Abstract
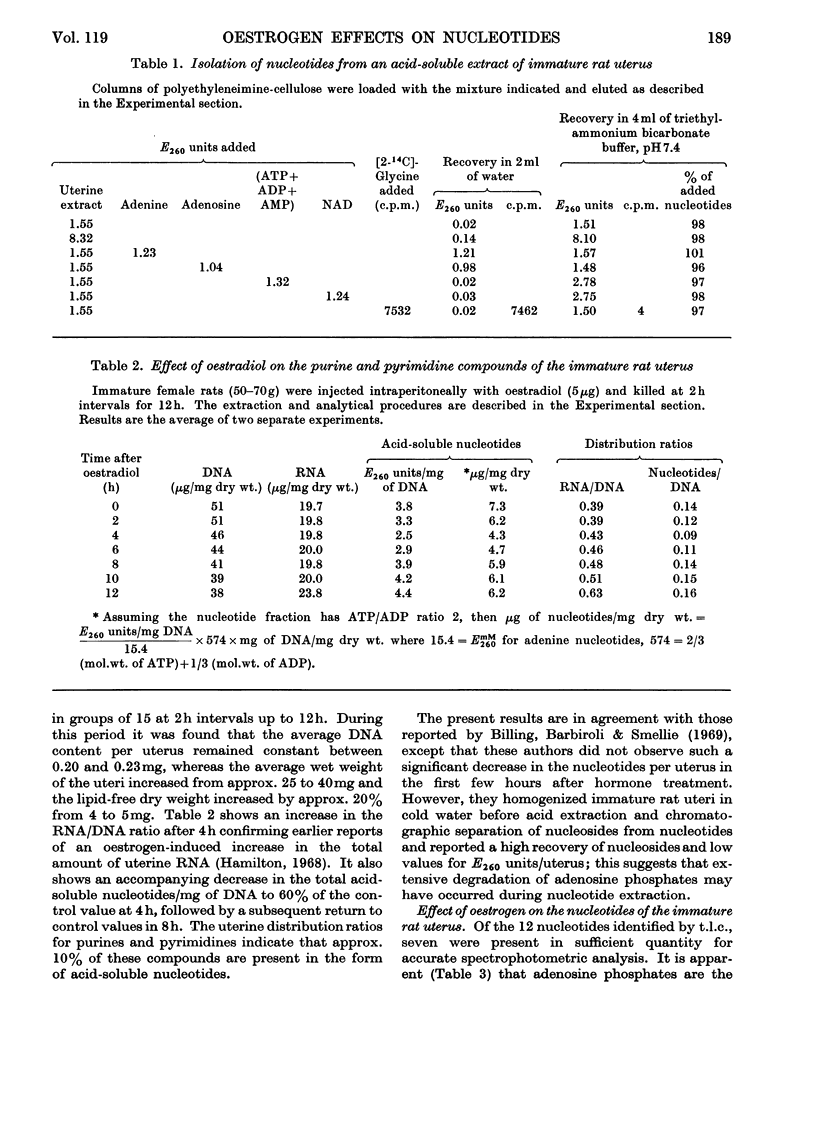
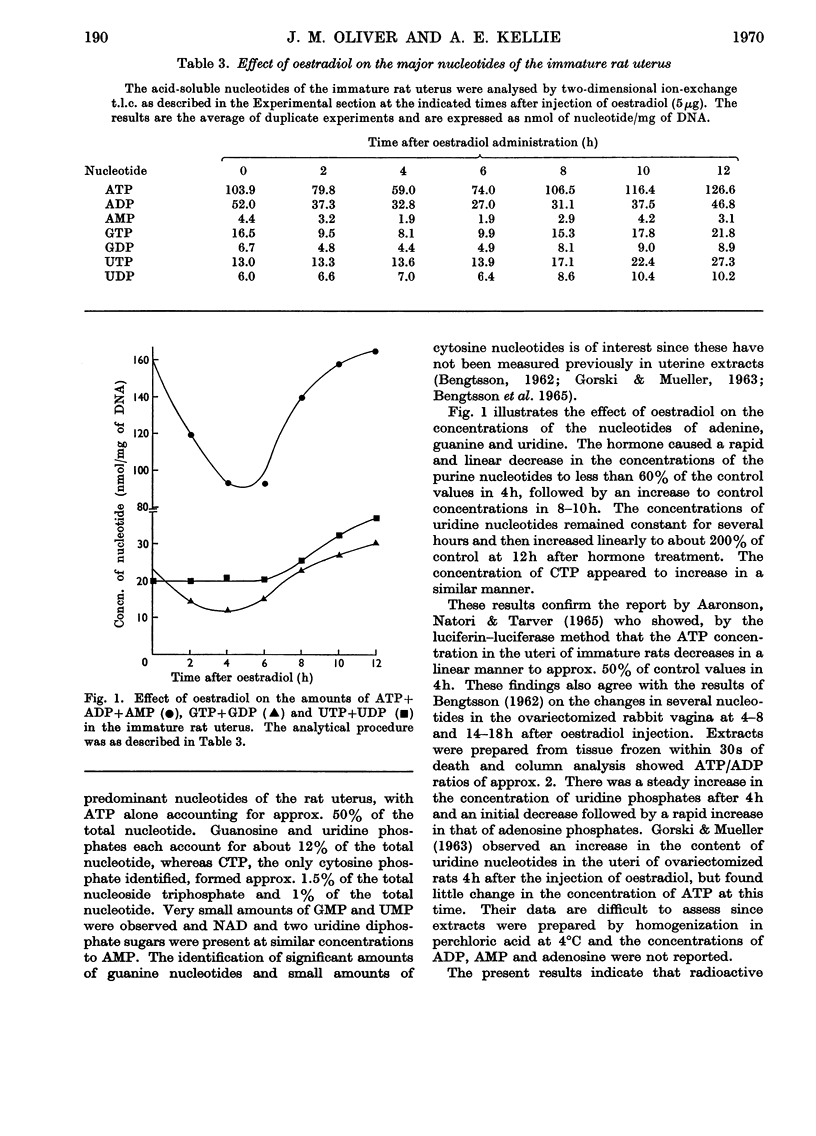
1. Techniques have been developed to measure the concentrations of the ribonucleotides of the immature rat uterus in vivo. Tissue was frozen rapidly in liquid nitrogen, ground to a fine powder, dispersed in frozen perchloric acid and thawed slowly. Nucleotides were separated from other acid-soluble constituents on short columns of polyethyleneimine-cellulose and the mixture was resolved into individual nucleotides by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography on polyethyl-eneimine-cellulose plates. 2. The nucleotides of immature rat uterus consisted of approximately 75% of ATP–ADP, 10–12% each of GTP–GDP and UTP–UDP and less than 2% of CTP. 3. Injection of oestradiol (5μg) promoted a linear decrease in the amounts of purine nucleotides to approximately 60% of control values in 4–5h, followed by a return to greater than control values in 8–10h. Concentrations of the pyrimidine nucleotides remained constant for 4–6h and then increased to 200% of control at 12h after hormone treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Natori Y., Tarver H. Effect of estrogen on uterine ATP levels. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):9–10. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENGTSSON L. P., DEUTSCH A., NILSSON R. THE EFFECT OF OESTROGEN ON THE ACID-SOLUBLE NUCLEOTIDE CONTENT OF THE RABBIT VAGINA. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1964;43:369–380. doi: 10.3109/00016346409162687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUMSOM N. L., BADDILEY J. Thymidine diphosphate mannose and thymidine diphosphate rhamnose in Streptomyces grieus. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:114–124. doi: 10.1042/bj0810114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L., Swaffield M. N. Nucleotide pools and [6-14C]orotic acid incorporation in early regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):445–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell I. C. Ion-exchange chromatography of tissue nucleotides. J Chromatogr. 1969 Oct 28;44(2):331–341. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92544-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. M., Schepartz A. I. Desalting of nucleic acid hydrolysates, nucleosides and bases by chromatography on poly-N-vinyl pyrrolidone. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 25;40(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. M., Abbott H., Terry M. L. A simple procedure for removing salts from samples applied to ion-exchange thin-layer plates. Anal Biochem. 1966 Jul;16(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. H. Control by estrogen of genetic transcription and translation. Binding to chromatin and stimulation of nucleolar RNA synthesis are primary events in the early estrogen action. Science. 1968 Aug 16;161(3842):649–661. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3842.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDERATH E., RANDERATH K. RESOLUTION OF COMPLEX NUCLEOTIDE MIXTURES BY TWO-DIMENSIONAL ANION-EXCHANGE THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Chromatogr. 1964 Oct;16:126–129. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reel J. R., Gorski J. Gonadotrophic regulation of precursor incorporation into ovarian RNA, protein, and acid-soluble fractions. I. Effects of pregnant mare serum gonadotrophin (PMSG), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). Endocrinology. 1968 Nov;83(5):1083–1091. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-5-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


