Abstract
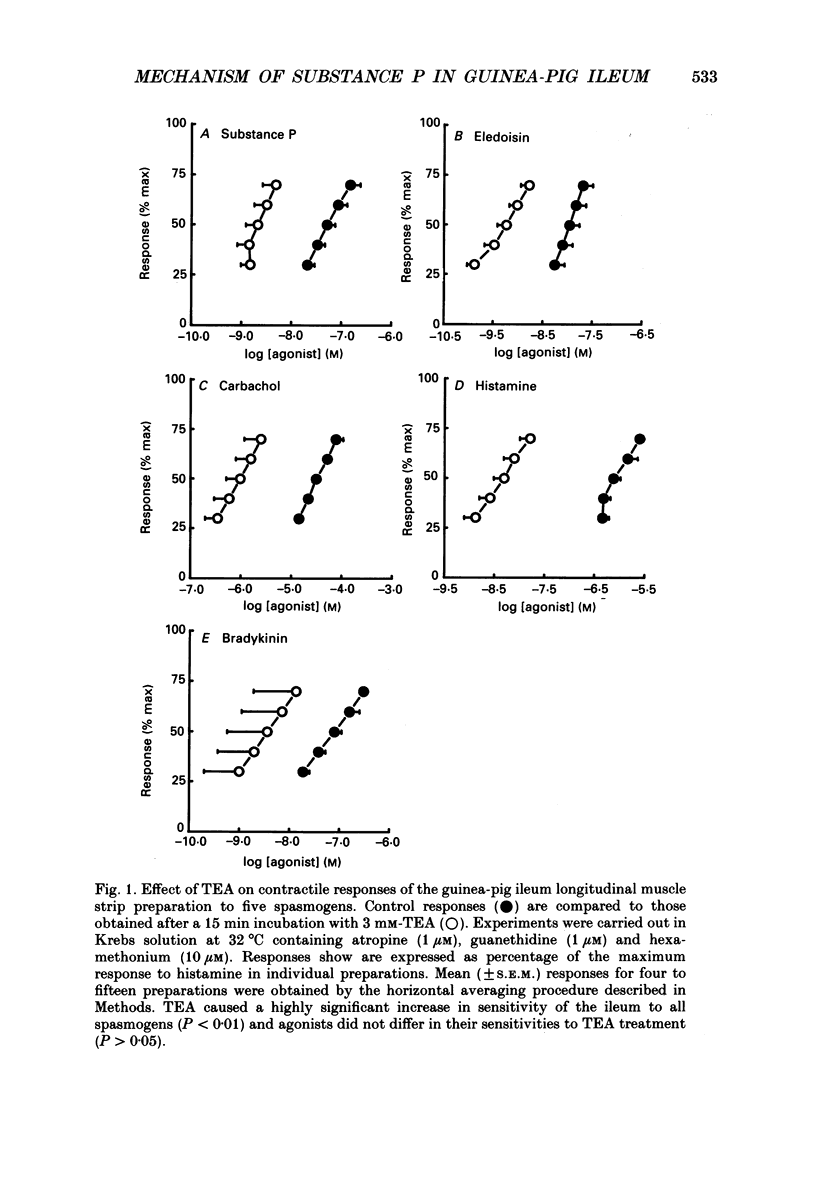
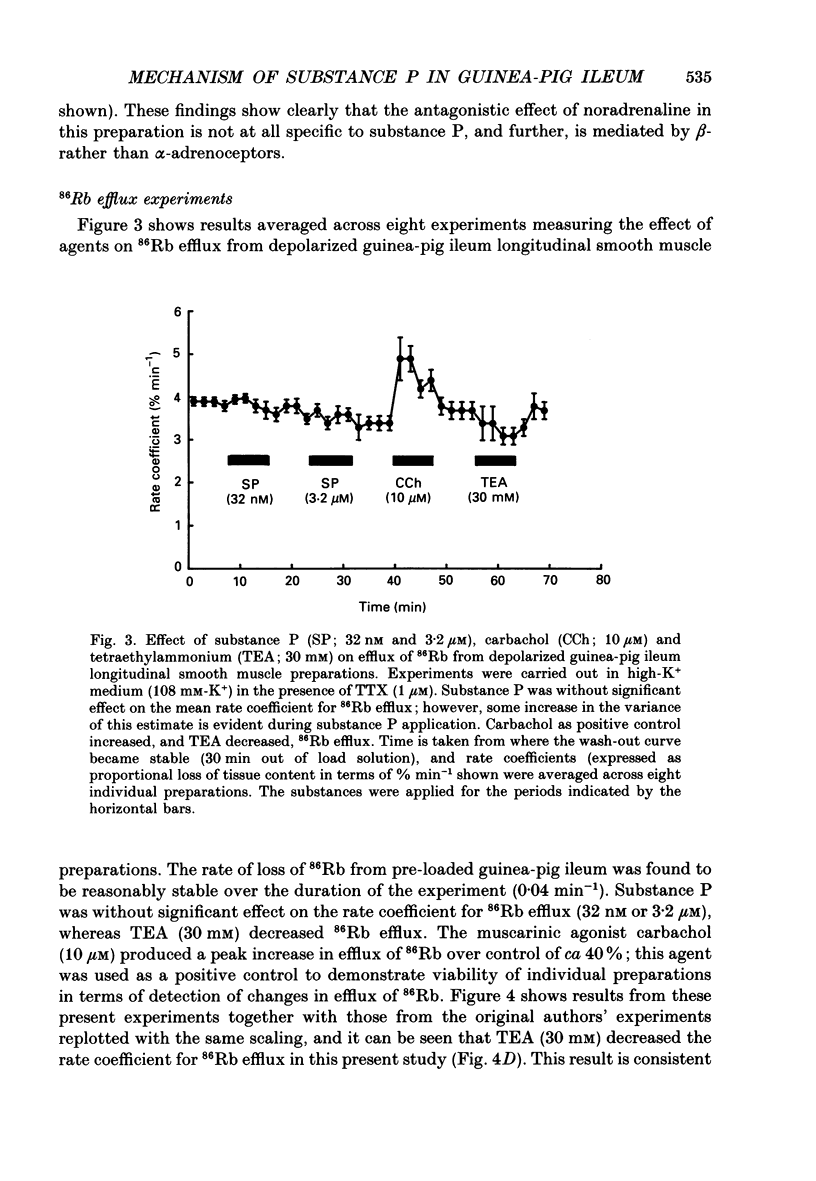
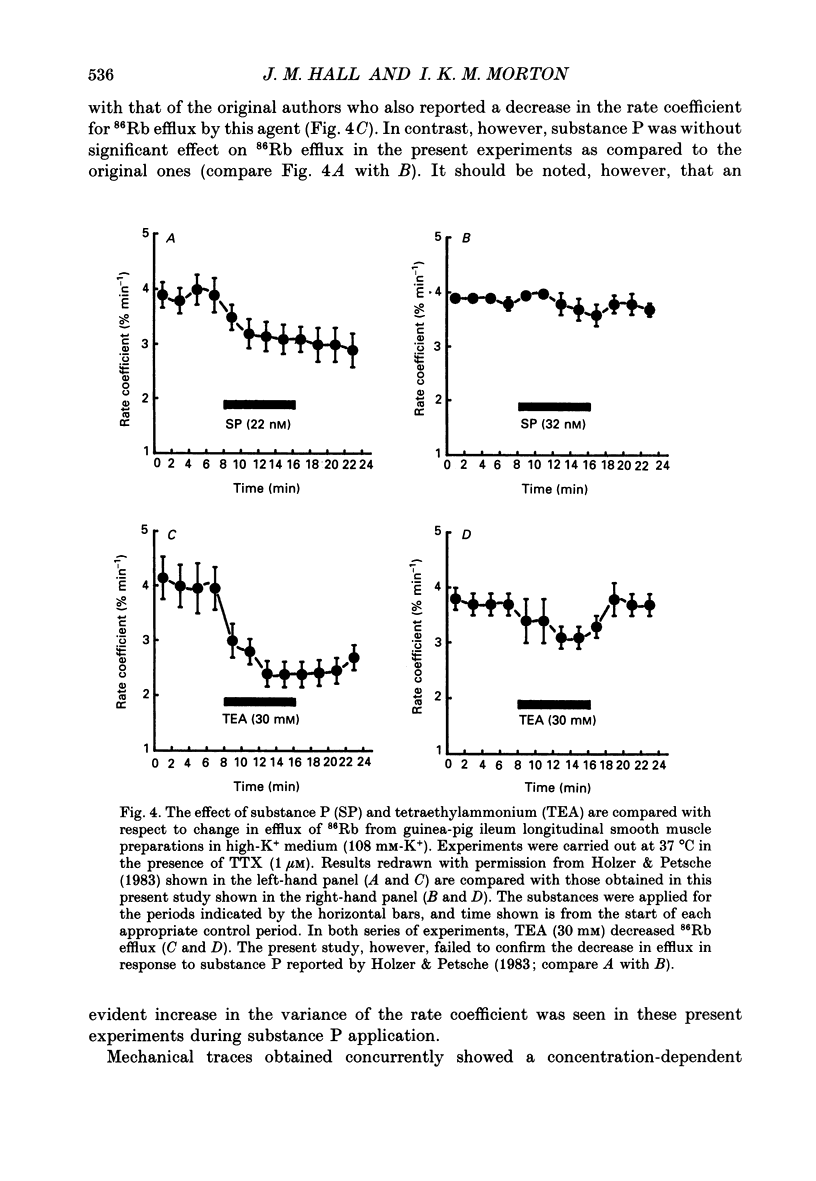
1. A proposed mechanism of contractile action of substance P in guinea-pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle involving a decrease in membrane K+ permeability (PK) has been re-examined. 2. Potentiation of responses to substance P by the K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA) was originally proposed as evidence for a mechanism of action of substance P involving a decrease in PK. Potentiation was confirmed; however this was found not to be specific to substance P since a similar potentiation of responses was seen with agonists not thought to act via a decrease in PK. 3. Antagonism of contractile responses to substance P by noradrenaline was similarly confirmed. However, this antagonism was found to represent a non-specific functional interaction through the inhibitory actions of beta-adrenoceptors rather than the proposed specific interaction with an increase in PK by noradrenaline which is normally alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediated. 4. Experiments were made measuring 86Rb efflux, in depolarized guinea-pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle, to estimate PK. These studies confirmed a reported decrease in PK with TEA, but failed to detect the previously reported decrease with substance P. 5. These results, although not disproving a suggested mechanism of direct contractile action of substance P in guinea-pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle involving a decrease in PK, do throw doubt on either the evidence, or its interpretation, as proposed by the original authors in support of such a mechanism.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Jones S. W. Substance P inhibits the M-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):330–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Featherstone R. L., Jordan C. C., Morton I. K. An examination of the pharmacology of two substance P antagonists and the evidence for tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V., Kuriyama H. Homogeneous and non-homogeneous distribution of inhibitory and excitatory adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;76(4):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Comparison of the excitatory actions of substance P, carbachol, histamine and prostaglandin F2 alpha on the smooth muscle of the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;80(3):409–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Mar;39(1):49–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Increase of membrane conductance by adrenaline in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):89–102. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Suppression of spontaneous spike generation by catecholamines in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):103–119. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creed K. E. Functional diversity of smooth muscle. Br Med Bull. 1979 Sep;35(3):243–247. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., JENKINSON D. H. The effect of carbachol on the permeability of depolarized smooth muscle to inorganic ions. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157:74–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanani M., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. The actions of receptor-selective substance P analogs on myenteric neurons: an electrophysiological investigation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 24;153(2-3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. An enquiry into the mechanism by which substance P facilitates the phasic longitudinal contractions of the rabbit ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:377–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Lippe I. T. Substance P action on phosphoinositides in guinea-pig intestinal muscle: a possible transduction mechanism? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;329(1):50–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00695192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Lippe I. T. Substance P can contract the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig small intestine by releasing intracellular calcium. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):259–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Petsche U. On the mechanism of contraction and desensitization induced by substance P in the intestinal muscle of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:549–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kuriyama H., Sakamoto Y. Effects of tetraethylammonium chloride on the membrane activity of guinea-pig stomach smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(2):445–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H., Morton I. K. The effect of noradrenaline on the permeability of depolarized intestinal smooth muscle to inorganic ions. J Physiol. 1967 Feb;188(3):373–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson D. H., Morton I. K. The role of alpha- and beta- adrenergic receptors in some actions of catecholamines on intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Feb;188(3):387–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A. Does substance P mediate slow synaptic excitation within the myenteric plexus? Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):387–388. doi: 10.1038/274387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Wormser U., Friedman Z. Y., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7444–7448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Inoue K., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. Difference between substance P- and acetylcholine-induced currents in mammalian smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;179(3):453–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90188-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Substance P and acetylcholine both suppress the same K+ current in dissociated smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C580–C587. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souquet J. C., Bitar K. N., Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Receptors for substance P on isolated intestinal smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):G666–G672. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.5.G666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Downes C. P. Substance P induced hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids in guinea-pig ileum and rat hypothalamus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 30;93(3-4):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


