Abstract
1. The ryanodine receptor protein of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes functions as a ligand-regulated ion channel following solubilization with the zwitterionic detergent CHAPS (3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)-dimethylammonio]-1- propane sulphonate); purification by density gradient centrifugation, reconstitution into proteo-liposomes and incorporation into planar phospholipid bilayers. 2. In the absence of divalent cations, measurable conductance is observed with the group 1a cations and with some larger organic cations. In symmetric 210 mM solutions the following conductance sequence was determined: K+ greater than Rb+ = NH4+ greater than Na+ = Cs+ greater than Li+ much greater than Tris+. 3. Other organic cations, e.g. TEA+, do not produce measurable current under these conditions. 4. Single-channel conductance saturates with increasing ionic activities of K+, Na+ and Li+. Saturation curves are described by Michaelis-Menten kinetic schemes with the following values of maximal conductance and apparent dissociation constant: K+ 900 pS, 19.9 mM; Na+ 516 pS, 17.8 mM; Li+ 248 pS, 9.1 mM. 5. The channel displays only minor differences in permeability amongst the group 1a cations. Relative permeability, monitored under bi-ionic conditions, yields the following sequence: Na+, 1.15 greater than K+, 1.00 = Li+, 0.99 greater than Rb+, 0.87 greater than Cs+, 0.61. Under similar conditions the permeability ratio of NH4+ to K+ was found to be 1.32 and that for Tris+ to K+ was 0.22. 6. The K+ conductance is reduced by low concentrations of the impermeant cation TEA+. Block appears as a smooth reduction in single-channel current amplitude and the degree of block is dependent upon applied voltage. These observations are consistent with a single-site blocking scheme in which TEA+ has access to a site within the voltage drop of the channel from only the cytosolic face of the channel protein and interacts with a site located approximately 90% of the electrical distance across the channel. The zero-voltage dissociation constant for TEA+ block is 50 mM. 7. Single-channel conductance measurements in mixtures of K(+)-Na+ and K(+)-Li+ reveal no anomalous behaviour as the mole fraction of the ions is varied. 8. With monovalent cations as permeant species, the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor protein functions as a poorly selective, ligand-regulated channel. Under the conditions described here the channel functions as a single-ion pore. It is proposed that discrimination is largely dependent upon the strength of interaction of the permeant ion with a binding site in the conduction pathway.
Full text
PDF






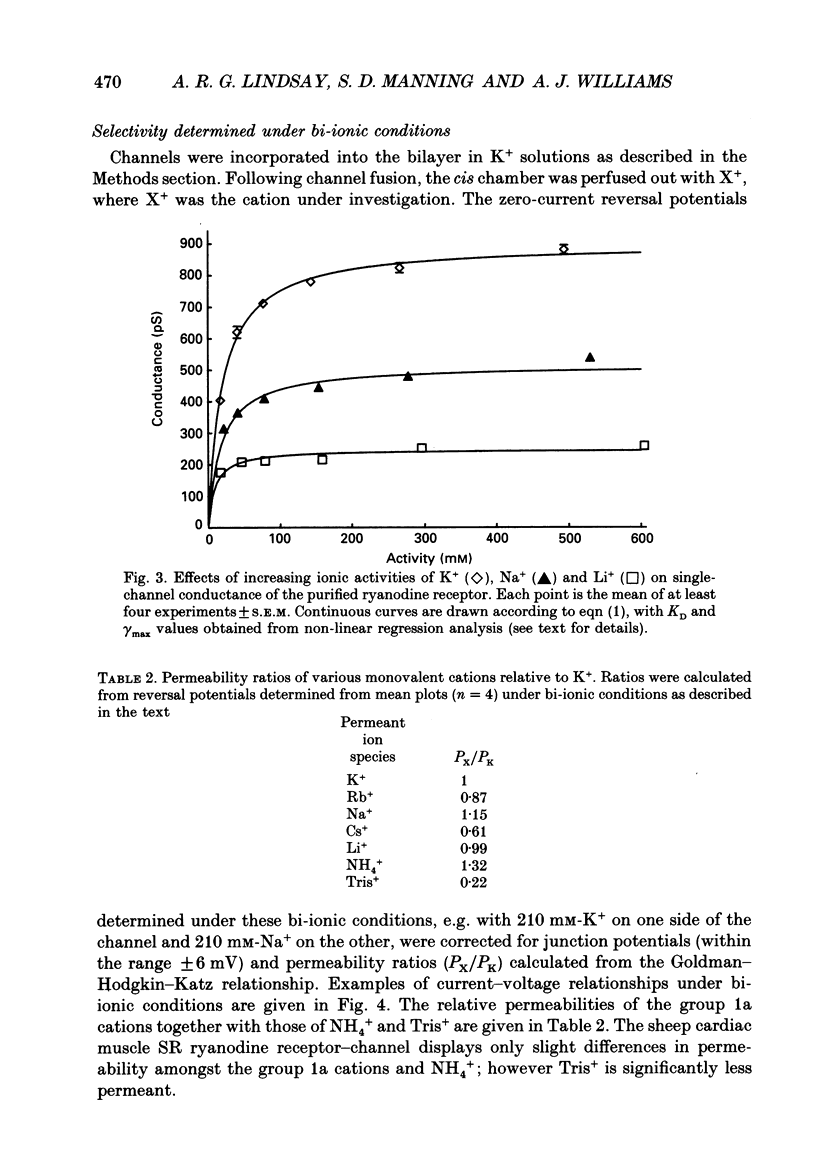

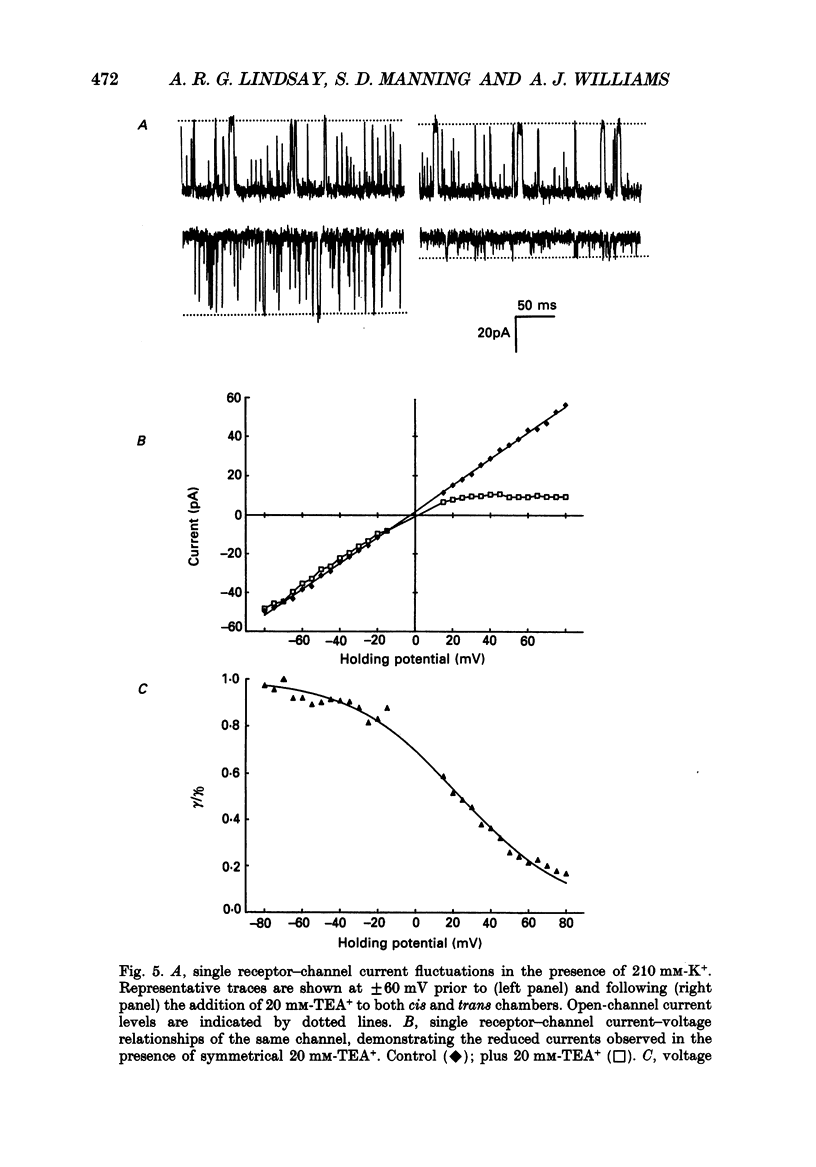
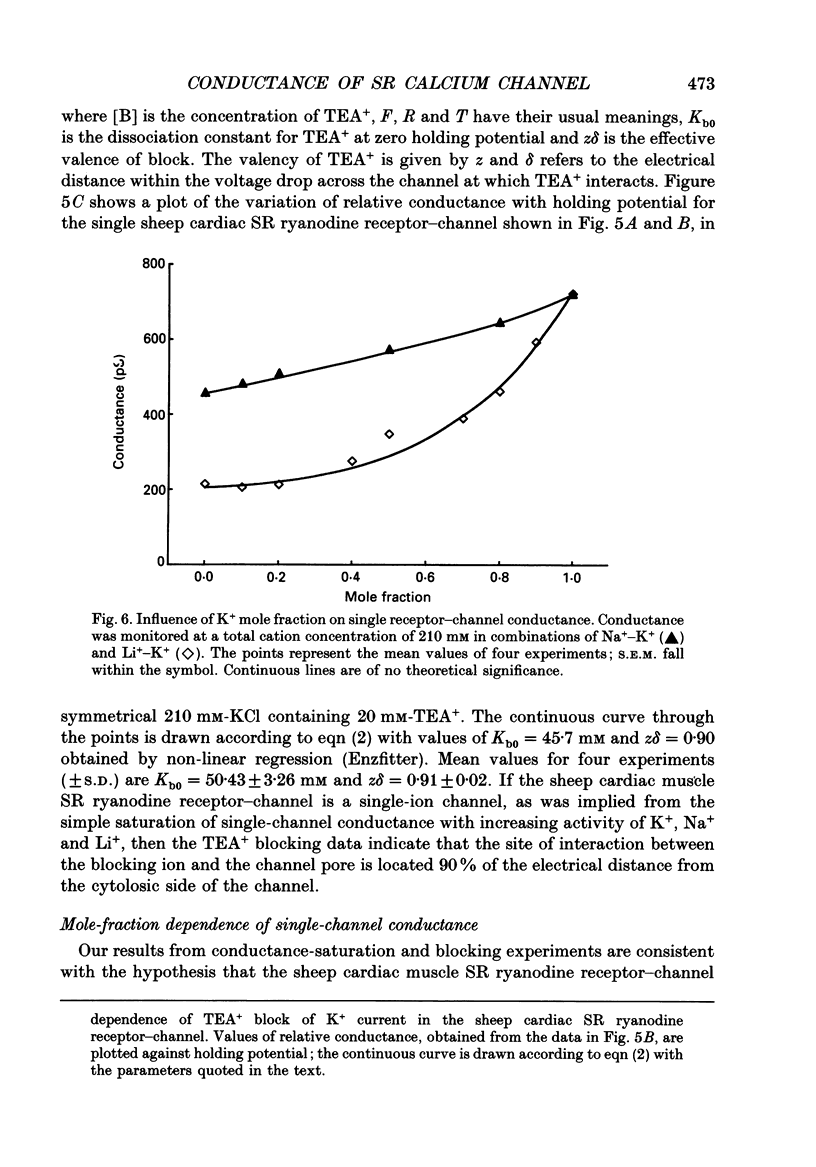







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K., Lai F. A., Liu Q. Y., Rousseau E., Erickson H. P., Meissner G. Structural and functional characterization of the purified cardiac ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1329–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R. H., Williams A. J. Divalent cation activation and inhibition of single calcium release channels from sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):981–1005. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Miller C. Conduction and block by organic cations in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum incorporated into planar phospholipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):529–547. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Smith J. S. Monovalent ion current through single calcium channels of skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biophys J. 1987 Mar;51(3):497–502. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83371-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Horn R. Ionic selectivity revisited: the role of kinetic and equilibrium processes in ion permeation through channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(3):197–225. doi: 10.1007/BF01870364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Latorre R., Miller C. Multi-ion conduction and selectivity in the high-conductance Ca++-activated K+ channel from skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Dec;50(6):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83546-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Appraisal of the physiological relevance of two hypothesis for the mechanism of calcium release from the mammalian cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum: calcium-induced release versus charge-coupled release. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Sep 7;89(2):135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00220765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):247–289. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. R., Williams A. J. Single channel recordings from human cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res. 1989 Nov;65(5):1445–1449. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.5.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Inui M., Fleischer S., Schindler H. Purified ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum forms Ca2+-activated oligomeric Ca2+ channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):441–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Schindler H., Inui M., Fleischer S. Reconstitution of purified cardiac muscle calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) in planar bilayers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Takasago T., Shigekawa M. Cardiac ryanodine receptor is absent in type I slow skeletal muscle fibers: immunochemical and ryanodine binding studies. J Biochem. 1989 Aug;106(2):342–348. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation of the ryanodine receptor from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identity with the feet structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15637–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Anderson K., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Evidence for a Ca2+ channel within the ryanodine receptor complex from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Misra M., Xu L., Smith H. A., Meissner G. The ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for a cooperatively coupled, negatively charged homotetramer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16776–16785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. Y., Lai F. A., Rousseau E., Jones R. V., Meissner G. Multiple conductance states of the purified calcium release channel complex from skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82835-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Fill M., Knudson C. M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle is a gap junction-type channel. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.2459777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks A. R., Tempst P., Hwang K. S., Taubman M. B., Inui M., Chadwick C., Fleischer S., Nadal-Ginard B. Molecular cloning and characterization of the ryanodine receptor/junctional channel complex cDNA from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8683–8687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Almers W. The Ca channel in skeletal muscle is a large pore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7149–7153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Willard H. F., Khanna V. K., Zorzato F., Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13472–13483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E., Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Numa S. Functional expression of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessah I. N., Francini A. O., Scales D. J., Waterhouse A. L., Casida J. E. Calcium-ryanodine receptor complex. Solubilization and partial characterization from skeletal muscle junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8643–8648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rardon D. P., Cefali D. C., Mitchell R. D., Seiler S. M., Jones L. R. High molecular weight proteins purified from cardiac junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles are ryanodine-sensitive calcium channels. Circ Res. 1989 Apr;64(4):779–789. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.4.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Hess P., Reeves J. P., Smilowitz H., Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in planar lipid bilayers: insights into mechanisms of ion permeation and gating. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1564–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2420007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Roberson M., Meissner G. Properties of single chloride selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur Biophys J. 1988;16(3):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00261900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Henderson J. S., Meissner G. Single channel and 45Ca2+ flux measurements of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83543-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitsapesan R., Williams A. J. Mechanisms of caffeine activation of single calcium-release channels of sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:425–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Sarcoplasmic reticulum contains adenine nucleotide-activated calcium channels. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):446–449. doi: 10.1038/316446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanifuji M., Sokabe M., Kasai M. An anion channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum incorporated into planar lipid bilayers: single-channel behavior and conductance properties. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):103–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01871230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Harding S. E., Kirby M. S., Poole-Wilson P. A., Williams A. J. Contamination of a cardiac sarcolemmal preparation with endothelial plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins B., Williams A. J., Montgomery R. A. The characterization of a monovalent cation-selective channel of mammalian cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(2):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01868775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Rosenberg R. L. Calcium channels: mechanisms of selectivity, permeation, and block. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:265–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. J., Ashley R. H. Reconstitution of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:163–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


