Abstract
A method was developed to determine the interspin distances of two or more nitroxide spin labels attached to specific sites in proteins. This method was applied to different conformations of spin-labeled insulins. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) line broadening due to dipolar interaction is determined by fitting simulated EPR powder spectra to experimental data, measured at temperatures below 200 K to freeze the protein motion. The experimental spectra are composed of species with different relative nitroxide orientations and interspin distances because of the flexibility of the spin label side chain and the variety of conformational substates of proteins in frozen solution. Values for the average interspin distance and for the distance distribution width can be determined from the characteristics of the dipolar broadened line shape. The resulting interspin distances determined for crystallized insulins in the R6 and T6 structure agree nicely with structural data obtained by x-ray crystallography and by modeling of the spin-labeled samples. The EPR experiments reveal slight differences between crystal and frozen solution structures of the B-chain amino termini in the R6 and T6 states of hexameric insulins. The study of interspin distances between attached spin labels can be applied to obtain structural information on proteins under conditions where other methods like two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy or x-ray crystallography are not applicable.
Full text
PDF

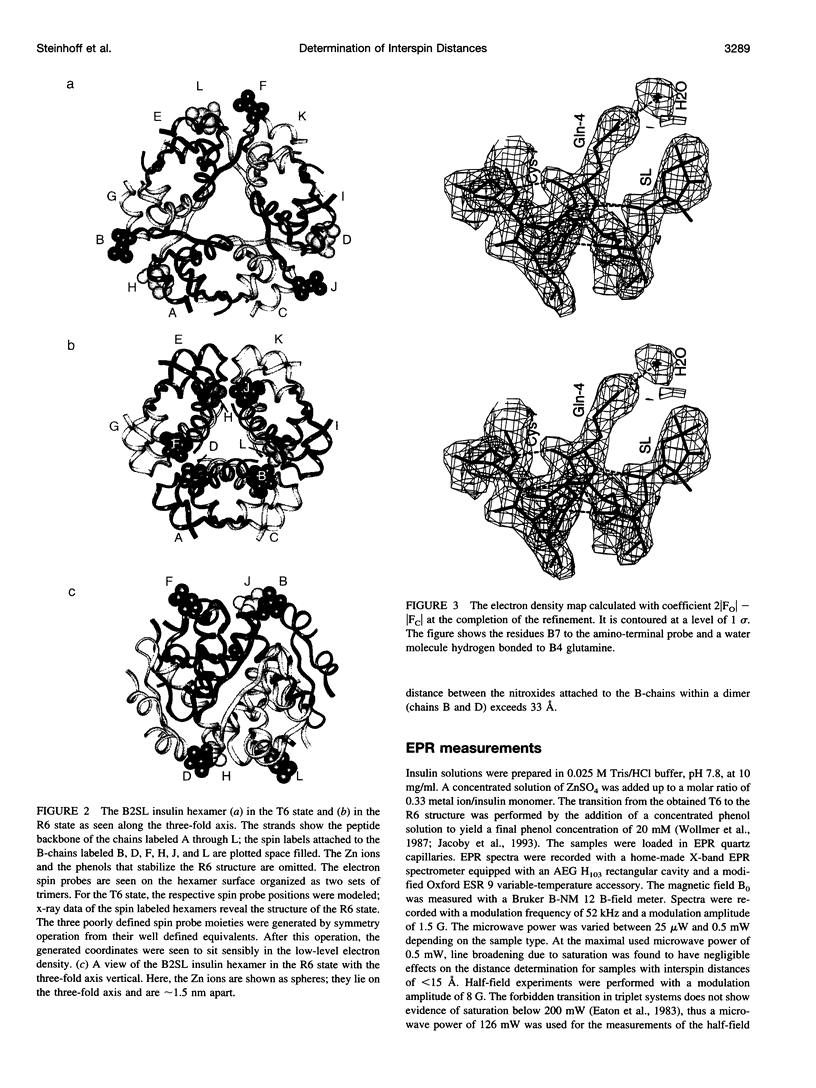









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. N., Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. M., Hubbard R. E., Isaacs N. W., Reynolds C. D. The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 A resolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1195):369–456. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda U., Derewenda Z., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Reynolds C. D., Smith G. D., Sparks C., Swenson D. Phenol stabilizes more helix in a new symmetrical zinc insulin hexamer. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):594–596. doi: 10.1038/338594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farahbakhsh Z. T., Huang Q. L., Ding L. L., Altenbach C., Steinhoff H. J., Horwitz J., Hubbell W. L. Interaction of alpha-crystallin with spin-labeled peptides. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 17;34(2):509–516. doi: 10.1021/bi00002a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrens D. L., Altenbach C., Yang K., Hubbell W. L., Khorana H. G. Requirement of rigid-body motion of transmembrane helices for light activation of rhodopsin. Science. 1996 Nov 1;274(5288):768–770. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiori W. R., Miick S. M., Millhauser G. L. Increasing sequence length favors alpha-helix over 3(10)-helix in alanine-based peptides: evidence for a length-dependent structural transition. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):11957–11962. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby E., Krüger P., Karatas Y., Wollmer A. Distinction of structural reorganisation and ligand binding in the T<==>R transition of insulin on the basis of allosteric models. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1993 Sep;374(9):877–885. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1993.374.7-12.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miick S. M., Casteel K. M., Millhauser G. L. Experimental molecular dynamics of an alanine-based helical peptide determined by spin label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 10;32(31):8014–8021. doi: 10.1021/bi00082a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miick S. M., Martinez G. V., Fiori W. R., Todd A. P., Millhauser G. L. Short alanine-based peptides may form 3(10)-helices and not alpha-helices in aqueous solution. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):653–655. doi: 10.1038/359653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miick S. M., Todd A. P., Millhauser G. L. Position-dependent local motions in spin-labeled analogues of a short alpha-helical peptide determined by electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9498–9503. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabenstein M. D., Shin Y. K. Determination of the distance between two spin labels attached to a macromolecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8239–8243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T., Riesle J., Oesterhelt D., Gerwert K., Steinhoff H. J. Spin-labeling studies of the conformational changes in the vicinity of D36, D38, T46, and E161 of bacteriorhodopsin during the photocycle. Biophys J. 1997 Aug;73(2):983–993. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78131-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin Y. K., Levinthal C., Levinthal F., Hubbell W. L. Colicin E1 binding to membranes: time-resolved studies of spin-labeled mutants. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):960–963. doi: 10.1126/science.8382373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff HJn, Dombrowsky O., Karin C., Schneiderhahn C. Two dimensional diffusion of small molecules on protein surfaces: an EPR study of the restricted translational diffusion of protein-bound spin labels. Eur Biophys J. 1991;20(5):293–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00450565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff H. J. A simple method for determination of rotational correlation times and separation of rotational and polarity effects from EPR spectra of spin-labeled biomolecules in a wide correlation time range. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1988 Dec;17(4):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(88)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff H. J., Hubbell W. L. Calculation of electron paramagnetic resonance spectra from Brownian dynamics trajectories: application to nitroxide side chains in proteins. Biophys J. 1996 Oct;71(4):2201–2212. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79421-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff H. J., Mollaaghababa R., Altenbach C., Hideg K., Krebs M., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Time-resolved detection of structural changes during the photocycle of spin-labeled bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):105–107. doi: 10.1126/science.7939627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff H., Lieutenant K., Schlitter J. Residual motion of hemoglobin-bound spin labels as a probe for protein dynamics. Z Naturforsch C. 1989 Mar-Apr;44(3-4):280–288. doi: 10.1515/znc-1989-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollmer A., Rannefeld B., Johansen B. R., Hejnaes K. R., Balschmidt P., Hansen F. B. Phenol-promoted structural transformation of insulin in solution. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Aug;368(8):903–911. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







