Abstract
Factor Va is an essential protein cofactor of the enzyme factor Xa, which activates prothrombin to thrombin during blood coagulation. Peptides with an apparent Mr of approximately 94,000 (heavy chain; HC) and approximately 74,000 or 72,000 (light chain; LC) interact in the presence of Ca2+ to form active Va. The two forms of Va-LC differ in their carboxyl-terminal C2 domain. Using Va reconstituted with either LC form, we examined the effects of the two LC species on membrane binding and on the activity of membrane-bound Va. We found that 1) Va composed of the 72,000 LC bound only slightly more tightly to membranes composed of a mixture of neutral and acidic lipids, the Kd being reduced by a factor of approximately 3 at 5 mM and by a factor of 6 at 2 mM Ca2+. 2) The two forms of Va seemed to undergo different conformational changes when bound to a membrane. 3) The activity of bovine Va varied somewhat with LC species, the difference being greatest at limiting Xa concentration. We have also addressed the role of the two Va peptides in membrane lipid rearrangements and binding: 1) Va binding increased lateral packing density in mixed neutral/acidic lipid membranes. In the solid phase, Va-HC had no effect, whereas Va-LC and whole Va had similar but small effects. In the fluid phase, Va-HC and whole Va both altered membrane packing, with Va-HC having the largest effect. 2) Va-HC bound reversibly and in a Ca2+-independent fashion to membranes composed of neutral phospholipid (Kd, approximately 0.3 microM; stoichiometry approximately 91). High ionic strength had little effect on binding. 3) The substantial effect of Va on packing within neutral phospholipid membranes was mimicked by Va-HC. 4) Based on measurements of membrane phase behavior, binding of Va or its peptide components did not induce thermodynamically discernible lateral membrane domains. These results suggest that the membrane association of factor Va is a complex process involving both chains of Va, changes in lipid packing, and changes in protein structure.
Full text
PDF



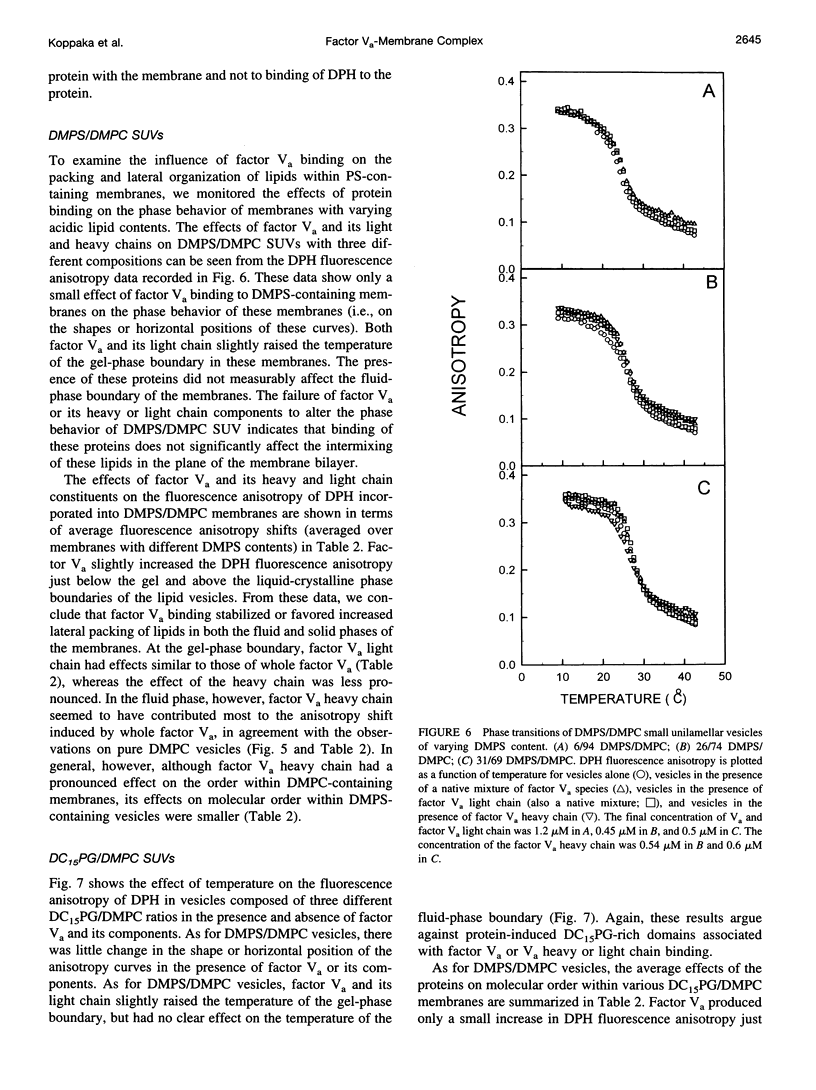
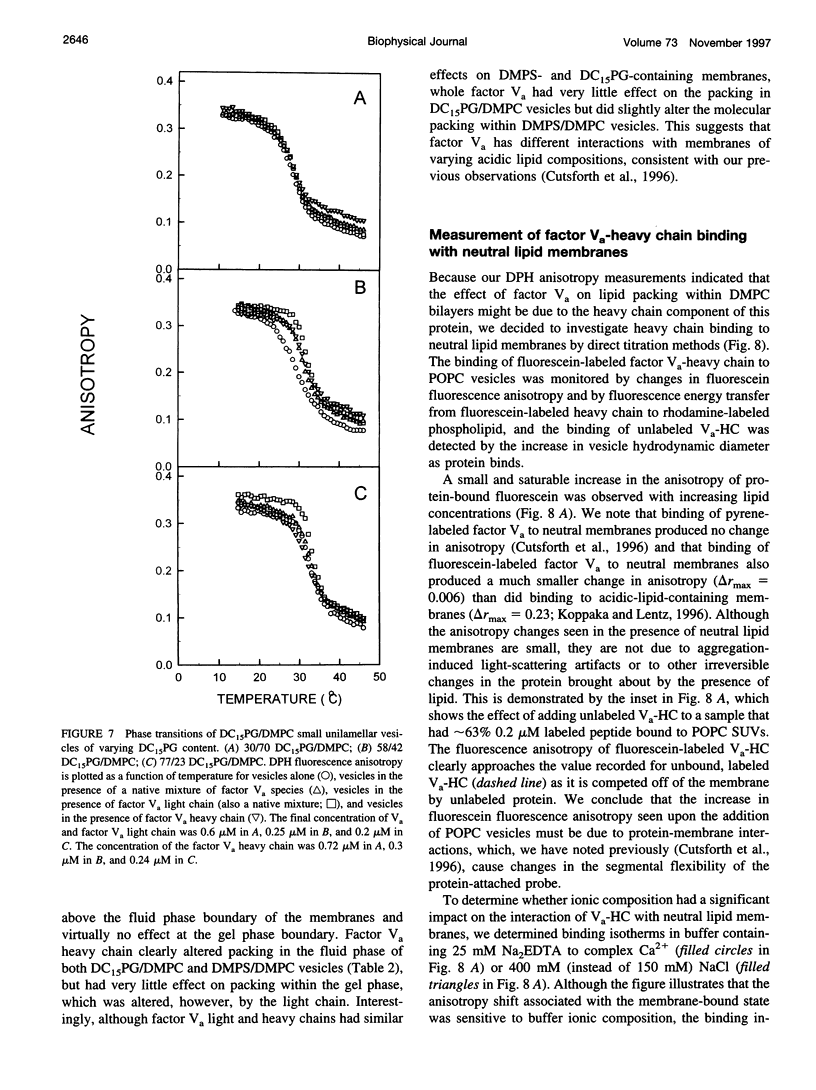
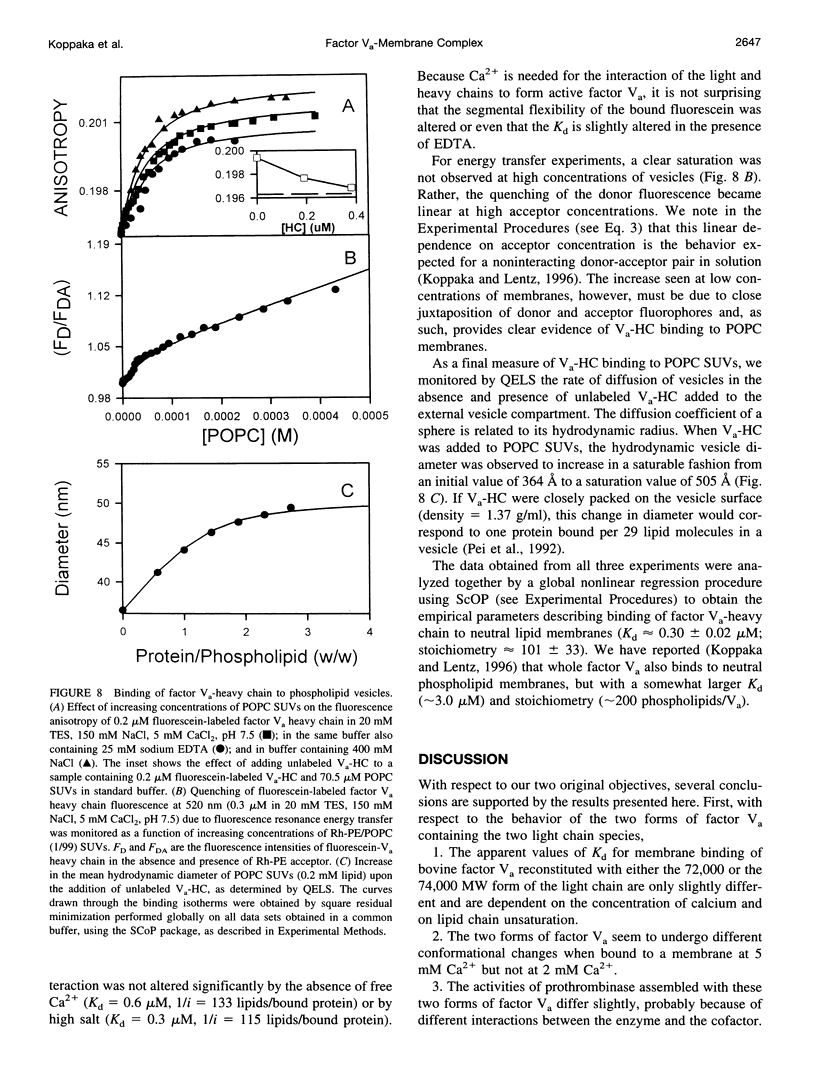





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardelle C., Furie B., Furie B. C., Gilbert G. E. Membrane binding kinetics of factor VIII indicate a complex binding process. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8815–8824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Phospholipid-binding properties of bovine factor V and factor Va. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4419–4425. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutsforth G. A., Koppaka V., Krishnaswamy S., Wu J. R., Mann K. G., Lentz B. R. Insights into the complex association of bovine factor Va with acidic-lipid-containing synthetic membranes. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2938–2949. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79864-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutsforth G. A., Whitaker R. N., Hermans J., Lentz B. R. A new model to describe extrinsic protein binding to phospholipid membranes of varying composition: application to human coagulation proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7453–7461. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrose F. A., Gitel S. N., Zawalich K., Jackson C. M. The association of bovine prothrombin fragment 1 with phospholipid. Quantitative characterization of the Ca2+ ion-mediated binding of prothrombin fragment 1 to phospholipid vesicles and a molecular model for its association with phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5027–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The subunit structure of thrombin-activated factor V. Isolation of activated factor V, separation of subunits, and reconstitution of biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):964–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster W. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. The factor Xa-catalyzed activation of factor V. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13970–13977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerads I., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Tans G., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Prothrombin activation on membranes with anionic lipids containing phosphate, sulfate, and/or carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7967–7974. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesen P. L., Willems G. M., Hemker H. C., Hermens W. T. Membrane-mediated assembly of the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18720–18725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govers-Riemslag J. W., Janssen M. P., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Prothrombin activation on dioleoylphosphatidylcholine membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 15;220(1):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinto E. R., Esmon C. T. Loss of prothrombin and of factor Xa-factor Va interactions upon inactivation of factor Va by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13986–13992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Mann K. G. The interaction of bovine factor V and factor V-derived peptides with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6503–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs B. S., Husten E. J., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. A domain of membrane-bound blood coagulation factor Va is located far from the phospholipid surface. A fluorescence energy transfer measurement. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4958–4969. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenny R. J., Pittman D. D., Toole J. J., Kriz R. W., Aldape R. A., Hewick R. M., Kaufman R. J., Mann K. G. Complete cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of human factor V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4846–4850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Nemerson Y. The activation of bovine coagulation factor X. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:95–107. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Jenny R. J., Mann K. G. Identification and characterization of a phospholipid-binding site of bovine factor Va. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21580–21589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Rand M. D., Mann K. G. Factor Va-membrane interaction is mediated by two regions located on the light chain of the cofactor. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):486–493. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. The interaction of human coagulation factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3963–3969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppaka V., Lentz B. R. Binding of bovine factor Va to phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2930–2937. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79863-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Isaacs B. S., Yemul S. S., Esmon C. T., Bayley H., Johnson A. E. Interaction of blood coagulation factor Va with phospholipid vesicles examined by using lipophilic photoreagents. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):103–109. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G. The binding of factor Va to phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5714–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Russell G. D., Mann K. G. The reassociation of factor Va from its isolated subunits. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3160–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Williams E. B., Mann K. G. The binding of activated protein C to factors V and Va. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9684–9693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Bouix G., Mann K. G. Electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions are involved in factor Va binding to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1905–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Fluorescence depolarization studies of phase transitions and fluidity in phospholipid bilayers. 1. Single component phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4521–4528. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Fluorescence depolarization studies of phase transitions and fluidity in phospholipid bilayers. 2 Two-component phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4529–4537. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Madden S., Alford D. R. Transbilayer redistribution of phosphatidylglycerol in small, unilamellar vesicles induced by specific divalent cations. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6799–6807. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., McIntyre G. F., Parks D. J., Yates J. C., Massenburg D. Bilayer curvature and certain amphipaths promote poly(ethylene glycol)-induced fusion of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2643–2653. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Zhou C. M., Wu J. R. Phosphatidylserine-containing membranes alter the thermal stability of prothrombin's catalytic domain: a differential scanning calorimetric study. Biochemistry. 1994 May 10;33(18):5460–5468. doi: 10.1021/bi00184a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. K., Bloomfield V. A., Nelsestuen G. L. Structure of the prothrombin- and blood clotting factor X-membrane complexes. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4177–4181. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Elion J., Butkowski R. J., Downing M., Nesheim M. E. Prothrombin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):286–302. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G. Prothrombin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:123–156. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Calcium and prothrombin-induced lateral phase separation in membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2457–2463. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Church W. R., DiOrio J. P., Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G., Hainfeld J. F., Wall J. S. Structural model of factors V and Va based on scanning transmission electron microscope images and mass analysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8863–8868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Foster W. B., Hewick R., Mann K. G. Characterization of Factor V activation intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3187–3196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Katzmann J. A., Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Factor V. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):249–274. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Myrmel K. H., Hibbard L., Mann K. G. Isolation and characterization of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):508–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Interactions of a fluorescent active-site-directed inhibitor of thrombin: dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard B., Mann K. Proteolysis of factor Va by factor Xa and activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11233–11238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel T. L., Devore-Carter D., Quinn-Allen M., Kane W. H. Deletion analysis of recombinant human factor V. Evidence for a phosphatidylserine binding site in the second C-type domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4189–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel T. L., Quinn-Allen M. A., Keller F. G., Peterson J. A., Larocca D., Kane W. H. Localization of functionally important epitopes within the second C-type domain of coagulation factor V using recombinant chimeras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15898–15905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei G., Laue T. M., Aulabaugh A., Fowlkes D. M., Lentz B. R. Structural comparisons of meizothrombin and its precursor prothrombin in the presence or absence of procoagulant membranes. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 4;31(30):6990–6996. doi: 10.1021/bi00145a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei G., Powers D. D., Lentz B. R. Specific contribution of different phospholipid surfaces to the activation of prothrombin by the fully assembled prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3226–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers D. D., Lentz B. R. Simulation of prothrombin proteolysis by the full prothrombinase assembled on varied phospholipid surfaces. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3234–3237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Mayer L. D., Wei G. J., Bloomfield V. A., Nelsestuen G. L. Kinetic and hydrodynamic analysis of blood clotting factor V-membrane binding. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5262–5269. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Nelsestuen G. L. Membrane binding properties of blood coagulation Factor V and derived peptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6202–6210. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Bakker H. M., Thomassen M. C., Hemker H. C., Tans G. Characterization of two forms of human factor Va with different cofactor activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21130–21136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoylova S., Mann K. G., Brisson A. Structure of membrane-bound human factor Va. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 12;351(3):330–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tendian S. W., Lentz B. R. Evaluation of membrane phase behavior as a tool to detect extrinsic protein-induced domain formation: binding of prothrombin to phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6720–6729. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Prothrombinase complex assembly on the platelet surface is mediated through the 74,000-dalton component of factor Va. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2380–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Coordinate binding of factor Va and factor Xa to the unstimulated platelet. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]