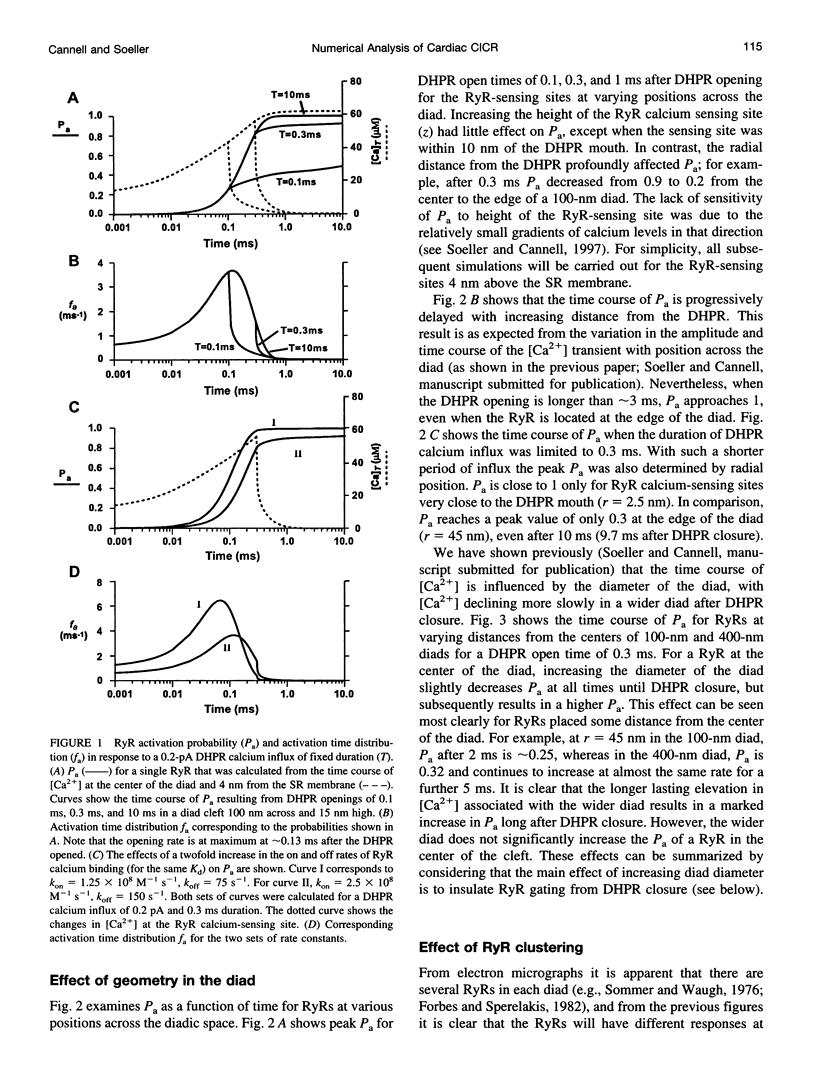
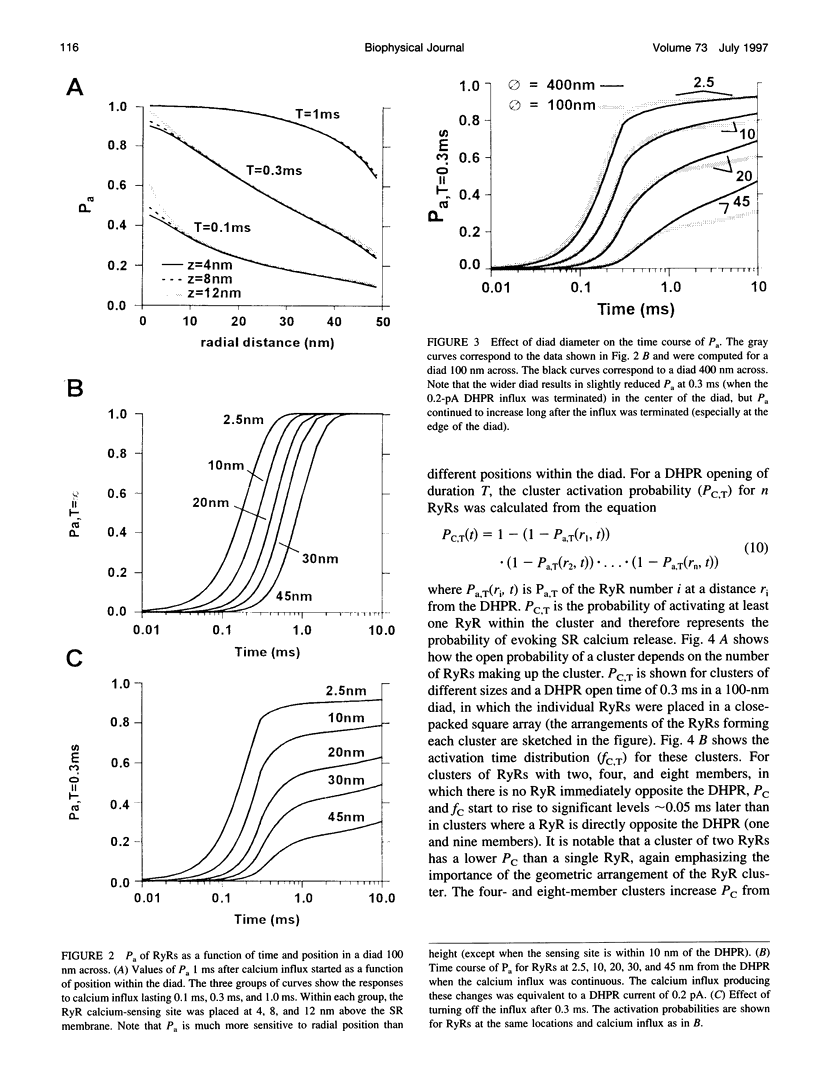
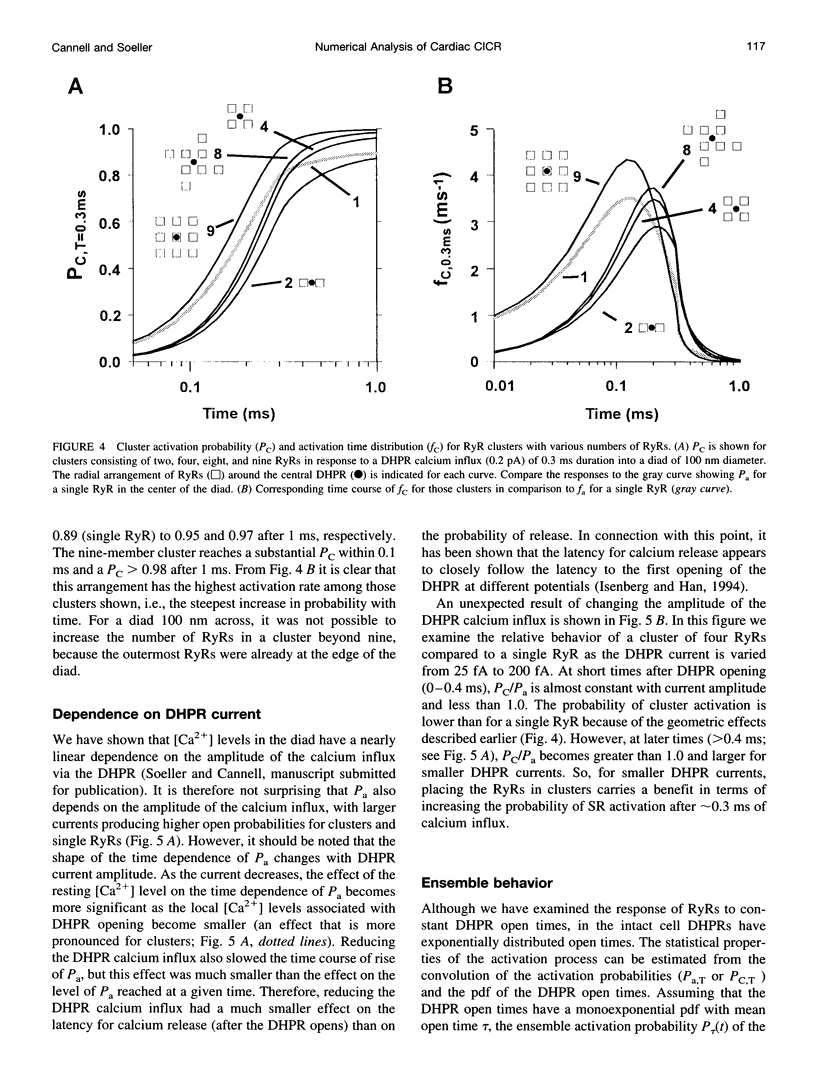
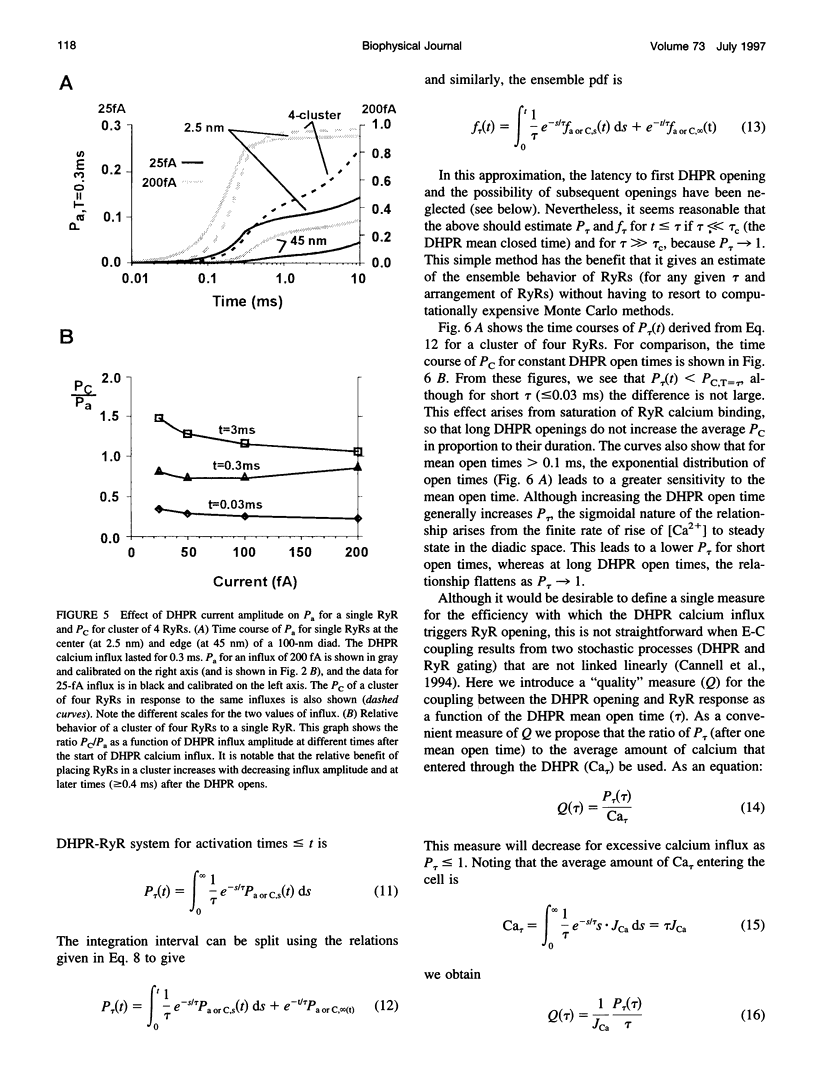
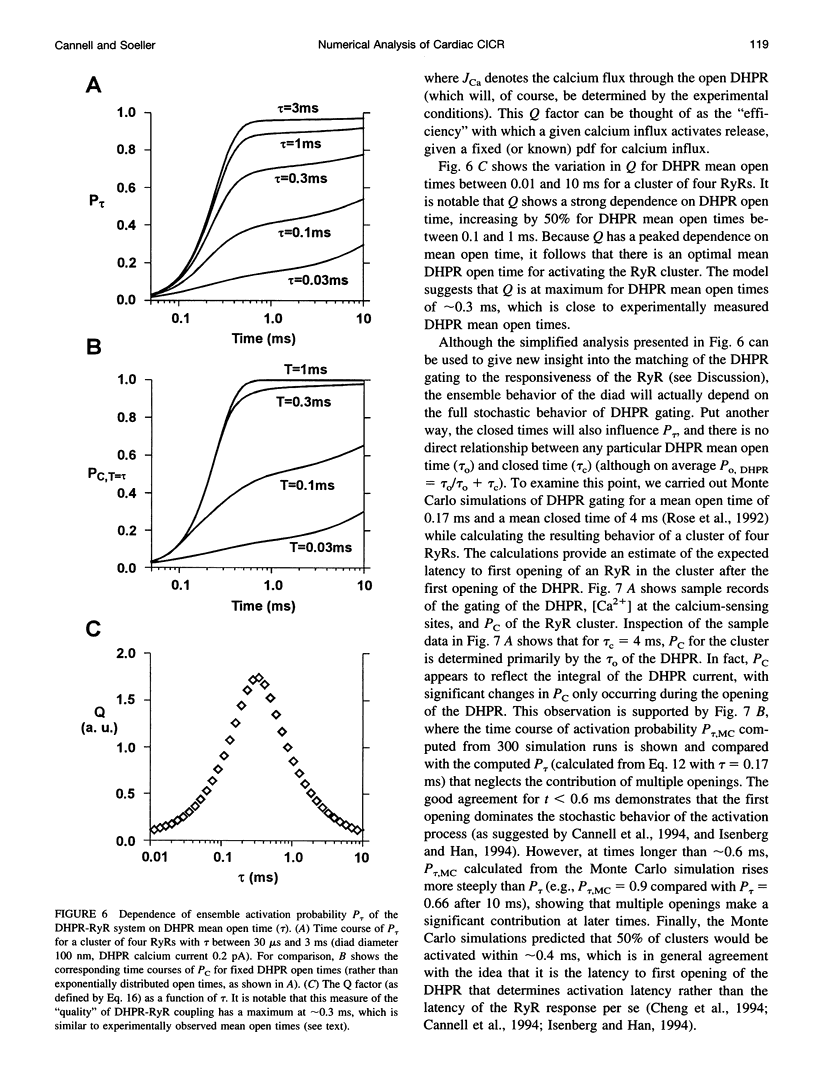
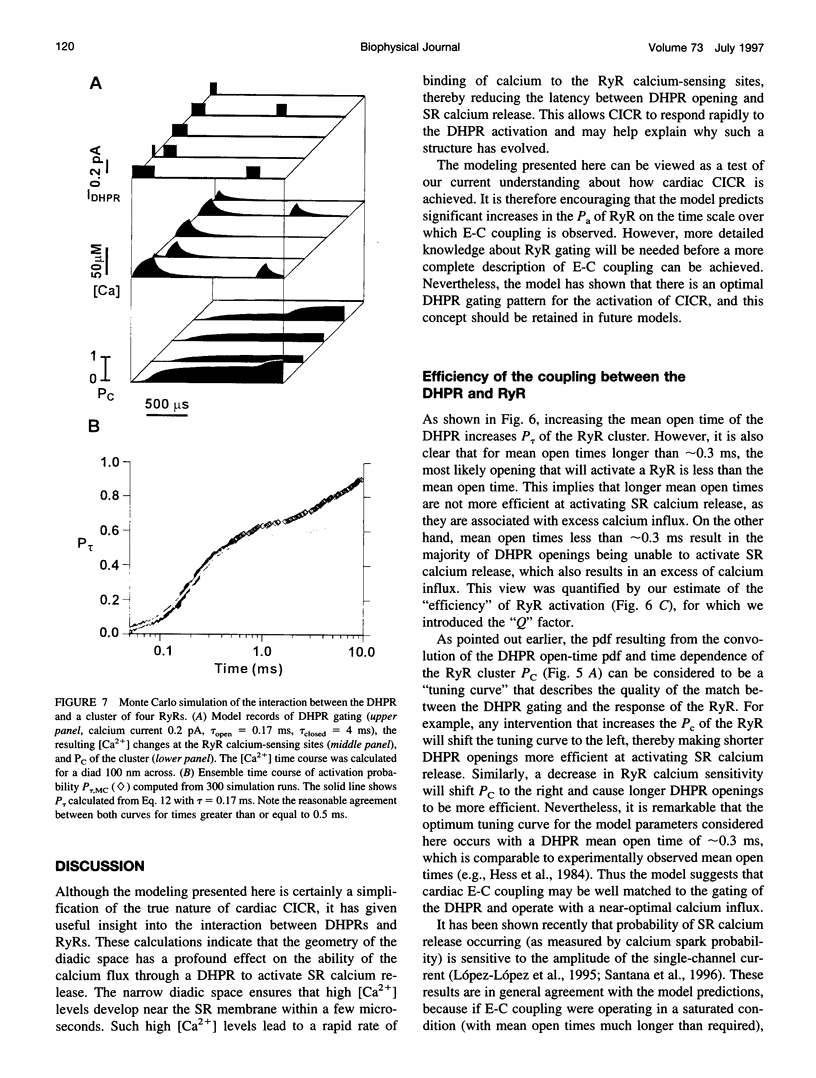
Abstract
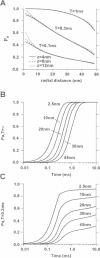
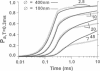
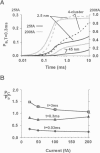
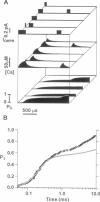
Computer simulations were used to examine the response of ryanodine receptors (RyRs) to the sarcolemmal calcium influx via L-type calcium channels (DHPRs). The effects of ryanodine receptor organization, diad geometry, DHPR single-channel current, and DHPR gating were examined. In agreement with experimental findings, the simulations showed that RyRs can respond rapidly (approximately 0.4 ms) to calcium influx via DHPRs. The responsiveness of the RyR depends on the geometrical arrangement between the RyRs and the DHPR in the diad, with wider diads being generally less responsive. When the DHPR single-channel current is small (approximately 25 fA), the organization of RyRs into small clusters results in an improved responsiveness. With experimentally observed DHPR mean open and closed times (0.17 ms and 4 ms, respectively) it is the first opening of the DHPR that is most likely to activate the RyR. A measure of the efficiency (Q) by which DHPR gating evokes sarcoplasmic reticulum release is defined. Q is at maximum for tau approximately 0.3 ms, and we interpret this finding in terms of the "tuning" of DHPR gating to RyR response. If certain cardiac myopathies are associated with a mismatch in the "tuning," then modification of DHPR gating with drugs to "retune" calcium-induced calcium release should be possible.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K., Lai F. A., Liu Q. Y., Rousseau E., Erickson H. P., Meissner G. Structural and functional characterization of the purified cardiac ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1329–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Effect of membrane potential changes on the calcium transient in single rat cardiac muscle cells. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1419–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2446391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. Spatial non-uniformities in [Ca2+]i during excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1942–1956. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80677-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. The control of calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1045–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.7754384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. Calcium domains associated with individual channels can account for anomalous voltage relations of CA-dependent responses. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):993–999. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84244-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. Partial inhibition of Ca2+ current by methoxyverapamil (D600) reveals spatial nonuniformities in [Ca2+]i during excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 1995 Feb;76(2):236–241. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. Propagation of excitation-contraction coupling into ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Oct;428(3-4):415–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00724526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):740–744. doi: 10.1126/science.8235594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Györke S., Fill M. Ryanodine receptor adaptation: control mechanism of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in heart. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):807–809. doi: 10.1126/science.8387229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation of the ryanodine receptor from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identity with the feet structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15637–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Han S. Gradation of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release by voltage-clamp pulse duration in potentiated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 1;480(Pt 3):423–438. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer G. A., Peskoff A. Calcium concentration and movement in the diadic cleft space of the cardiac ventricular cell. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1169–1182. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79677-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Niggli E. Submicroscopic calcium signals as fundamental events of excitation--contraction coupling in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 1;492(Pt 1):31–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J. R., Shacklock P. S., Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Local calcium transients triggered by single L-type calcium channel currents in cardiac cells. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.7754383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J. R., Shacklock P. S., Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Local, stochastic release of Ca2+ in voltage-clamped rat heart cells: visualization with confocal microscopy. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):21–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai J., Imagawa T., Hakamat Y., Shigekawa M., Takeshima H., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNA of the cardiac ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Willard H. F., Khanna V. K., Zorzato F., Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13472–13483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Rao V., Grassucci R., Frank J., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Wagenknecht T. Cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):411–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose W. C., Balke C. W., Wier W. G., Marban E. Macroscopic and unitary properties of physiological ion flux through L-type Ca2+ channels in guinea-pig heart cells. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:267–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Inui M., Radermacher M., Frank J., Fleischer S. Ultrastructure of the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santana L. F., Cheng H., Gómez A. M., Cannell M. B., Lederer W. J. Relation between the sarcolemmal Ca2+ current and Ca2+ sparks and local control theories for cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Circ Res. 1996 Jan;78(1):166–171. doi: 10.1161/01.res.78.1.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeller C., Cannell M. B. Numerical simulation of local calcium movements during L-type calcium channel gating in the cardiac diad. Biophys J. 1997 Jul;73(1):97–111. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78051-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. R., Waugh R. A. The ultrastructure of the mammalian cardiac muscle cell--with special emphasis on the tubular membrane systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jan;82(1):192–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Theory of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):497–517. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81615-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia H. H., Kaplan J. H., Ellis-Davies G. C., Lederer W. J. Rapid adaptation of cardiac ryanodine receptors: modulation by Mg2+ and phosphorylation. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1997–2000. doi: 10.1126/science.7701323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradníková A., Zahradník I. Description of modal gating of the cardiac calcium release channel in planar lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1780–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80048-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]