Abstract
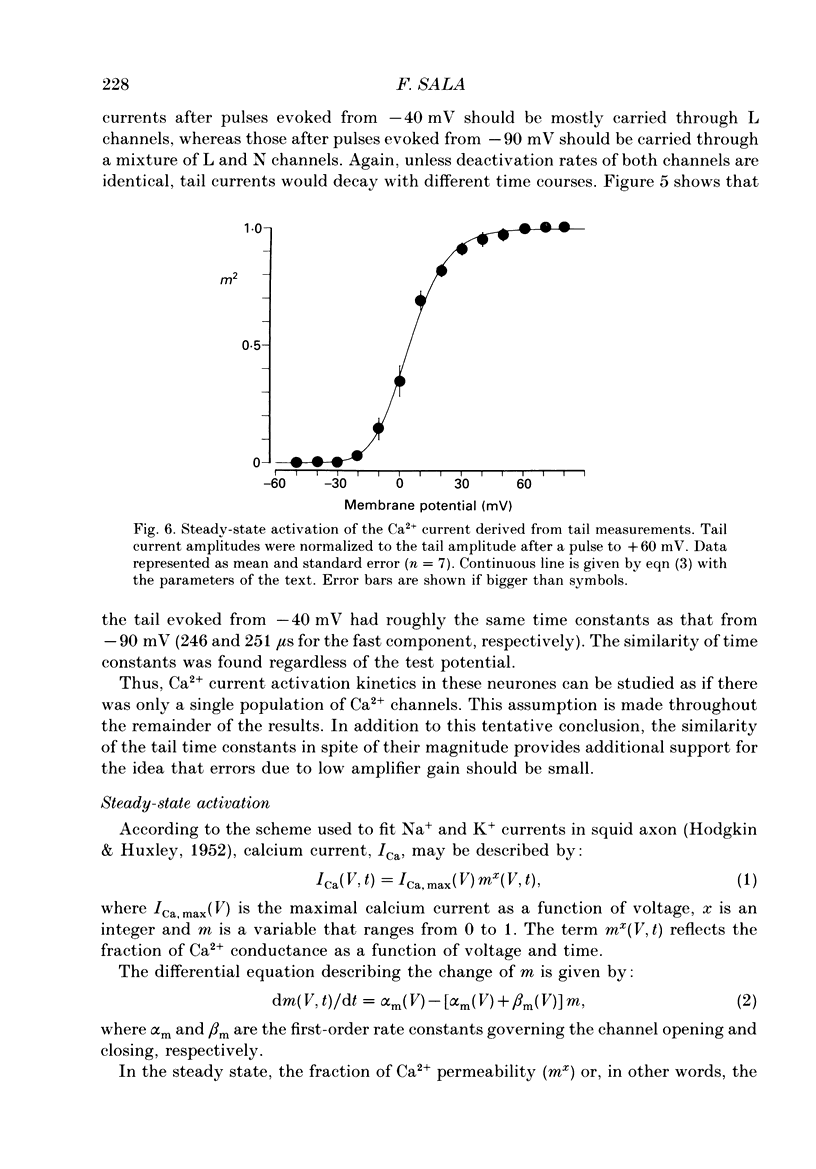
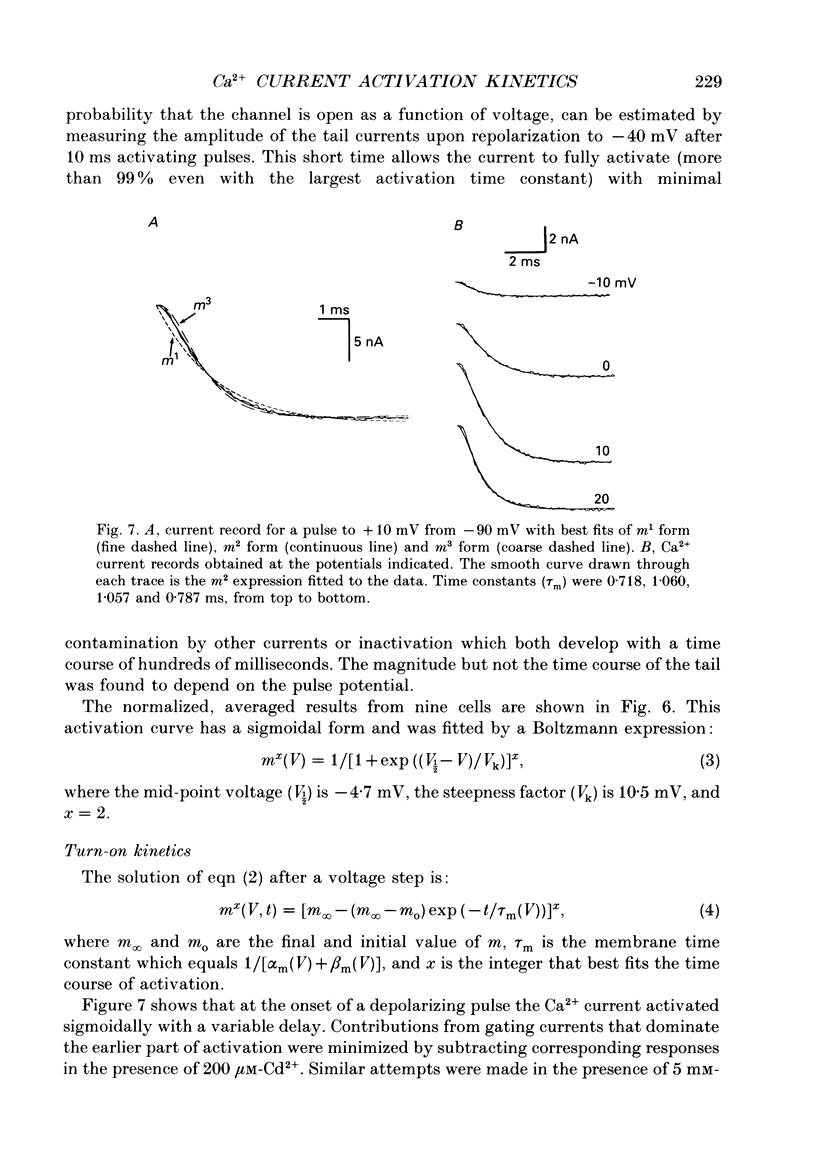
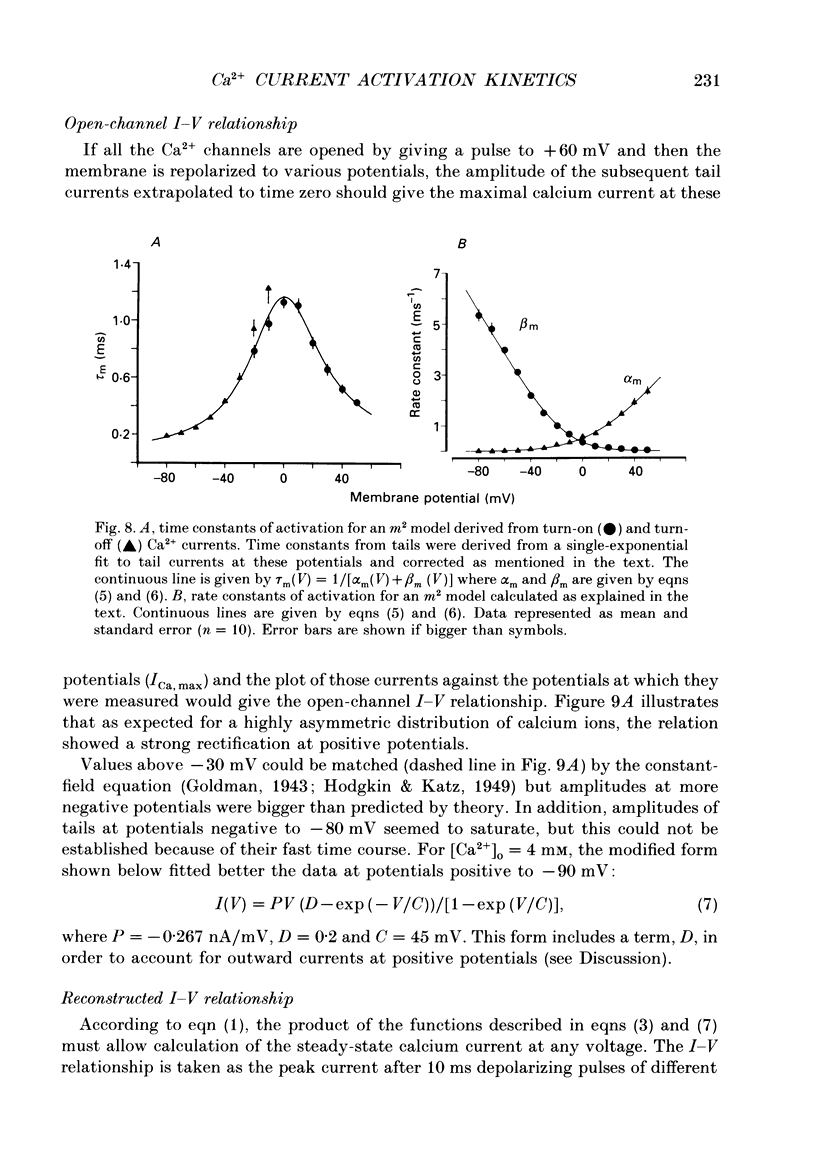
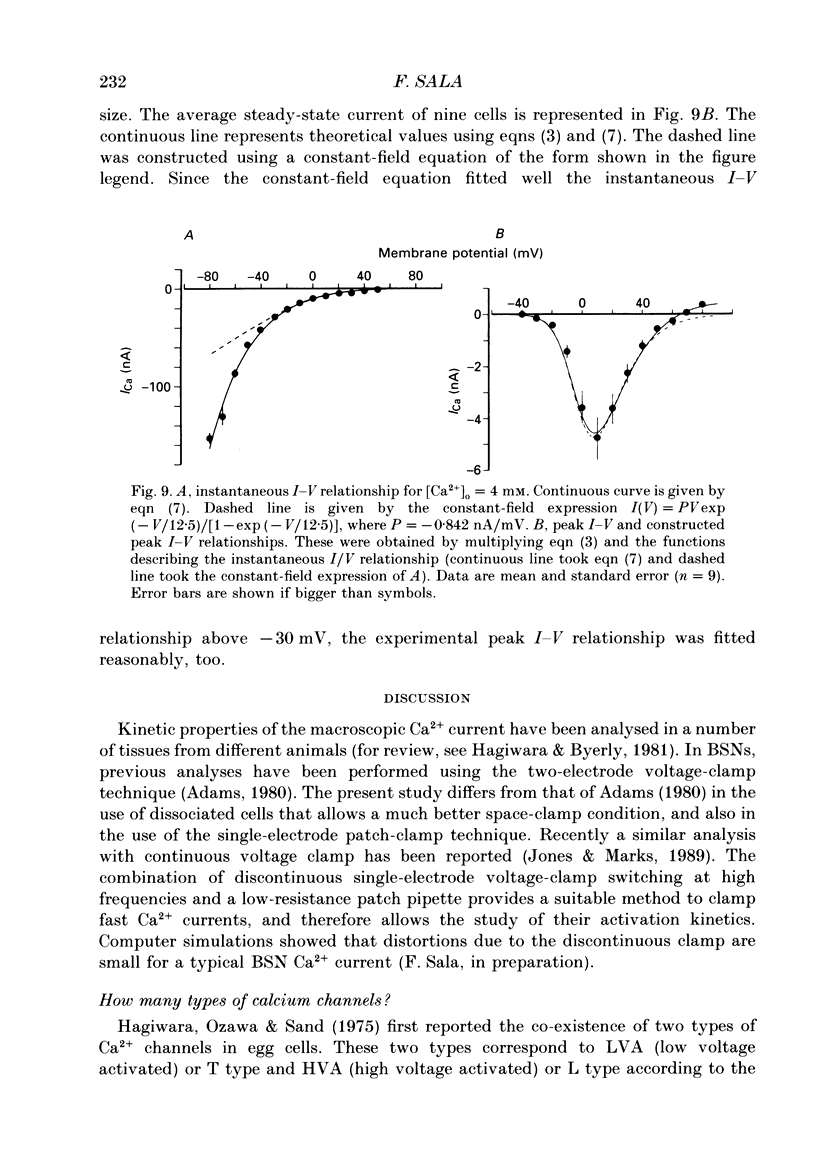
1. Calcium currents were recorded in dissociated bull-frog sympathetic neurones (BSNs) through patch pipettes using discontinuous voltage clamp. Activation kinetics were examined by analysing turn-on and turn-off currents. 2. After short depolarizing pulses turn-off tail currents were fitted with the sum of two exponentials. The fast component (time constant, tau approximately 240 microseconds at -40 mV) was undoubtedly due to the closure of calcium channels. The significance of a small and slower component is discussed. 3. Neither activation nor deactivation time courses changed as channels inactivated during progressively longer pulses or when the holding potential was less negative. No specific component was selectively suppressed by these manipulations. 4. Steady-state activation of the Ca2+ current was described by the Boltzmann distribution raised to the second power. Currents had an apparent threshold at -30 mV and were half-activated at +5 mV. 5. Calcium current turned on following m2 kinetics throughout the range of activation. The slowest time constant was around 1.2 ms between 0 and +10 mV. Turn-on was faster at negative or more positive potentials. 6. The time course of decay of tail currents became progressively faster at more negative potentials. 7. The instantaneous current-voltages (I-V) curve was obtained from tail current measurements and fitted by a modified constant-field equation. 8. The measured peak I-V curve could be reconstructed from the activation curve and the instantaneous I-V curve. 9. The activation kinetics of the calcium current in BSNs were consistent with the existence of a single kinetic class of channels and can be described with a simple m2 Hodgkin-Huxley model.
Full text
PDF

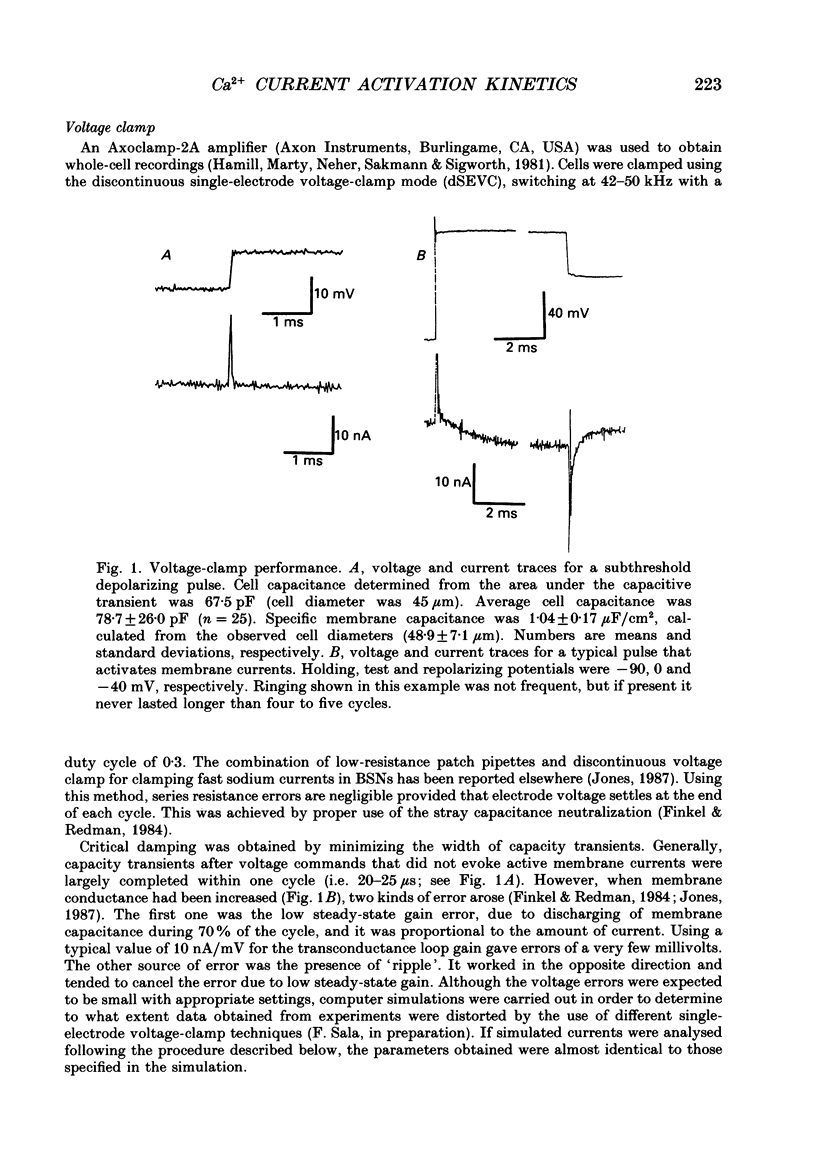
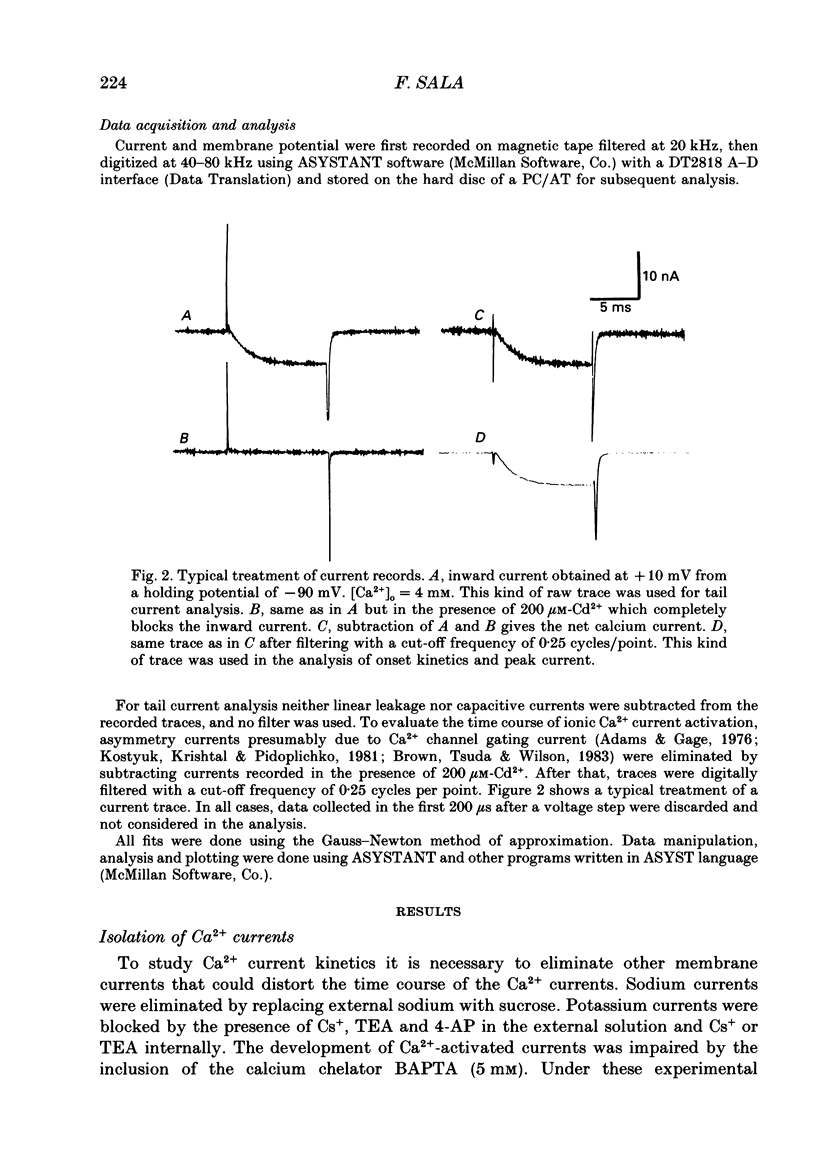

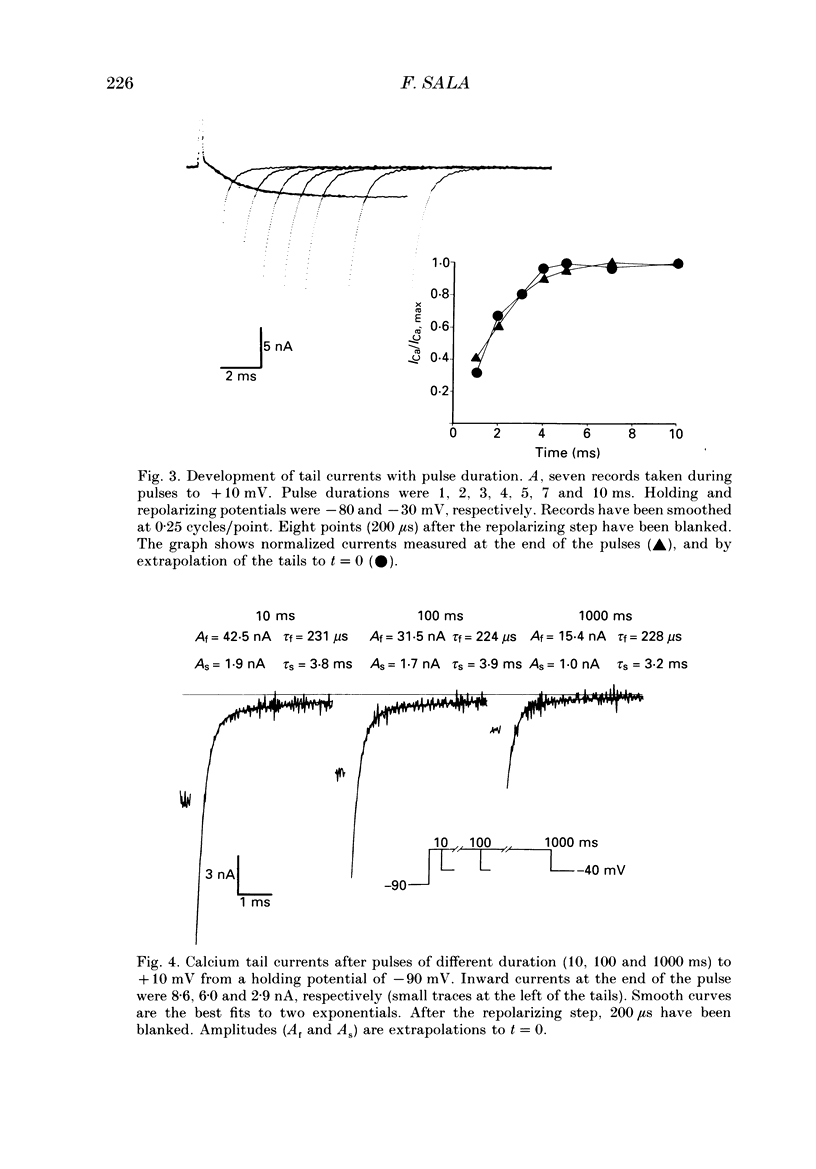
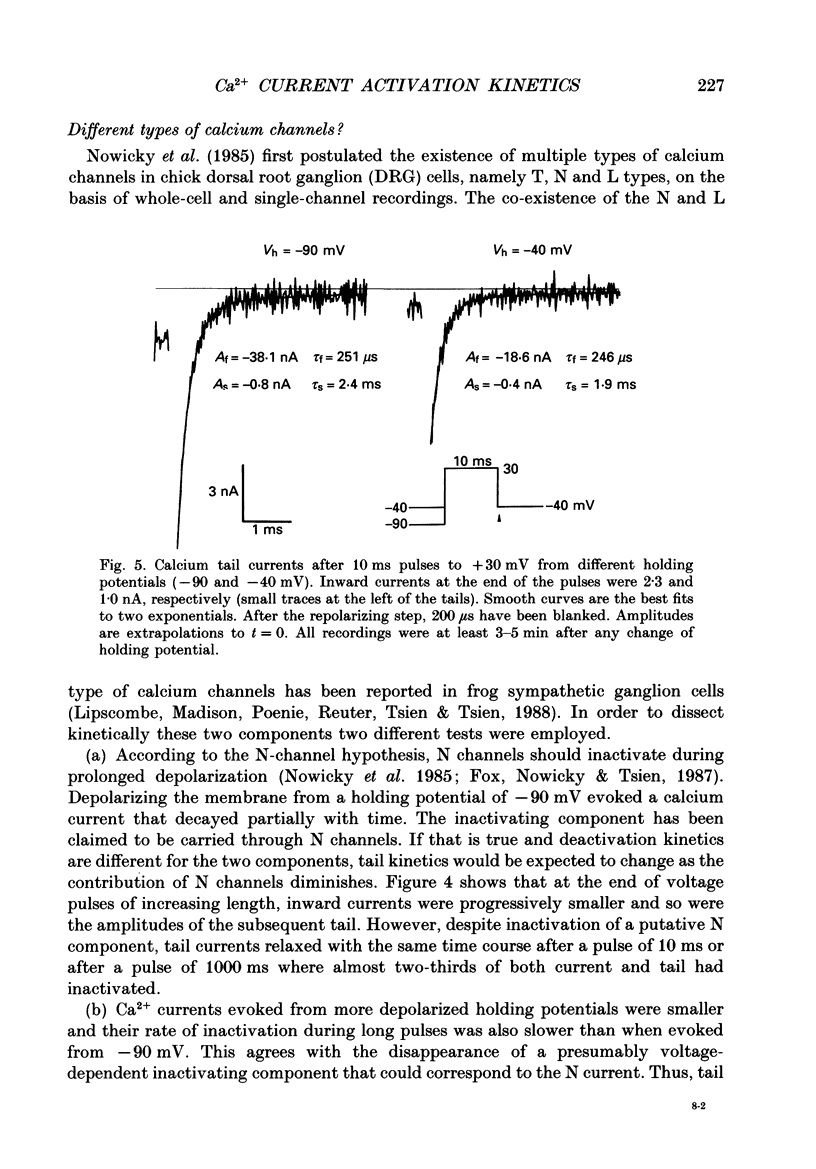







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Gage P. W. Gating currents associated with sodium and calcium currents in an Aplysia neuron. Science. 1976 May 21;192(4241):783–784. doi: 10.1126/science.1265479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O. Calcium currents in the normal adult rat sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:493–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Tsuda Y., Wilson D. L. A description of activation and conduction in calcium channels based on tail and turn-on current measurements in the snail. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:549–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Chase P. B., Stimers J. R. Calcium current activation kinetics in neurones of the snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:187–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Chase P. B., Stimers J. R. Permeation and interaction of divalent cations in calcium channels of snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Apr;85(4):491–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Meech R., Moody W., Jr Rapidly activating hydrogen ion currents in perfused neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:199–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Potassium ion current in the squid giant axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys J. 1960 Sep;1:1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86871-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. Theory and operation of a single microelectrode voltage clamp. J Neurosci Methods. 1984 Jun;11(2):101–127. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(84)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Tsien R. W. Voltage-gated calcium channels: direct observation of the anomalous mole fraction effect at the single-channel level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of single calcium channel currents in rat clonal pituitary cells. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:649–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ozawa S., Sand O. Voltage clamp analysis of two inward current mechanisms in the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):617–644. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Rothlein J., Smith S. J. Facilitation of Ca2+-channel currents in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5871–5875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Marks T. N. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. I. Activation kinetics and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):151–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W. Sodium currents in dissociated bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:605–627. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Calcium inward current and related charge movements in the membrane of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:403–421. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Shirokov R. E. Deactivation kinetics of different components of calcium inward current in the membrane of mice sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:343–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I., Shakhovalov Y. A. Conductance of the calcium channel in the membrane of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:423–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Sejnowski T. J. Peptidergic and muscarinic excitation at amphibian sympathetic synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:257–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. Y., Tsien R. W. Spatial distribution of calcium channels and cytosolic calcium transients in growth cones and cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2398–2402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):289–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Properties of two types of calcium channels in clonal pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):161–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala F., Hernández-Cruz A. Calcium diffusion modeling in a spherical neuron. Relevance of buffering properties. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82533-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Interactions between intrinsic membrane protein and electric field. An approach to studying nerve excitability. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85490-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Armstrong C. M. Fast-deactivating calcium channels in chick sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R. Permeation of barium and cadmium through slowly inactivating calcium channels in cat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:433–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R. Two-suction-electrode voltage-clamp analysis of the sustained calcium current in cat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:405–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


