Abstract
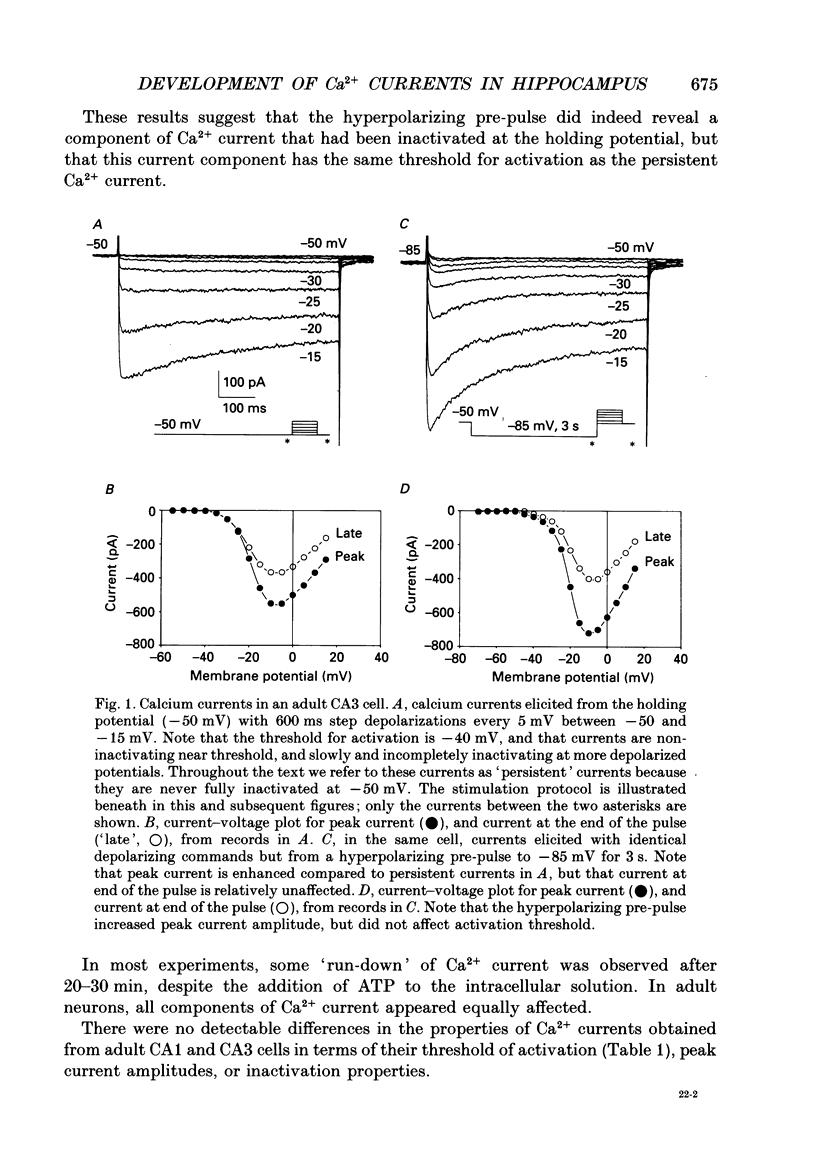
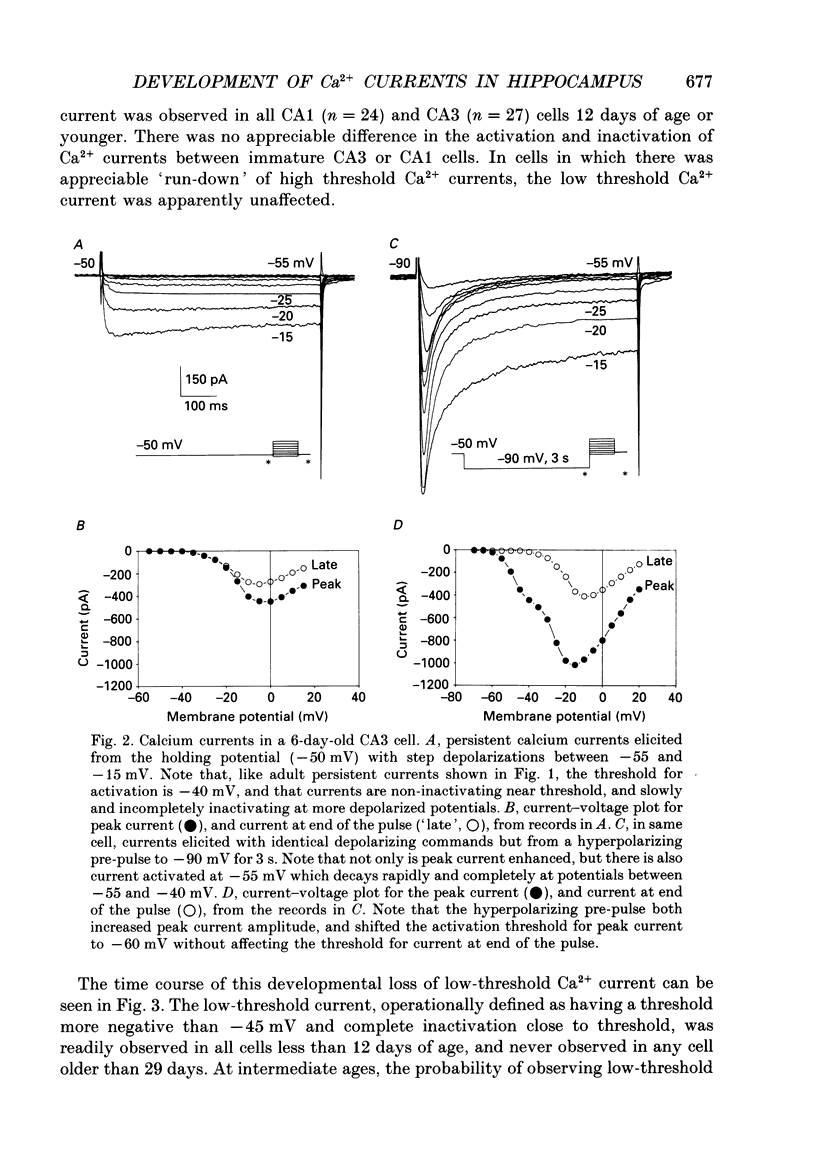
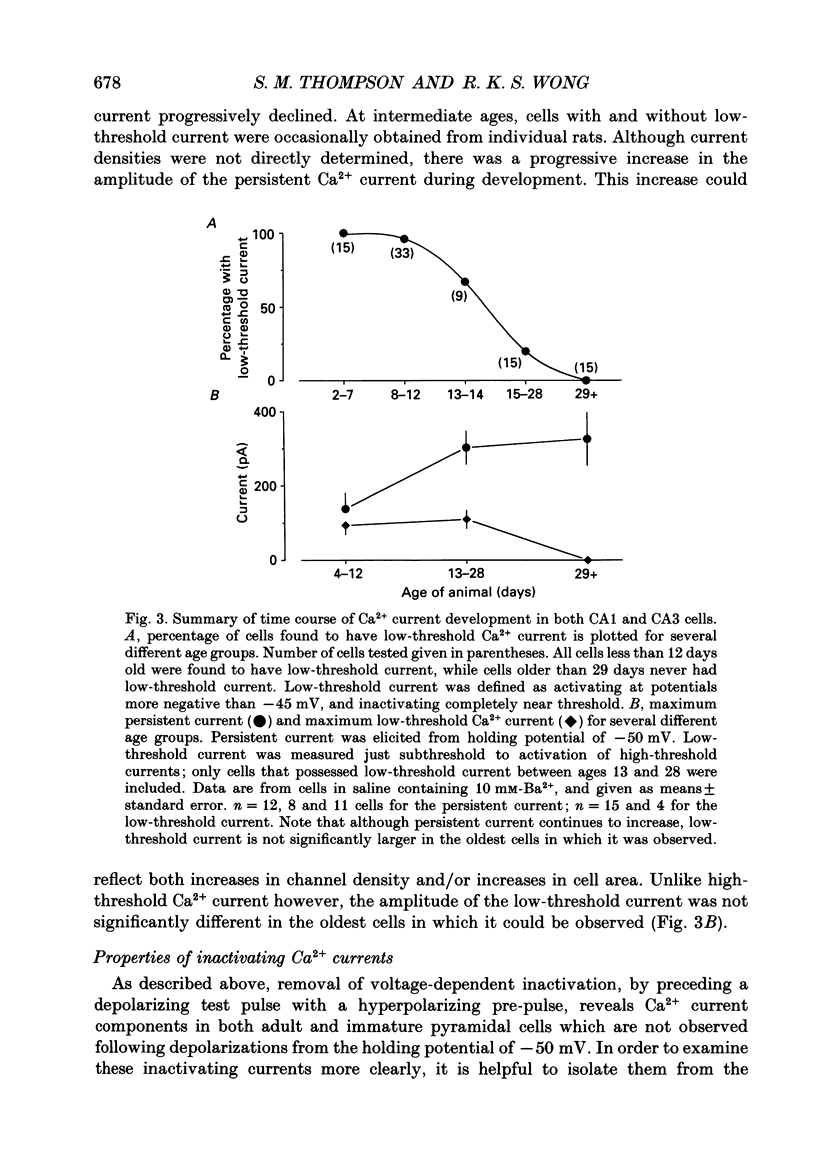
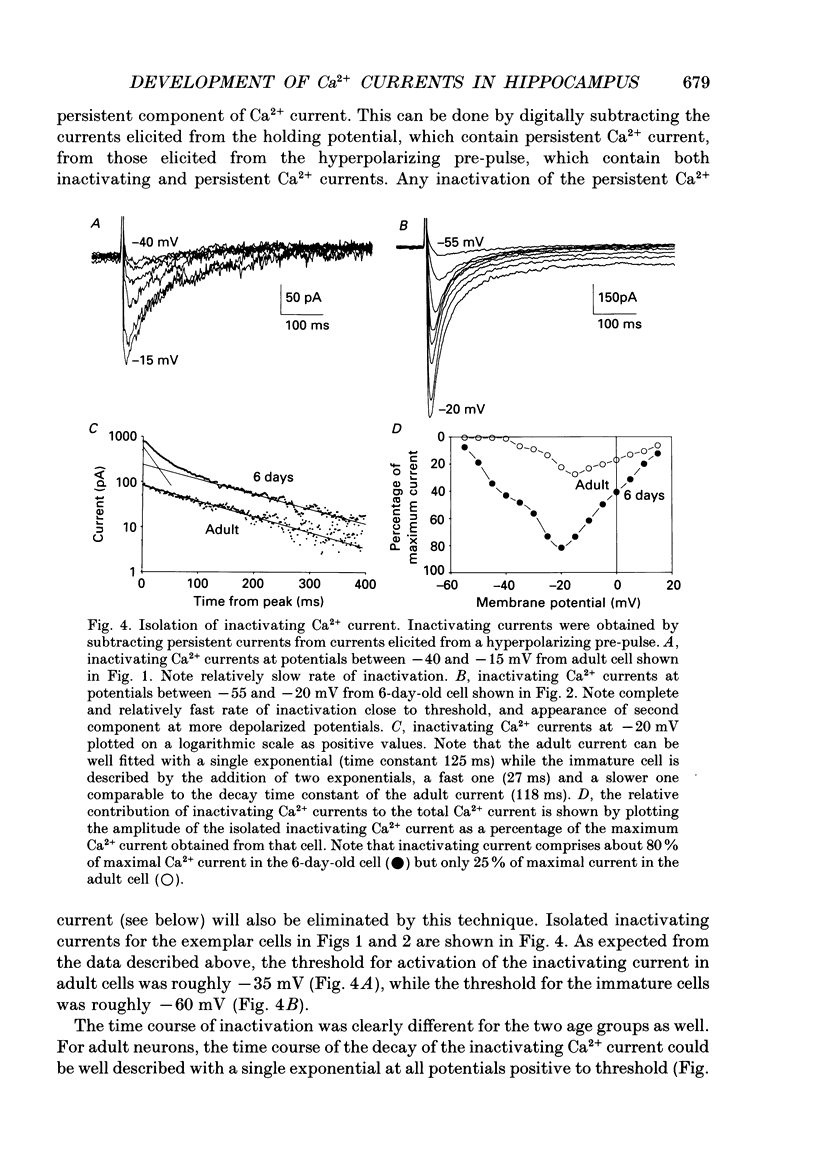
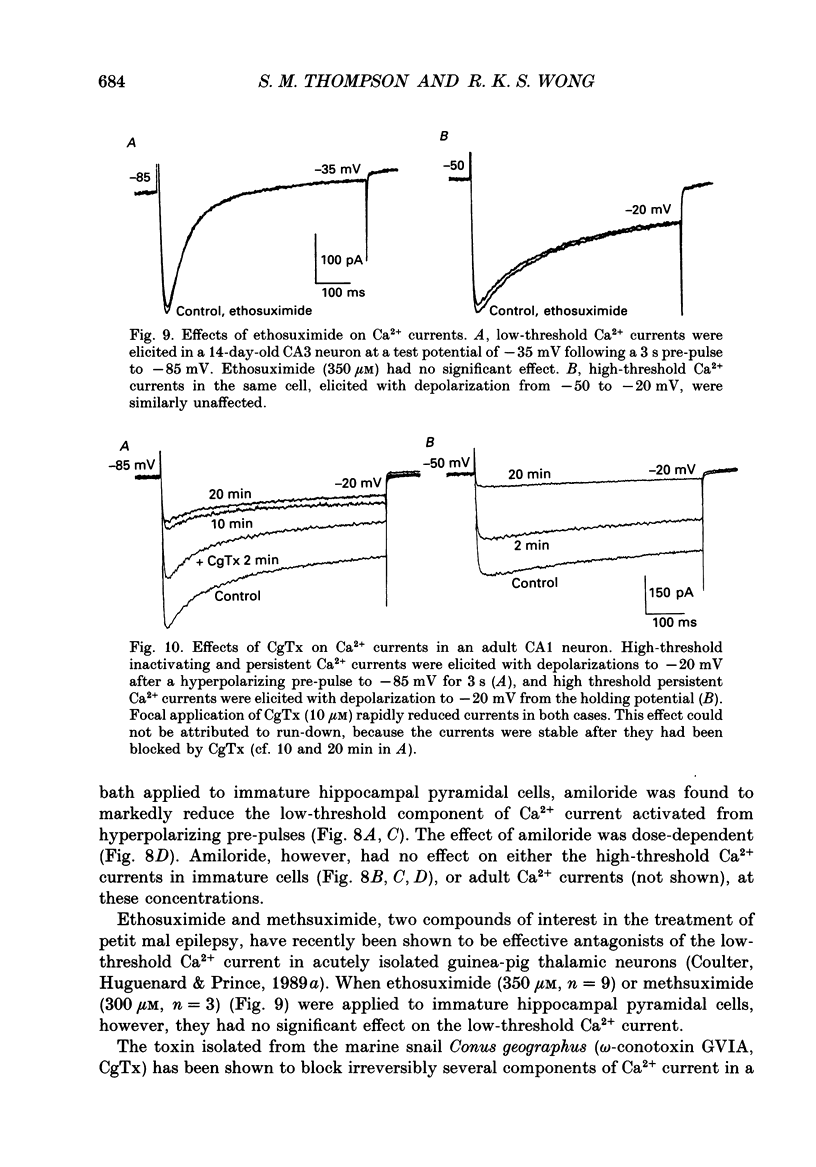
1. Patch-clamp techniques were used to record from acutely dissociated rat hippocampal pyramidal cells of different postnatal ages to study the development, kinetics of activation and inactivation, and pharmacology of various components of whole-cell calcium current. 2. In both adult and immature pyramidal cells, the threshold of activation for Ca2+ current from the holding potential of -50 mV was about -35 mV. The current was non-inactivating near threshold, and slowly inactivating with stronger depolarizations. 3. In adult pyramidal cells, hyperpolarizing pre-pulses (-85 mV, 3 s) increased the peak amplitude of current, but had little effect on the amplitude of sustained current or on the threshold. In immature cells, hyperpolarizing pre-pulses (-85 mV, 3 s) revealed an additional component of Ca2+ current that had a threshold for activation around -60 mV, and inactivated rapidly and completely at potentials between -60 and -35 mV. This low-threshold Ca2+ current was found in all cells less than 12 days of age, and in no cells older than 29 days of age. 4. No difference was observed between the Ca2+ currents elicited from CA3 or CA1 pyramidal cells. 5. The time course of decay for inactivating Ca2+ currents in adult cells at -20 mV was well fit with a single exponential of roughly 120 ms time constant. In immature cells, the addition of a second, faster time constant (roughly 25 ms) was required to describe the decay of the inactivating current adequately. The persistent Ca2+ current elicited from the holding potential of -50 mV decayed with a time constant of roughly 750 ms. The rate of inactivation for all Ca2+ current components was faster with stronger depolarizations. Inactivating Ca2+ currents contributed a significantly larger percentage of the total Ca2+ current in immature than adult cells. 6. Steady-state inactivation of the low-threshold Ca2+ current in immature cells was described by the Boltzmann equation with half maximal inactivation at -76 mV and a slope factor of 6.8. Recovery from inactivation was exponential, with a time constant of 820 ms (at -85 mV). Steady-state inactivation of the high-threshold inactivating Ca2+ current in adult cells was described by the Boltzmann equation with half maximal inactivation at -78 mV and a slope factor of 9.9. 7. The low-threshold Ca2+ current in immature cells was blocked in a reversible and dose-dependent manner by amiloride (100-250 microM). Amiloride had no effect on high-threshold Ca2+ currents.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Selected References
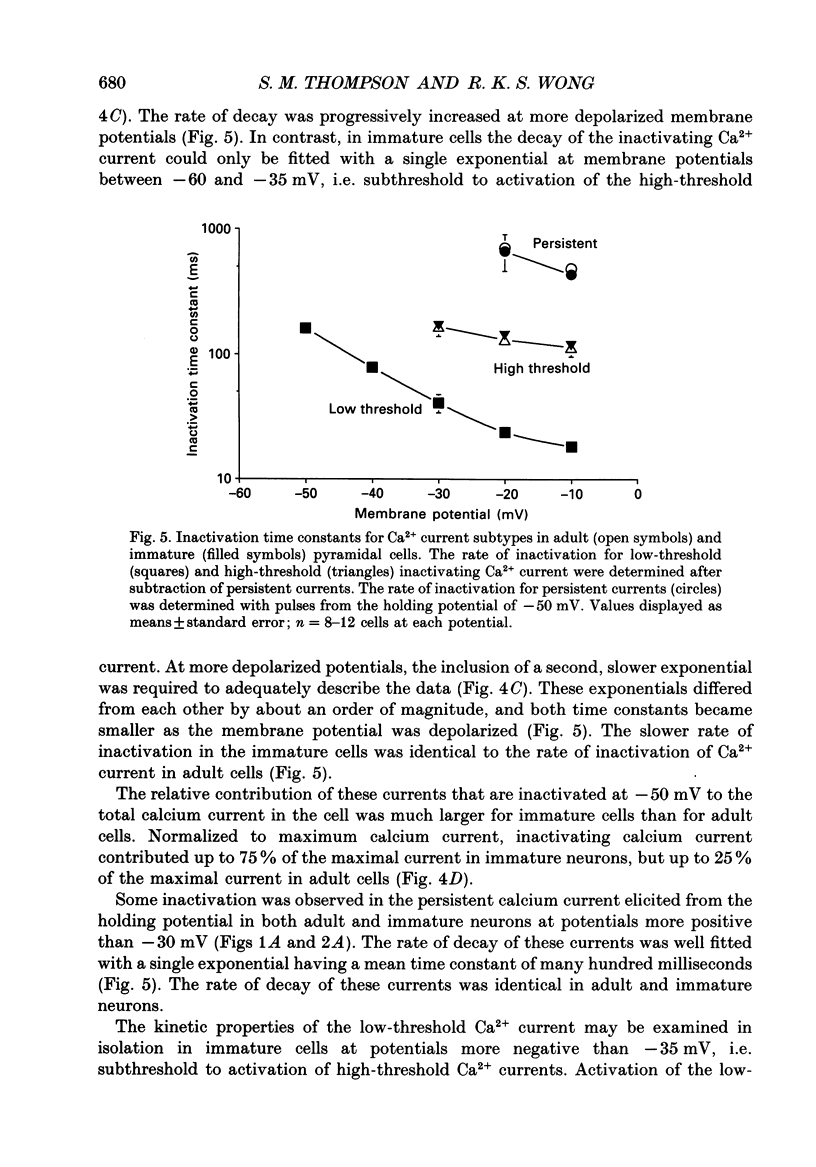
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
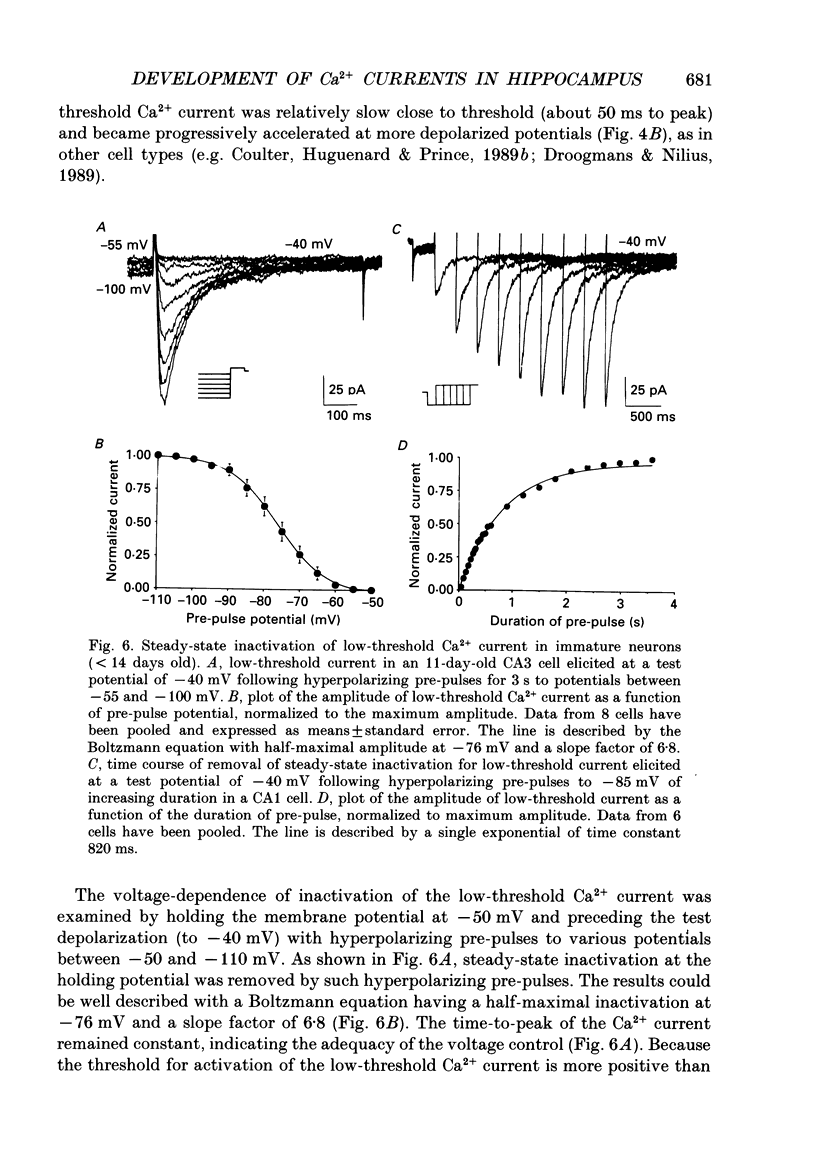
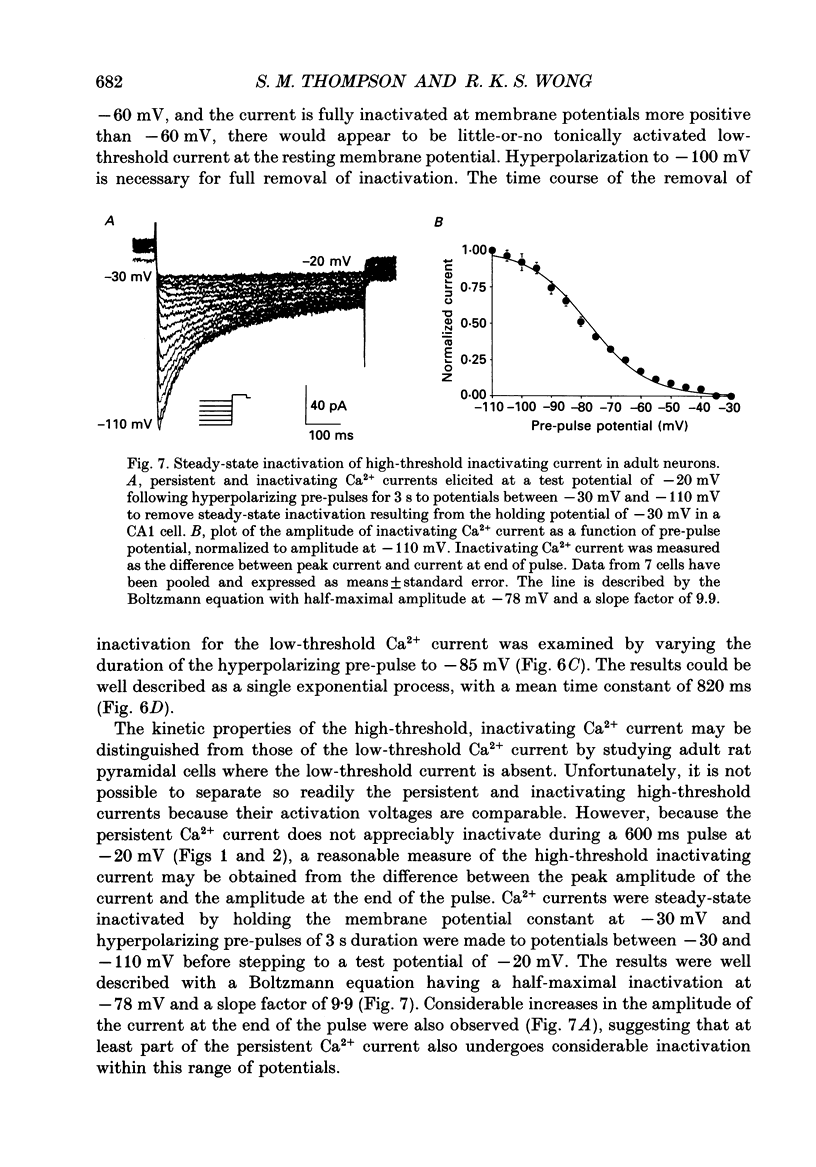
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
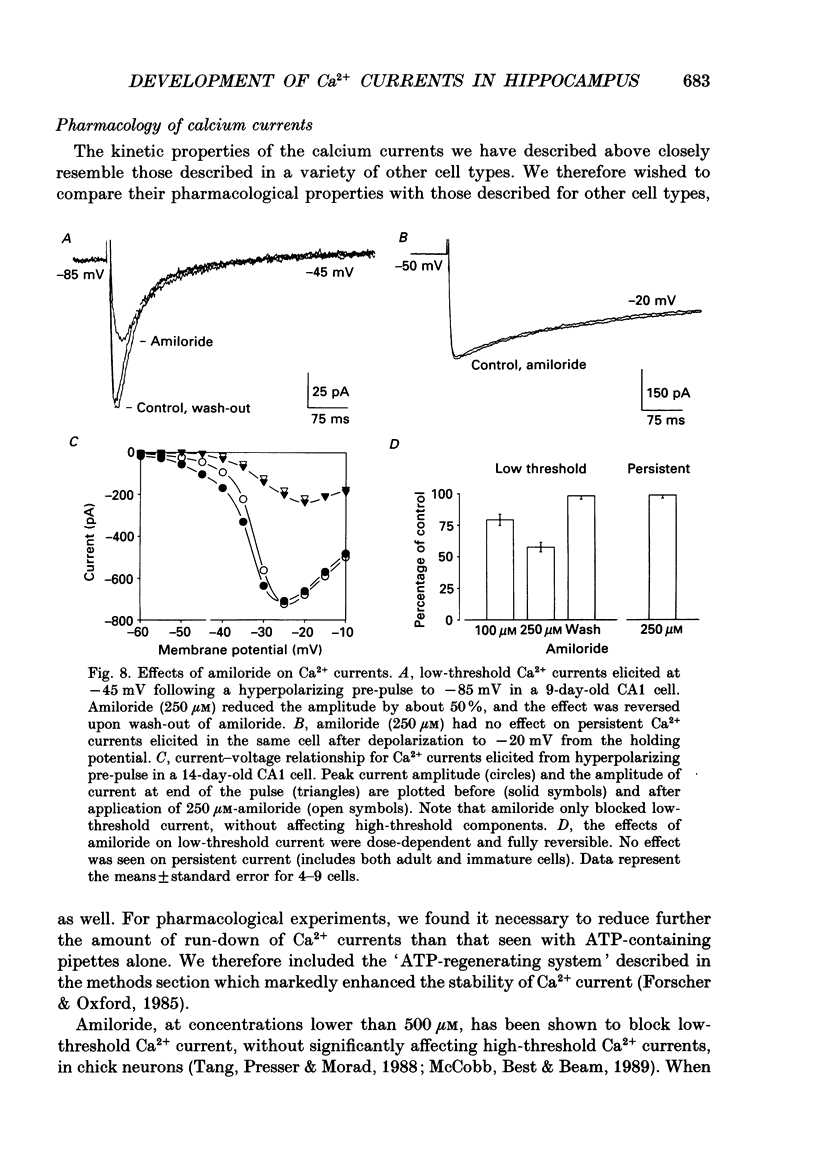
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Kinetics and selectivity of a low-voltage-activated calcium current in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:547–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Single low-voltage-activated calcium channels in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:571–601. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. A., Huguenard J. R., Prince D. A. Calcium currents in rat thalamocortical relay neurones: kinetic properties of the transient, low-threshold current. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:587–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. A., Huguenard J. R., Prince D. A. Specific petit mal anticonvulsants reduce calcium currents in thalamic neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Mar 13;98(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty R. J., Brown D. A. Interaction of 1,4-dihydropyridines with somatic Ca currents in hippocampal CA1 neurones of the guinea pig in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Sep 25;70(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerner D., Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C activators block specific calcium and potassium current components in isolated hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4069–4078. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04069.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Nilius B. Kinetic properties of the cardiac T-type calcium channel in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:627–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. E., Gray R., Johnston D. Properties and distribution of single voltage-gated calcium channels in adult hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jul;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:173–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonoi T., Hasegawa S. Post-natal disappearance of transient calcium channels in mouse skeletal muscle: effects of denervation and culture. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:617–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottmann K., Dietzel I. D., Lux H. D., Huck S., Rohrer H. Development of inward currents in chick sensory and autonomic neuronal precursor cells in culture. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3722–3732. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. Effects of dihydropyridines on calcium currents in CA3 pyramidal cells in slice cultures of rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):731–738. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Miles R., Wong R. K. Intracellular fluoride alters the kinetic properties of calcium currents facilitating the investigation of synaptic events in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):2915–2920. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-02915.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Isolation of neurons suitable for patch-clamping from adult mammalian central nervous systems. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 May;16(3):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D. H., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M., Tsien R. W., Yoshikami D. Omega-conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCobb D. P., Best P. M., Beam K. G. Development alters the expression of calcium currents in chick limb motoneurons. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1633–1643. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. E., Barker J. L. Whole-cell patch-clamp analysis of voltage-dependent calcium conductances in cultured embryonic rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Mar;61(3):467–477. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):443–446. doi: 10.1038/316443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Tateishi N., Kaneda M., Akaike N. Comparison of low-threshold Ca2+ currents in the hippocampal CA1 neurons among the newborn, adult and aged rats. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Aug 14;103(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90480-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Wakamori M., Akaike N. Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells of rats have four voltage-dependent calcium conductances. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Sep 25;104(1-2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Presser F., Morad M. Amiloride selectively blocks the low threshold (T) calcium channel. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2451291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 29;159(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaari Y., Hamon B., Lux H. D. Development of two types of calcium channels in cultured mammalian hippocampal neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):680–682. doi: 10.1126/science.2433765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


