Abstract
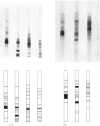
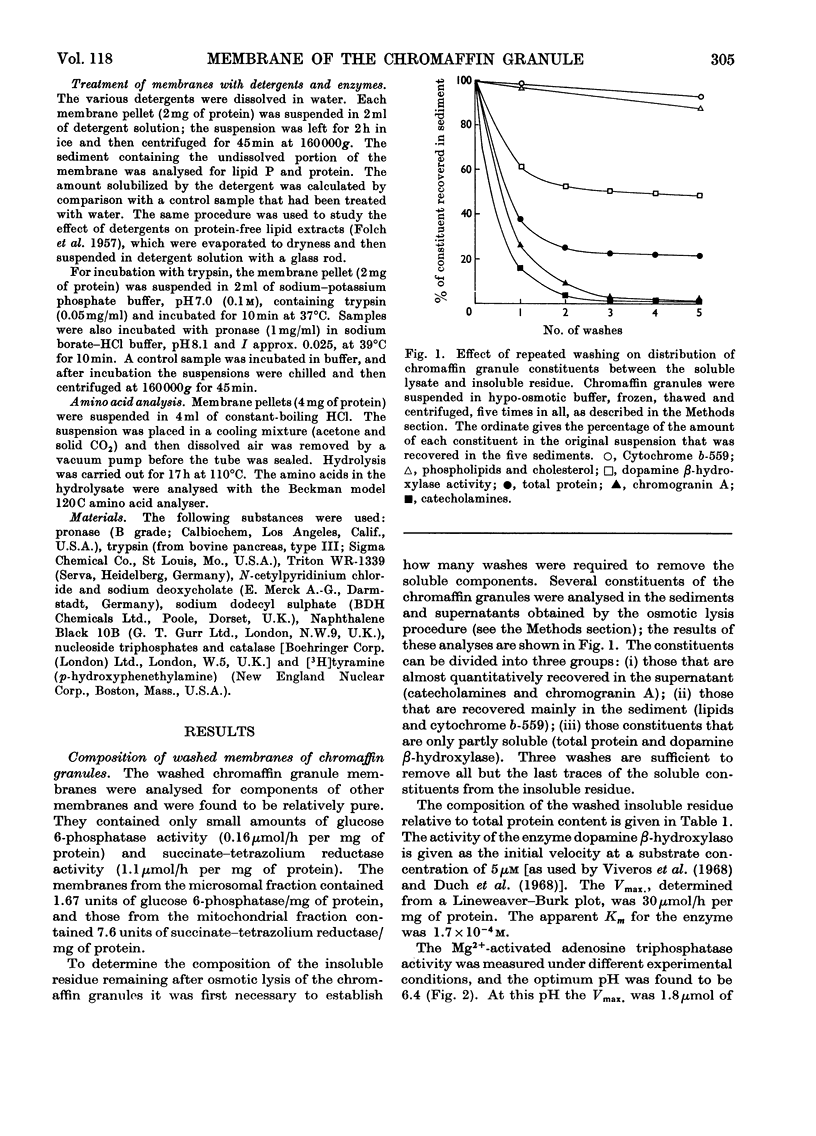
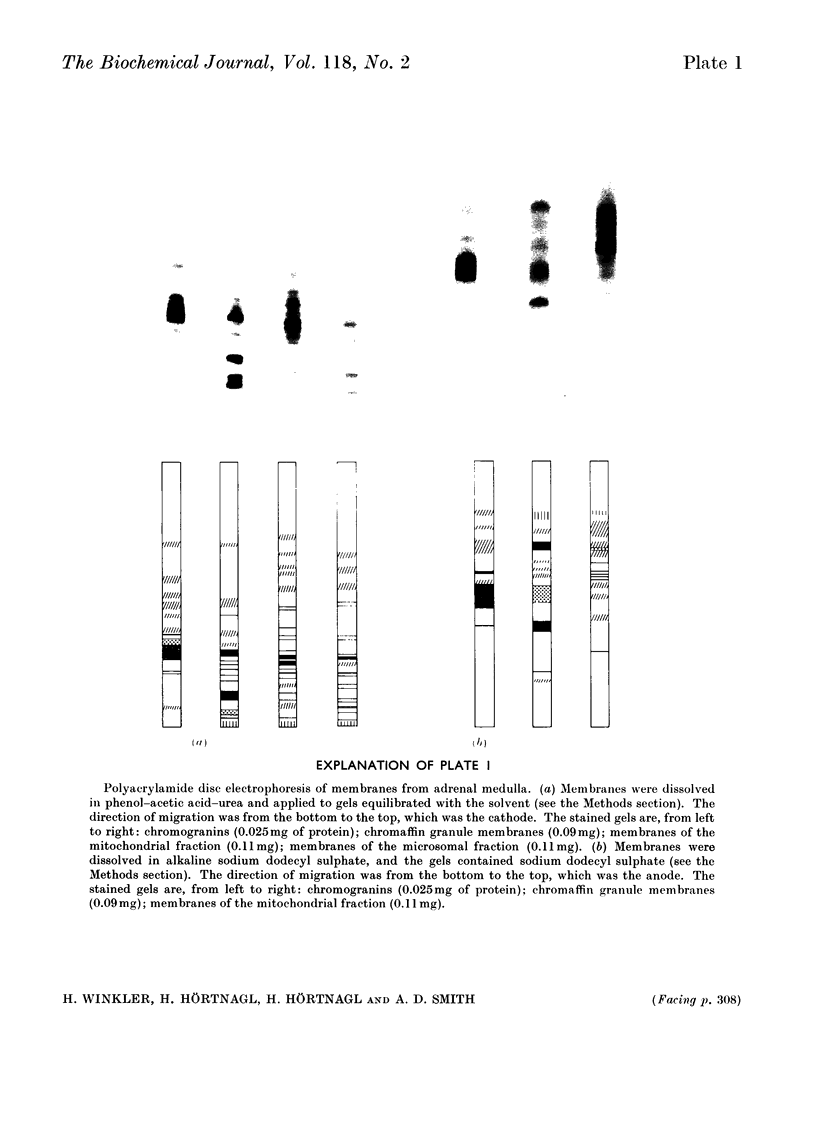
Washed membranes of bovine adrenal chromaffin granules contained most of the cholesterol and phospholipids of the particle and 22% of the total protein. The protein/lipid ratio was about 0.45 (w/w). Dopamine(3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine)β-hydroxylase, Mg2+-activated nucleoside triphosphatase and cytochrome b-559 activities were present in the membrane. ATP was the best substrate for the nucleoside triphosphatase, whose pH optimum was 6.4, Km 7×10−4m and Vmax. 1.8μmol/h per mg of protein. Treatment of the membranes with various detergents caused a preferential solubilization of protein compared with lipids. Membranes dissolved in sodium dodecyl sulphate or phenol–acetic acid–urea were subjected to polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis at alkaline and acid pH respectively. The electrophoretic patterns given by the proteins of the chromaffin granule membrane were distinct from those given by the chromogranins, and from those given by mitochondrial and microsomal membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANKS P. THE ADENOSINE-TRIPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY OF ADRENAL CHROMAFFIN GRANULES. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:490–496. doi: 10.1042/bj0950490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belpaire F., Laduron P. Tissue fractionation and catecholamines. I. Latency and activation properties of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in adrenal medulla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;17(3):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Firemark H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Lipids of the adrenal medulla. Lysolecithin, a characteristic constituent of chromaffin granules. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):545–549. doi: 10.1042/bj1040545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Mahler H. R. Resolution of insoluble proteins in rat brain subcellular fractions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 May;120(2):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vito E., Santomé J. A. Disc electrophoresis of proteins in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Experientia. 1966 Feb 15;22(2):124–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01900194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C. P., West D. Complete separation of lipid classes on a single thin-layer plate. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):324–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S., Kaufman S. 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine beta-hydroxylase. Physical properties, copper content, and role of copper in the catalytic acttivity. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4763–4773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. I., Lucy J. A. Cell fusion induced by lysolecithin. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(3):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Yamano T. Cytochrome 559 in the microsomes of the adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jul 26;20(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner N., Kirshner A. G., Kamin D. L. Adenosine triphosphatase activity of adrenal medulla catecholamine granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):332–335. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamed S., Poisner A. M., Trifaró J. M., Douglas W. W. The fate of the chromaffin granule during catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla. 3. Recovery of a purified fraction of electron-translucent structures. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Feb;17(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka M., Kajikawa K., Ohuchi T., Yoshida H., Imaizumi R. Distribution of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in subcellular fractions of adrenal medulla. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 1;6(5):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTEOUS J. W., CLARK B. THE ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SUBCELLULAR COMPONENTS OF THE EPITHELIAL CELLS OF RABBIT SMALL INTESTINE. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:159–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0960159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider F. H., Smith A. D., Winkler H. Secretion from the adrenal medulla: biochemical evidence for exocytosis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):94–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. A simple method for the isolation of adrenal chromaffin granules on a large scale. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1030480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. J., Kirshner N. A specific soluble protein from the catecholamine storage vesicles of bovine adrenal medulla. I. Purification and chemical characterization. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jan;3(1):52–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieder N., Ziegler E., Winkler H., Smith A. D. Some properties of soluble proteins from chromaffin granules of different species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;17(8):1553–1556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., MacLennan D. H., Tzagoloff A., Stoner C. D. Studies on the electron transfer system. LXVII. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the mitochondrial electron transfer complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Arqueros L., Kirshner N. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. V. Retention of storage vesicle membranes following release of adrenaline. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Hörtnagl H. Chromaffine Granula des Rindernebennierenmarks: Charakterisierung der Membran. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Oct;350(10):1176–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von chromaffinen Noradrenalin-Granula aus Schweine-Nebennierenmark. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1969;263(2):340–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Smith A. D. Lipids of adrenal chromaffin granules: fatty acids composition of phospholipids, in particular lysolecithin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(4):379–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00537182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Strieder N., Ziegler E. Uber Lipide, insbesondere Lysolecithin, in den chromaffinen Granula verschiedener Species. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;256(4):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLATKIS A., ZAK B., BOYLE A. J. A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]