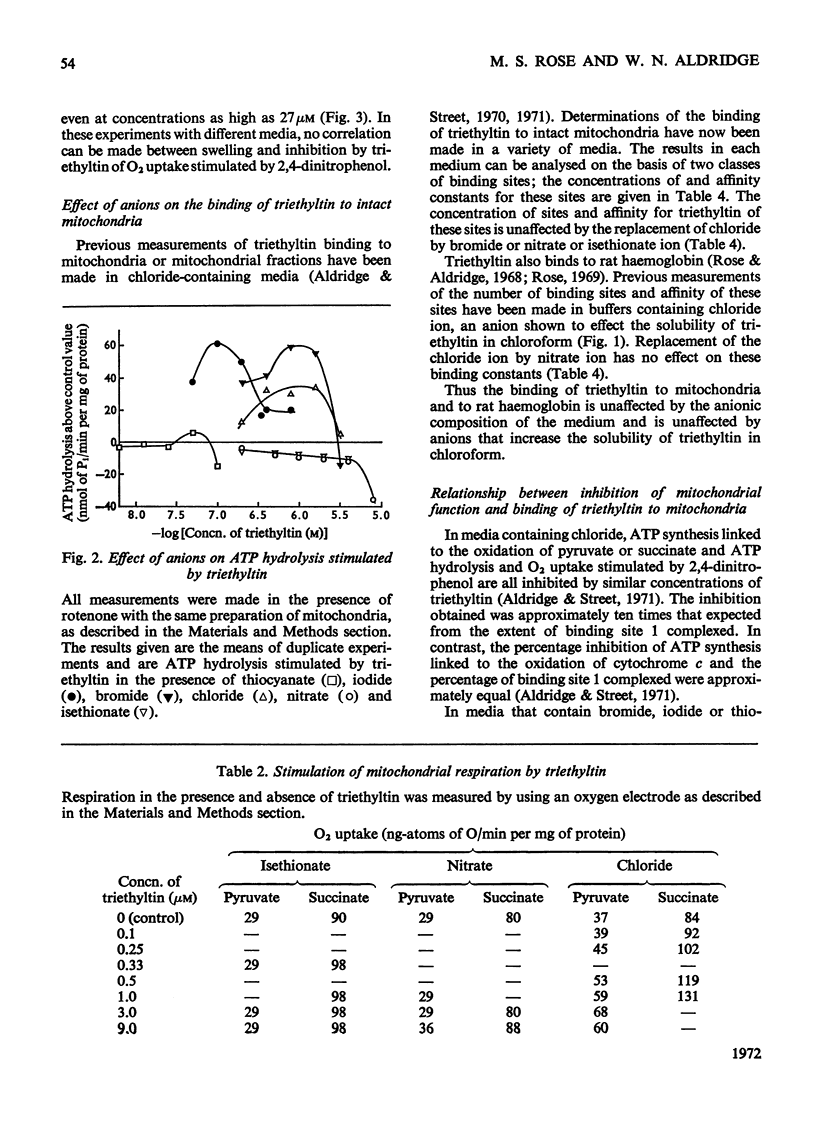
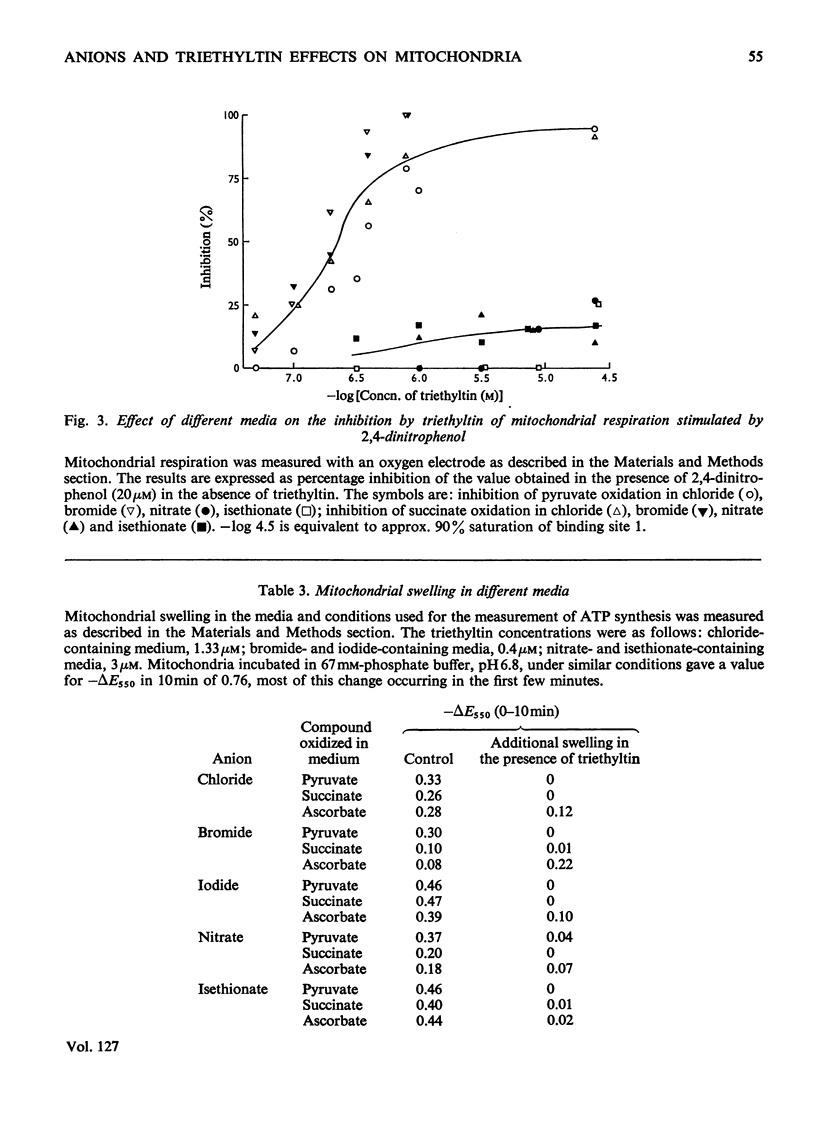
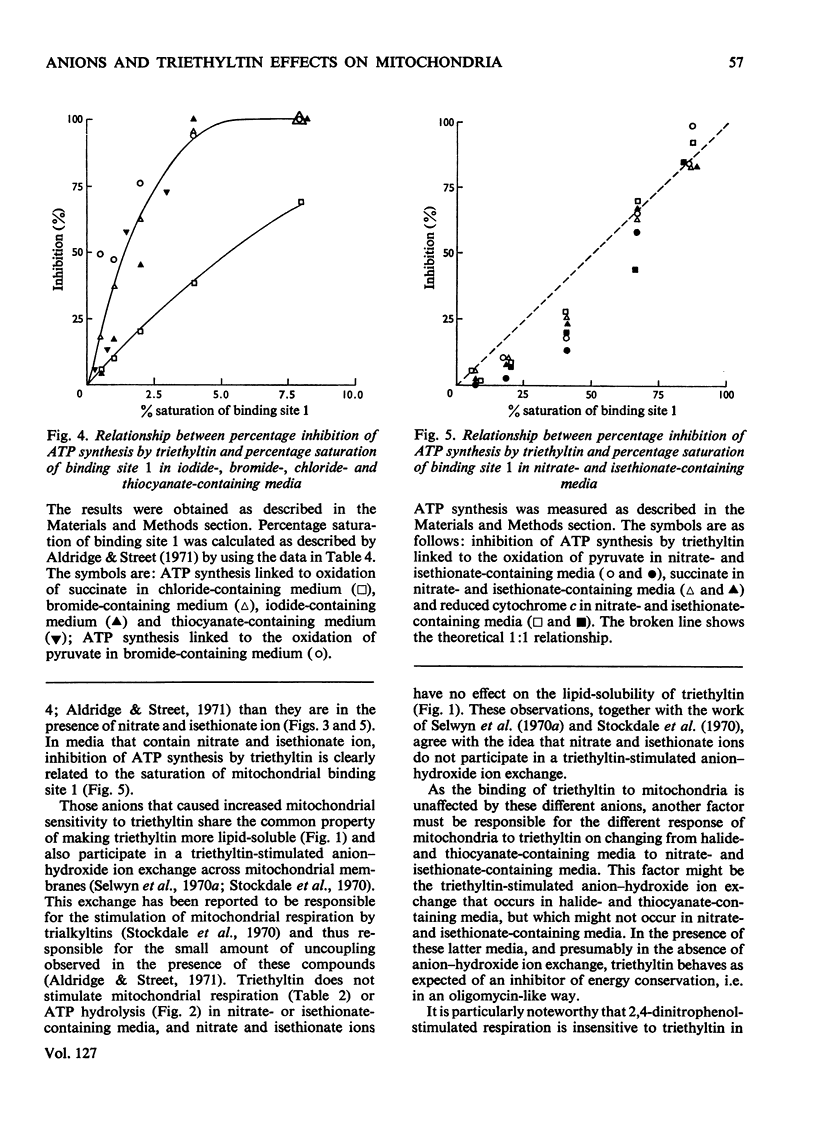
1. The binding of triethyltin to rat liver mitochondria is unaffected by the nature of the predominant anion in the incubation medium. 2. With chloride, bromide or iodide as the predominant anion, ATP synthesis linked to the oxidation of pyruvate or succinate and ATP hydrolysis stimulated by 2,4-dinitrophenol are much more sensitive to triethyltin than they are when nitrate or isethionate is the predominant anion. 3. When nitrate or isethionate is the predominant anion, oxygen uptake stimulated by 2,4-dinitrophenol is not inhibited by triethyltin. 4. In the presence of nitrate or isethionate anions, inhibition of ATP synthesis is directly related to the binding of triethyltin to mitochondria. 5. The relationship of the above effects to the anion–hydroxide ion exchange mediated by triethyltin and the relevance of this to published arrangements for coupling of electron transport to ATP synthesis are discussed.
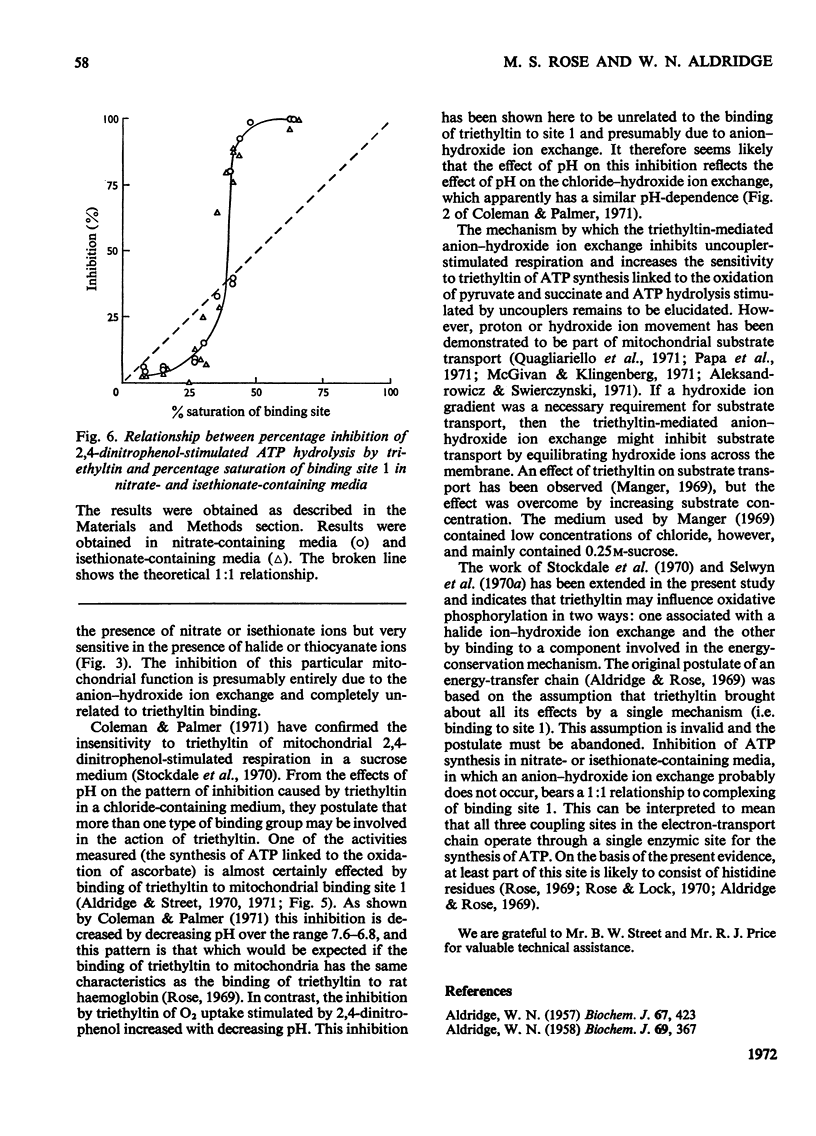
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Adenosine triphosphatase in the microsomal fraction from rat brain. Biochem J. 1962 Jun;83:527–533. doi: 10.1042/bj0830527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., CREMER J. E. The biochemistry of organo-tin compounds; diethyltin dichloride and triethyltin sulphate. Biochem J. 1955 Nov;61(3):406–418. doi: 10.1042/bj0610406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Liver and brain mitochondria. Biochem J. 1957 Nov;67(3):423–431. doi: 10.1042/bj0670423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. The biochemistry of organotin compounds: trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):367–376. doi: 10.1042/bj0690367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Rose M. S. The mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation A hypothesis derived from studies of trimethyltin and triethyltin compounds. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemical effects and properties of trialkyltins. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):287–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0910287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. The relation between the specific binding of trimethylytin and triethyltin to mitochondria and their effects on various mitochondrial functions. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):221–234. doi: 10.1042/bj1240221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Oxidative phosphorylation. The specific binding of trimethyltin and triethyltin to rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):171–179. doi: 10.1042/bj1180171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrowicz Z., Swierczyński J. Fumarate transport by rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 1;15(4):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80635-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. O., Palmer J. M. The influence of pH on the inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation and electron transport by triethyltin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 7;245(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger J. R. The effect of triethyltin on mitochondrial ion accumulation. FEBS Lett. 1969 Dec 30;5(5):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Klingenberg M. Correlation between H+ and anion movement in mitochondria and the key role of the phosphate carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):392–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Francavilla A., Paradies G., Meduri B. The transport of pyruvate in rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jan 30;12(5):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliariello E., Genchi G., Palmieri F. Respiration-dependent anion uptake by rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1971 Mar 22;13(5):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Aldridge W. N. The interaction of triethyltin with components of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):821–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1060821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S. Evidence for histidine in the triethyltin-binding site of rat haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):129–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1110129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Lock E. A. The interaction of triethyltin with a component of guinea-pig liver supernatant. Evidence for histidine in the binding sites. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):151–157. doi: 10.1042/bj1200151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONE N., HAGIHARA B. INHIBITORY ACTION OF TRIALKYLTIN COMPOUNDS ON OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN MITOCHONDRIA. J Biochem. 1964 Aug;56:151–156. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Dunnett S. J. Calcium transport in mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 18;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn M. J., Dawson A. P., Stockdale M., Gains N. Chloride-hydroxide exchange across mitochondrial, erythrocyte and artificial lipid membranes mediated by trialkyl- and triphenyltin compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):120–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale M., Dawson A. P., Selwyn M. J. Effects of trialkyltin and triphenyltin compounds on mitochondrial respiration. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):342–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


