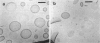Abstract
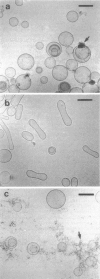
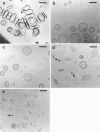
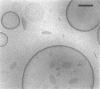
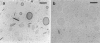
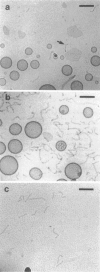
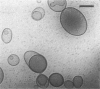
Phospholipids with covalently attached poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG lipids) are commonly used for the preparation of long circulating liposomes. Although it is well known that lipid/PEG-lipid mixed micelles may form above a certain critical concentration of PEG-lipid, little is known about the effects of PEG-lipids on liposome structure and leakage at submicellar concentrations. In this study we have used cryogenic transmission electron microscopy to investigate the effect of PEG(2000)-PE on aggregate structure in preparations of liposomes with different membrane compositions. The results reveal a number of important aggregate structures not documented before. The micrographs show that enclosure of PEG-PE induces the formation of open bilayer discs at concentrations well below those where mixed micelles begin to form. The maximum concentration of PEG-lipid that may be incorporated without alteration of the liposome structure depends on the phospholipid chain length, whereas phospholipid saturation or the presence of cholesterol has little or no effect. The presence of cholesterol does, however, affect the shape of the mixed micelles formed at high concentrations of PEG-lipid. Threadlike micelles form in the absence of cholesterol but adapt a globular shape when cholesterol is present.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. M., Chonn A. Large unilamellar liposomes with low uptake into the reticuloendothelial system. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80506-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellare J. R., Davis H. T., Scriven L. E., Talmon Y. Controlled environment vitrification system: an improved sample preparation technique. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988 Sep;10(1):87–111. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chonn A., Cullis P. R. Recent advances in liposomal drug-delivery systems. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1995 Dec;6(6):698–708. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(95)80115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie J. D., Rakusan T. A., Martinez M. A., Lucia H. L., Rajaraman S., Edwards S. B., Hayden C. K., Jr Hydranencephaly caused by congenital infection with herpes simplex virus. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;5(4):473–478. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198607000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Phillips M. C. The stability and structure of cholesterol-rich codispersions of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine. J Lipid Res. 1982 Feb;23(2):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Adrian M., Chang J. J., Homo J. C., Lepault J., McDowall A. W., Schultz P. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q Rev Biophys. 1988 May;21(2):129–228. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grit M., Crommelin D. J. Chemical stability of liposomes: implications for their physical stability. Chem Phys Lipids. 1993 Sep;64(1-3):3–18. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(93)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy A. K., Hristova K., Needham D., McIntosh T. J. Range and magnitude of the steric pressure between bilayers containing phospholipids with covalently attached poly(ethylene glycol). Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1921–1936. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80369-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy A. K., Simon S. A., McIntosh T. J. Structure and phase behavior of lipid suspensions containing phospholipids with covalently attached poly(ethylene glycol). Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1903–1920. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80368-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasic D. D. A molecular model for vesicle formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):501–502. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Liu D. Serum independent liposome uptake by mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Jan 12;1278(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham D., Nunn R. S. Elastic deformation and failure of lipid bilayer membranes containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):997–1009. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82444-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel H. M. Serum opsonins and liposomes: their interaction and opsonophagocytosis. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1992;9(1):39–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson P. K., Talmon Y., Walter A. Vesicle-micelle transition of phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside elucidated by cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):669–681. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82714-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter A., Vinson P. K., Kaplun A., Talmon Y. Intermediate structures in the cholate-phosphatidylcholine vesicle-micelle transition. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1315–1325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82169-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodle M. C., Lasic D. D. Sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 14;1113(2):171–199. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90038-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodle M. C., Matthay K. K., Newman M. S., Hidayat J. E., Collins L. R., Redemann C., Martin F. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Versatility in lipid compositions showing prolonged circulation with sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 13;1105(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90194-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]