Abstract
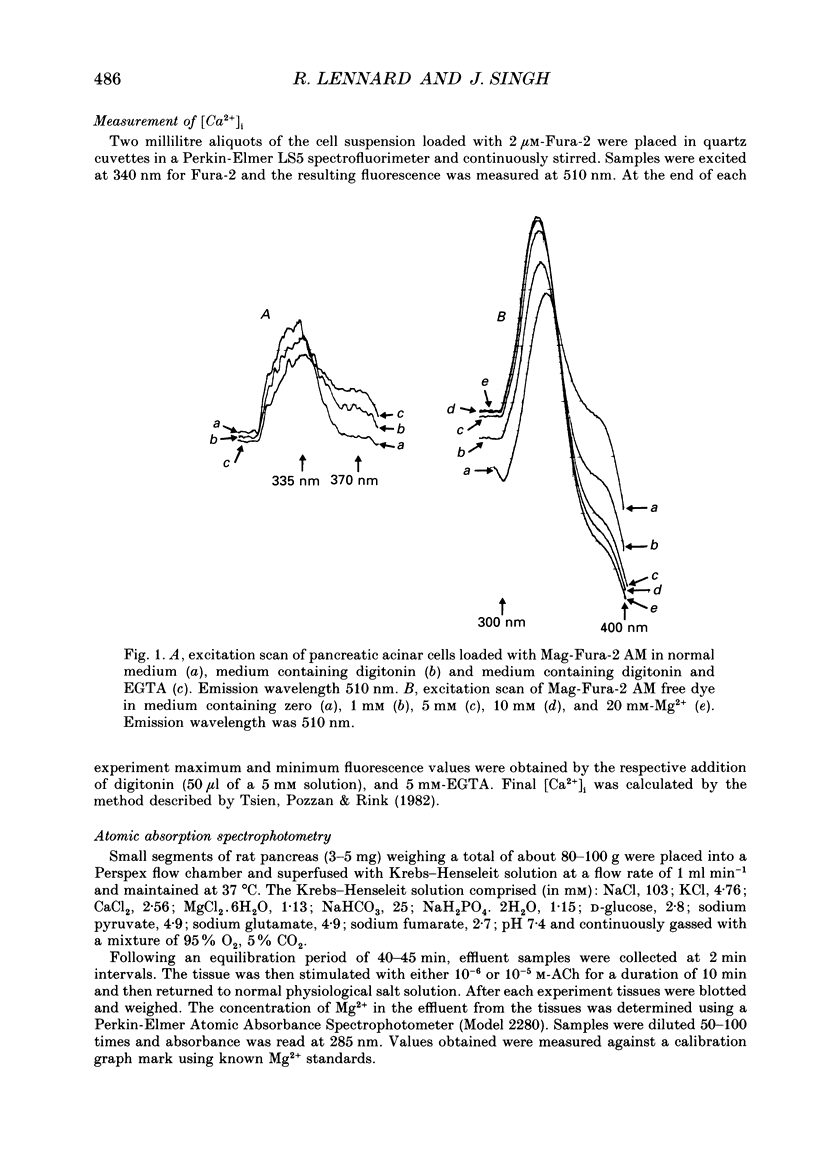
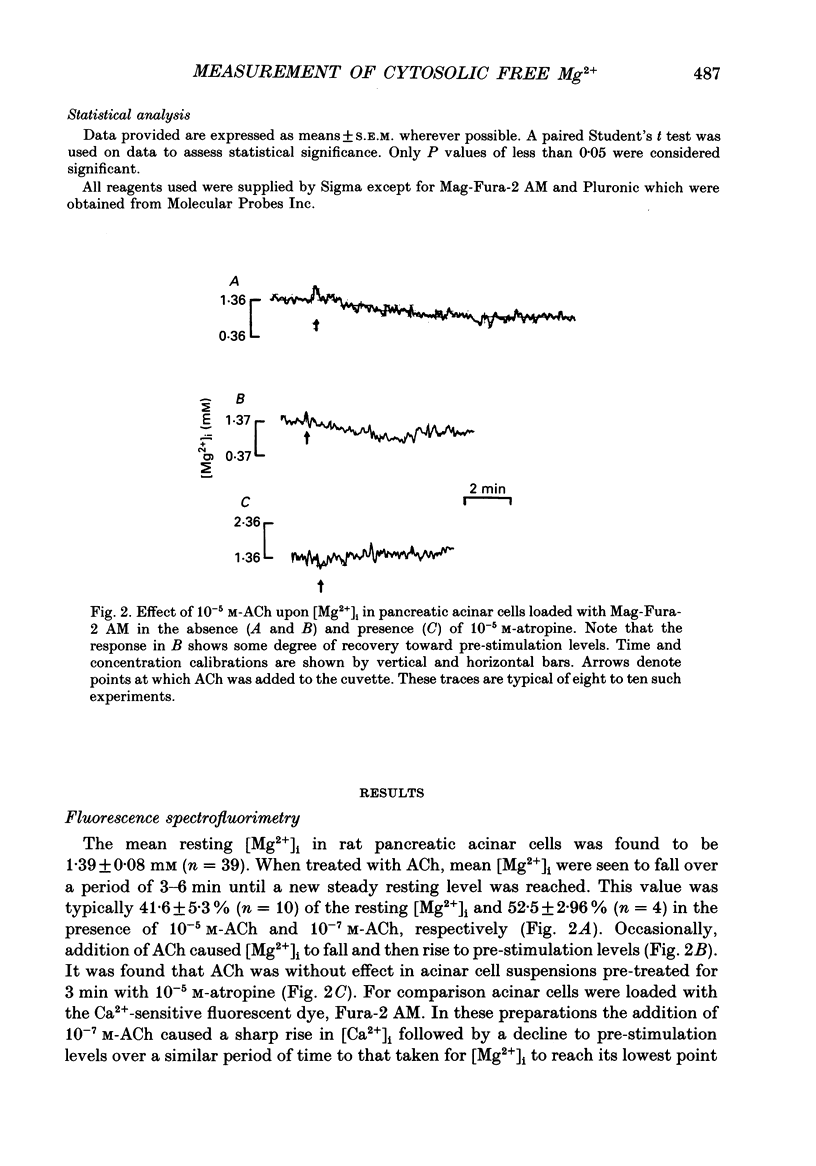
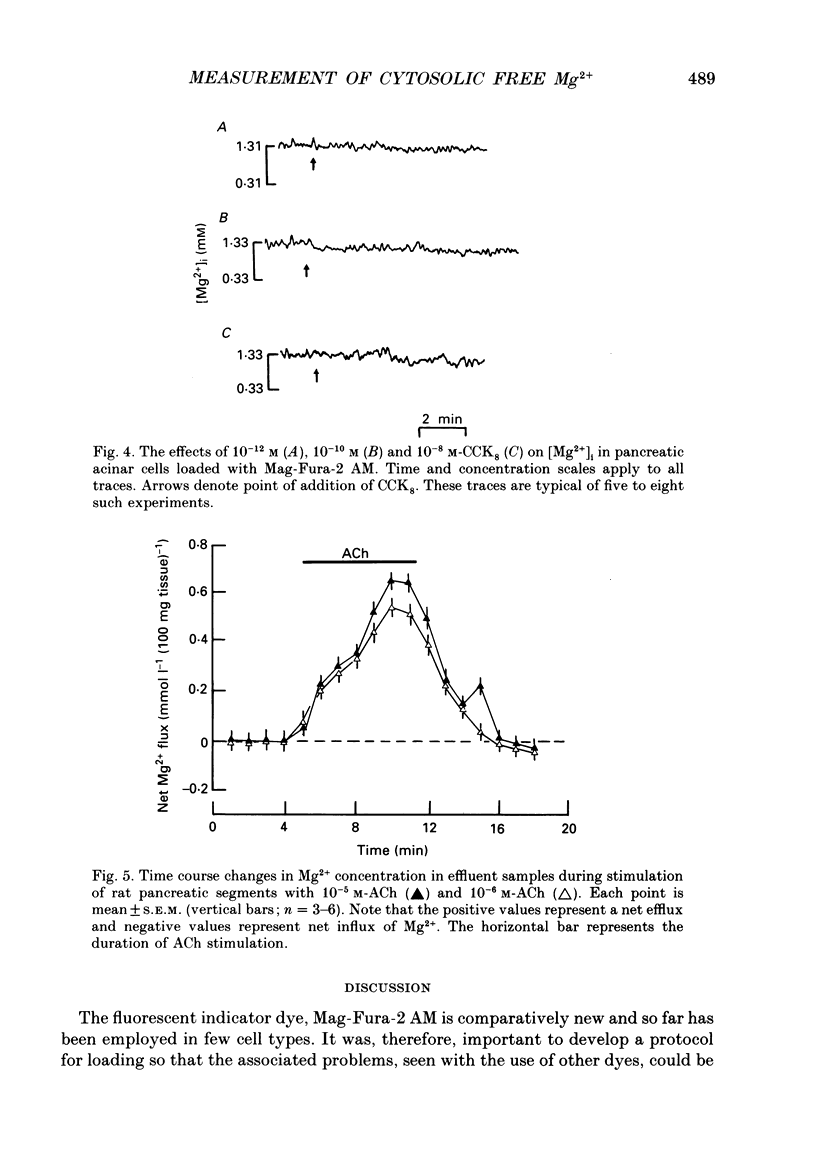
1. This study employs the fluorescent dye Mag-Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester (AM) to measure intracellular free magnesium concentration [Mg2+]i in isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells. Initially a number of protocols were investigated to develop optimal loading conditions for the dye Mag-Fura-2 AM. The procedure yielding cells which showed minimal dye loss and no adverse compartmentalization was adopted for subsequent experiments. 2. The mean resting [Mg2+]i is 1.39 +/- 0.08 mM (n = 39). 3. Acetylcholine (ACh), cholescystokinin-octapeptide (CCK8), carbamylcholine chloride evoked marked reduction in [Mg2+]i in pancreatic acinar cells compared to resting values in the absence of secretagogues. The ACh-evoked decrease in [Mg2+]i was abolished by pre-treatment with atropine. In contrast, noradrenaline, adrenaline and histamine had no significant effect on [Mg2+]i. 4. In acinar cells loaded with the Ca(2+)-sensitive dye, Fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester (AM), ACh stimulation resulted in a marked elevation in intracellular free Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i. This response was blocked by pre-treatment with atropine. 5. Atomic absorption spectrophotometry was used to measure Mg2+ levels in effluent samples from pancreatic segments. Stimulation of pancreatic segments with ACh resulted in a marked elevation in Mg2+ concentrations (net efflux). On removal of ACh, Mg2+ concentration returned to resting level followed by a small net influx of Mg2+ into pancreatic tissue. 6. The results demonstrate that secretagogue-evoked alteration in [Mg2+]i may occur concurrently with Mg2+ release from pancreatic tissue.
Full text
PDF


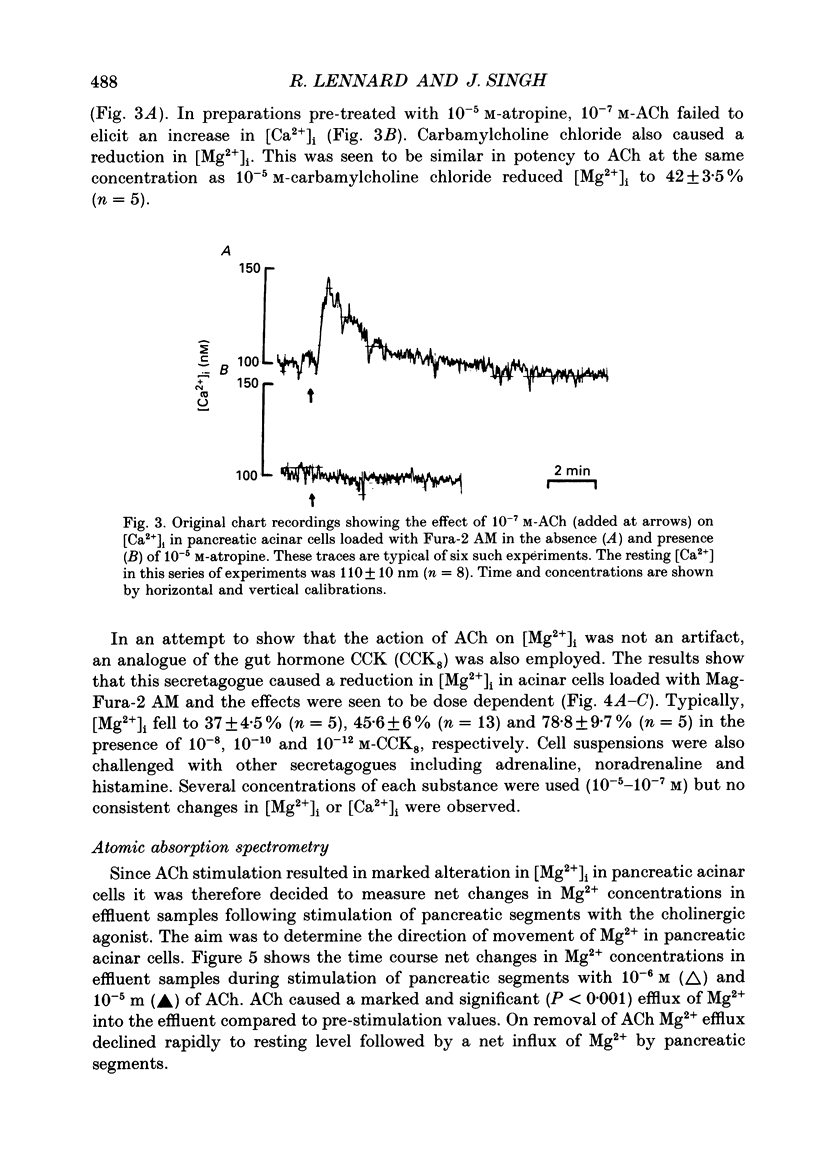



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Giraldez F., Gamiño S. M. Intracellular free magnesium in excitable cells: its measurement and its biologic significance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 May;65(5):915–925. doi: 10.1139/y87-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cittadini A., Scarpa A. Intracellular Mg2+ homeostasis of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Nov;227(1):202–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. Magnesium transport across cell membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01868686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis L. P., Lennard R., Singh J. Mechanism of action of magnesium on acetylcholine-evoked secretory responses in isolated rat pancreas. Exp Physiol. 1990 Sep;75(5):669–680. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1990.sp003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Gupta P., Moore R. D. NMR studies of intracellular metal ions in intact cells and tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:221–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard R., Francis L. P., Singh J. Extracellular magnesium regulates acetylcholine-evoked amylase secretion and calcium mobilization in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 Sep;74(5):747–750. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rubin R. P. Pancreatic amylase secretion and cytoplasmic free calcium. Effects of ionomycin, phorbol dibutyrate and diacylglycerols alone and in combination. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):151–159. doi: 10.1042/bj2300151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. D., Becker P. L., Fogarty K. E., Williams D. A., Fay F. S. Ca2+ imaging in single living cells: theoretical and practical issues. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):157–179. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osipchuk Y. V., Wakui M., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by receptor stimulation, G-protein activation, internal application of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+: simultaneous microfluorimetry and Ca2+ dependent Cl- current recording in single pancreatic acinar cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandol S. J., Schoeffield M. S., Sachs G., Muallem S. Role of free cytosolic calcium in secretagogue-stimulated amylase release from dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10081–10086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju B., Murphy E., Levy L. A., Hall R. D., London R. E. A fluorescent indicator for measuring cytosolic free magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C540–C548. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J. Measurement of cytosolic calcium: fluorescent calcium indicators. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1988;14(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of cell junction depends on local cytoplasmic calcium activity. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):250–252. doi: 10.1038/254250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. E. The biochemistry of magnesium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Aug 15;162(2):717–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


