Abstract
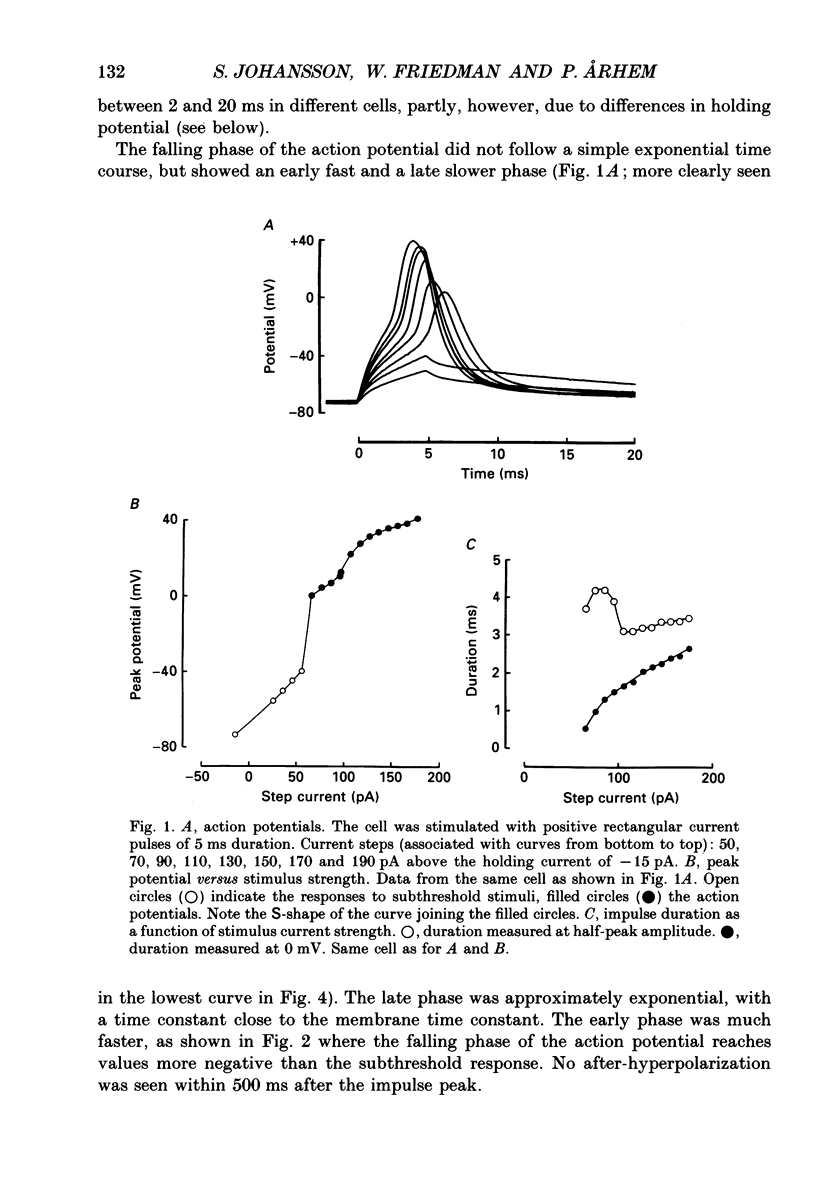
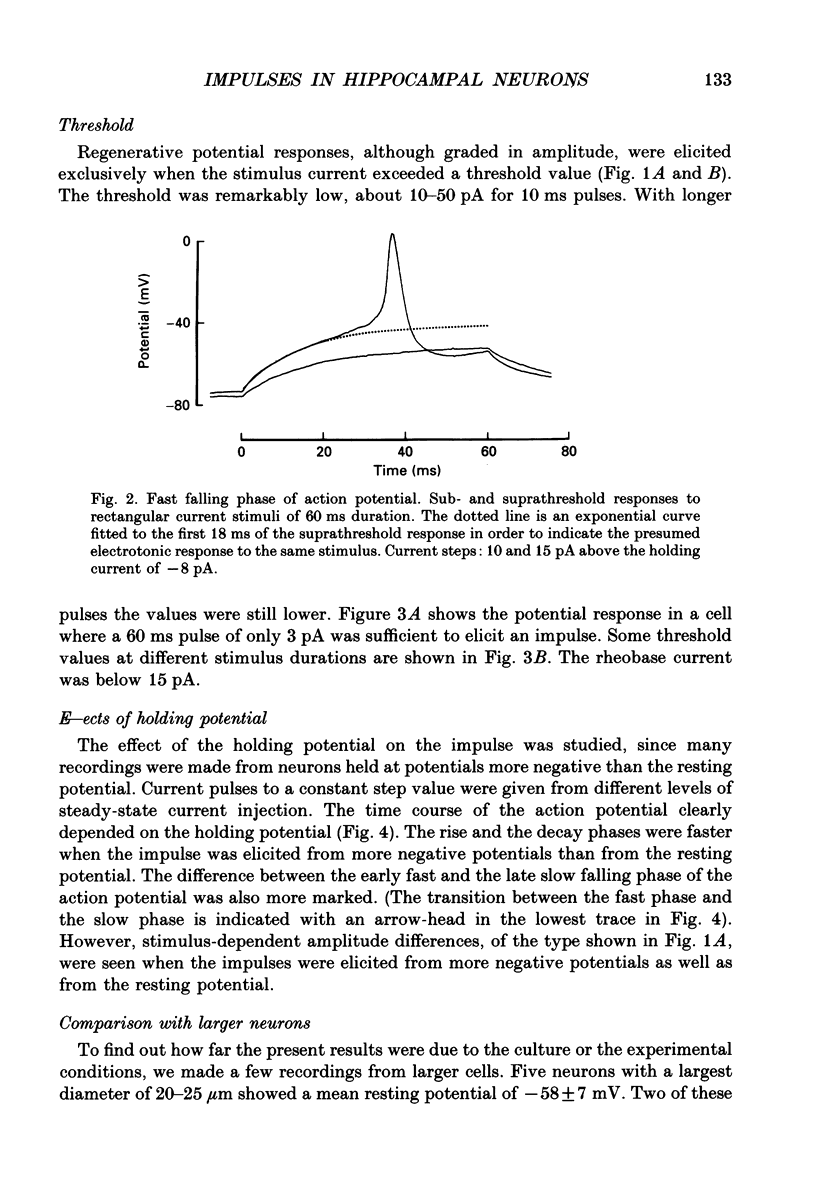
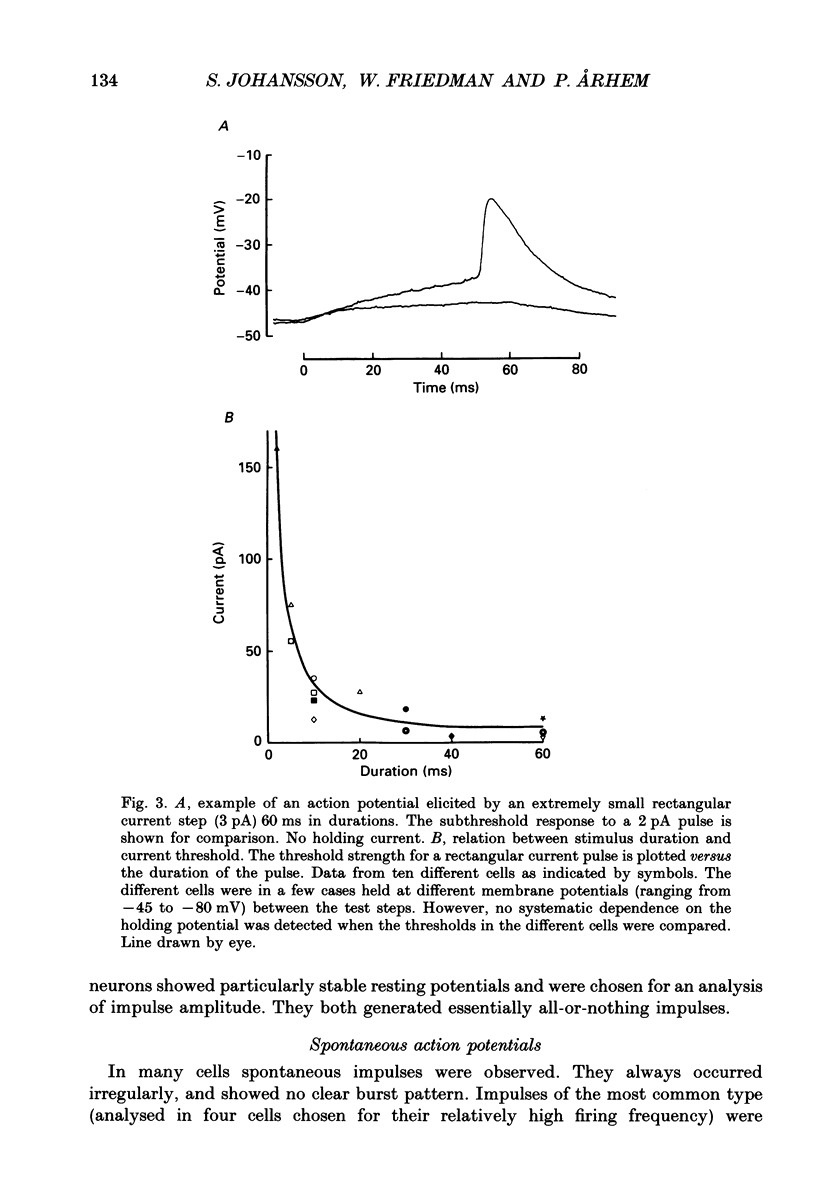
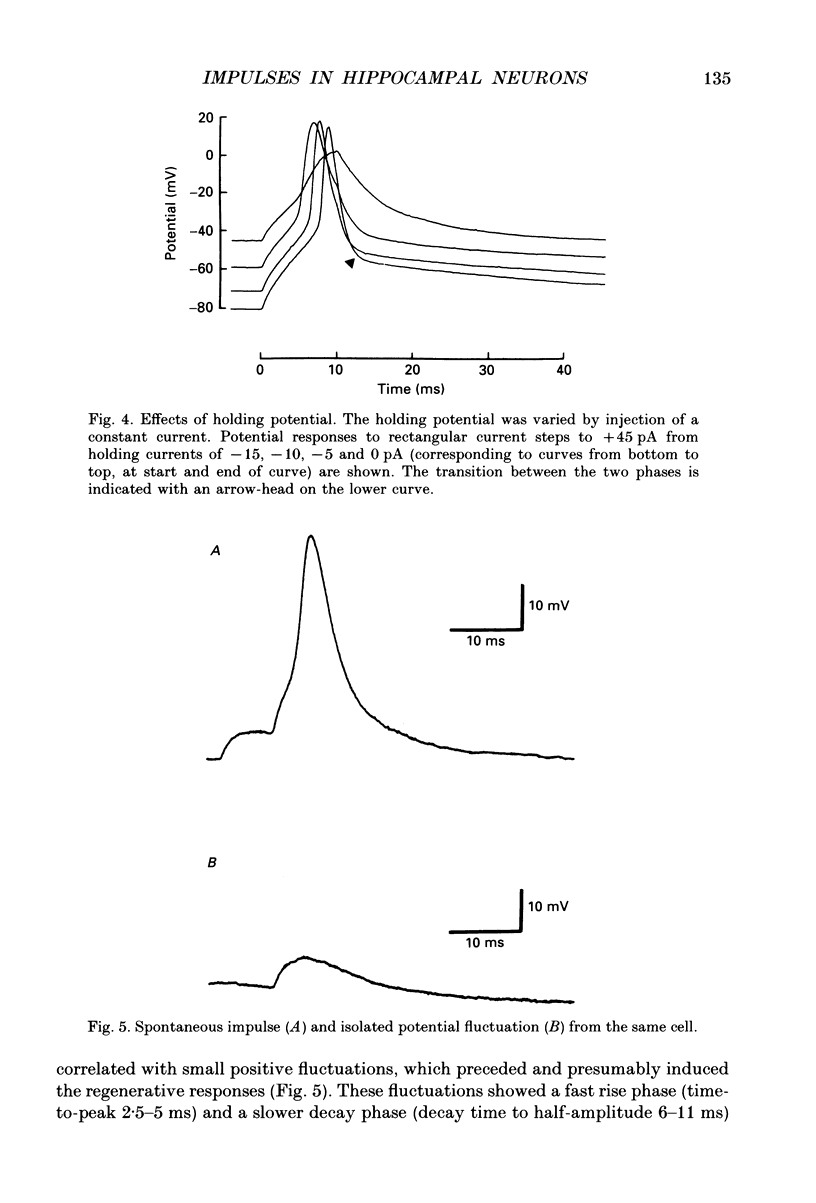
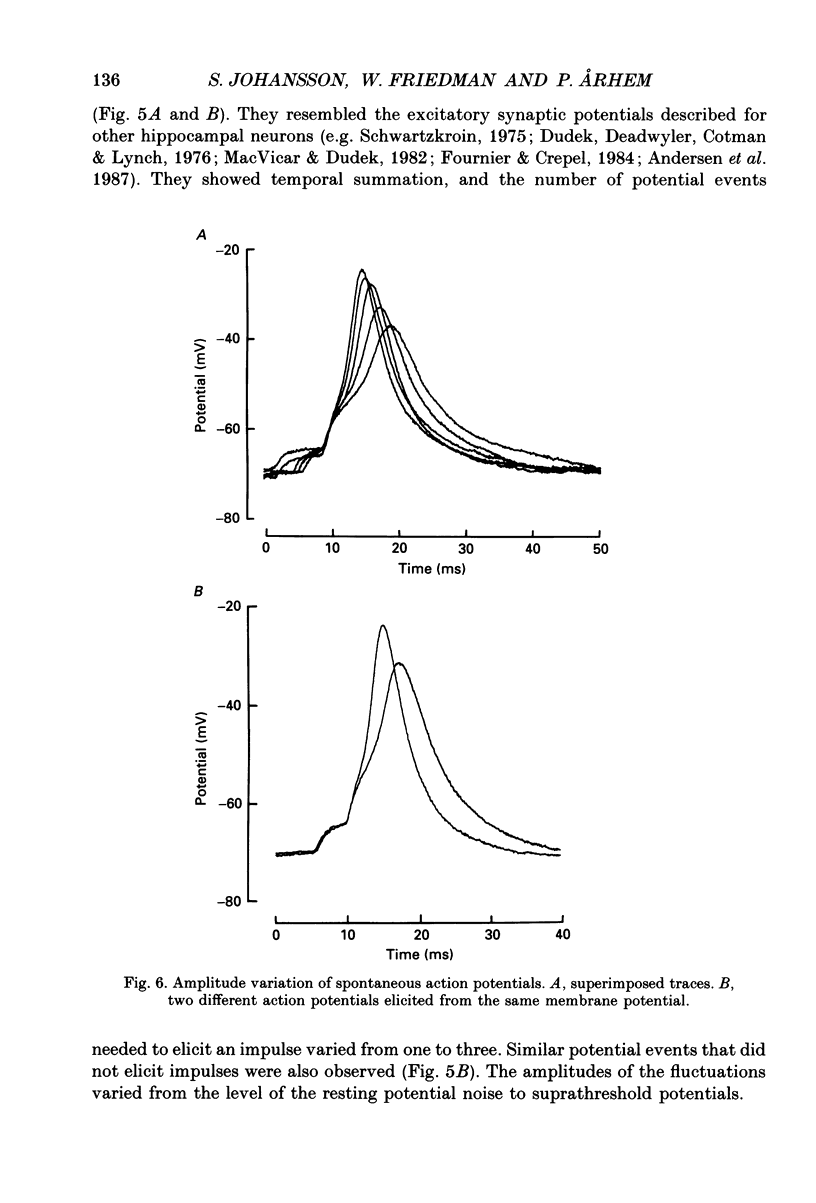
1. The impulses and resting membrane parameters of small (soma diameter less than 10 microM) cultured hippocampal neurons from rat embryos were studied with the tight-seal whole-cell recording technique. 2. Mean resting potential was -47 mV, mean input resistance 3.3 G omega, mean capacitance 11 pF, and mean time constant 33 ms. 3. Rectangular suprathreshold current steps elicited regenerative potential responses. The amplitude and time course of the responses were clearly stimulus dependent: stronger current steps caused impulses of larger amplitude. 4. The current threshold was very low: rheobase current was less than 15 pA. 5. The potential response depended on the preceding holding potential, responses from more negative potentials showing sharper peaks than those from more positive potentials. 6. Spontaneous impulses with pre-potentials similar to synaptically induced events were recorded from several cells. The amplitude of the spontaneous impulses varied similarly to that of the stimulus-induced responses.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Forbes A. The all-or-nothing response of sensory nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1922 Jul 21;56(5):301–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1922.sp002013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Storm J., Wheal H. V. Thresholds of action potentials evoked by synapses on the dendrites of pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:509–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes C. A., McNaughton B. L. Physiological compensation for loss of afferent synapses in rat hippocampal granule cells during senescence. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:473–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Fricke R. A., Perkel D. H. Passive electrical constants in three classes of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Oct;46(4):812–827. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.4.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The electrical constants of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):505–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley J. W., Dodge F. A., Jr Digital computer solutions for excitation and propagation of the nerve impulse. Biophys J. 1966 Sep;6(5):583–599. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86679-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Marshall C. G., Ogden D. Voltage-activated membrane currents in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek F. E., Deadwyler S. A., Cotman C. W., Lynch G. Intracellular responses from granule cell layer in slices of rat hippocampus: perforant path synapse. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Mar;39(2):384–393. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D., Carlen P. L., Gurevich N., Ho A., Kunov H. Electrotonic parameters of rat dentate granule cells measured using short current pulses and HRP staining. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Nov;50(5):1080–1097. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.5.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B., Takahashi T. A thin slice preparation for patch clamp recordings from neurones of the mammalian central nervous system. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):600–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00580998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Crepel F. Electrophysiological properties of dentate granule cells in mouse hippocampal slices maintained in vitro. Brain Res. 1984 Oct 8;311(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91400-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockberger P. E., Tseng H. Y., Connor J. A. Immunocytochemical and electrophysiological differentiation of rat cerebellar granule cells in explant cultures. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1370–1383. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01370.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Arhem P. Computed potential responses of small cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:157–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Arhem P. Graded action potentials in small cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 16;118(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90615-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Arhem P. Membrane currents in small cultured rat hippocampal neurons: a voltage-clamp study. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:141–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S., Rydqvist B., Swerup C., Heilbronn E., Arhem P. Action potentials of cultured human oat cells: whole-cell measurements with the patch-clamp technique. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Apr;135(4):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G., GERARD R. W. The normal membrane potential of frog sartorius fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Dec;34(3):383–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E. Electrotonic coupling between granule cells of rat dentate gyrus: physiological and anatomical evidence. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Apr;47(4):579–592. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.4.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Stanton P. K., Heinemann U. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors parallels changes in cellular and synaptic properties of dentate gyrus granule cells after kindling. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):1033–1054. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nó R. L., Condouris G. A. DECREMENTAL CONDUCTION IN PERIPHERAL NERVE. INTEGRATION OF STIMULI IN THE NEURON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Apr;45(4):592–617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.4.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A. Characteristics of CA1 neurons recorded intracellularly in the hippocampal in vitro slice preparation. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 7;85(3):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90817-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: responses to electrical and chemical stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;50(6):1249–1264. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm J. F. Action potential repolarization and a fast after-hyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:733–759. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


