Abstract
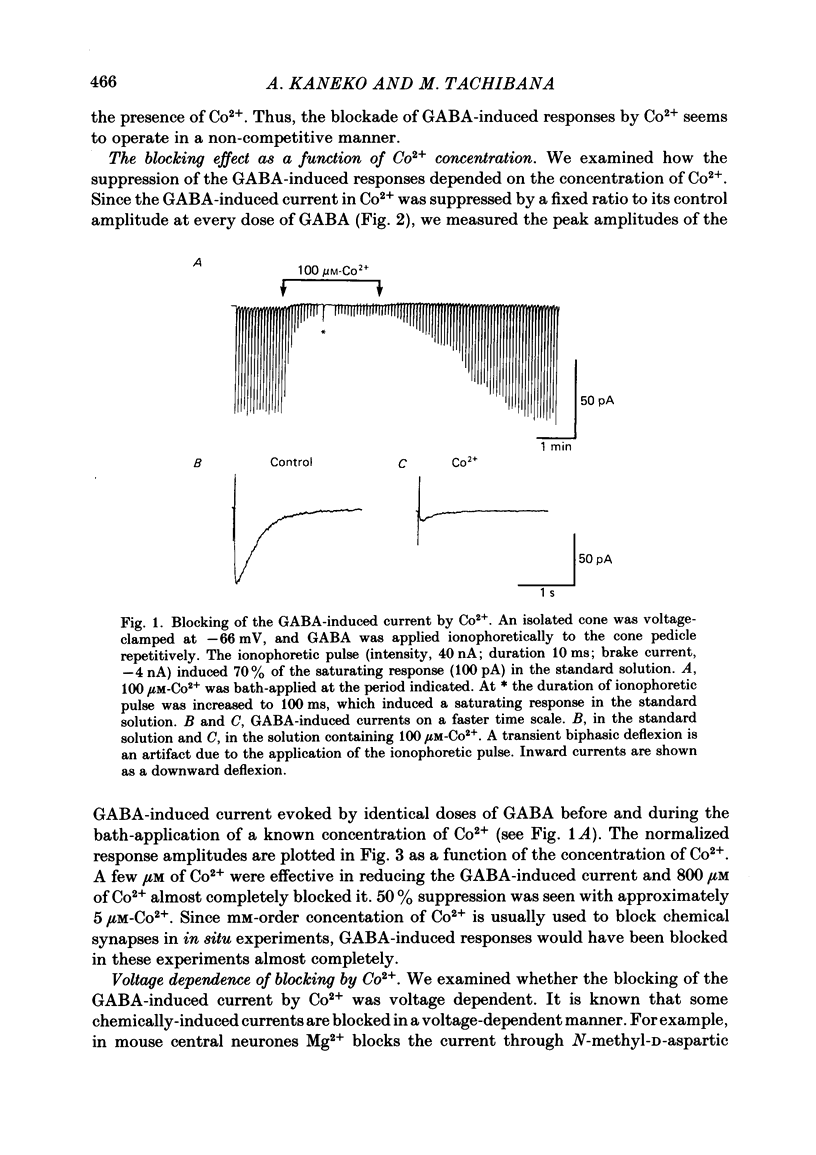
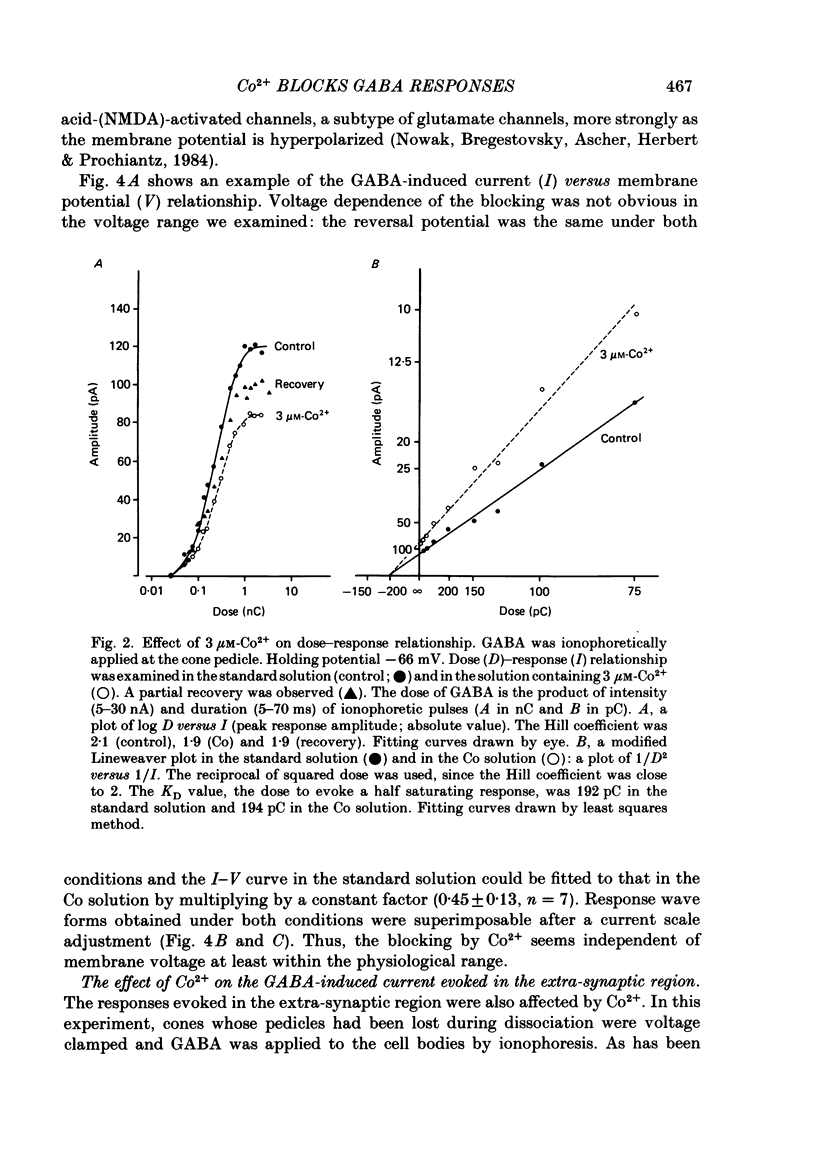
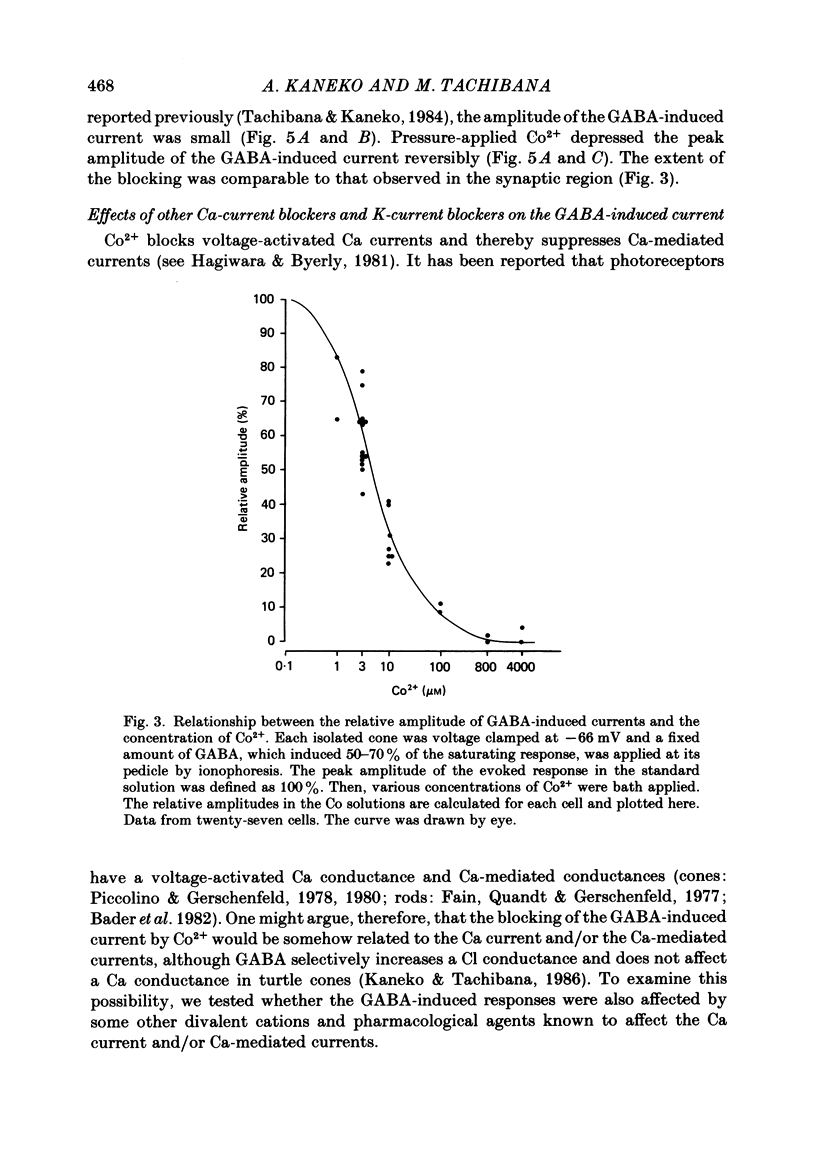
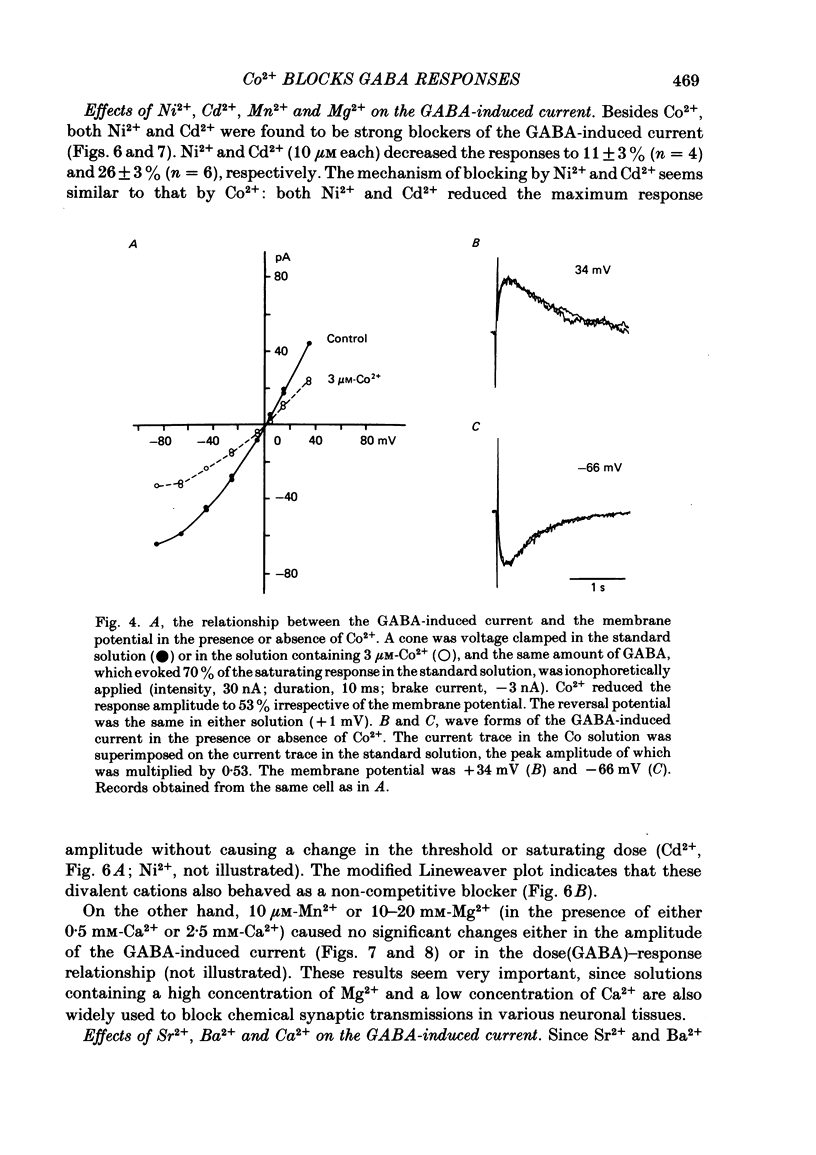
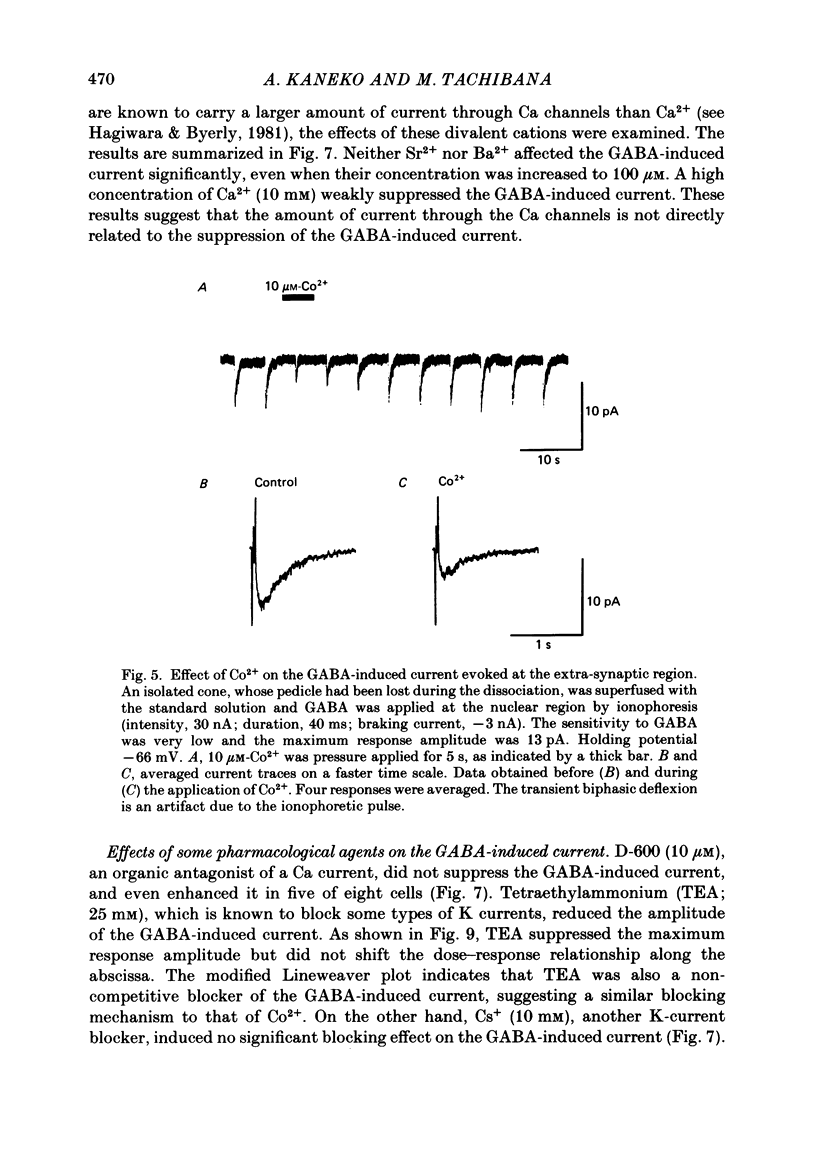
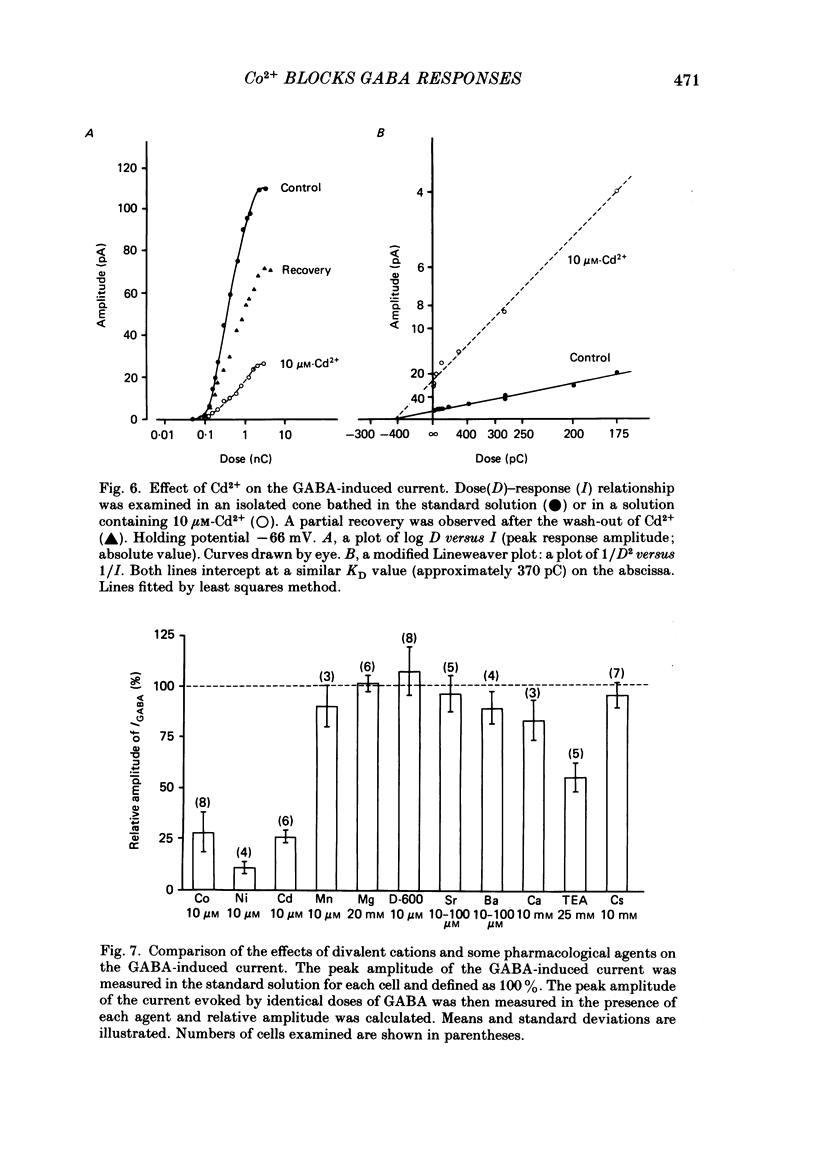
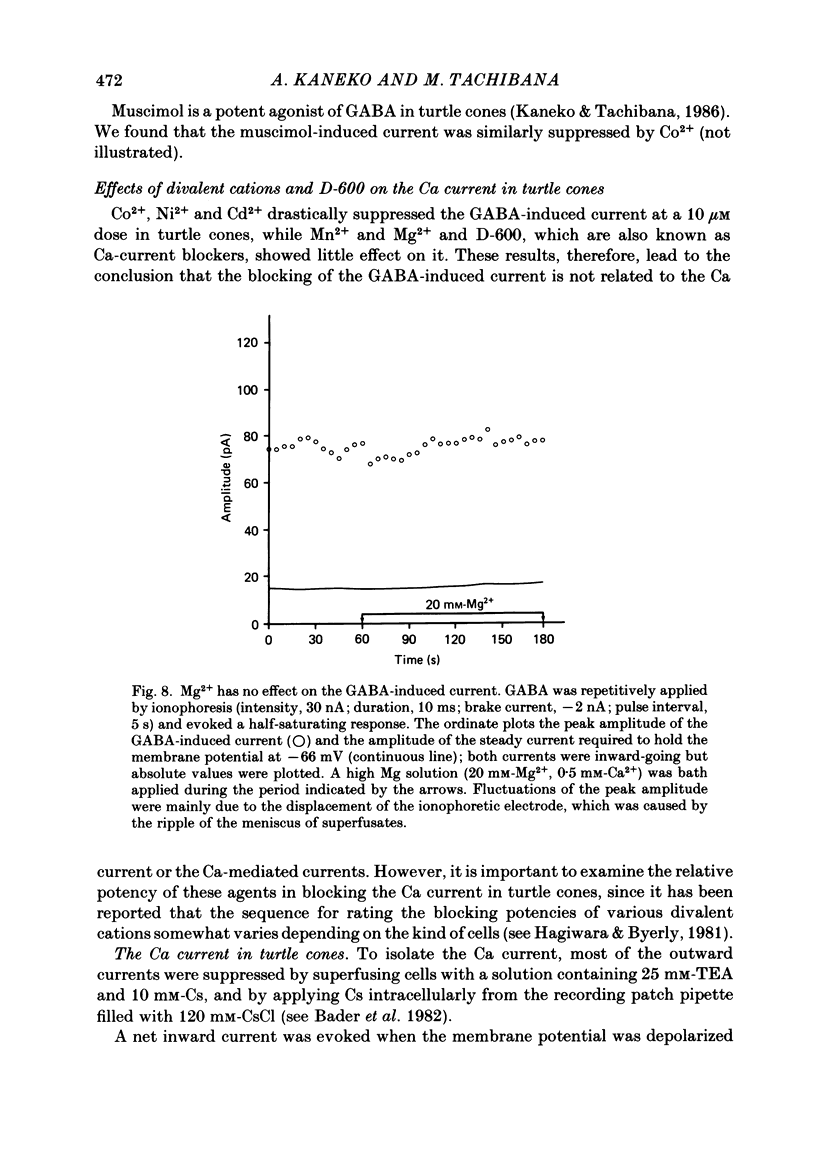
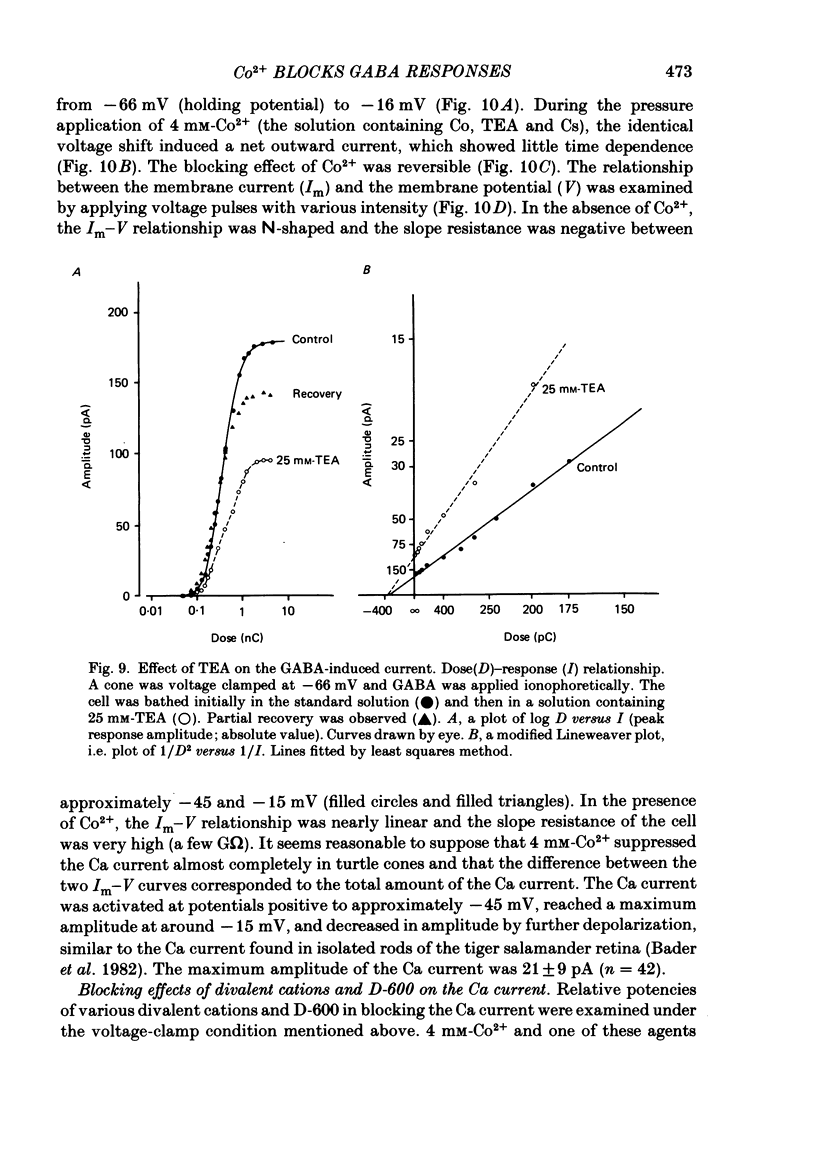
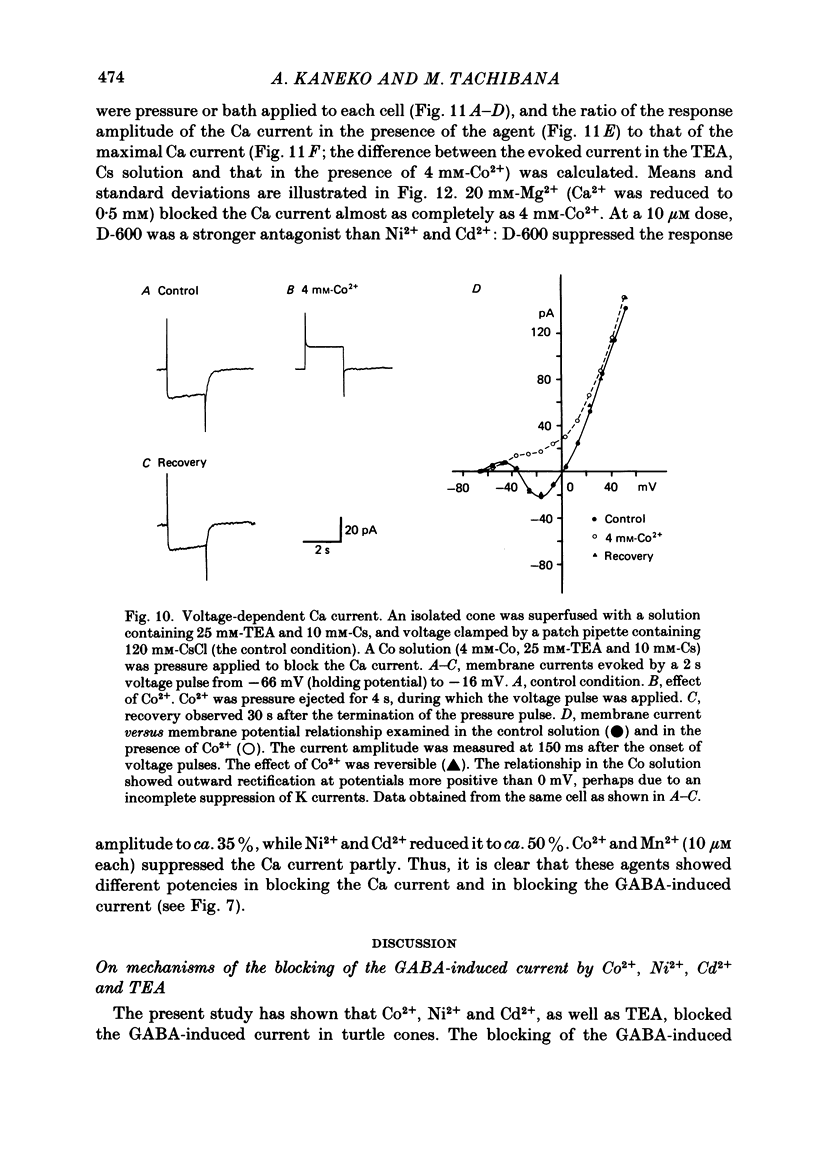
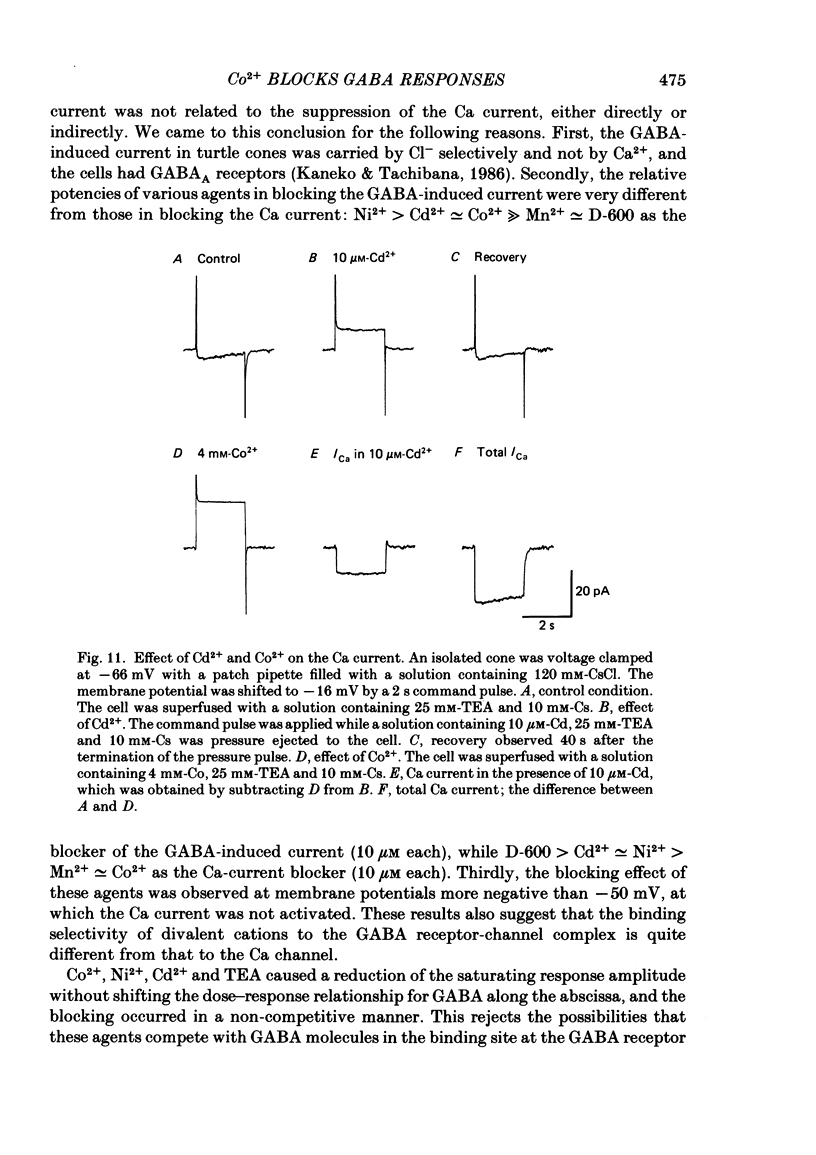
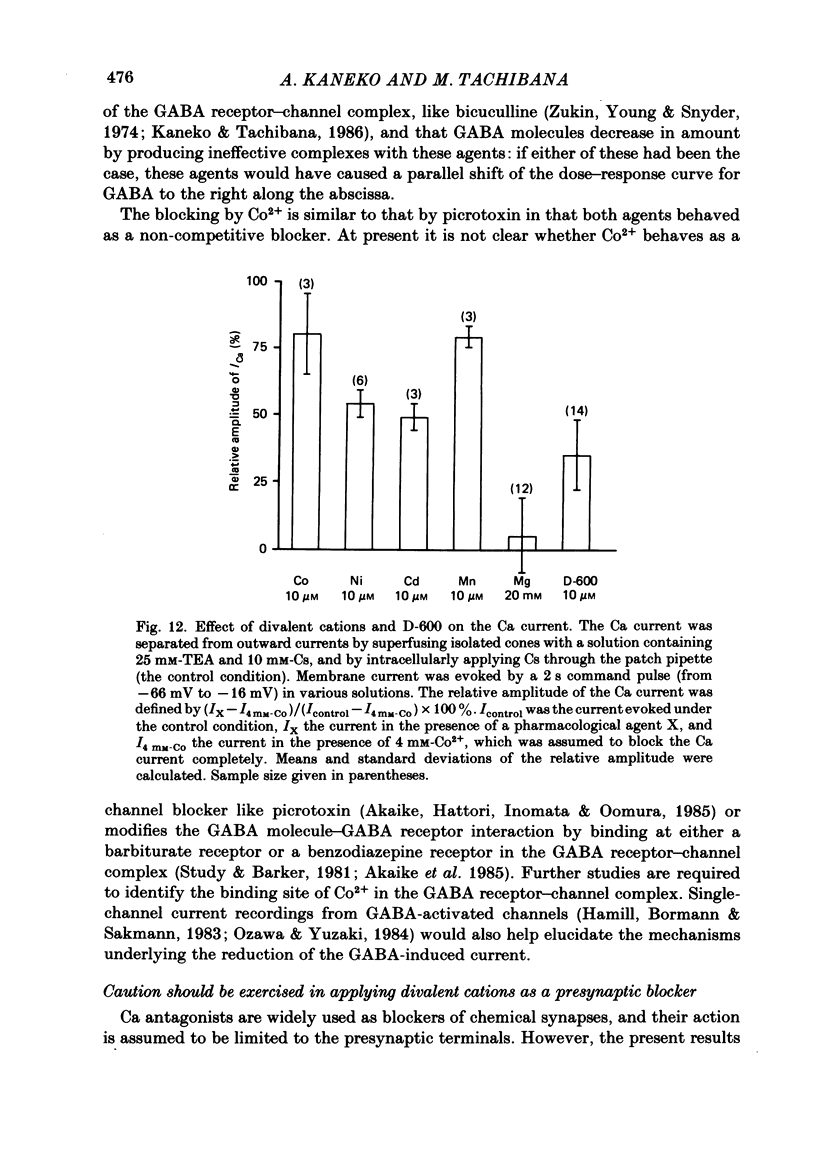
Red-sensitive cone photoreceptors were isolated from the turtle retina, and GABA-induced currents were recorded under voltage clamp. The effect of Co2+, widely used as a blocker of chemical synapses, on the GABA-induced current was studied. Co2+ blocked the GABA-induced current evoked by local application either at the synaptic region (cone pedicle) or at the extra-synaptic region (cell body). 5 microM-Co2+ suppressed the GABA-induced current by 50%, and a few hundred microM-Co2+ blocked it almost completely. Co2+ suppressed the GABA-induced current non-competitively: the saturating response amplitude decreased without a change in the threshold or saturating dose of GABA. The blocking was not voltage dependent in the physiological range of the membrane potential. Ni2+ and Cd2+ also blocked the GABA-induced current non-competitively, and were as effective as Co2+. Tetraethylammonium (25 mM) showed a similar but weaker blocking effect. On the other hand, Mg2+ (20 mM), Mn2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ (10-100 microM each), D-600 (10 microM) or Cs+ (10 mM) did not affect the GABA-induced current. The Ca current in the turtle cones was blocked almost completely by 20 mM-Mg2+ or 4 mM-Co2+, or strongly suppressed by 10 microM-D-600. However, Cd2+ and Ni2+ (10 microM each) blocked the Ca current by ca. 50%, and Co2+ and Mn2+ (10 microM each) suppressed it only partially. The blocking of the GABA-induced current by these agents was, therefore, not directly related to the blocking of the Ca current and/or Ca-mediated currents. These observations present a warning on the use of some divalent cations, such as Co2+, Ni2+ or Cd2+, as a presynaptic blocker at the GABAergic synapse. High concentrations of Mg2+ are recommended as a more appropriate blocker.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Hattori K., Inomata N., Oomura Y. gamma-Aminobutyric-acid- and pentobarbitone-gated chloride currents in internally perfused frog sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:367–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schwartz E. A. Voltage-activated and calcium-activated currents studied in solitary rod inner segments from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:253–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., MacLeish P. R., Schwartz E. A. Responses to light of solitary rod photoreceptors isolated from tiger salamander retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3507–3511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G., O'Bryan P. M. Receptive fields of cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):265–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Gerschenfeld H. M. Calcium-dependent regenerative responses in rods. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):707–710. doi: 10.1038/269707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Responses of solitary retinal horizontal cells from Carassius auratus to L-glutamate and related amino acids. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:255–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Lam D. M. Regenerative and passive membrane properties of isolated horizontal cells from a teleost retina. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):451–454. doi: 10.1038/292451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. A voltage-clamp analysis of membrane currents in solitary bipolar cells dissociated from Carassius auratus. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:131–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Effects of L-glutamate on the anomalous rectifier potassium current in horizontal cells of Carassius auratus retina. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:169–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on isolated cone photoreceptors of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam D. M., Su Y. Y., Swain L., Marc R. E., Brandon C., Wu J. Y. Immunocytochemical localisation of L-glutamic acid decarboxylase in the goldfish retina. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):565–567. doi: 10.1038/278565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam D. M. The biosynthesis and content of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the goldifsh retina. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):225–231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E. Carp horizontal cells in culture respond selectively to L-glutamate and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Shimoda Y., Nakatani K., Miyachi E., Watanabe S. GABA-mediated negative feedback from horizontal cells to cones in carp retina. Jpn J Physiol. 1982;32(6):911–926. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.32.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. Drug interactions at the GABA receptor-ionophore complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:245–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Yuzaki M. Patch-clamp studies of chloride channels activated by gamma-aminobutyric acid in cultured hippocampal neurones of the rat. Neurosci Res. 1984 Oct;1(5):275–293. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(84)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccolino M., Gerschenfeld H. M. Activation of a regenerative calcium conductance in turtle cones by peripheral stimulation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 May 16;201(1144):309–315. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccolino M., Gerschenfeld H. M. Characteristics and ionic processes involved in feedback spikes of turtle cones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Jan 17;206(1165):439–463. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Calcium-independent release of GABA from isolated horizontal cells of the toad retina. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:211–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingai R., Christensen B. N. Sodium and calcium currents measured in isolated catfish horizontal cells under voltage clamp. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):893–897. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Study R. E., Barker J. L. Diazepam and (--)-pentobarbital: fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in cultured central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Ionic currents of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:329–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M., Kaneko A. gamma-Aminobutyric acid acts at axon terminals of turtle photoreceptors: difference in sensitivity among cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7961–7964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Membrane properties of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:141–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Permeability changes induced by L-glutamate in solitary retinal horizontal cells isolated from Carassius auratus. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:153–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakly J. N. The action of cobalt ions on neuromuscular transmission in the frog. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):597–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


