Abstract
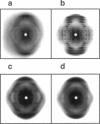
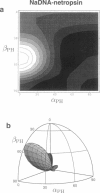
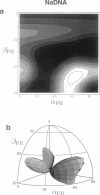
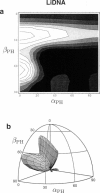
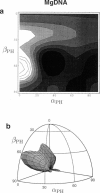
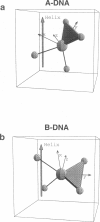
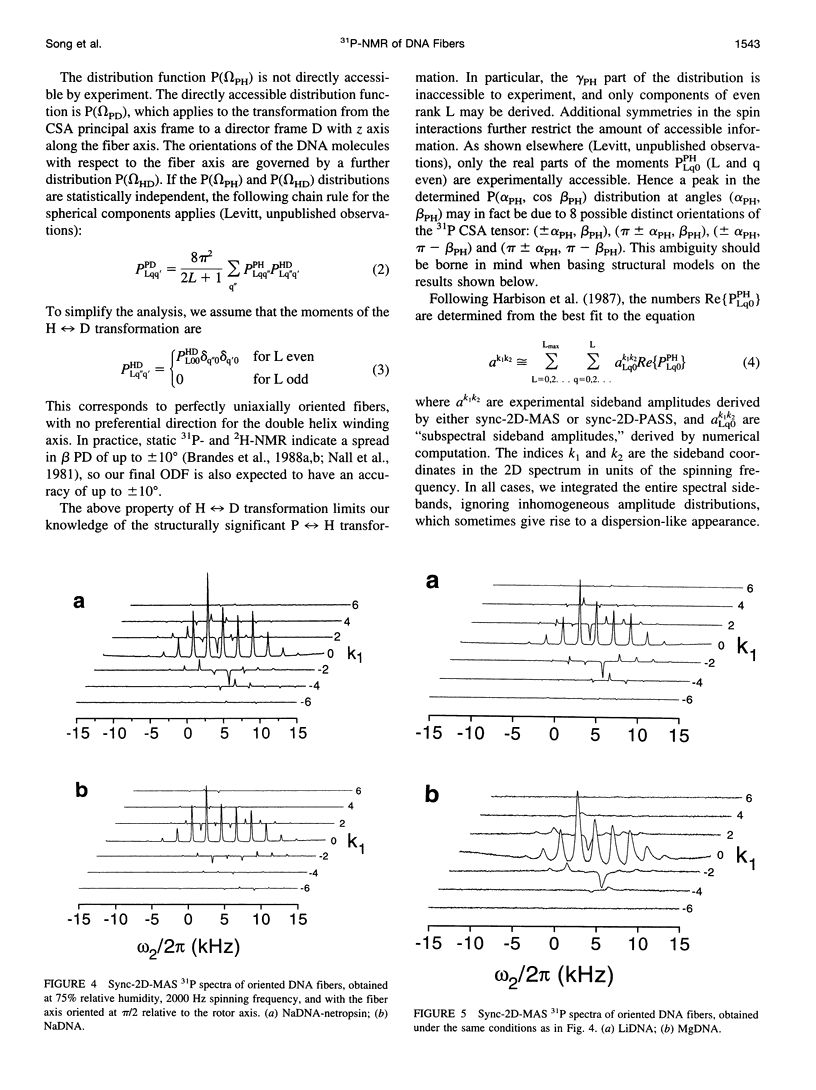
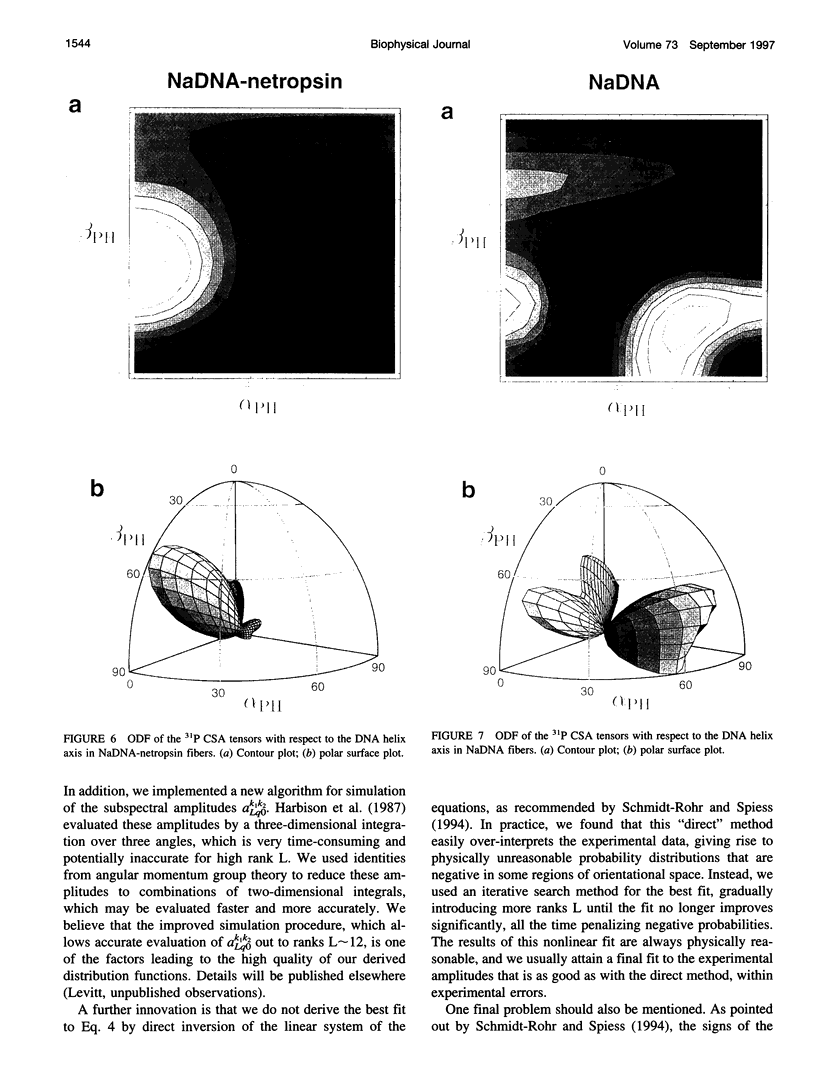
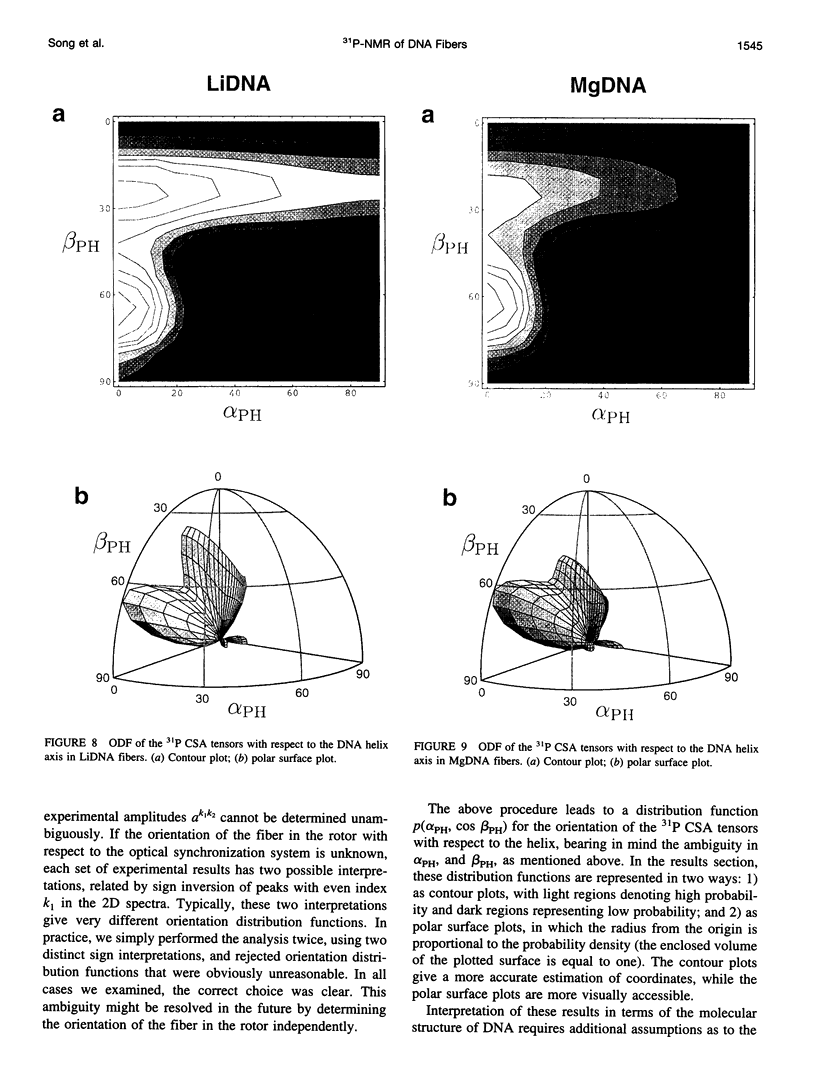
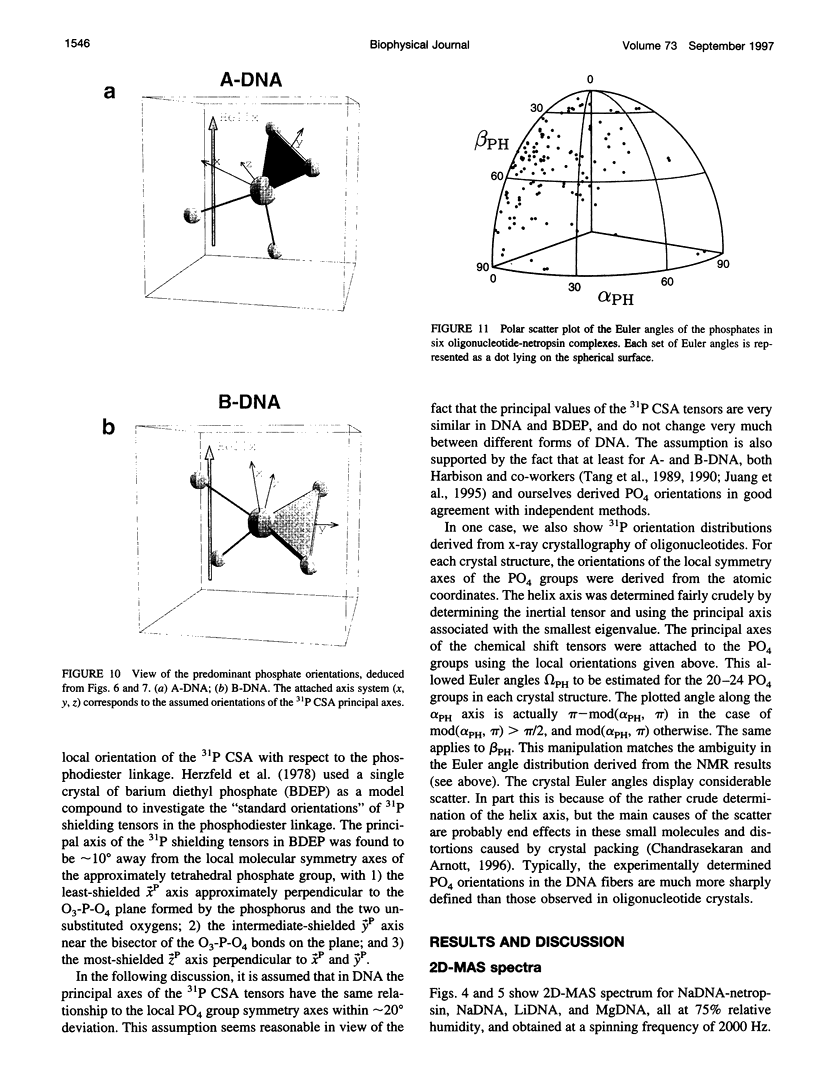
Solid-state 31P-NMR is used to investigate the orientation of the phosphodiester backbone in NaDNA-, LiDNA-, MgDNA-, and NaDNA-netropsin fibers. The results for A- and B-DNA agree with previous interpretations. We verify that the binding of netropsin to NaDNA stabilizes the B form, and find that in NaDNA, most of the phosphate groups adopt a conformation typical of the A form, although there are minor components with phosphate orientations close to the B form. For LiDNA and MgDNA samples, on the other hand, we find phosphate conformations that are in variance with previous models. These samples display x-ray diffraction patterns that correspond to C-DNA. However, we find two distinct phosphate orientations in these samples, one resembling that in B-DNA, and one displaying a twist of the PO4 groups about the O3-P-O4 bisectors. The latter conformation is not in accordance with previous models of C-DNA structure.
Full text
PDF


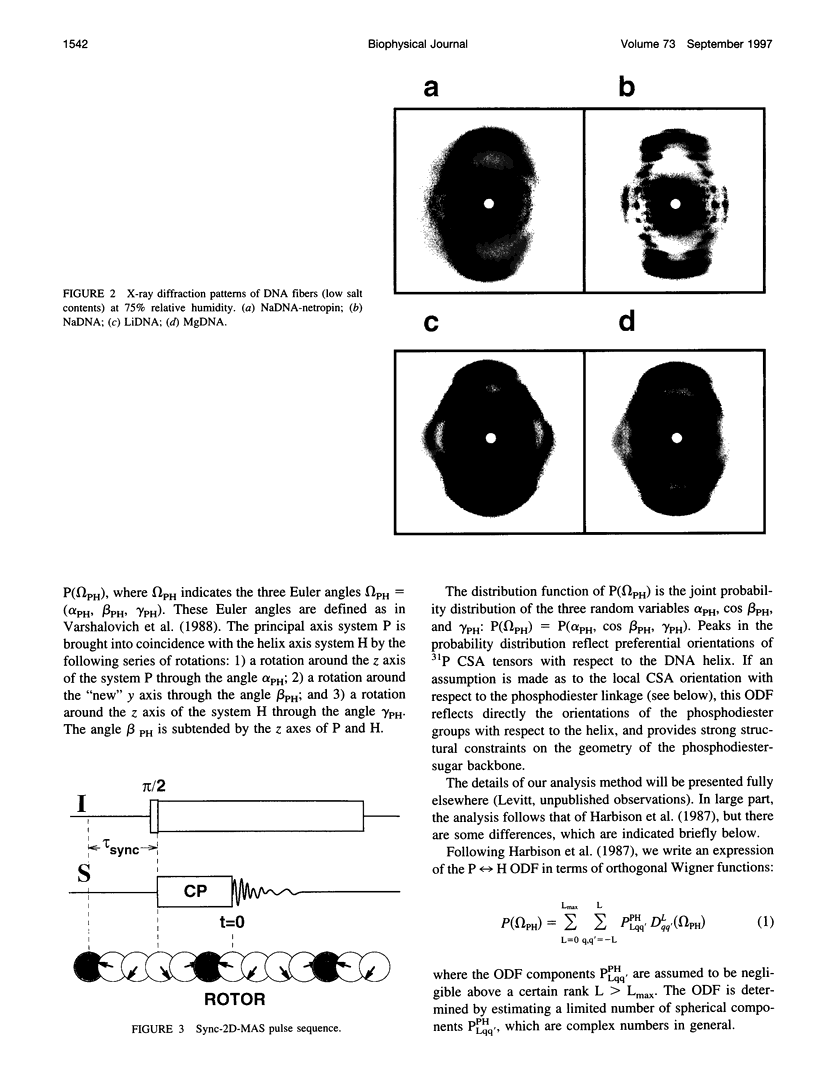

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Refinement of the structure of B-DNA and implications for the analysis of x-ray diffraction data from fibers of biopolymers. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. The conformation of C-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):265–269. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balendiran K., Rao S. T., Sekharudu C. Y., Zon G., Sundaralingam M. X-ray structures of the B-DNA dodecamer d(CGCGTTAACGCG) with an inverted central tetranucleotide and its netropsin complex. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Mar 1;51(Pt 2):190–198. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994010759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J., Pilet J., Phuong Lan T. T., Hill L. R. Direct evidence of the C-like form of sodium deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3352–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Vold R. R., Kearns D. R., Rupprecht A. A 2H-NMR study of the A-DNA conformation in films of oriented Na-DNA: evidence of a disordered B-DNA contribution. Biopolymers. 1988 Jul;27(7):1159–1170. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Vold R. R., Kearns D. R., Rupprecht A. Static disorder and librational motions of the purine bases in films of oriented Li-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran R., Arnott S. The structure of B-DNA in oriented fibers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1996 Jun;13(6):1015–1027. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1996.10508916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran R., Wang M., He R. G., Puigjaner L. C., Byler M. A., Millane R. P., Arnott S. A re-examination of the crystal structure of A-DNA using fiber diffraction data. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Jun;6(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10506544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Aymami J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A., Wang A. H. Molecular structure of the netropsin-d(CGCGATATCGCG) complex: DNA conformation in an alternating AT segment. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):310–320. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULLER W., WILKINS M. H., WILSON H. R., HAMILTON L. D. THE MOLECULAR CONFIGURATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. IV. X-RAY DIFFRACTION STUDY OF THE A FORM. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:60–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan M. E., Rollins S. B., Williams R. M. Netropsin and spermine conjugates of a water-soluble quinocarcin analog: analysis of sequence-specific DNA interactions. Chem Biol. 1995 Mar;2(3):147–156. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche H., Brandes R., Rupprecht A., Song Z., Weidlich T., Kearns D. R. The formation of A-DNA in NaDNA films is suppressed by netropsin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1223–1228. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche H. Infrared linear dichroism studies of DNA-drug complexes: quantitative determination of the drug-induced restriction of the B-A transition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):787–791. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche H., Rupprecht A., Richter M. Infrared linear dichroism of oriented DNA-ligand complexes prepared with the wet-spinning method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9165–9177. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Shindo H. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance of highly oriented DNA fibers. 2. Molecular motions in hydrated DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):896–902. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriëlse W., van Well H. F., Veeman W. S. Determination of the 13C magnetic shielding tensor in partially oriented polymer systems. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 1996 Jun;6(3):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0926-2040(95)01217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S., Kopka M. L., Dickerson R. E. Refinement of netropsin bound to DNA: bias and feedback in electron density map interpretation. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 18;34(15):4983–4993. doi: 10.1021/bi00015a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Alings C., Hahn M. Crystallographic studies of DNA helix structure. Biophys Chem. 1994 May;50(1-2):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)85028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld J., Griffin R. G., Haberkorn R. A. Phosphorus-31 chemical-shift tensors in barium diethyl phosphate and urea-phosphoric acid: model compounds for phospholipid head-group studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2711–2718. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juang C. L., Tang P., Harbison G. S. Solid-state NMR of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1995;261:256–270. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(95)61013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. Binding of an antitumor drug to DNA, Netropsin and C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-BrC-G-C-G. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARVIN D. A., SPENCER M., WILKINS M. H., HAMILTON L. D. The molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. III. X-ray diffraction study of the C form of the lithium salt. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:547–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nall B. T., Rothwell W. P., Waugh J. S., Rupprecht A. Structural studies of A-form sodium deoxyribonucleic acid: phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance of oriented fibers. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1881–1887. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L. Molecular recognition in noncovalent antitumor agent-DNA complexes: NMR studies of the base and sequence dependent recognition of the DNA minor groove by netropsin. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):887–915. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilet J., Brahms J. Dependence of B-A conformational change in DNA on base composition. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):99–100. doi: 10.1038/newbio236099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohle W., Zhurkin V. B., Fritzsche H. The DNA phosphate orientation. Infrared data and energetically favorable structures. Biopolymers. 1984 Nov;23(11 Pt 2):2603–2622. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premilat S., Albiser G. Conformations of A-DNA and B-DNA in agreement with fiber X-ray and infrared dichroism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1897–1908. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A. A wet spinning apparatus and auxiliary equipment suitable for preparing samples of oriented DNA. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Jan;12(1):93–121. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A., Forslind B. Variation of electrolyte content in wet-spun lithium- and sodium-DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):304–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A. Preparation of oriented DNA by wet spinning. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(2):494–504. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Rupprecht A., Song Z., Piskur J., Nordenskiöld L., Lahajnar G. A mechanochemical study of MgDNA fibers in ethanol-water solutions. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):810–819. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80857-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Fujiwara T., Akutsu H., Matsumoto U., Kyogoku Y. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance of highly oriented DNA fibers. 1. Static geometry of DNA double helices. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):887–895. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabernero L., Verdaguer N., Coll M., Fita I., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A., Aymamí J. Molecular structure of the A-tract DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) complexed with the minor groove binding drug netropsin. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8403–8410. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P., Juang C. L., Harbison G. S. Intercalation complex of proflavine with DNA: structure and dynamics by solid-state NMR. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2367853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. C., Sundaralingam M. New crystal structures of nucleic acids and their complexes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995 Jun;5(3):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(95)80089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Netropsin. A specific probe for A-T regions of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6719–6731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]