Abstract
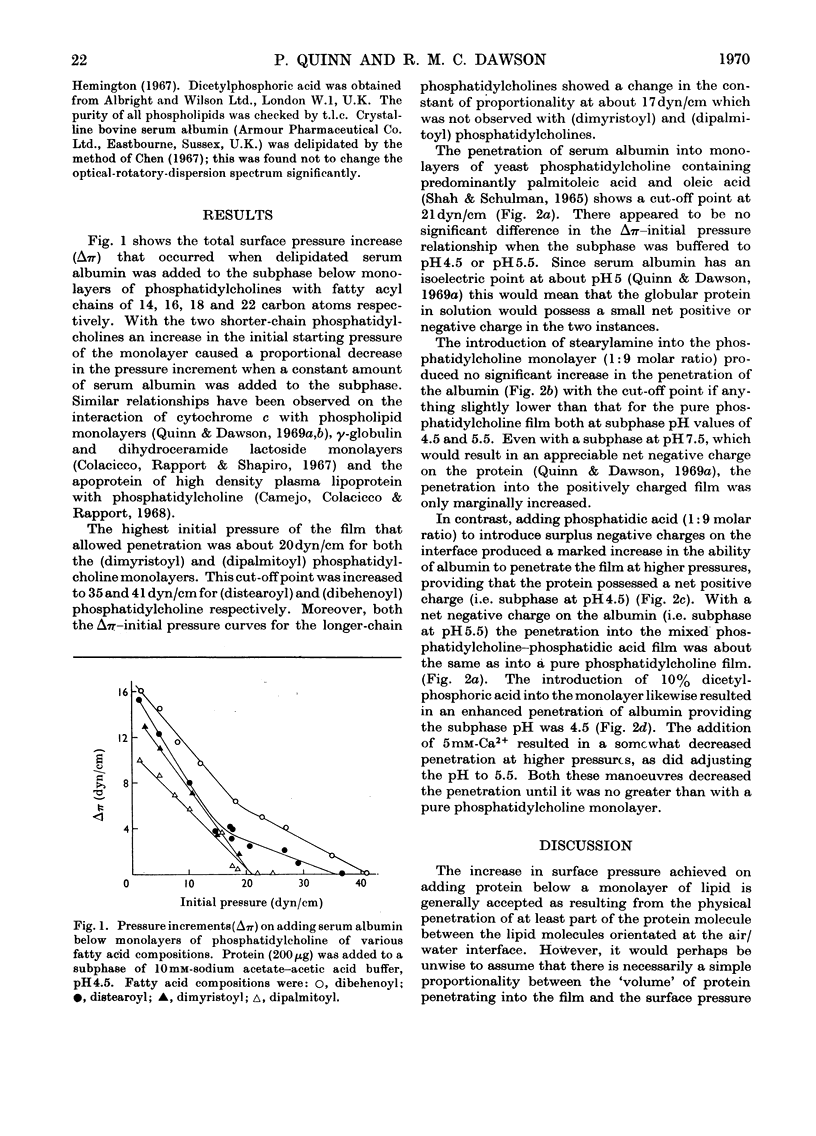
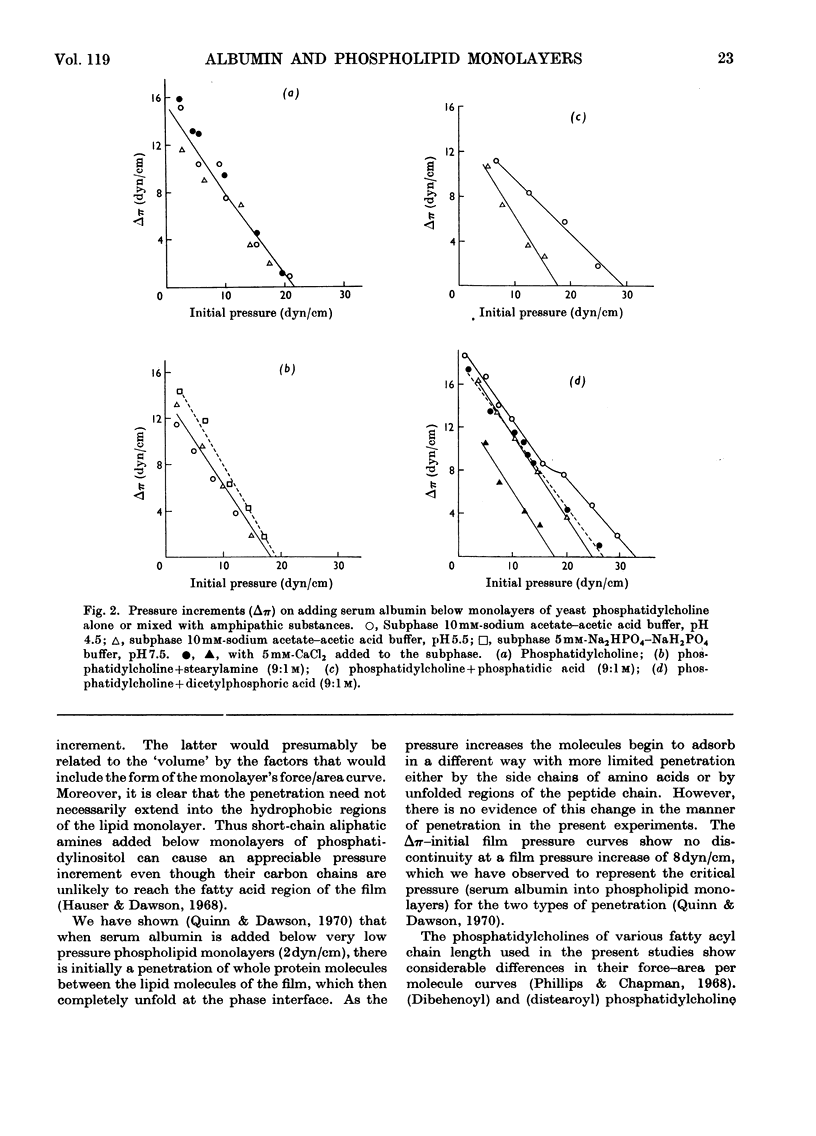
1. The highest surface pressure of phosphatidylcholine monolayers allowing penetration of delipidated serum albumin decreased in the order dibehenoyl>distearoyl>dipalmitoyl=dimyristoyl. This pressure was not related to the area occupied or to the space available between the phospholipid molecules at the interface. 2. Penetration of albumin into yeast phosphatidylcholine monolayers was increased by adding a small percentage of long-chain anions (phosphatidic acid, dicetylphosphoric acid) to the film but only when the protein was below its isoelectric point (i.e. positively charged). 3. Stearylamine added to phosphatidylcholine monolayers had no effect on albumin penetration even when the protein was oppositely charged to that of the phospholipid/water interface. 4. The results are discussed in relation to the activation of certain phospholipases by anionic amphipathic substances.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON M. B., KATZMAN R., WILSON C. E., GREGOR H. P. IONIC PROPERTIES OF AQUEOUS DISPERSIONS OF PHOSPHATIDIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4066–4072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. Electrokinetic requirements for the reaction between Cl. perfringens alpha-toxin (phospholipase C) and phospholipid substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:103–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. The physicochemical requirements for the action of Penicillium notatum phospholipase B on unimolecular films of lecithin. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:133–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0750133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. The relation between the activity of a lecithinase and the electrophoretic charge of the substrate. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:486–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0720486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. B., Breese K. Binding of fatty acids by proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 May;120(2):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Colacicco G., Rapport M. M. Lipid monolayers: interactions with the apoprotein of high density plasma lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):562–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the hydrolysis of lecithin by a Penicillium notatum phospholipase B preparation. Biochem J. 1958 Dec;70(4):559–570. doi: 10.1042/bj0700559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N. Some properties of purified phospholipase D and especially the effect of amphipathic substances. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):76–86. doi: 10.1042/bj1020076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The displacement of calcium ions from phospholipid monolayers by pharmacologically active and other organic bases. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):909–916. doi: 10.1042/bj1090909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Taylor J. The stability and properties of bimolecular lipid leaflets in aqueous solutions. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):281–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. C., Chapman D. Monolayer characteristics of saturated 1,2,-diacyl phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) and phosphatidylethanolamines at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of monolayers of phosphatidyl(Me-14C)choline by phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(4):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj1130697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. An analysis of the interaction of protein with lipid monolayers at the air-water interface. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(4):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj1160671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. Interactions of cytochrome c and [14C]. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):65–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1150065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Dawson R. M. The interaction of cytochrome c with monolayers of phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;113(5):791–803. doi: 10.1042/bj1130791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. O., SCHULMAN J. H. BINDING OF METAL IONS TO MONOLAYERS OF LECITHINS, PLASMALOGEN, CARDIOLIPIN, AND DICETYL PHOSPHATE. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Freer J. H., Colacicco G., Weissmann G. Interaction of alytic polypeptide, melittin, with lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3575–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K., Fletcher J. E. Binding of long-chain fatty acids to bovine serum albumin. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


