Abstract
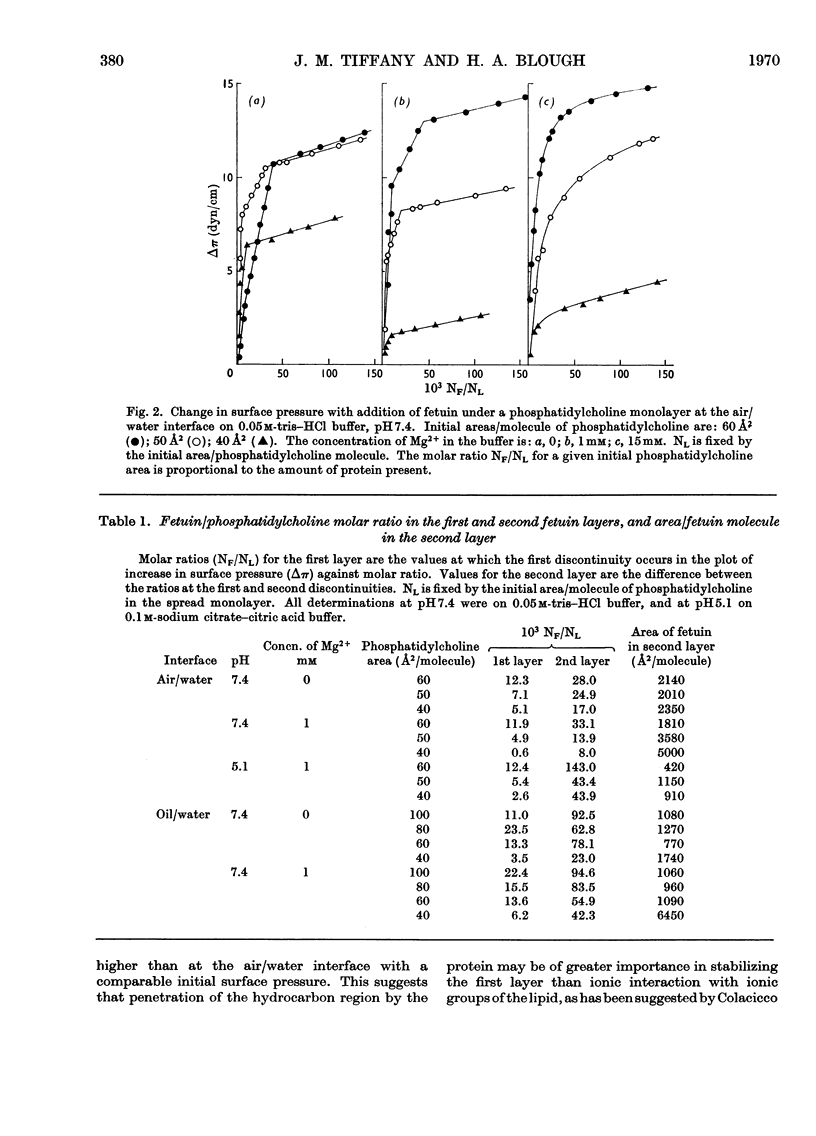
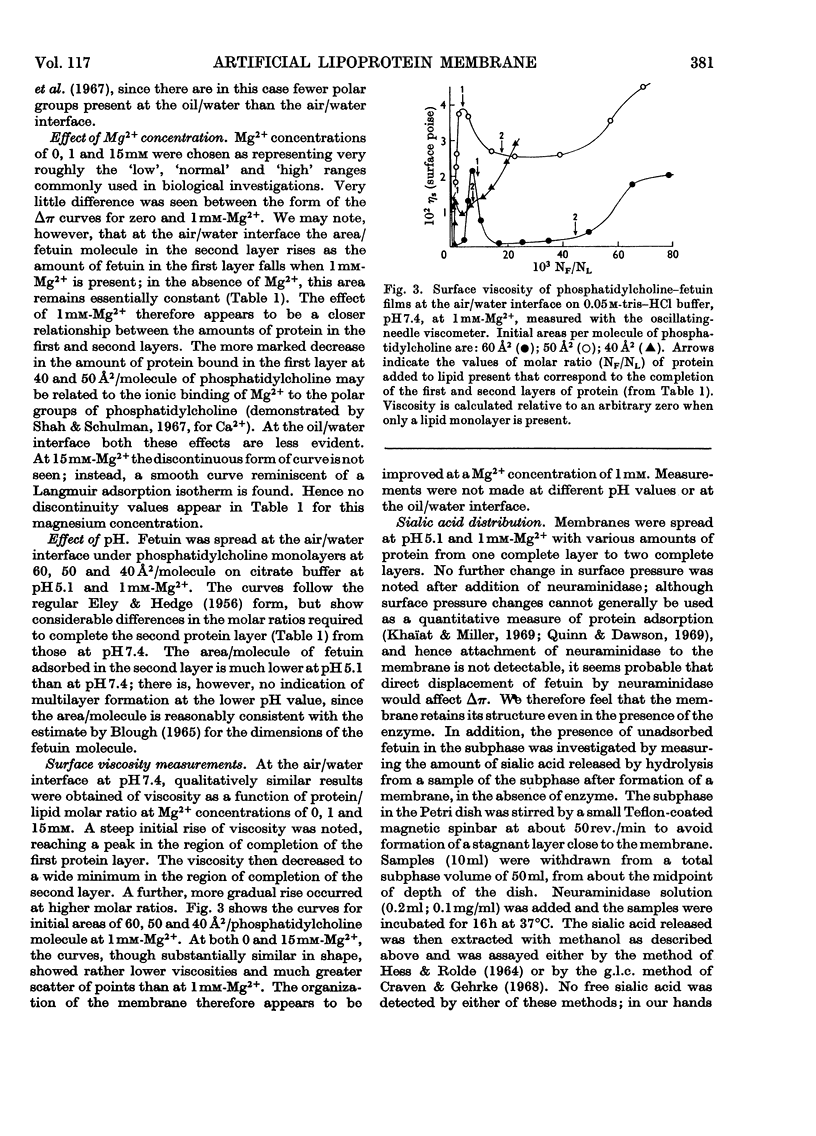
1. An artificial membrane system was formed by spreading at air/water and oil/water interfaces, by using phosphatidylcholine and the glycoprotein fetuin (mol.wt. 48400). 2. The plot of increase of interfacial pressure against amount of protein added beneath a monomolecular film of phosphatidylcholine showed two discontinuities, corresponding to the completion of two distinct layers of protein: (a) largely denatured and closely associated with the polar head groups of phosphatidylcholine, possibly with penetration of non-polar protein groups between the phosphatidylcholine molecules and (b) an additional adsorbed layer of substantially native fetuin in either a close-packed or open-lattice array. A more compactly organized membrane was apparently formed at pH7.4 with 1mm-Mg2+ in the aqueous phase than without Mg2+; at 15mm-Mg2+, more random adsorption of protein appeared to take place. Qualitatively similar results were obtained at pH5.1 with 1mm-Mg2+. Closer initial packing of the phosphatidylcholine layer decreased both the magnitude of the interfacial pressure change and the amounts of protein bound in the two layers. 3. The amount of N-acetylneuraminic acid released by neuraminidase (EC 3.2.1.18) in the subphase was measured at pH5.1; a mean distribution of 9.7×1013 residues/cm2 was calculated for the completed second protein layer.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON R. M. THE ACTION OF NEURAMINIDASE FROM CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS ON GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Jul;10:503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb09853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough H. A. Viral neuraminidase: a cytochemical binding method using a glycoprotein coupled to ferritin. Virology. 1967 Mar;31(3):514–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIRNS H. J., FAZEKAS DE ST. GROTH S. The number of allantoic cells in the chick embryo. J Immunol. 1957 Mar;78(3):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Colacicco G., Rapport M. M. Lipid monolayers: interactions with the apoprotein of high density plasma lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):562–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Jourdian G. W., Roseman S. The sialic acids. VI. Purification and properties of sialidase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3501–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G. Applications of monolayer techniques to biological systems: symptoms of specific lipid-protein interactions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1969 Feb;29(2):345–364. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(69)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. A., Gehrke C. W. Quantitative determination of N-acetylneuraminic acid by gas-liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1968 Oct 22;37(3):414–421. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)99137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE BERNARD L. Associations moléculaires entre les lipides. II. Lecithine et cholestérol. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1958;40(1):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diatlovitskaia E. V., Volkova V. I., Bergel'son L. D. Sravenie molekuliarnogo sostava fostatidilétanolaminov i fostatidilkholinov. Biokhimiia. 1967 Nov-Dec;32(6):1227–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS H., ROLDE E. FLUOROMETRIC ASSAY OF SIALIC ACID IN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3215–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaïat A., Miller I. R. Adsorption of ribonuclease at the air-water interface and on phospholipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 15;183(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. 8. Entry of influenza virus. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):925–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.925-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro Y., Eylar E. H. Physical and chemical studies on glycoproteins. 3. The microheterogeneity of fetuin, a fetal calf serum glycoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):476–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro Y., Eylar E. H. Physical and chemical studies on glycoproteins. IV. The influence of sialic acid on the conformation of fetuin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. The interaction of cytochrome c with monolayers of phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;113(5):791–803. doi: 10.1042/bj1130791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO M. J., SPIRO R. G. Composition of the peptide portion of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1507–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO R. G. Studies on fetuin, a glycoprotein of fetal serum. II. Nature of the carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:382–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. O., Schulman J. H. The ionic structure of lecithin monolayers. J Lipid Res. 1967 May;8(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Studies on fetuin, a glycoprotein of fetal serum. I. Isolation, chemical composition, and physiochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235(10):2860–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


