Abstract
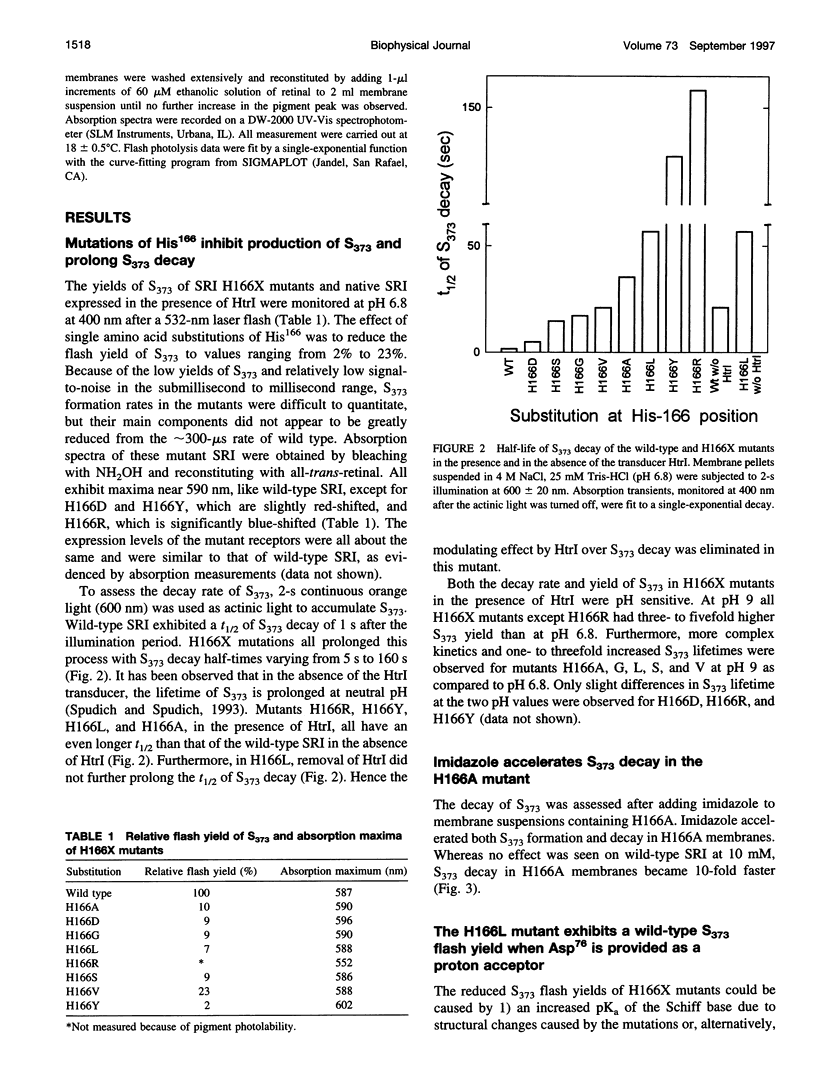
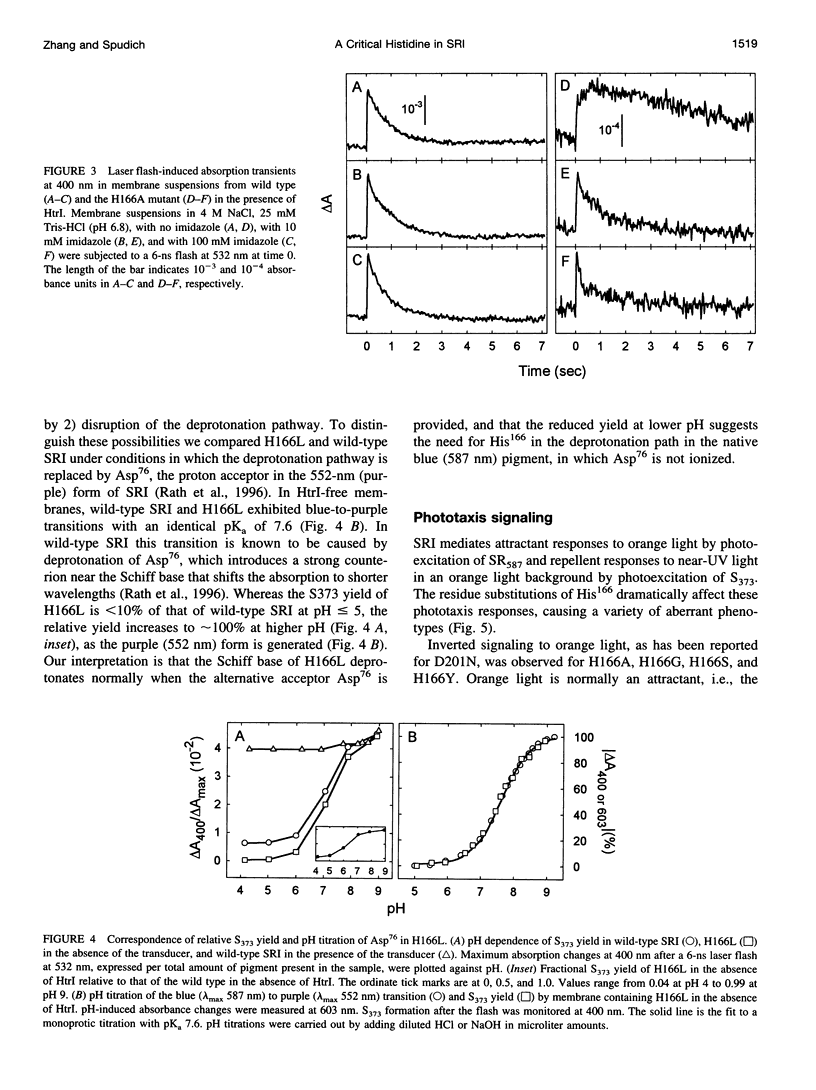
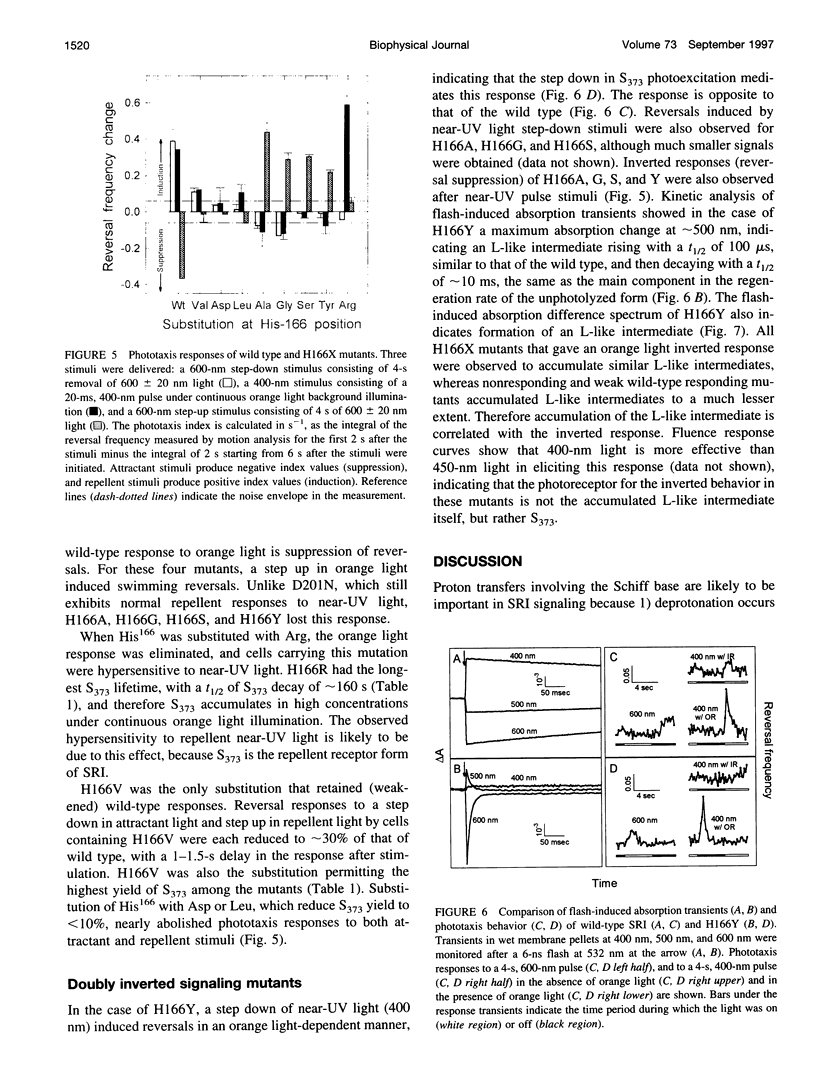
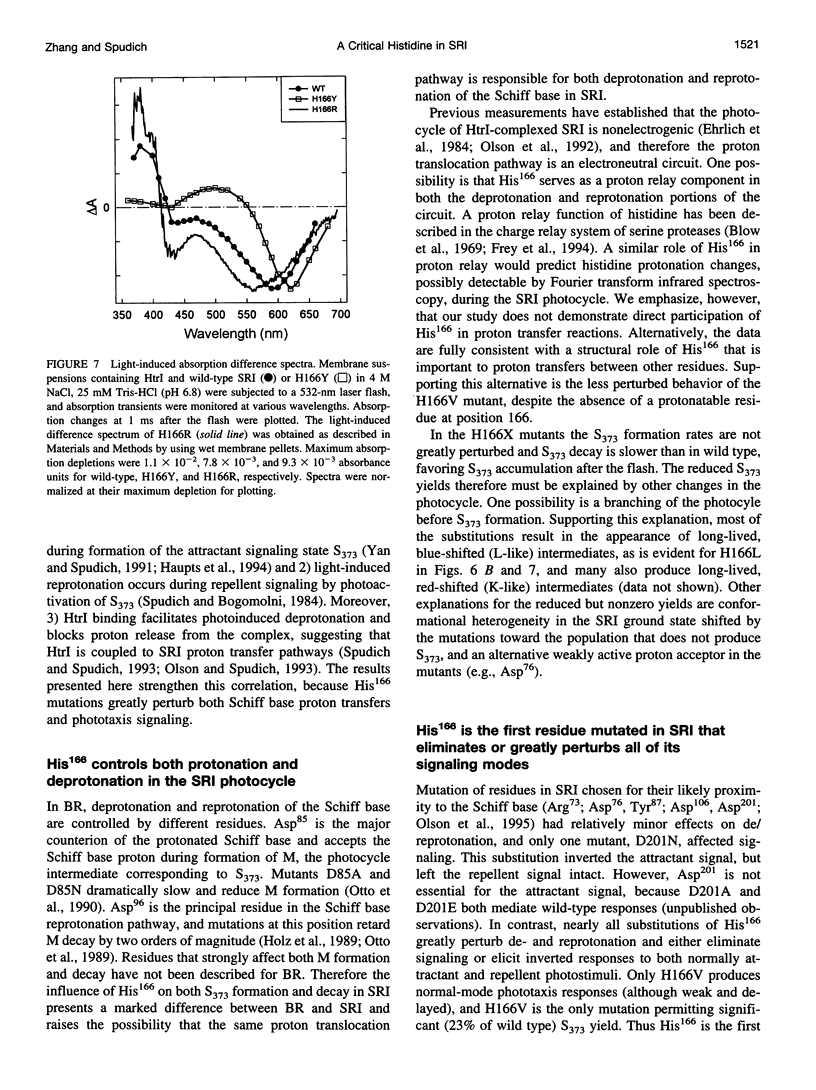
Photoinduced deprotonation of the retinylidene Schiff base in the sensory rhodopsin I transducer (SRI-Htrl) complex results in formation of the phototaxis signaling state S373. Here we report identification of a residue, His166, critical to this process, as well as to reprotonation of the Schiff base during the recovery phase of the SRI photocycle. Each of the residue substitutions A, D, G, L, S, V, or Y at position 166 reduces the flash yield of S373, to values ranging from 2% of wild type for H166Y to 23% for H166V. The yield of S373 is restored to wild-type levels in Htrl-free H166L by alkaline deprotonation of Asp76, a Schiff base proton acceptor normally not ionized in the SRI-Htrl complex, showing that proton transfer from the Schiff base in H166L occurs when an acceptor is made available. The flash yield and rate of decay of S373 of the mutants are pH dependent, even when complexed with Htrl, which confers pH insensitivity to wild-type SRI, suggesting that partial disruption of the complex has occurred. The rates of S373 reprotonation at neutral pH are also prolonged in all H166X mutants, with half-times from 5 s to 160 s (wild type, 1 s). All mutations of His166 tested disrupt phototaxis signaling. No response (H166D, H166L), dramatically reduced responses (H166V), or inverted responses to orange light (H166A, H166G, H166S, and H166Y) or to both orange and near-UV light (H166Y) are observed. Our conclusions are that His166 1) plays a role in the pathways of proton transfer both to and from the Schiff base in the SRI-Htrl complex, either as a structurally important residue or possibly as a participant in proton transfers; 2) is involved in the modulation of SRI photoreaction kinetics by Htrl; and 3) is important in phototaxis signaling. Consistent with the involvement of the His imidazole moiety, the addition of 10 mM imidazole to membrane suspensions containing H166A receptors accelerates S373 decay 10-fold at neutral pH, and a negligible effect is seen on wild-type SRI.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D., Ferrando E., Schegk E. S., Lottspeich F. Primary structure of sensory rhodopsin I, a prokaryotic photoreceptor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3963–3971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Birktoft J. J., Hartley B. S. Role of a buried acid group in the mechanism of action of chymotrypsin. Nature. 1969 Jan 25;221(5178):337–340. doi: 10.1038/221337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W., Szundi I., Perozo E., Olson K. D., Spudich J. L. Removal of transducer HtrI allows electrogenic proton translocation by sensory rhodopsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B., Przybyla A. E. An efficient site-directed mutagenesis method based on PCR. Biotechniques. 1994 Oct;17(4):657–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Dresselhaus D., Zaccai G., Büldt G. Structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin during proton translocation revealed by neutron diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7876–7879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dér A., Száraz S., Tóth-Boconádi R., Tokaji Z., Keszthelyi L., Stoeckenius W. Alternative translocation of protons and halide ions by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Schen C. R., Spudich J. L. Bacterial rhodopsins monitored with fluorescent dyes in vesicles and in vivo. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(1):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01870735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrens D. L., Altenbach C., Yang K., Hubbell W. L., Khorana H. G. Requirement of rigid-body motion of transmembrane helices for light activation of rhodopsin. Science. 1996 Nov 1;274(5288):768–770. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Whitt S. A., Tobin J. B. A low-barrier hydrogen bond in the catalytic triad of serine proteases. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1927–1930. doi: 10.1126/science.7661899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorieff N., Ceska T. A., Downing K. H., Baldwin J. M., Henderson R. Electron-crystallographic refinement of the structure of bacteriorhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jun 14;259(3):393–421. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupts U., Eisfeld W., Stockburger M., Oesterhelt D. Sensory rhodopsin I photocycle intermediate SRI380 contains 13-cis retinal bound via an unprotonated Schiff base. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 12;356(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01226-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz M., Drachev L. A., Mogi T., Otto H., Kaulen A. D., Heyn M. P., Skulachev V. P., Khorana H. G. Replacement of aspartic acid-96 by asparagine in bacteriorhodopsin slows both the decay of the M intermediate and the associated proton movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung K. H., Spudich J. L. Protonatable residues at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane helix-2 in the signal transducer HtrI control photochemistry and function of sensory rhodopsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6557–6561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamikubo H., Kataoka M., Váró G., Oka T., Tokunaga F., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Structure of the N intermediate of bacteriorhodopsin revealed by x-ray diffraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1386–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch M. H., Dencher N. A., Oesterhelt D., Plöhn H. J., Rapp G., Büldt G. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction study of structural changes associated with the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., Khorana H. G. Mechanism of light-dependent proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1555–1560. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1555-1560.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., Spudich E. N., Khorana H. G., Spudich J. L. Synthesis of a gene for sensory rhodopsin I and its functional expression in Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3486–3490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton translocation mechanism and energetics in the light-driven pump bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 7;1183(2):241–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam C. F., Sonar S., Lee C. P., Coleman M., Herzfeld J., RajBhandary U. L., Rothschild K. J. Site-directed isotope labeling and ATR-FTIR difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin: the peptide carbonyl group of Tyr 185 is structurally active during the bR-->N transition. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 10;34(1):2–6. doi: 10.1021/bi00001a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Otto H., Rösselet S. J., Heyn M. P., Khorana H. G. Anion binding to the Schiff base of the bacteriorhodopsin mutants Asp-85----Asn/Asp-212----Asn and Arg-82----Gln/Asp-85----Asn/Asp-212----Asn. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16922–16927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Bibikov S. I., Montrone M., Oesterhelt D. Mechanism of photosensory adaptation in Halobacterium salinarium. J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 3;246(4):493–499. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R. A., Lin S. W., Ames J. B., Pollard W. T. From femtoseconds to biology: mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin's light-driven proton pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakasako M., Kataoka M., Amemiya Y., Tokunaga F. Crystallographic characterization by X-ray diffraction of the M-intermediate from the photo-cycle of bacteriorhodopsin at room temperature. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):73–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80837-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J., Bamberg E. A unifying concept for ion translocation by retinal proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00762676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. D., Deval P., Spudich J. L. Absorption and photochemistry of sensory rhodopsin--I: pH effects. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Dec;56(6):1181–1187. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb09743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. D., Spudich J. L. Removal of the transducer protein from sensory rhodopsin I exposes sites of proton release and uptake during the receptor photocycle. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2578–2585. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81295-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson K. D., Zhang X. N., Spudich J. L. Residue replacements of buried aspartyl and related residues in sensory rhodopsin I: D201N produces inverted phototaxis signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Lindau M., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Aspartic acid-96 is the internal proton donor in the reprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9228–9232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto H., Marti T., Holz M., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Engel F., Khorana H. G., Heyn M. P. Substitution of amino acids Asp-85, Asp-212, and Arg-82 in bacteriorhodopsin affects the proton release phase of the pump and the pK of the Schiff base. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. N., Kembhavi A. A., Pant A. Implication of tryptophan and histidine in the active site of endo-polygalacturonase from Aspergillus ustus: elucidation of the reaction mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Sep 5;1296(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(96)00067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath P., Olson K. D., Spudich J. L., Rothschild K. J. The Schiff base counterion of bacteriorhodopsin is protonated in sensory rhodopsin I: spectroscopic and functional characterization of the mutated proteins D76N and D76A. Biochemistry. 1994 May 10;33(18):5600–5606. doi: 10.1021/bi00184a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath P., Spudich E., Neal D. D., Spudich J. L., Rothschild K. J. Asp76 is the Schiff base counterion and proton acceptor in the proton-translocating form of sensory rhodopsin I. Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6690–6696. doi: 10.1021/bi9600355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren X., Tu C., Laipis P. J., Silverman D. N. Proton transfer by histidine 67 in site-directed mutants of human carbonic anhydrase III. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8492–8498. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J. FTIR difference spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin: toward a molecular model. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Apr;24(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00762674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh S. P., Zvyaga T. A., Lichtarge O., Sakmar T. P., Bourne H. R. Rhodopsin activation blocked by metal-ion-binding sites linking transmembrane helices C and F. Nature. 1996 Sep 26;383(6598):347–350. doi: 10.1038/383347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoni E., Nachliel E., Gutman M. Gaugement of the inner space of the apomyoglobin's heme binding site by a single free diffusing proton. II. Interaction with a bulk proton. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):480–483. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81390-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. The photochemical reactions of sensory rhodopsin I are altered by its transducer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16095–16097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Sundberg S. A., Manor D., Spudich J. L. Properties of a second sensory receptor protein in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Zhang W., Alam M., Spudich J. L. Constitutive signaling by the phototaxis receptor sensory rhodopsin II from disruption of its protonated Schiff base-Asp-73 interhelical salt bridge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):4960–4965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L. Protein-protein interaction converts a proton pump into a sensory receptor. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):747–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff H. J., Mollaaghababa R., Altenbach C., Hideg K., Krebs M., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Time-resolved detection of structural changes during the photocycle of spin-labeled bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):105–107. doi: 10.1126/science.7939627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Gerstein M., Oesterhelt D., Henderson R. Electron diffraction analysis of structural changes in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S., Greenhalgh D. A., Khorana H. G. Aspartic acid 85 in bacteriorhodopsin functions both as proton acceptor and negative counterion to the Schiff base. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25730–25733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tittor J., Soell C., Oesterhelt D., Butt H. J., Bamberg E. A defective proton pump, point-mutated bacteriorhodopsin Asp96----Asn is fully reactivated by azide. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3477–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonck J. A three-dimensional difference map of the N intermediate in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: part of the F helix tilts in the M to N transition. Biochemistry. 1996 May 7;35(18):5870–5878. doi: 10.1021/bi952663c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan B., Spudich J. L. Evidence that the repellent receptor form of sensory rhodopsin I is an attractant signaling state. Photochem Photobiol. 1991 Dec;54(6):1023–1026. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1991.tb02125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao V. J., Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Identification of distinct domains for signaling and receptor interaction of the sensory rhodopsin I transducer, HtrI. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(22):6931–6935. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.22.6931-6935.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Brooun A., Mueller M. M., Alam M. The primary structures of the Archaeon Halobacterium salinarium blue light receptor sensory rhodopsin II and its transducer, a methyl-accepting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8230–8235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot H. J., Harbison G. S., Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the Schiff base in bacteriorhodopsin: counterion effects on the 15N shift anisotropy. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3346–3353. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]