Abstract
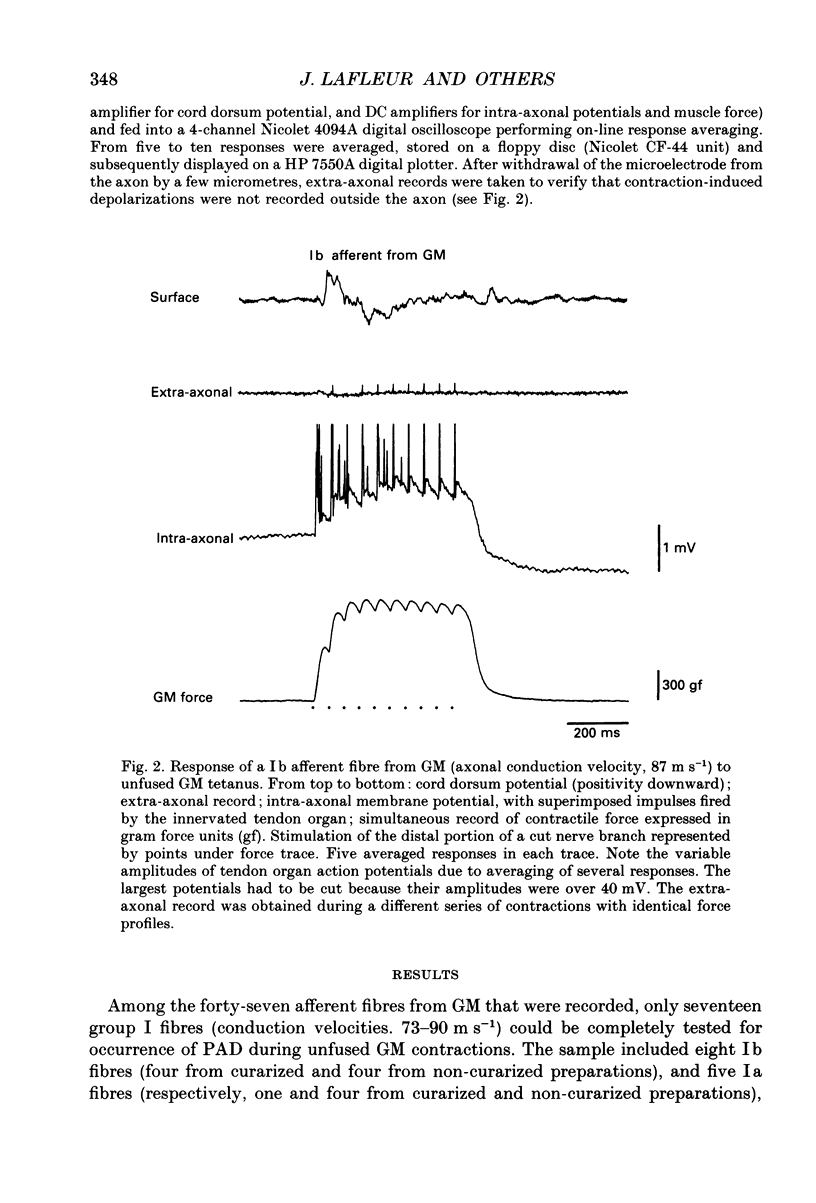
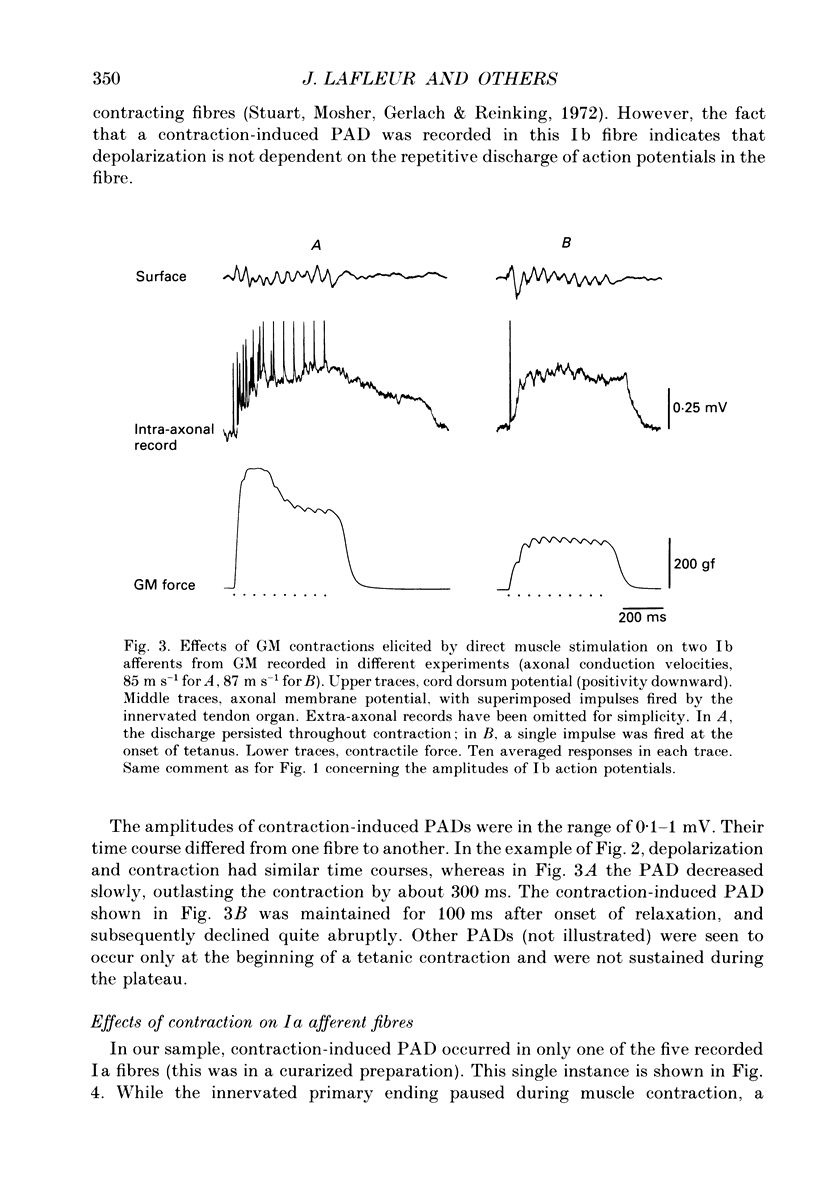
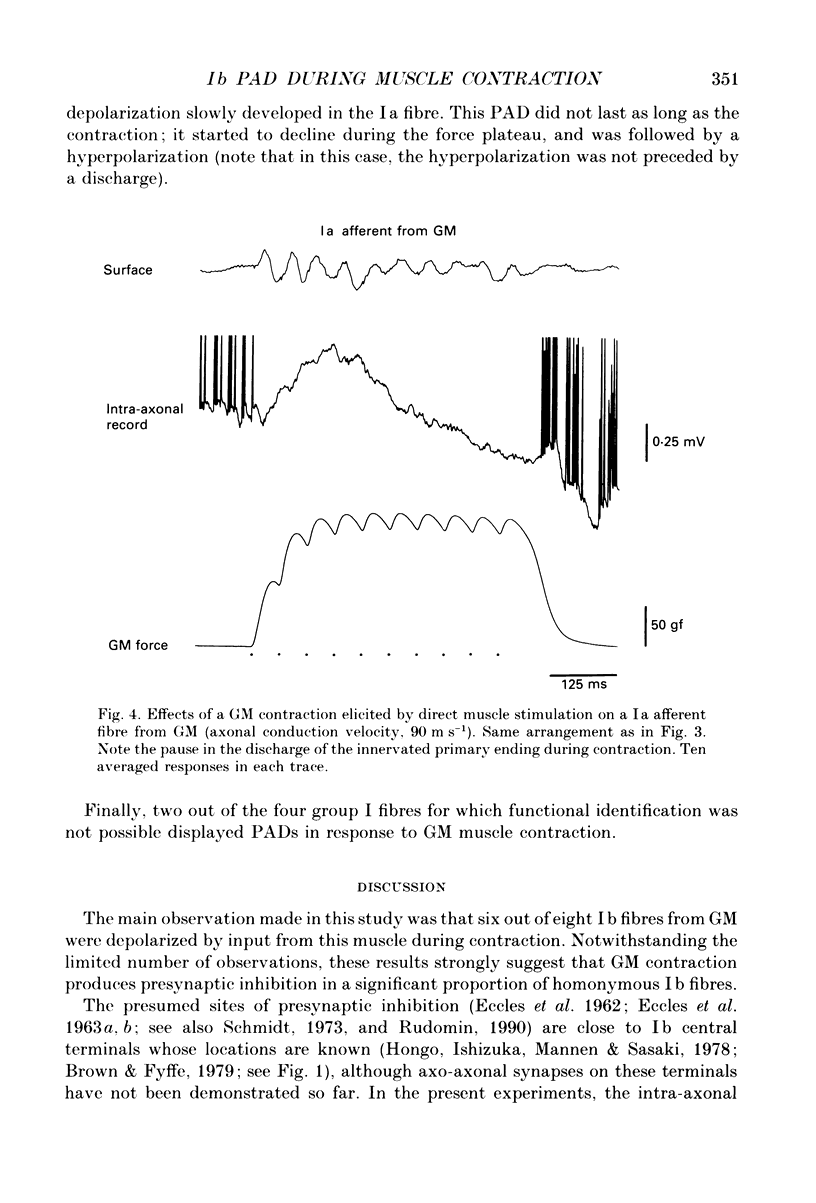
1. Intra-axonal records from the intraspinal course of Ib and Ia afferent fibres innervating the gastrocnemius medialis muscle were obtained in chloralose or Nembutal-anaesthetized cats during submaximal contractions of the muscle. 2. Afferent fibres in continuity with their muscle of origin were functionally identified by their responses to muscle stretch or contraction. 3. In six out of eight Ib afferents, primary depolarizations (PADs) were recorded during contraction. They were independent of the presence of orthodromic impulses fired by tendon organs. 4. These observations support the assumption that the reduction of Ib autogenetic inhibition in homonymous and synergic motoneurones during GM contractions is due to presynaptic inhibition of transmission in Ib pathways.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brink E., Jankowska E., Skoog B. Convergence onto interneurons subserving primary afferent depolarization of group I afferents. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Mar;51(3):432–449. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
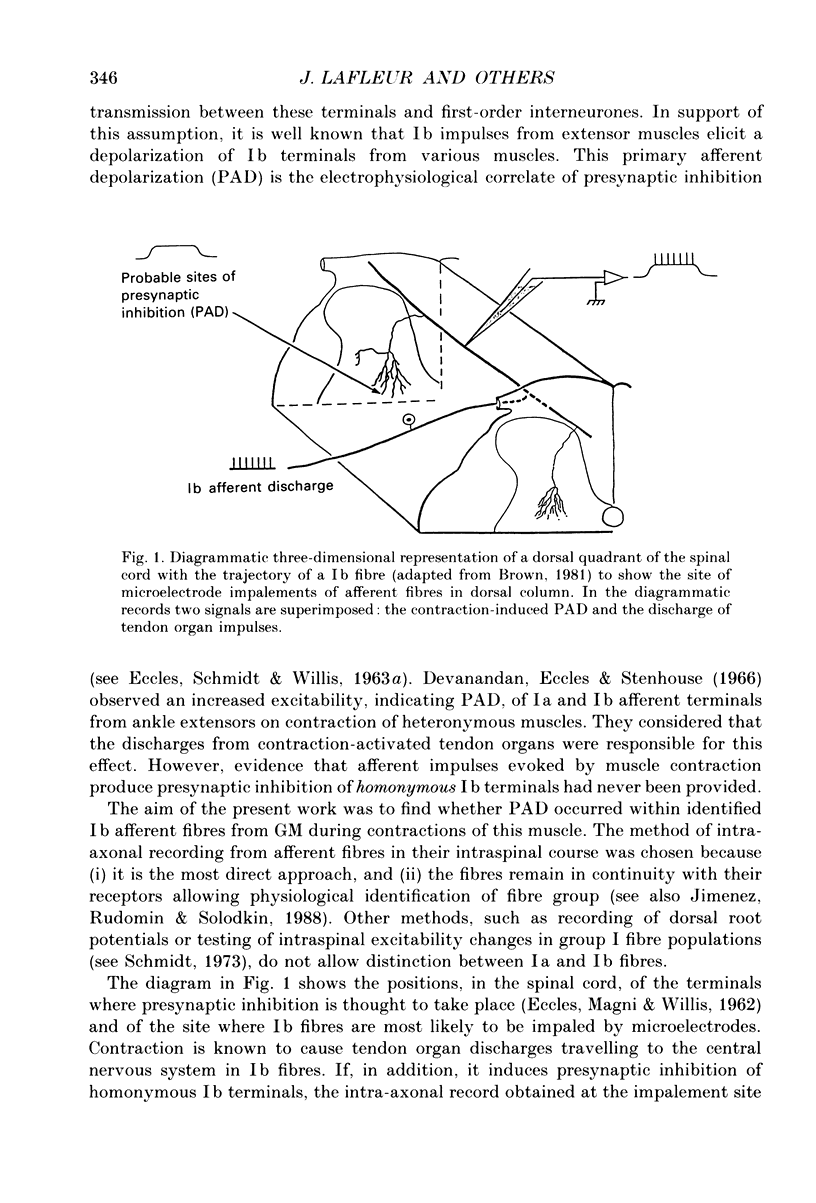
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. The morphology of group Ib afferent fibre collaterals in the spinal cord of the cat. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:215–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland C. L., Hayward L., Rymer W. Z. Neural mechanisms underlying the clasp-knife reflex in the cat. II. Stretch-sensitive muscular-free nerve endings. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1319–1330. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devanandan M. S., Eccles R. M., Stenhouse D. Presynaptic inhibition evoked by muscle contraction. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):471–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuc R., Cabelguen J. M., Rossignol S. Rhythmic fluctuations of dorsal root potentials and antidromic discharges of primary afferents during fictive locomotion in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Dec;60(6):2014–2036. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.6.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueñas S. H., Rudomin P. Excitability changes of ankle extensor group Ia and Ib fibers during fictive locomotion in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1988;70(1):15–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00271842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KRNJEVIC K. Potential changes recorded inside primary afferent fibres within the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:250–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Magni F., Willis W. D. Depolarization of central terminals of Group I afferent fibres from muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160(1):62–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kellerth J. O., Szumski A. J. Intracellular autogenetic effects of muscular contration on extensor motoneurones. The silent period. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horcholle-Bossavit G., Jami L., Lafleur J., Lamy F., Zytnicki D. Effets de contractions partielles non-fusionnées du muscle gastrocnémien médian sur les motoneurones homonymes et synergistes chez le chat. C R Acad Sci III. 1988;307(10):591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Rudomín P., Sykova E. Observations on neuronal pathways subserving primary afferent depolarization. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Sep;46(3):506–516. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.3.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez I., Rudomin P., Solodkin M. PAD patterns of physiologically identified afferent fibres from the medial gastrocnemius muscle. Exp Brain Res. 1988;71(3):643–657. doi: 10.1007/BF00248758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mense S., Meyer H. Different types of slowly conducting afferent units in cat skeletal muscle and tendon. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:403–417. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Gating of the afferent volley of the monosynaptic stretch reflex during movement in man. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:753–763. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudomin P. Presynaptic inhibition of muscle spindle and tendon organ afferents in the mammalian spinal cord. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Dec;13(12):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90084-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturart D. G., Mosher C. G., Gerlach R. I., Reinking R. M. Mechanical arrangement and transducing properties of Golgi tendon organs. Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(3):274–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00816163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zytnicki D., Lafleur J., Horcholle-Bossavit G., Lamy F., Jami L. Reduction of Ib autogenetic inhibition in motoneurons during contractions of an ankle extensor muscle in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Nov;64(5):1380–1389. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.5.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


