Abstract
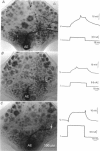
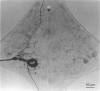
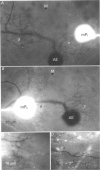
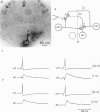
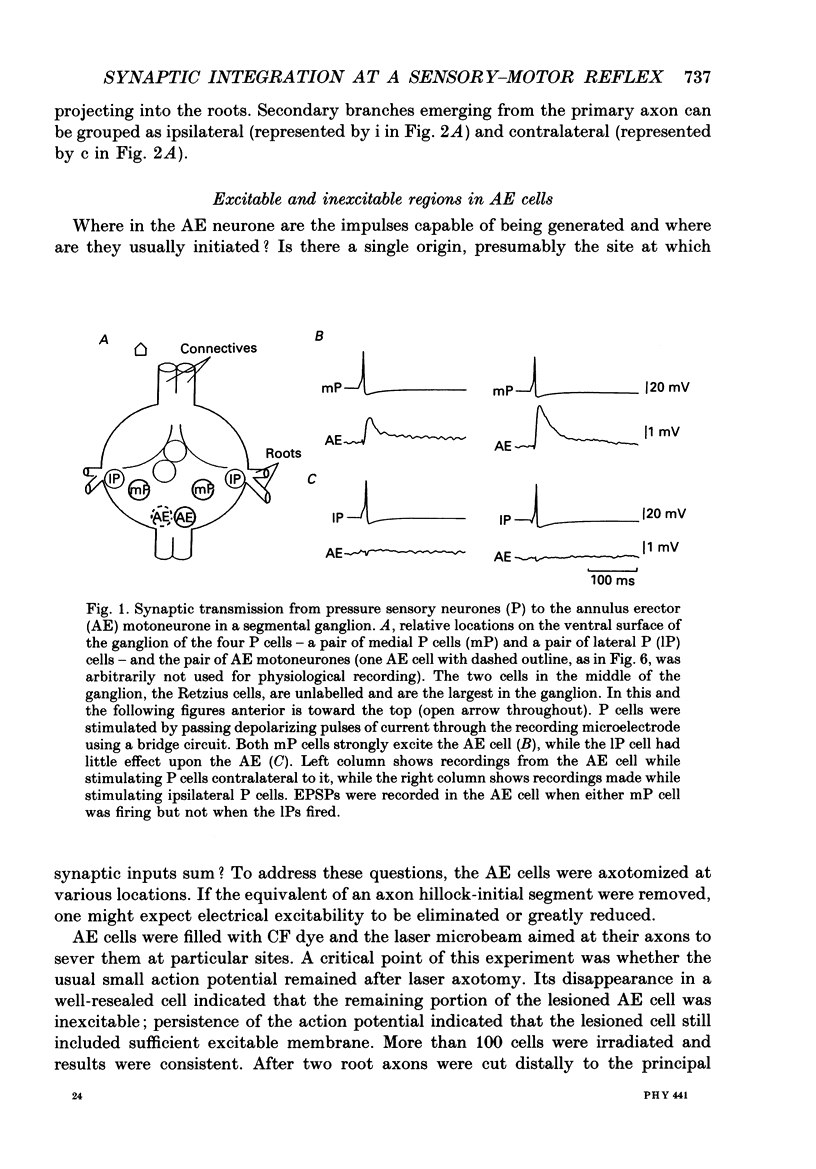
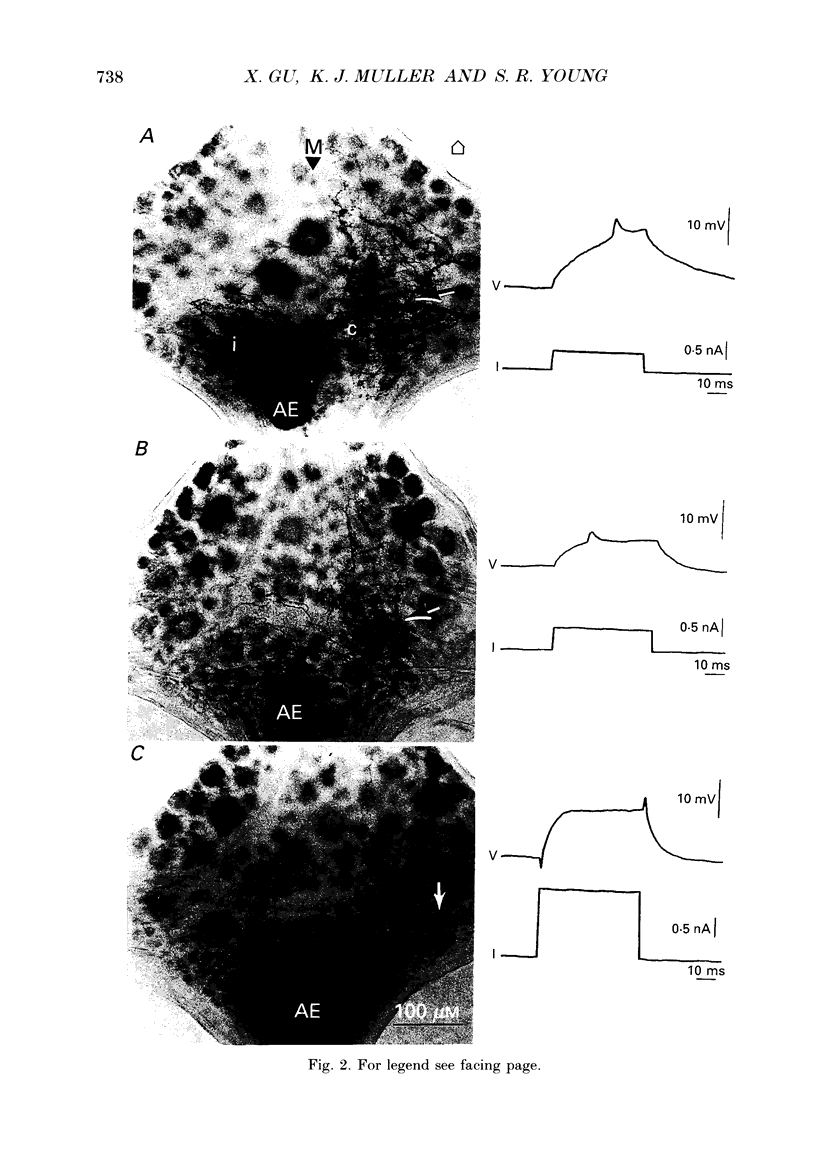
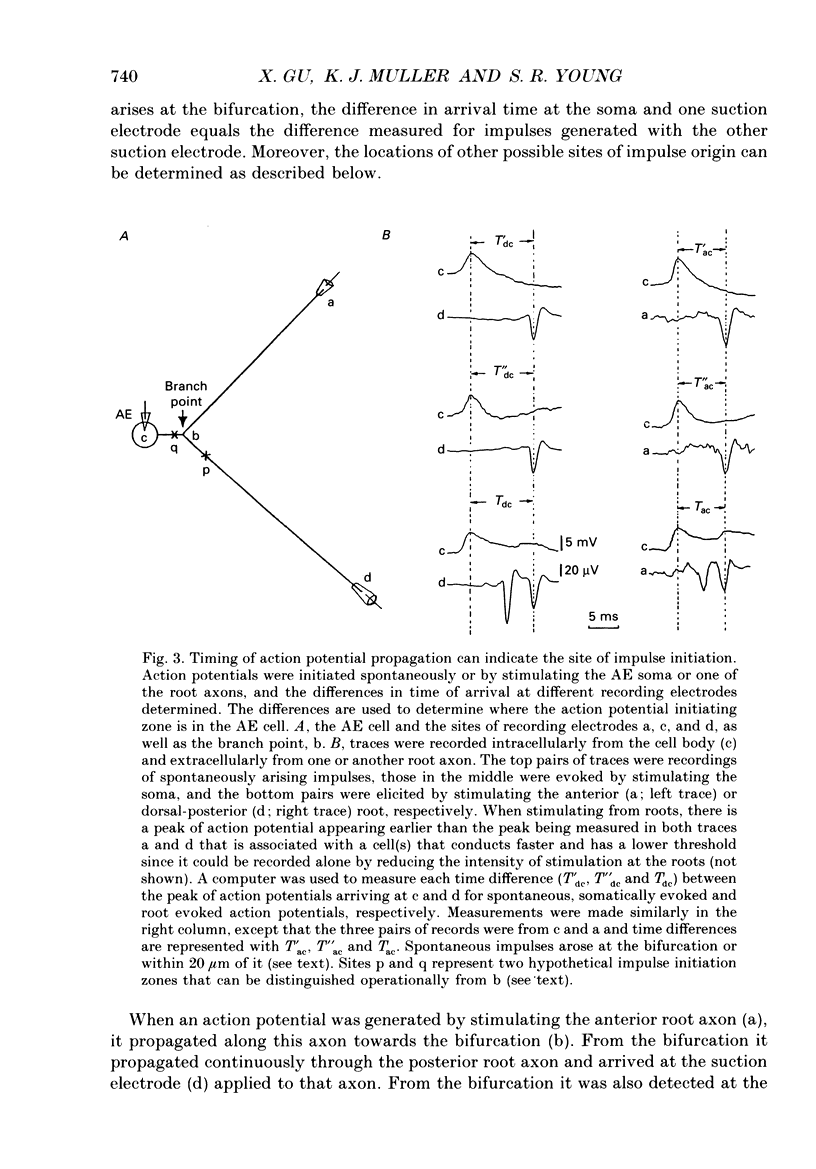
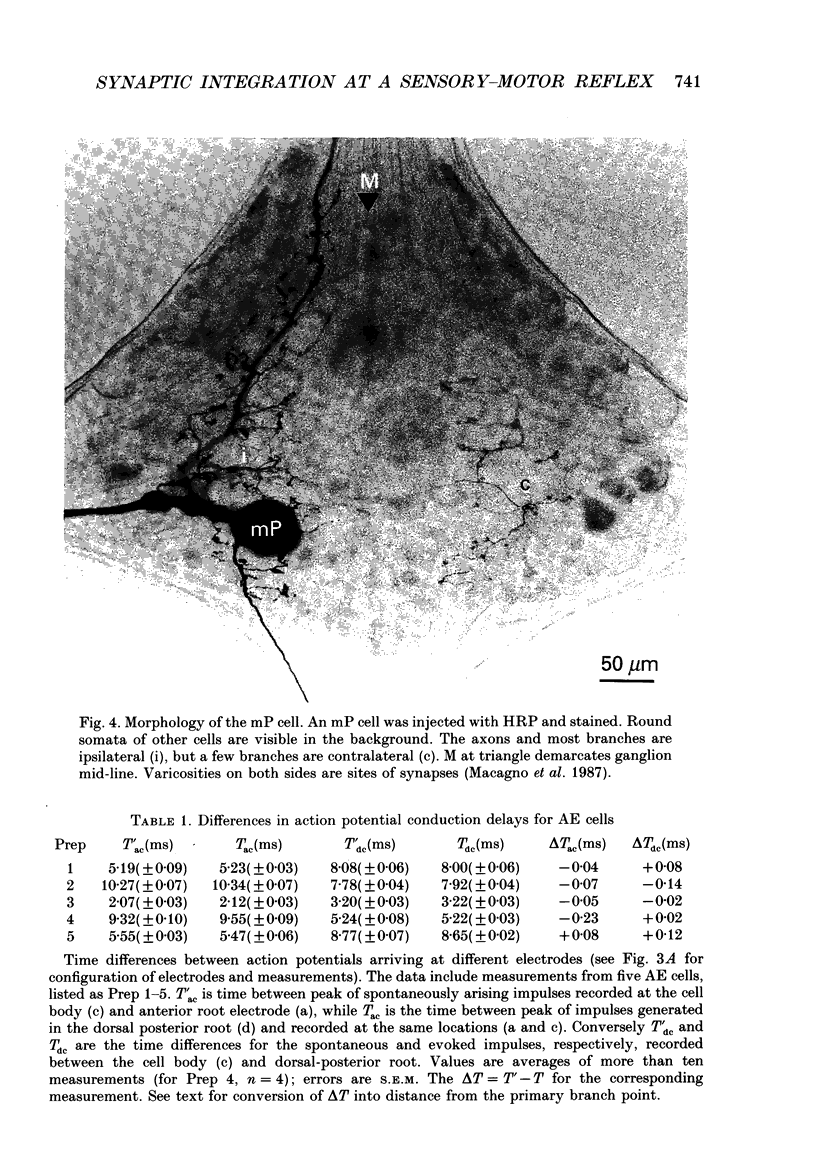
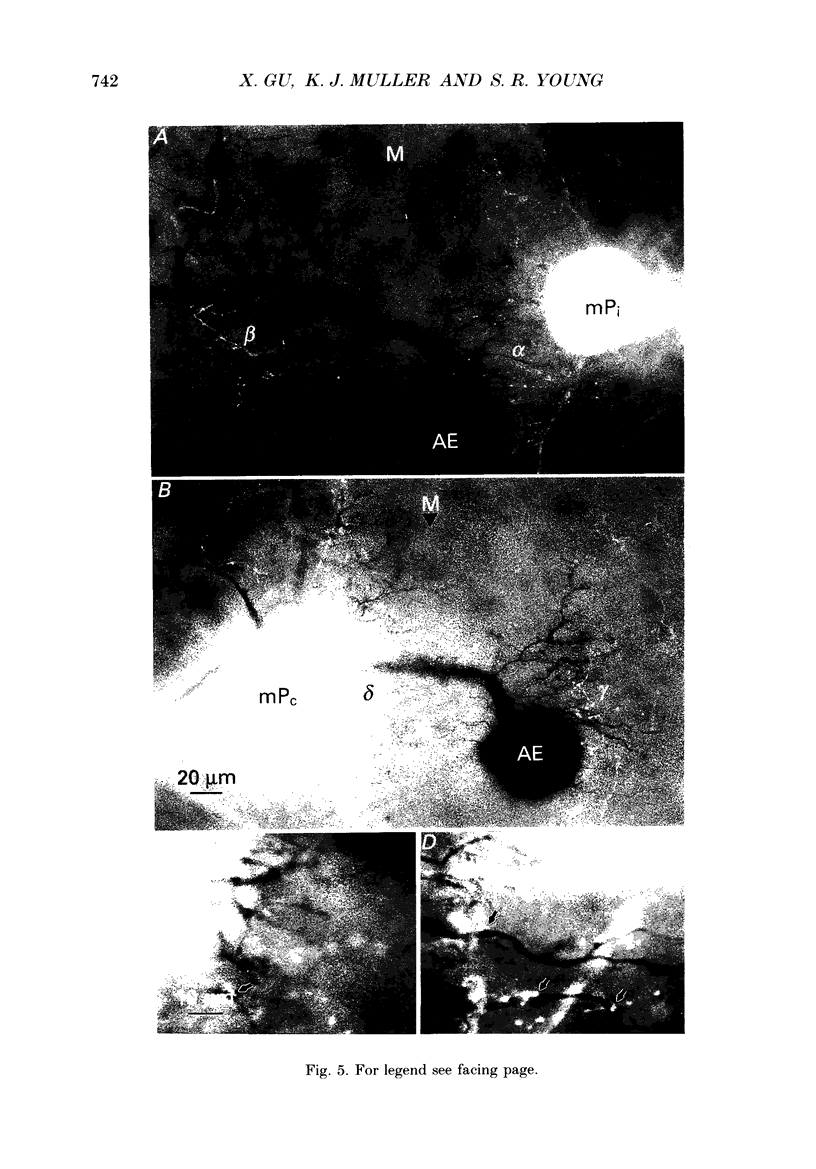
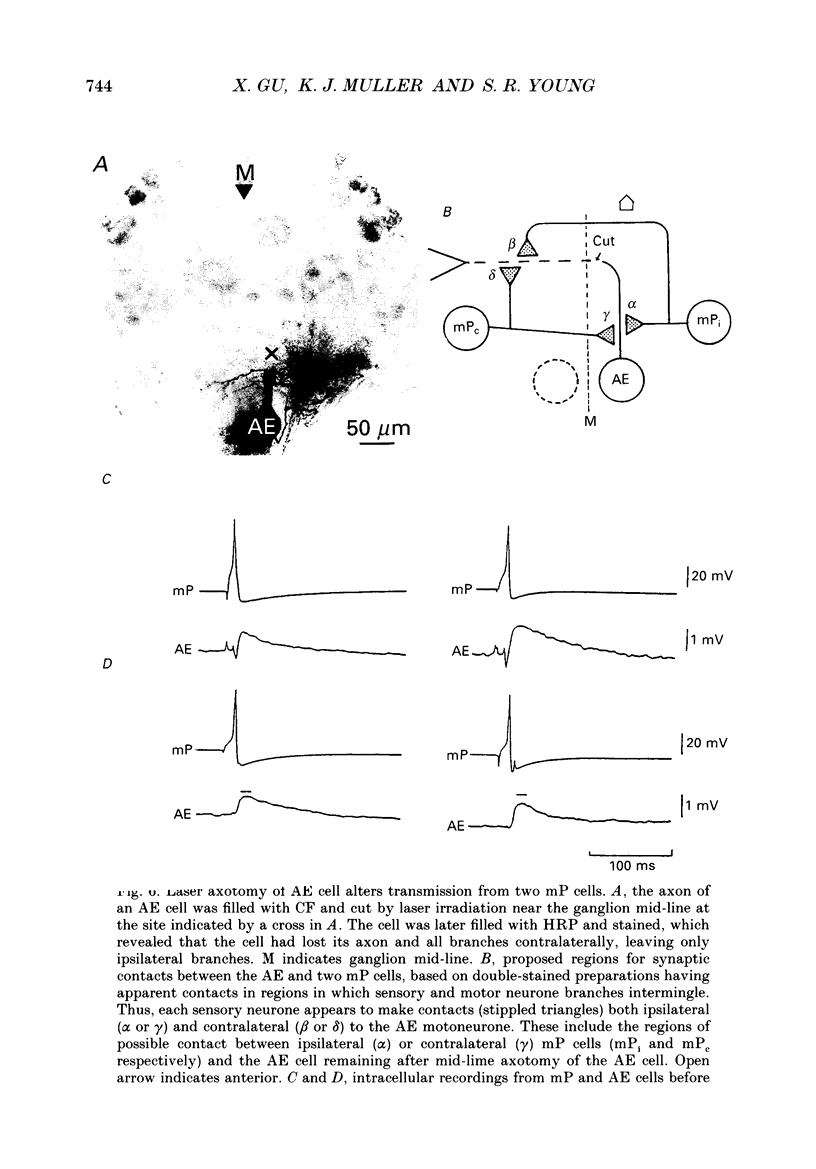
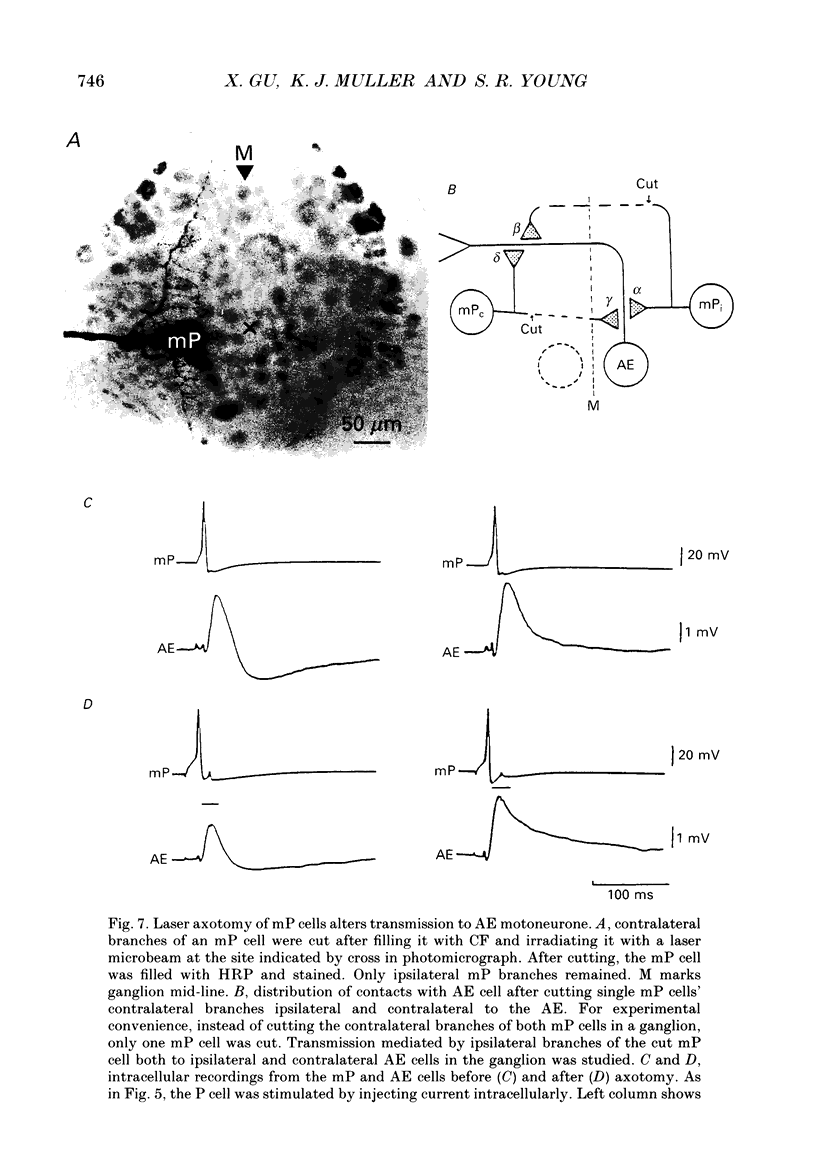
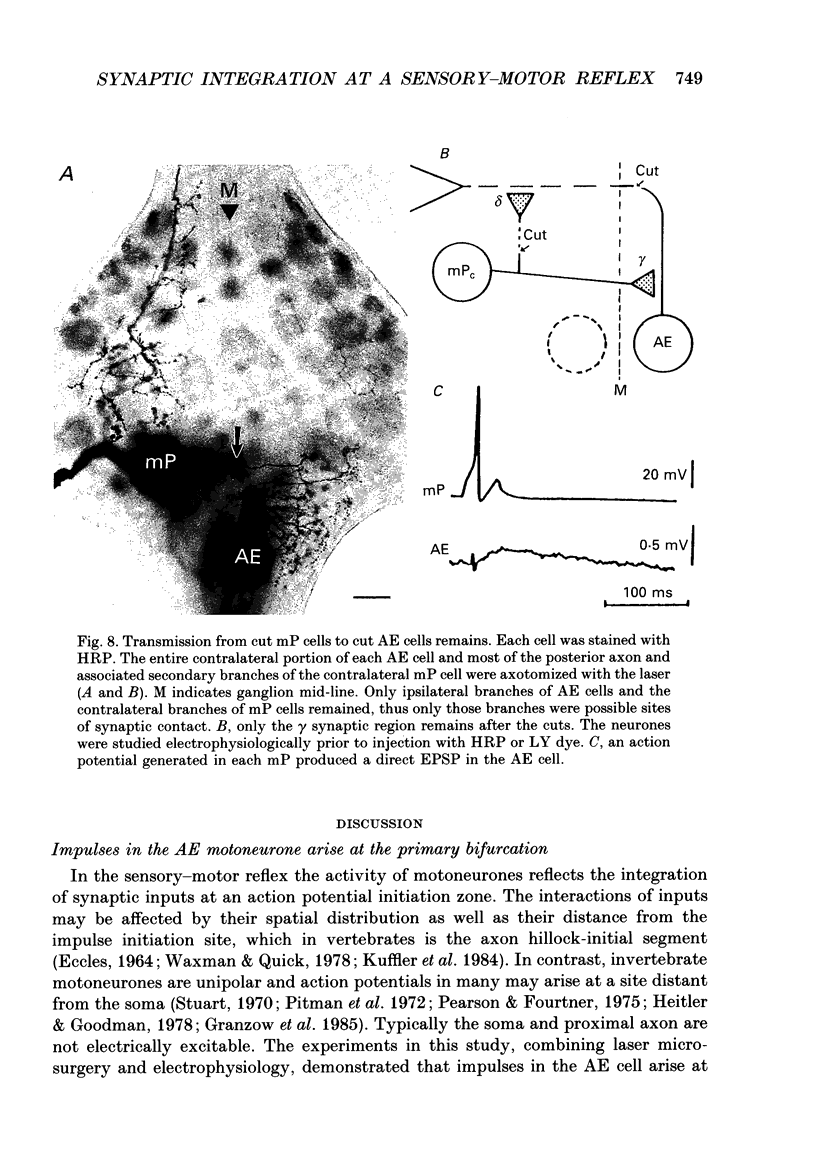
1. In the medicinal leech the distribution of synapses from the pressure sensory (P) neurone to the annulus erector (AE) motoneurone and the site of impulse initiation in the AE cell were determined to understand better the integration of sensory inputs by the motoneurone. 2. The axon of the AE cell bifurcates before leaving the ganglion. Laser photoablation experiments indicated that the axon proximal to the bifurcation is inexcitable. Two techniques, laser photoablation and measurement of impulse timing, each located the site of impulse initiation at the bifurcation. 3. The medial P cell makes a monosynaptic connection with the AE cell, eliciting an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) of 1-3 mV amplitude recorded in the AE cell soma. 4. Intracellular injection of dyes into separate cells showed that P cell branches appear to contact AE cell branches both ipsilaterally and contralaterally. Laser photoablation of selected portions of the P and AE cells' axons revealed functional contacts on both sides. 5. The primary axon bifurcation of the AE cell is the site of integration of synaptic potentials that spread passively from both sides of the ganglion. These summed synaptic potentials account for the concerted activity of the two AE cells in each ganglion.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelides K. J., Elmer L. W., Loftus D., Elson E. Distribution and lateral mobility of voltage-dependent sodium channels in neurons. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1911–1925. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshaw S. E. Morphology and distribution of touch cell terminals in the skin of the leech. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:219–228. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshaw S. E., Nicholls J. G., Parnas I. Physiological responses, receptive fields and terminal arborizations of nociceptive cells in the leech. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:251–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G., Fyffe R. E. Direct observations on the contacts made between Ia afferent fibres and alpha-motoneurones in the cat's lumbosacral spinal cord. J Physiol. 1981;313:121–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. Y., Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Excitatory synaptic responses in turtle cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:143–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Nicholls J. G., Ready D. F. Membrane properties and selective connexions of identified leech neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:203–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimlich R. L., Braun J. Improved fluorescent compounds for tracing cell lineage. Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;109(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman C. S., Heitler W. J. Electrical properties of insect neurones with spiking and non-spiking somata: normal, axotomized, and colchicine-treated neurones. J Exp Biol. 1979 Dec;83:95–121. doi: 10.1242/jeb.83.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantyn R., Shapovalov A. I., Shiriaev B. I. Tracing of frog sensory-motor synapses by intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:441–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granzow B., Friesen W. O., Kristan W. B., Jr Physiological and morphological analysis of synaptic transmission between leech motor neurons. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2035–2050. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02035.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. N., Macagno E. R., Muller K. J. Laser microbeam axotomy and conduction block show that electrical transmission at a central synapse is distributed at multiple contacts. J Neurobiol. 1989 Jul;20(5):422–434. doi: 10.1002/neu.480200512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Dendrite processing in more ways than one . Trends Neurosci. 1989 Sep;12(9):313–315. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Midtgaard J. Synaptic control of excitability in turtle cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:157–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs G. A., Miller J. P., Murphey R. K. Integrative mechanisms controlling directional sensitivity of an identified sensory interneuron. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2298–2311. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02298.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. K., Jr, Muller K. J., Nicholls J. G. Persistent modification of synaptic interactions between sensory and motor nerve cells following discrete lesions in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):289–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauthamer V., Ross W. N. Regional variations in excitability of barnacle neurons. J Neurosci. 1984 Mar;4(3):673–682. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-03-00673.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwada J. Y. Ionic and metabolic dependence of axotomy-induced somatic membrane changes in crayfish. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:463–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman J. W., Jhaveri S., Frank E. Anatomical basis of specific connections between sensory axons and motor neurons in the brachial spinal cord of the bullfrog. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1754–1763. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01754.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton W. W., Kristan W. B. Localization of a leech inhibitory synapse by photo-ablation of individual dendrites. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 11;504(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macagno E. R., Muller K. J., DeRiemer S. A. Regeneration of axons and synaptic connections by touch sensory neurons in the leech central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2510–2521. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02510.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macagno E. R., Muller K. J., Kristan W. B., Deriemer S. A., Stewart R., Granzow B. Mapping of neuronal contacts with intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase and Lucifer yellow in combination. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 27;217(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macagno E. R., Muller K. J., Pitman R. M. Conduction block silences parts of a chemical synapse in the leech central nervous system. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:649–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller K. J., Carbonetto S. The morphological and physiological properties of a regenerating synapse in the C.N.S. of the leech. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jun 1;185(3):485–516. doi: 10.1002/cne.901850305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller K. J., McMahan U. J. The shapes of sensory and motor neurones and the distribution of their synapses in ganglia of the leech: a study using intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Nov 12;194(1117):481–499. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller K. J., Nicholls J. G. Different properties of synapses between a single sensory neurone and two different motor cells in the leech C.N.S. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):357–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller K. J., Scott S. A. Transmission at a 'direct' electrical connexion mediated by an interneurone in the leech. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Baylor D. A. Specific modalities and receptive fields of sensory neurons in CNS of the leech. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):740–756. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J. G., Purves D. Monosynaptic chemical and electrical connexions between sensory and motor cells in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):647–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson K. G., Fourtner C. R. Nonspiking interneurons in walking system of the cockroach. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):33–52. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman R. M., Tweedle C. D., Cohen M. J. Electrical responses of insect central neurons: augmentation by nerve section or colchicine. Science. 1972 Nov 3;178(4060):507–509. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4060.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Lichtman J. W. Geometrical differences among homologous neurons in mammals. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):298–302. doi: 10.1126/science.3983631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready D. F., Nicholls J. Identified neurones isolated from leech CNS make selective connections in culture. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):67–69. doi: 10.1038/281067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roederer E., Cohen M. J. Regeneration of an identified central neuron in the cricket. II. Electrical and morphological responses of the soma. J Neurosci. 1983 Sep;3(9):1848–1859. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-09-01848.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E. Physiological and morphological properties of motoneurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):627–646. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titmus M. J., Faber D. S. Altered excitability of goldfish Mauthner cell following axotomy. II. Localization and ionic basis. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1440–1454. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W. Physiological properties and receptive fields of mechanosensory neurones in the head ganglion of the leech: comparison with homologous cells in segmental ganglia. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):489–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]