Abstract
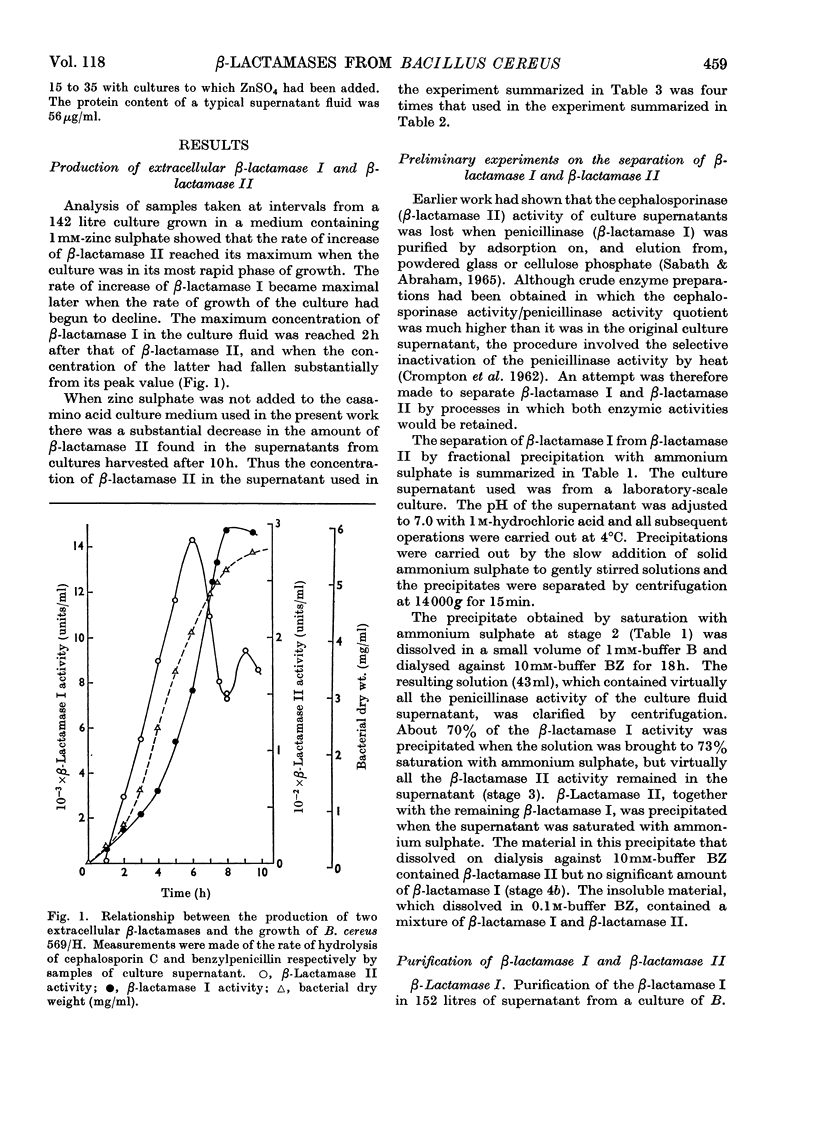
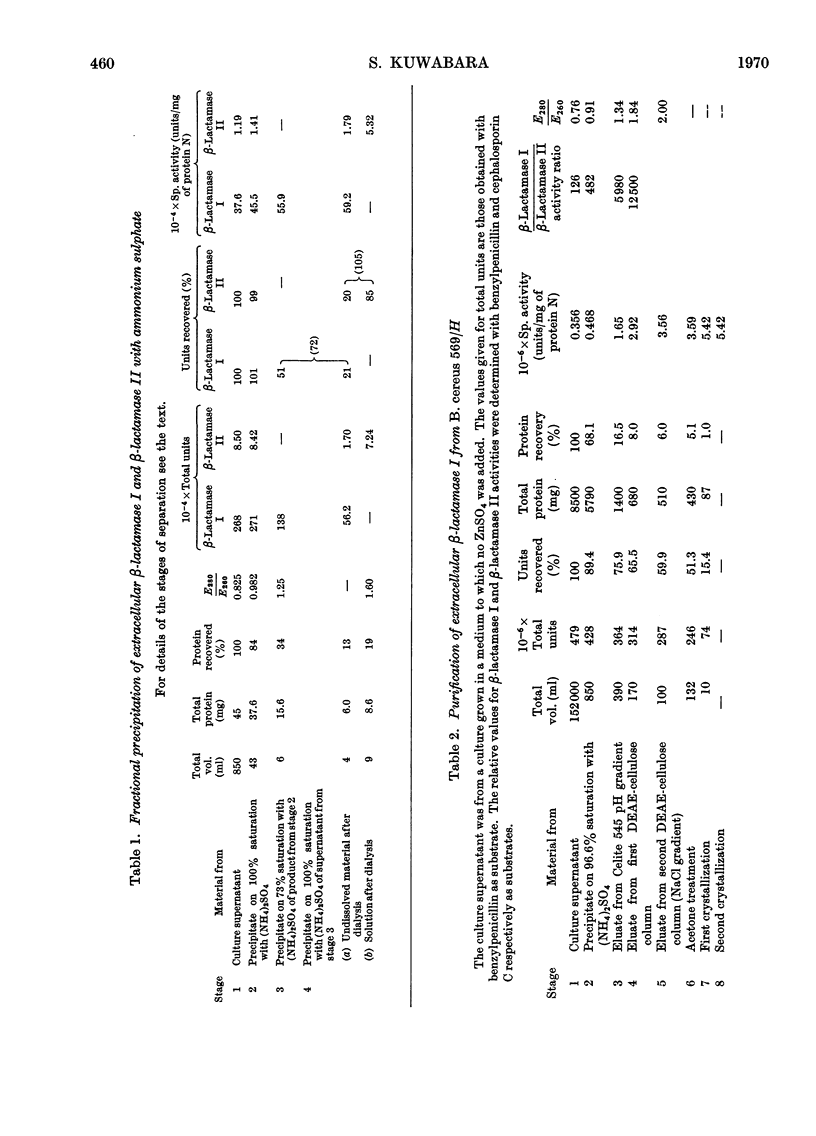
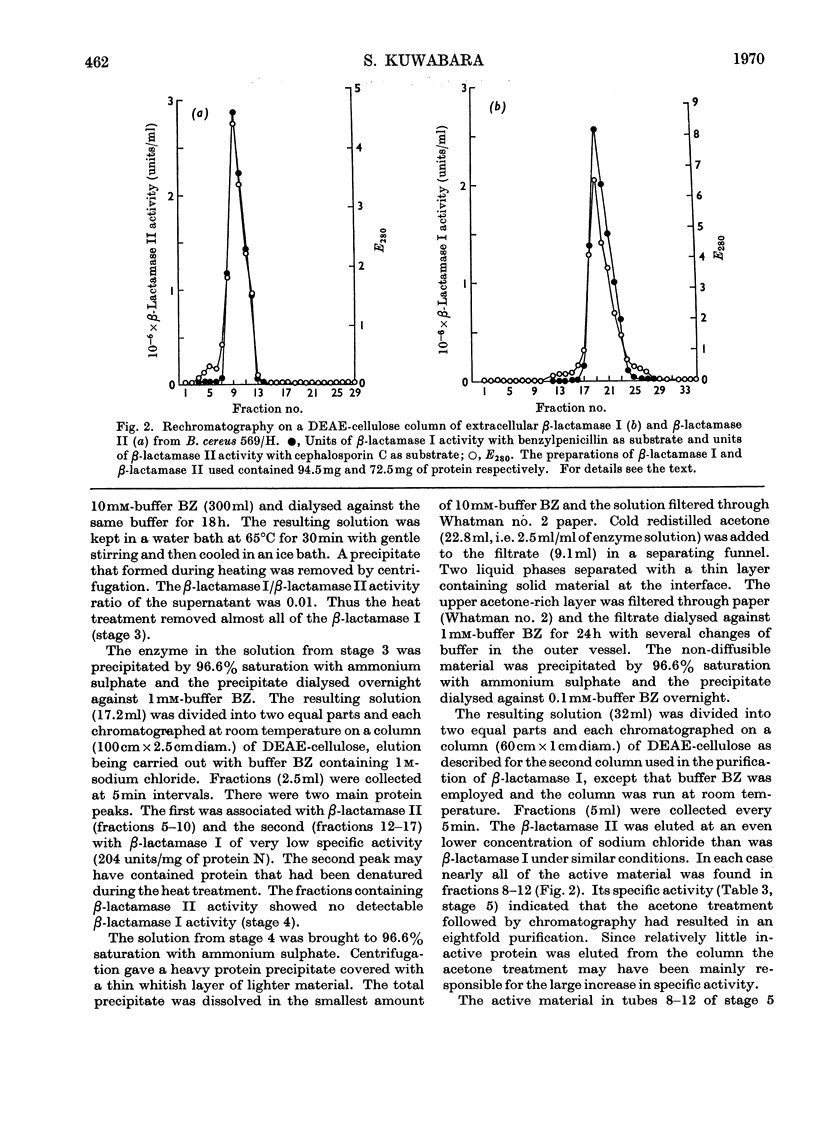
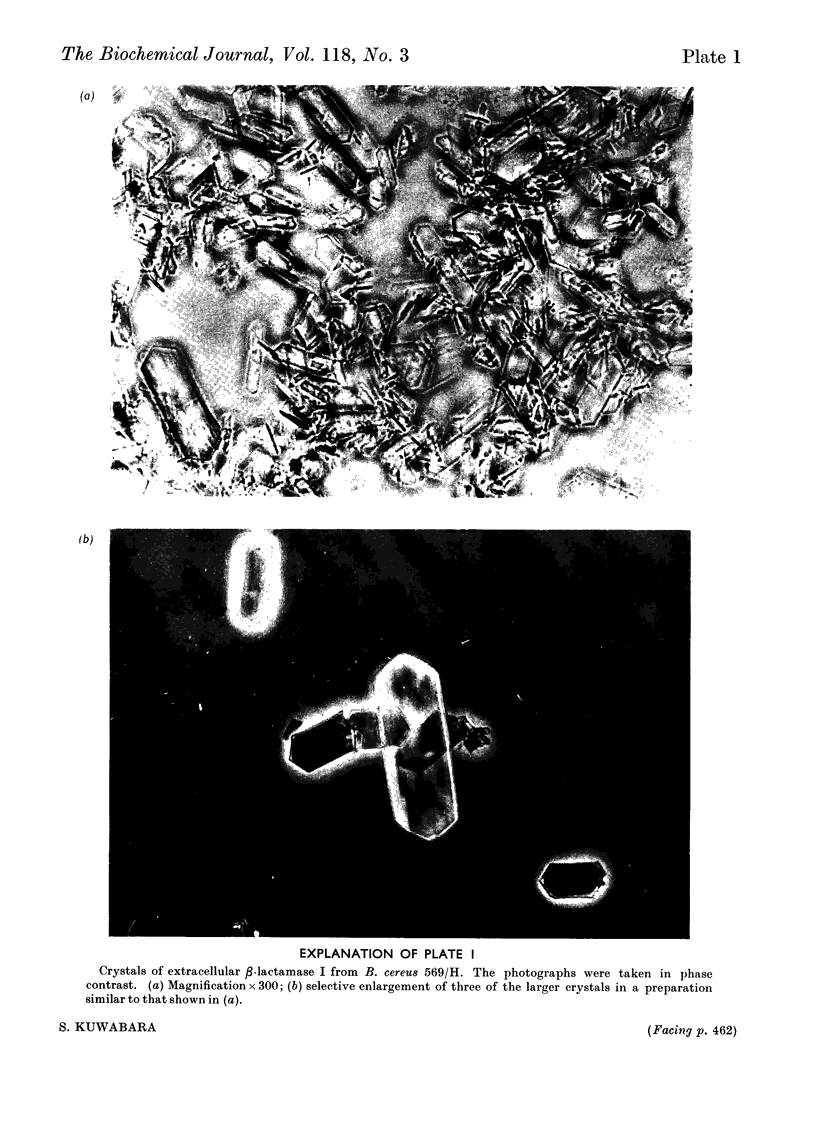
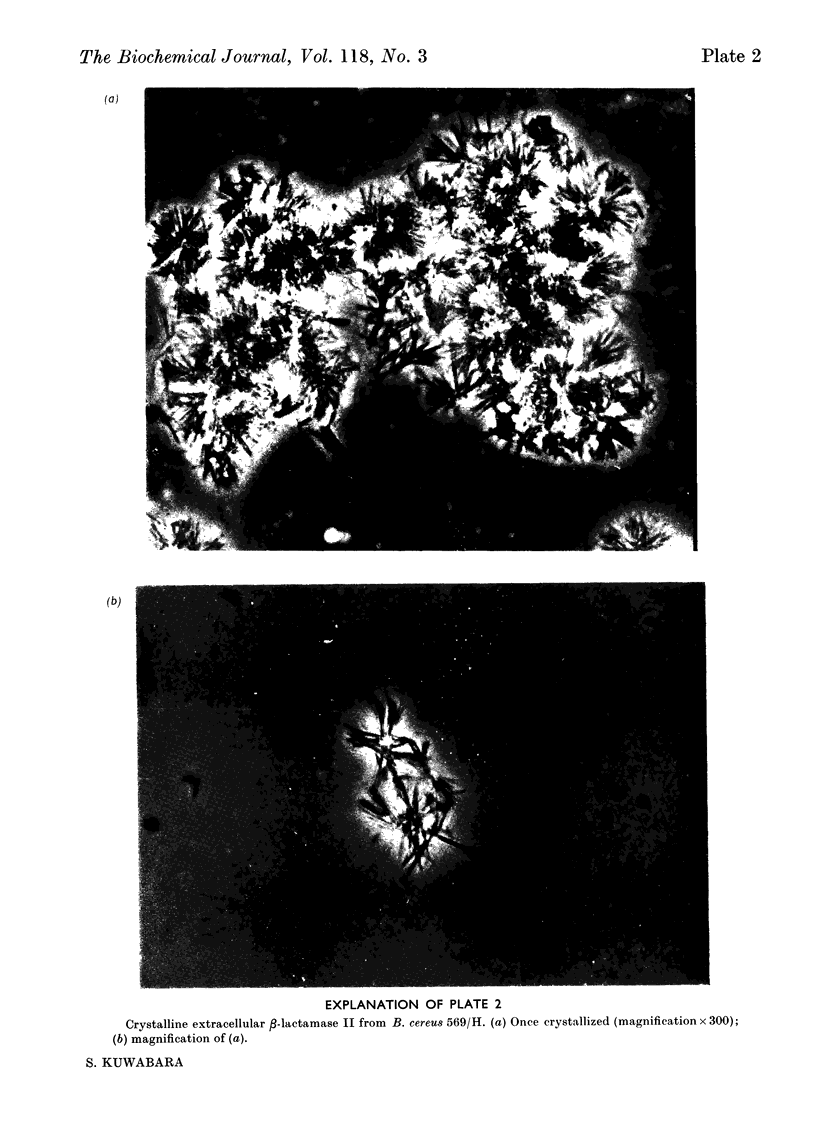
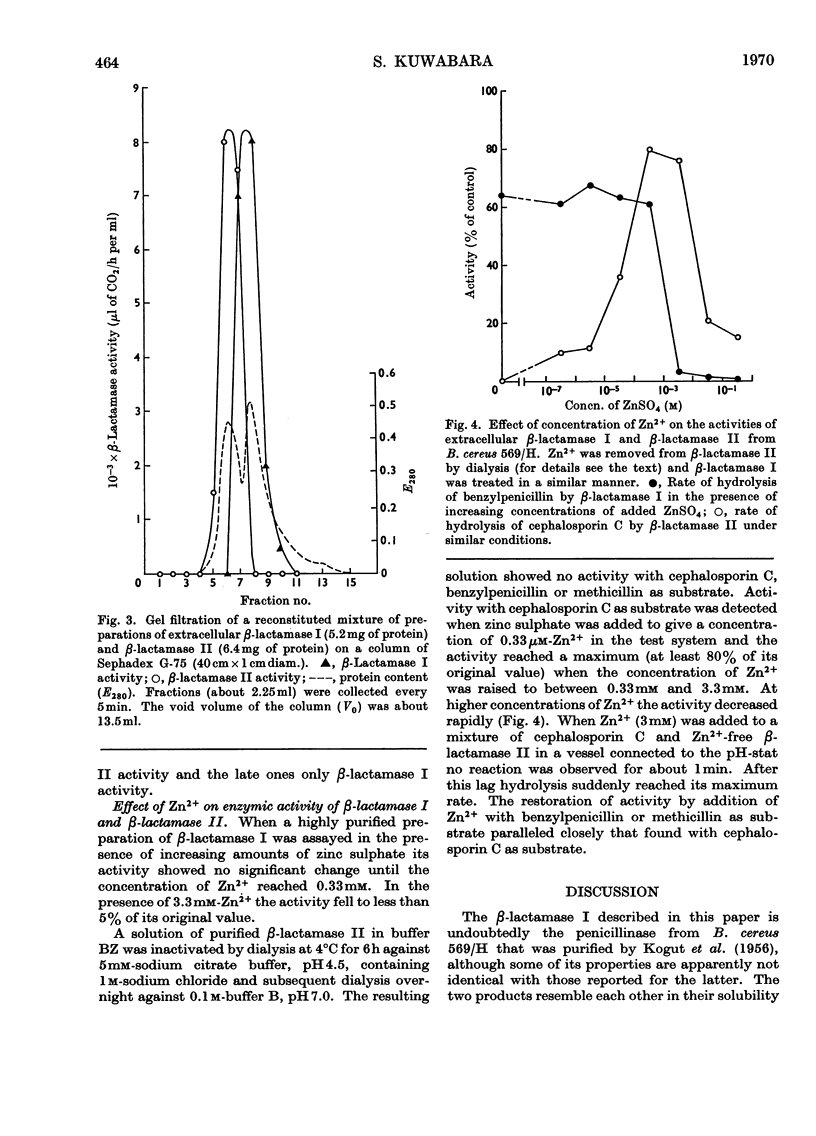
1. When Bacillus cereus 569/H was grown in a casamino acid (casein-hydrolysate) medium containing zinc sulphate rapid production of extracellular β-lactamase II preceded that of β-lactamase I. 2. β-Lactamase I was separated from β-lactamase II by fractional precipitation with ammonium sulphate. 3. β-Lactamase I was purified by a process involving chromatography on Celite and DEAE-cellulose and β-lactamase II by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose after denaturation of β-lactamase I by heat. Both enzymes were obtained in crystalline form. 4. β-Lactamase II prepared in this way appeared to have a higher molecular weight than β-lactamase I and required Zn2+ as a cofactor for both cephalosporinase and penicillinase activities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAHAM E. P., NEWTON G. G. A comparison of the action of penicillinase on benzylpenicillin and cephalosporin N and the competitive inhibition of penicillinase by cephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):628–634. doi: 10.1042/bj0630628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN J. E., VALLEE B. L. Metallocarboxypeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:390–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROMPTON B., JAGO M., CRAWFORD K., NEWTON G. G., ABRAHAM E. P. Behaviour of some derivatives of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid and 6-aminopenicillanic acidas substrates, inhibitors and inducers of penicillinases. Biochem J. 1962 Apr;83:52–63. doi: 10.1042/bj0830052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. R., OGSTON A. G. Sedimentation and diffusion of samples of penicillinase. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):401–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOGUT M., POLLOCK M. R., TRIDGELL E. J. Purification of penicillin-induced penicillinase of Bacillus cereus NRRL 569: a comparison of its properties with those of a similarly purified penicillinase produced spontaneously by a constitutive mutant strain. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):391–401. doi: 10.1042/bj0620391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation and fixation of penicillin sulphur by Bacillus cereus spores. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Feb;8(1):186–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-1-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation in B. cereus; adaptive enzyme formation in the absence of free substrate. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Dec;31(6):739–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R. Penicillinase adaptation in Bacillus cereus; an analysis of three phases in the response of logarithmically growing cultures to induction of penicillinase formation by penicillin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Dec;33(6):587–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R., TORRIANI A. M. Purification et caractéristiques physicochimiques de la pénicillinase de Bacillus cereus. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1953 Jul 20;237(3):276–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Abraham E. P. Cephalosporinase and penicillinase activity of Bacillus cereus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:392–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Finland M. Thiol-group binding of zinc to a beta-lactamase of Bacillus cereus: differential effects on enzyme activity with penicillin and cephalosporins as substrates. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1513–1519. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1513-1519.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Williams R. J. Enzyme action: views derived from metalloenzyme studies. Chem Br. 1968 Sep;4(9):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]