Abstract
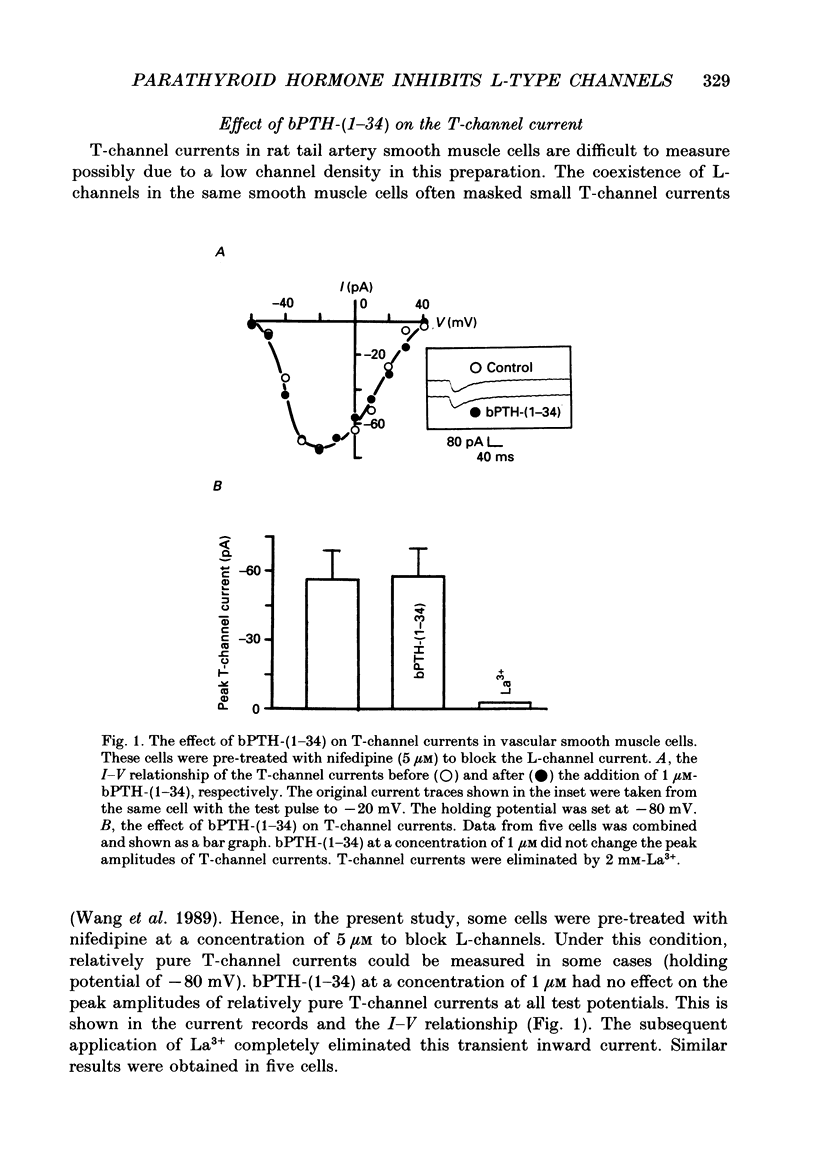
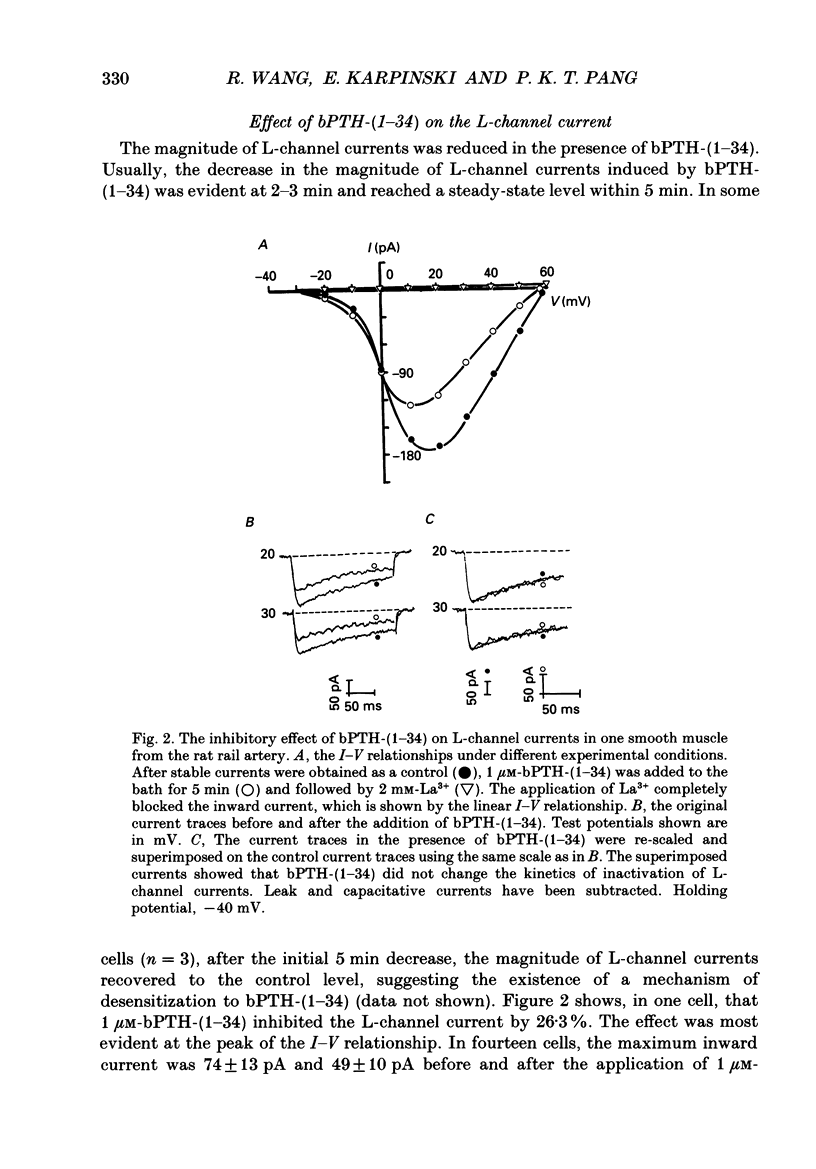
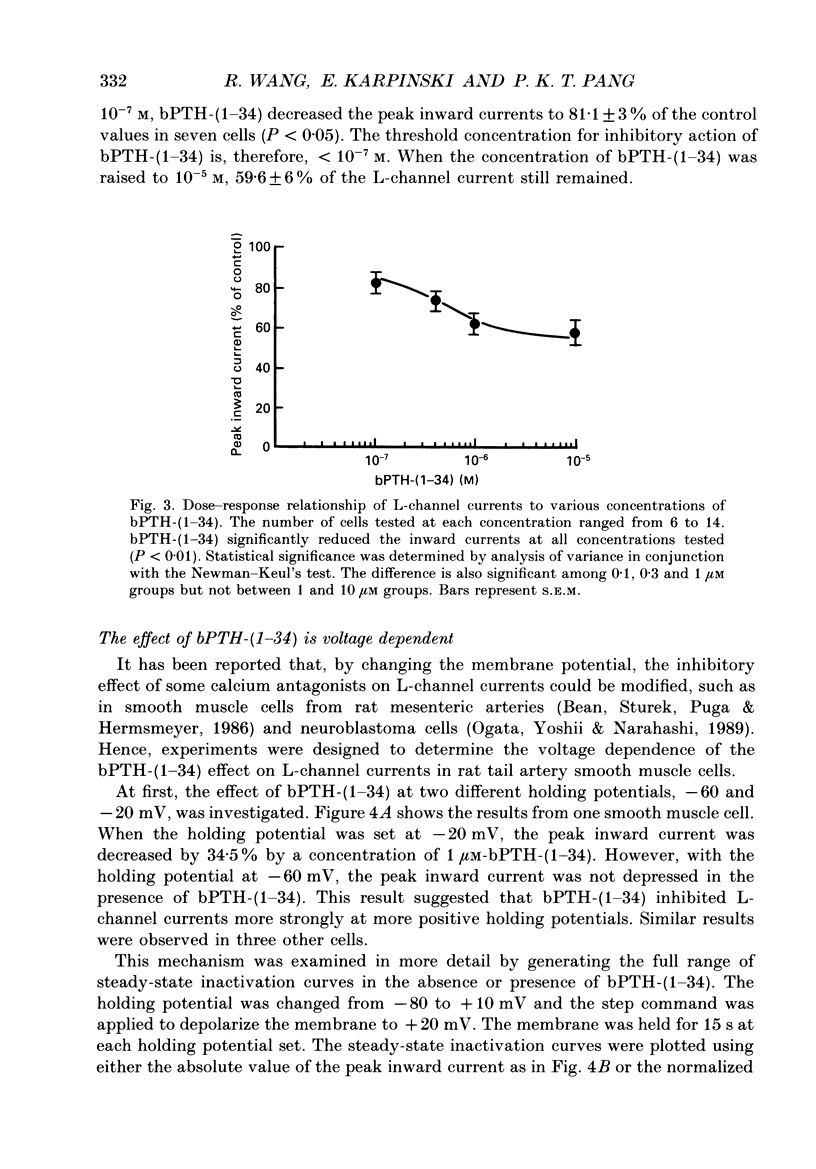
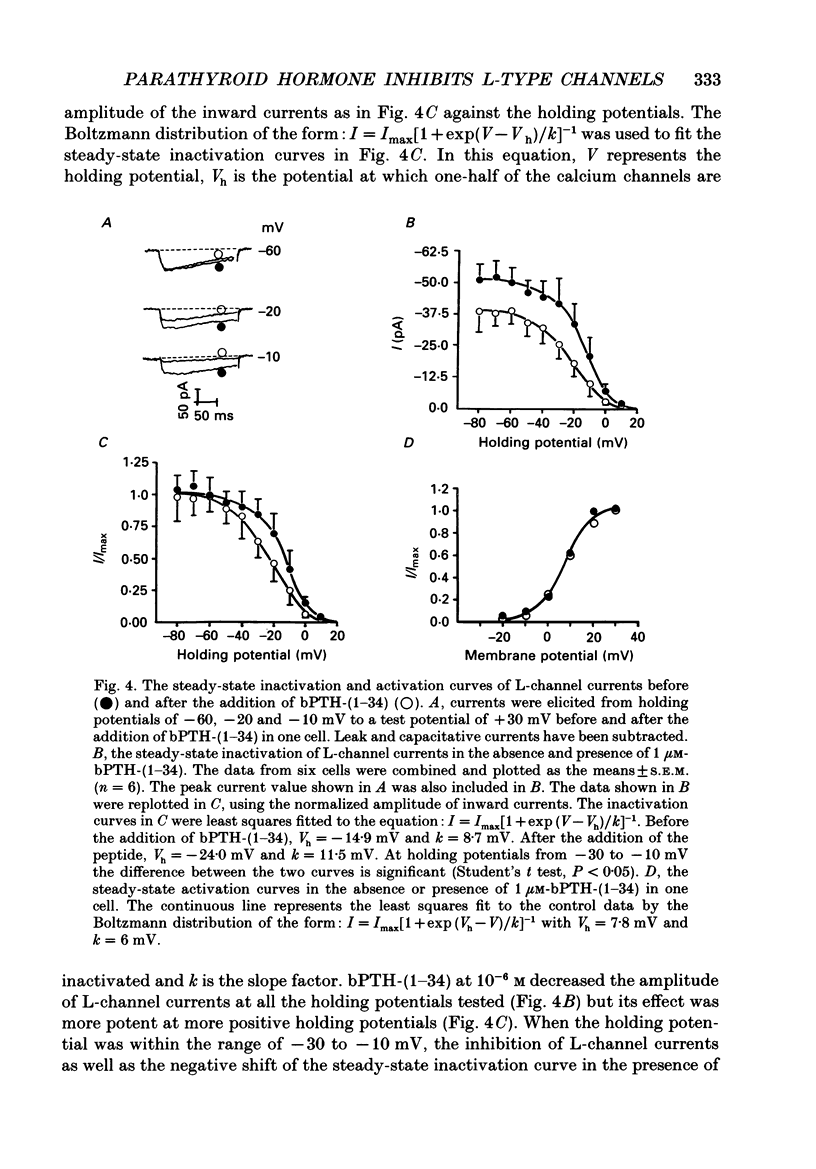
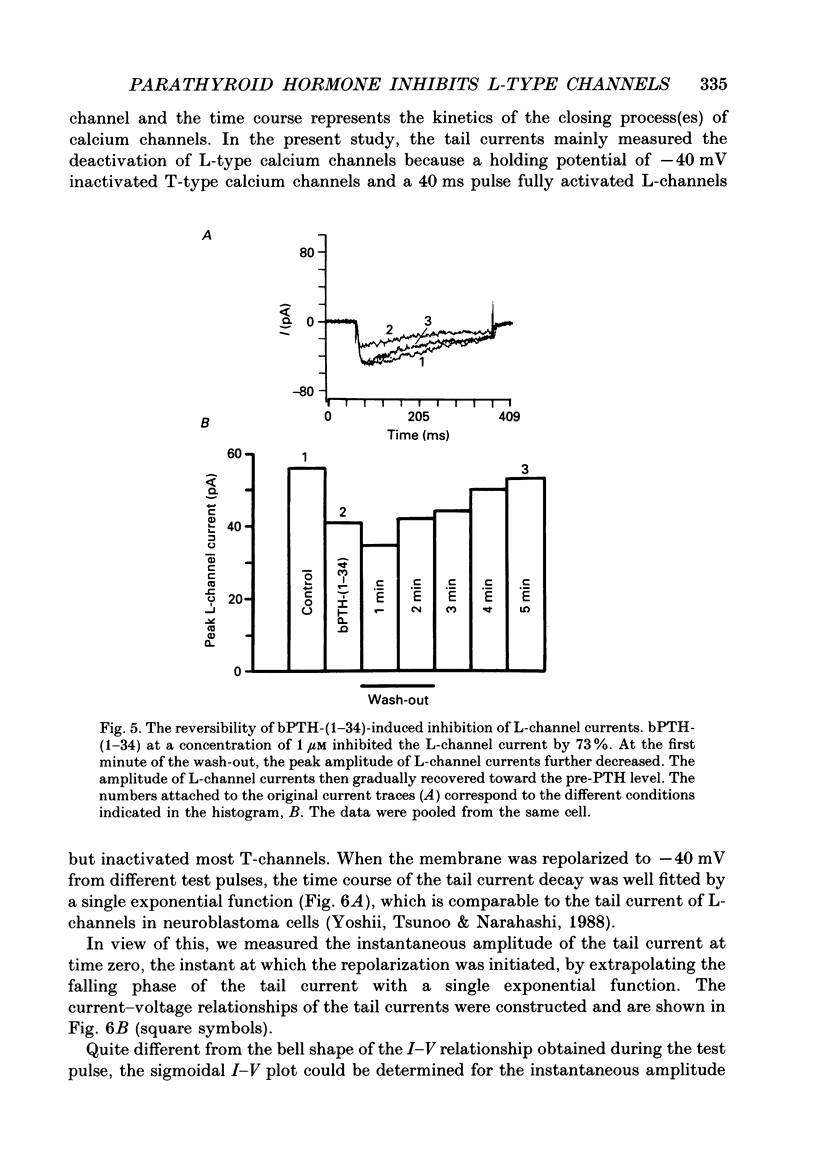
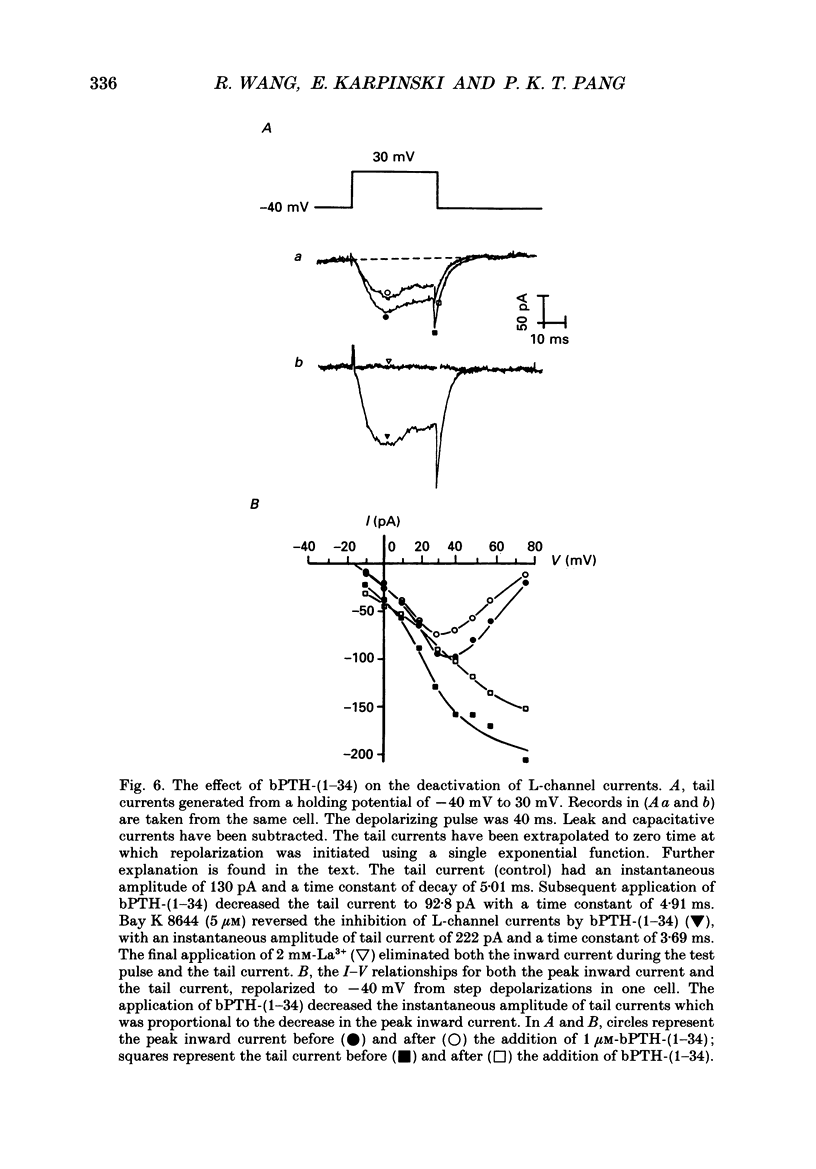
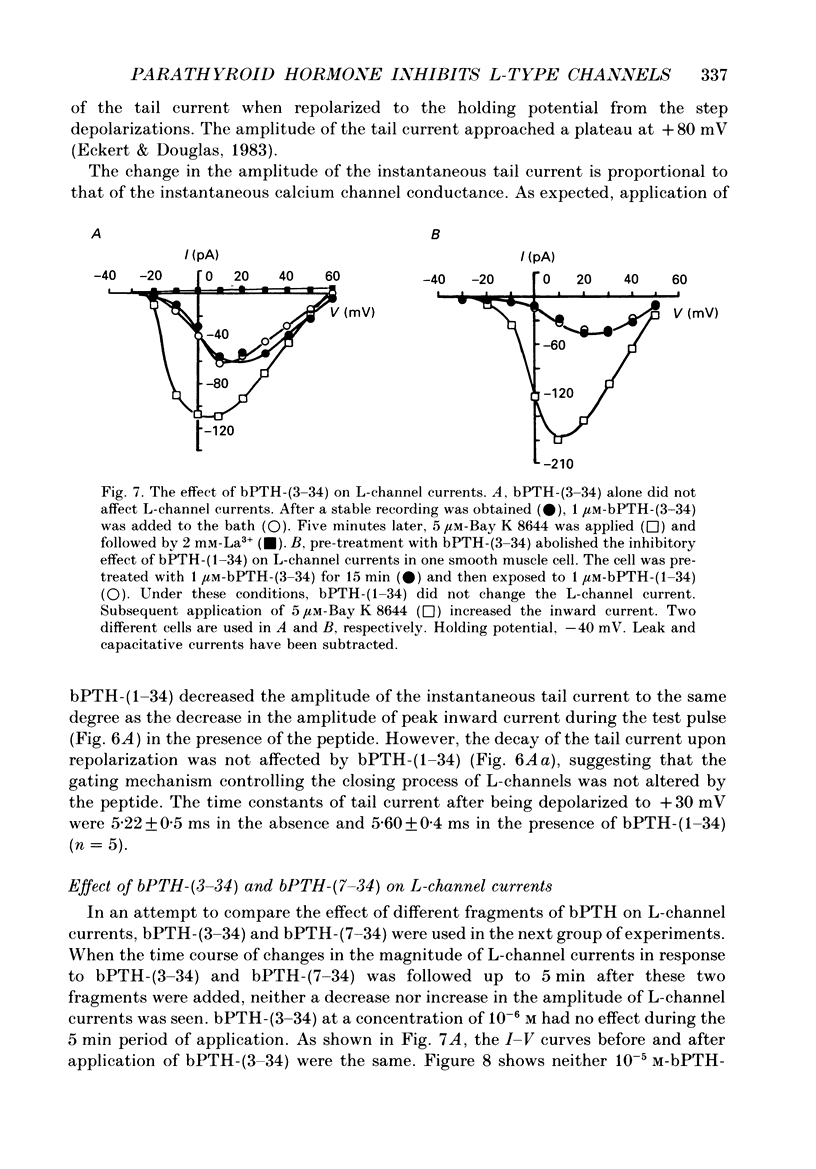
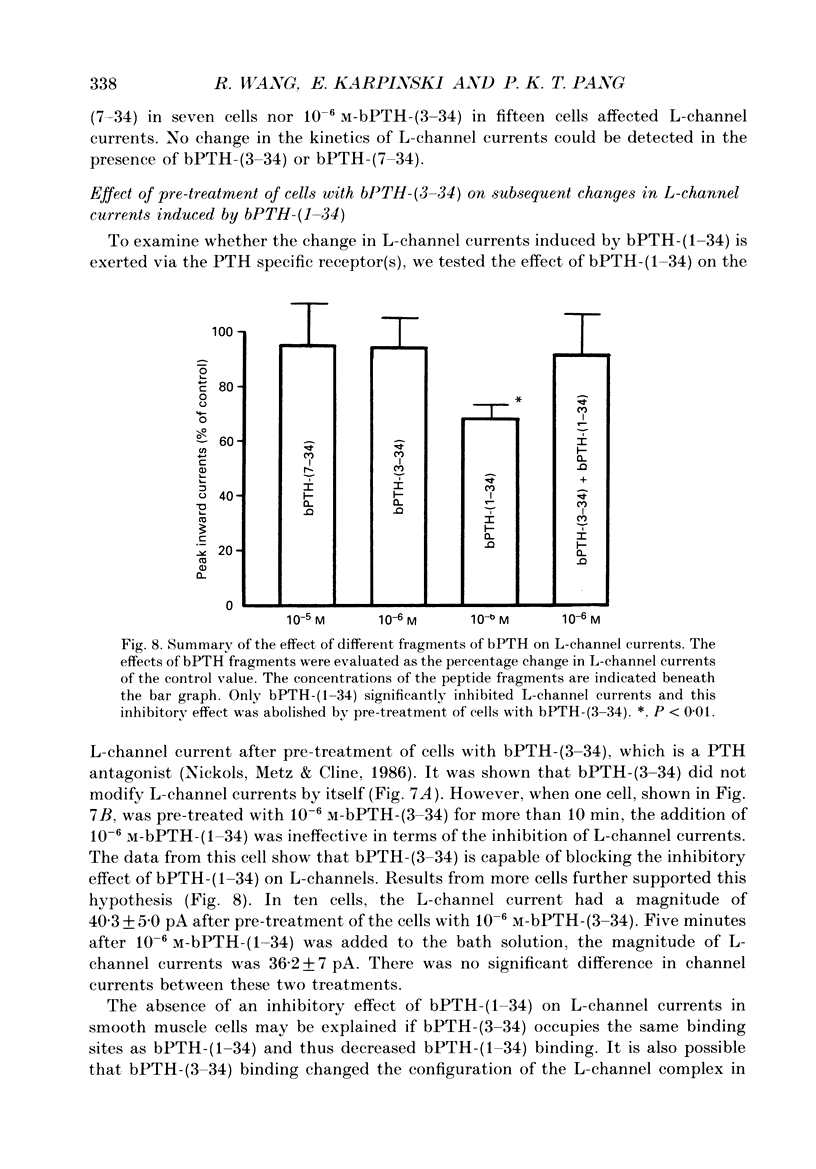
1. The active synthetic N-terminal fragment of bovine parathyroid hormone, bPTH-(1-34) at a concentration of 1 microM, decreased the peak amplitude of the long-lasting (L-type) calcium channel current by 37% (n = 14, P less than 0.01) in rat tail artery smooth muscle cells. By contrast, this fragment of parathyroid hormone (PTH) (1 microM) had no effect on the transient (T-type) calcium channel current in the same cell preparation. 2. The inhibitory effect of bPTH-(1-34) on L-channel currents was reversible and could be antagonized by the L-channel agonist, Bay K 8644. In contrast, bPTH-(1-34) inhibited Bay K 8644-induced amplification of L-channel currents. 3. The inhibitory effect of bPTH-(1-34) on L-Channel currents was dose dependent with a threshold concentration of less than 10(-7), and voltage dependent with increased inhibition at more positive holding potentials. However, this effect of bPTH-(1-34) was not dependent on different pulse lengths or interpulse intervals. 4. The kinetics of deactivation of L-channel currents were not changed although the instantaneous amplitude of the L-channel tail current was reduced by bPTH-(1-34). 5. Application of bPTH-(1-34) antagonists (10(-6) M-bPTH-(3-34) and 10(-5) M-bPTH-(7-34] did not result in any significant change in the magnitude of L-channel currents (n = 15 and n = 7, respectively). 6. Pre-incubation of cells with bPTH-(3-34) for more than 15 min abolished the inhibitory effect of bPTH-(1-34) on L-channel currents. 7. The present study provides direct evidence to demonstrate the PTH, an endogenous circulating hormone, is a selective inhibitor of L-channel currents in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Taylor S. R. Interaction of barium ions with potassium channels in squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):473–488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85108-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacskai B. J., Friedman P. A. Activation of latent Ca2+ channels in renal epithelial cells by parathyroid hormone. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):388–391. doi: 10.1038/347388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Sturek M., Puga A., Hermsmeyer K. Calcium channels in muscle cells isolated from rat mesenteric arteries: modulation by dihydropyridine drugs. Circ Res. 1986 Aug;59(2):229–235. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. The mechanism of action of Ba2+ and TEA on single Ca2+-activated K+ -channels in arterial and intestinal smooth muscle cell membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Feb;403(2):120–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00584088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. Noradrenaline modulation of calcium channels in single smooth muscle cells from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:767–784. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnes D. L., Anast C. S., Forte L. R. Renal parathyroid hormone-dependent adenylate cyclase activity after repletion of vitamin D-deficient rats with vitamin D-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 22;629(3):546–552. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:519–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Ewald D. Calcium tail currents in voltage-clamped intact nerve cell bodies of Aplysia californica. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:533–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Binswanger U., Dietrich F. M. Human parathyroid hormone. Immunological characterization of antibodies against a glandular extract and the synthetic amino-terminal fragments 1-12 and 1-34 and their use in the determination of immunoreactive hormone in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1382–1394. doi: 10.1172/JCI107885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost B. R., Gerke D. C., Frewin D. B. The effects of 2-phenylalanine 8-lysine vasopressin (octapressin) on blood vessels in the rat tail. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Aug;54(4):403–411. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Kasuya Y., Matsuki N., Takuwa Y., Kurihara H., Ishikawa T., Kimura S., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin activates the dihydropyridine-sensitive, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3915–3918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A. Calcium channels and calcium channel antagonists. Ann Neurol. 1987 Apr;21(4):317–330. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helwig J. J., Schleiffer R., Judes C., Gairard A. Distribution of parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase in isolated rabbit renal cortex microvessels and glomeruli. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 24;35(26):2649–2657. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Tang M., Jastorff B., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of histamine induced enhancement of the cardiac Ca2+ current. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00581891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements by second messengers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:299–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Blalock J. B., Schonbrunn A. Characterization of the cyclic AMP-independent actions of somatostatin in GH cells. I. An increase in potassium conductance is responsible for both the hyperpolarization and the decrease in intracellular free calcium produced by somatostatin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):216–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo N., Shibata S., Tenner T. E., Jr, Pang P. K. Electromechanical effects of bPTH-(1-34) on rabbit sinus node cells and guinea pig papillary muscles. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 May;11(5):619–625. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198805000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laethem R., Zull J. E. Characterization of the interaction of parathyroid hormone with the mitochondrial ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Oct;282(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwik C. W., van Leeuwen J. P., van der Meer J. M., van Zeeland J. K., Scheven B. A., Herrmann-Erlee M. P. A two-receptor model for the action of parathyroid hormone on osteoblasts: a role for intracellular free calcium and cAMP. Cell Calcium. 1985 Aug;6(4):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti C., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00586670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollard P., Vacher P., Rogawski M. A., Dufy B. Vasopressin enhances a calcium current in human ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma cells. FASEB J. 1988 Oct;2(13):2907–2912. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.13.2844618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickols G. A., Cline W. H., Jr Parathyroid hormone-induced changes in cyclic nucleotide levels during relaxation of the rabbit [correction of rat] aorta. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 15;40(24):2351–2359. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90509-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickols G. A. Increased cyclic AMP in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells and relaxation of aortic strips by parathyroid hormone. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 8;116(1-2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickols G. A., Metz M. A., Cline W. H., Jr Vasodilation of the rat mesenteric vasculature by parathyroid hormone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):419–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Yoshii M., Narahashi T. Psychotropic drugs block voltage-gated ion channels in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 2;476(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91546-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Sperelakis N. ATP regulation of the slow calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells of guinea pig mesenteric artery. Circ Res. 1989 Jan;64(1):145–154. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang P. K., Hong B. S., Yen L., Yang M. C. Parathyroid hormone. A specific potent vasodilator. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;41:137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang P. K., Wang R., Shan J., Karpinski E., Benishin C. G. Specific inhibition of long-lasting, L-type calcium channels by synthetic parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):623–627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang P. K., Yang M. C., Sham J. S. Parathyroid hormone and calcium entry blockade in a vascular tissue. Life Sci. 1988;42(14):1395–1400. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang P. K., Yang M. C., Tenner T. E., Jr, Kenny A. D., Cooper C. W. Cyclic AMP and the vascular action of parathyroid hormone. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;64(12):1543–1547. doi: 10.1139/y86-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Isolation and kinetic analysis of inward currents in neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu P. D., Gerber G., Murase K., Randic M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances calcium current of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons and spinal excitatory synaptic transmission. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jul 8;89(3):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada H., Kojima M., Sperelakis N. Fast inward current properties of voltage-clamped ventricular cells of embryonic chick heart. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):H540–H553. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.3.H540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Lederis K., Huang M., LeBlanc F. E., Rorstad O. P. Relaxation of bovine, porcine and human brain arteries by parathyroid hormone. Life Sci. 1983 Dec 19;33(25):2497–2503. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Blocking actions of Ca2+ antagonists on the Ca2+ channels in the smooth muscle cell membrane of rabbit small intestine. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(6):552–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00581155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Bean B. P., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Nilius B., Nowycky M. C. Mechanisms of calcium channel modulation by beta-adrenergic agents and dihydropyridine calcium agonists. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Jul;18(7):691–710. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80941-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Karpinski E., Pang P. K. Two types of calcium channels in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat tail artery. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):H1361–H1368. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.5.H1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii M., Tsunoo A., Narahashi T. Gating and permeation properties of two types of calcium channels in neuroblastoma cells. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):885–895. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83025-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Y. Y., Benishin C. G., Pang P. K. Guanine nucleotide binding proteins may modulate gating of calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle. I. Studies with fluoride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):343–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Saida K. Cellular mechanisms regulating [Ca2+]i smooth muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:315–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


