Abstract
A potential energy function for unsaturated hydrocarbons is proposed and is shown to agree well with experiment, using molecular dynamics simulations of a water/octene interface and a dioleoyl phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) bilayer. The simulation results verify most of the assumptions used in interpreting the DOPC experiments, but suggest a few that should be reconsidered. Comparisons with recent results of a simulation of a dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) lipid bilayer show that disorder is comparable, even though the temperature, hydration level, and surface area/lipid for DOPC are lower. These observations highlight the dramatic effects of unsaturation on bilayer structure.
Full text
PDF

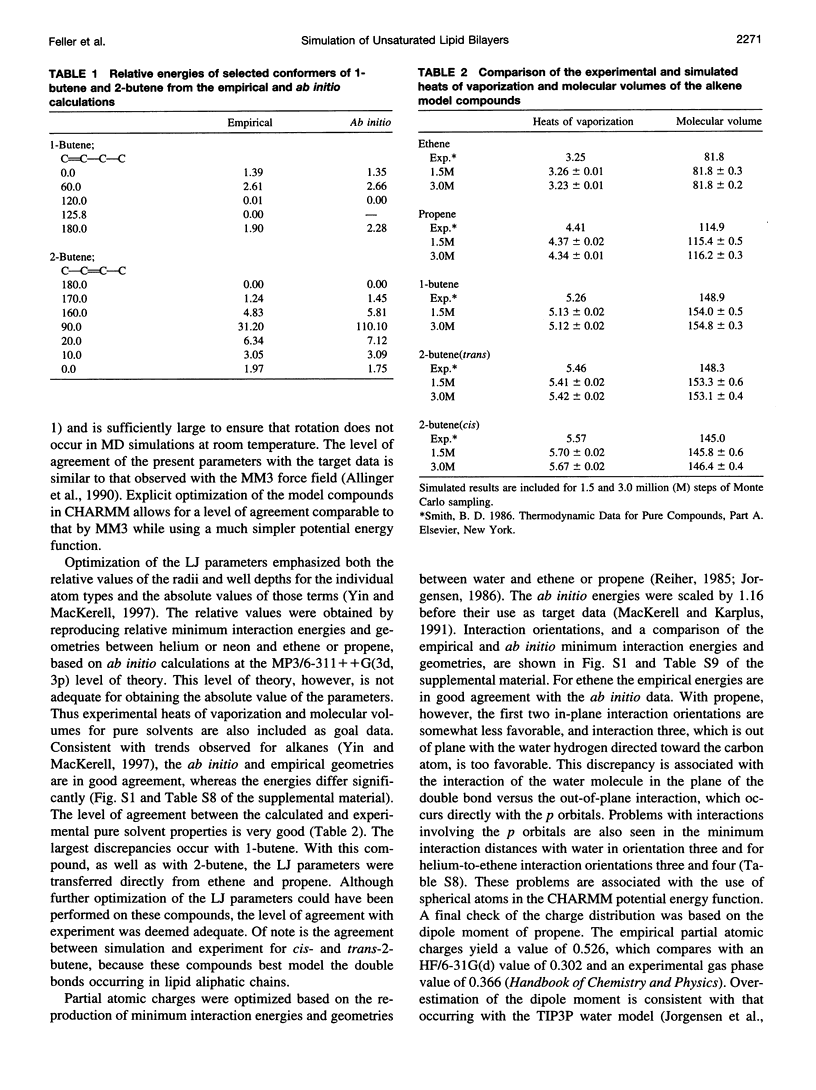


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. F. Modulation of rhodopsin function by properties of the membrane bilayer. Chem Phys Lipids. 1994 Sep 6;73(1-2):159–180. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douliez J. P., Léonard A., Dufourc E. J. Restatement of order parameters in biomembranes: calculation of C-C bond order parameters from C-D quadrupolar splittings. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1727–1739. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80350-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holte L. L., Peter S. A., Sinnwell T. M., Gawrisch K. 2H nuclear magnetic resonance order parameter profiles suggest a change of molecular shape for phosphatidylcholines containing a polyunsaturated acyl chain. Biophys J. 1995 Jun;68(6):2396–2403. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80422-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holte L. L., Separovic F., Gawrisch K. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of hydrocarbon chain packing in bilayers of polyunsaturated phospholipids. Lipids. 1996 Mar;31 (Suppl):S199–S203. doi: 10.1007/BF02637076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover WG. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1985 Mar;31(3):1695–1697. doi: 10.1103/physreva.31.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P., Perez J. J., Loew G. H. Molecular dynamics simulations of phospholipid bilayers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Apr;11(5):927–956. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman B. J., Mitchell D. C. A role for phospholipid polyunsaturation in modulating membrane protein function. Lipids. 1996 Mar;31 (Suppl):S193–S197. doi: 10.1007/BF02637075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Zhang R., Tristram-Nagle S., Sun W., Petrache H. I., Suter R. M. X-ray structure determination of fully hydrated L alpha phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1419–1431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79701-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascher I., Lundmark M., Nyholm P. G., Sundell S. Crystal structures of membrane lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 11;1113(3-4):339–373. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce L. L., Harvey S. C. Langevin dynamics studies of unsaturated phospholipids in a membrane environment. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81143-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Waespe-Sarcevic N. Molecular order in cis and trans unsaturated phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3310–3315. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristram-Nagle S., Zhang R., Suter R. M., Worthington C. R., Sun W. J., Nagle J. F. Measurement of chain tilt angle in fully hydrated bilayers of gel phase lecithins. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1097–1109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81475-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., King G. I., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. I. Scaling of neutron data and the distributions of double bonds and water. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82086-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of x-ray and neutron diffraction. I. Fluid bilayer models and the limits of resolution. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):162–173. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82208-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Fluid bilayer structure determination by the combined use of x-ray and neutron diffraction. II. "Composition-space" refinement method. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):174–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82209-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. II. Distribution and packing of terminal methyl groups. Biophys J. 1992 Feb;61(2):428–433. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81848-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure. Biophys J. 1992 Feb;61(2):434–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Transbilayer distribution of bromine in fluid bilayers containing a specifically brominated analogue of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6997–7008. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]