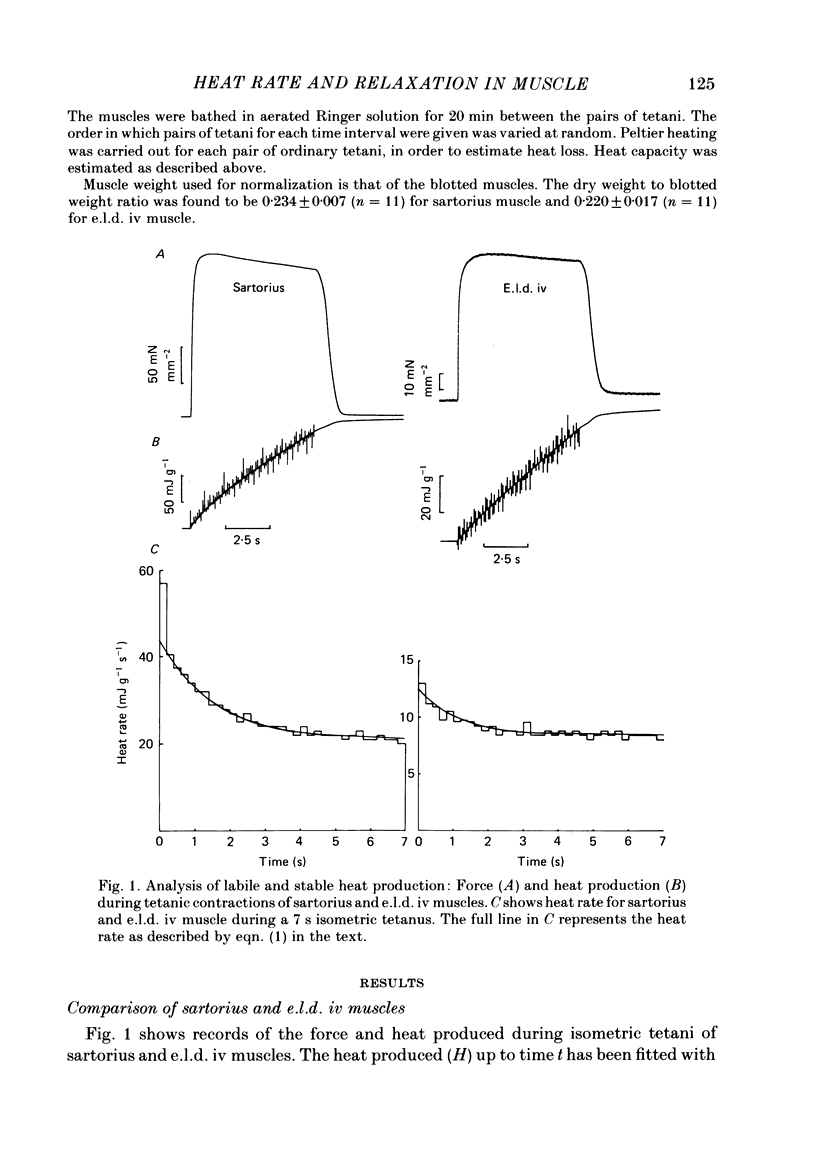
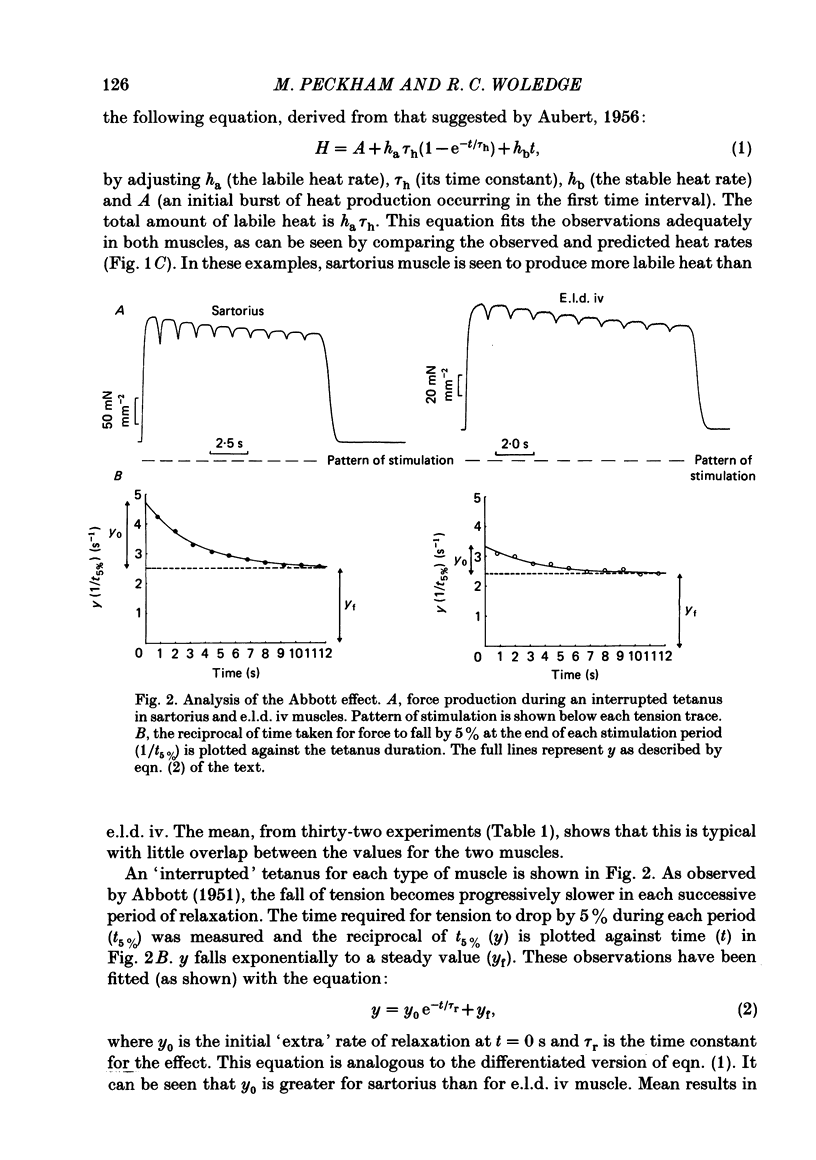
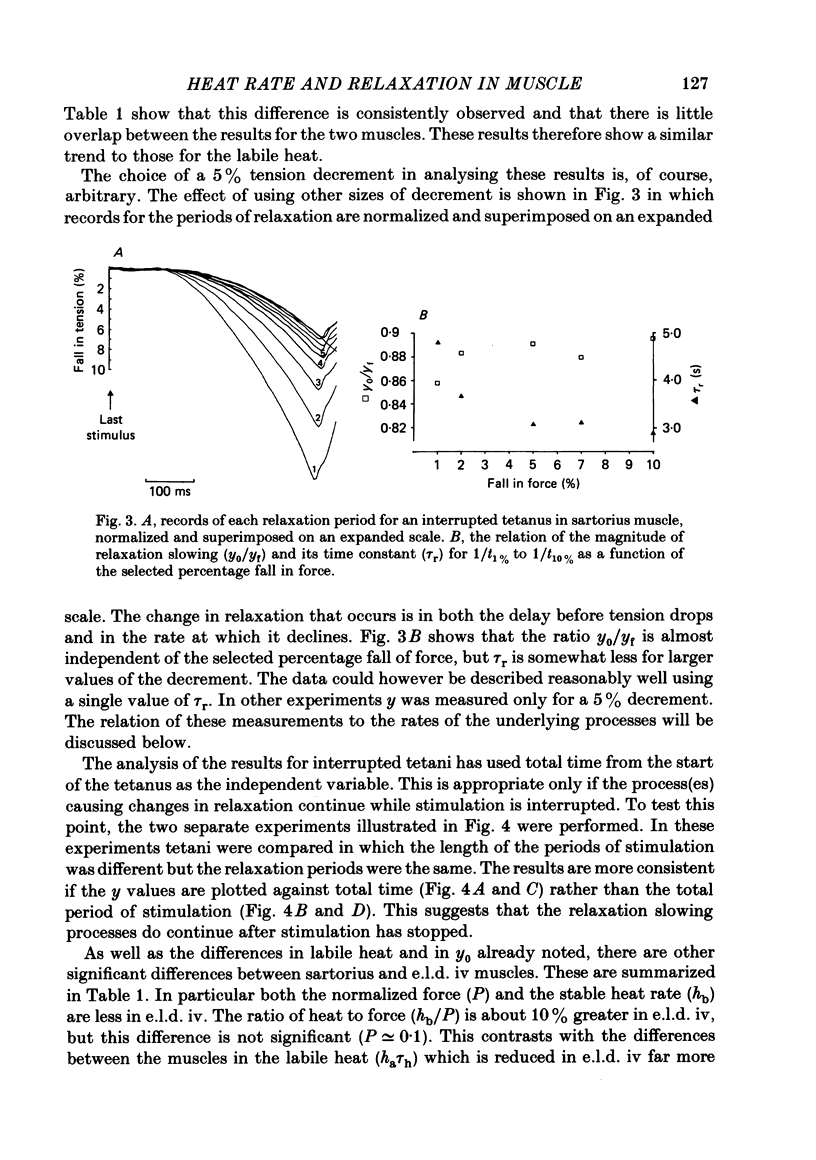
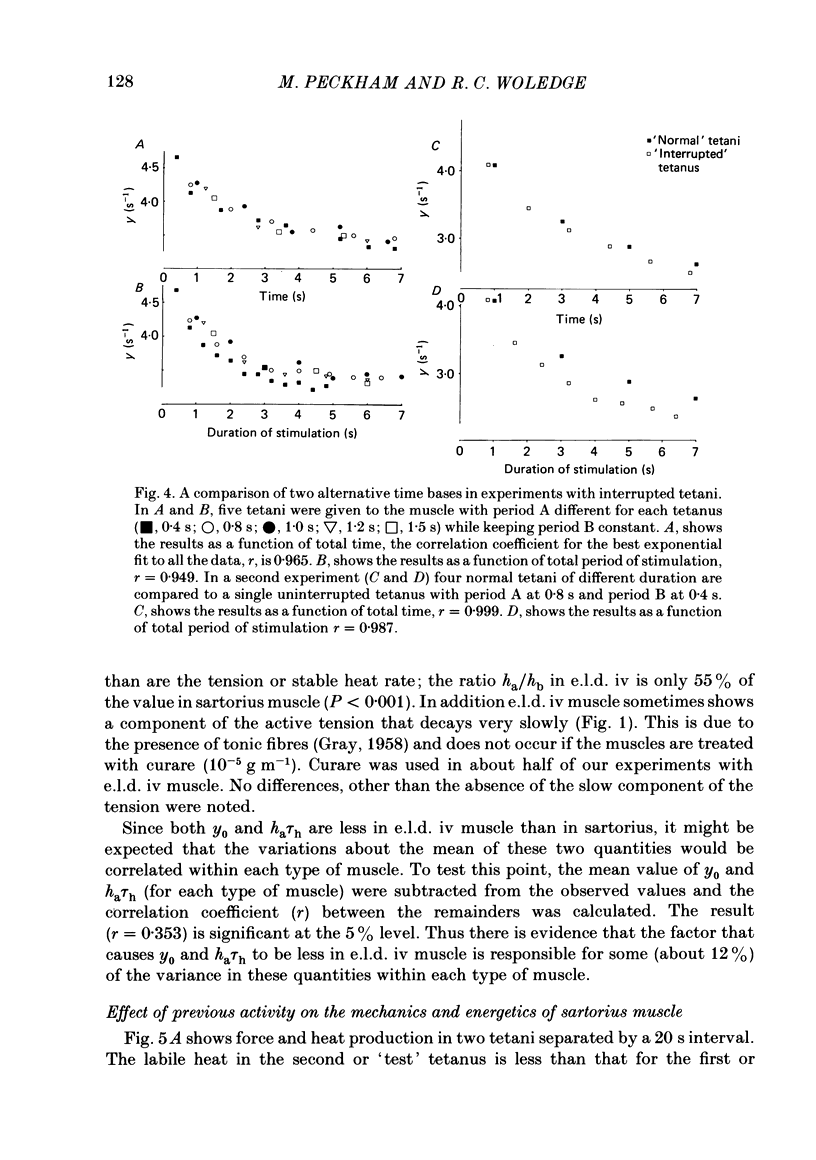
Abstract
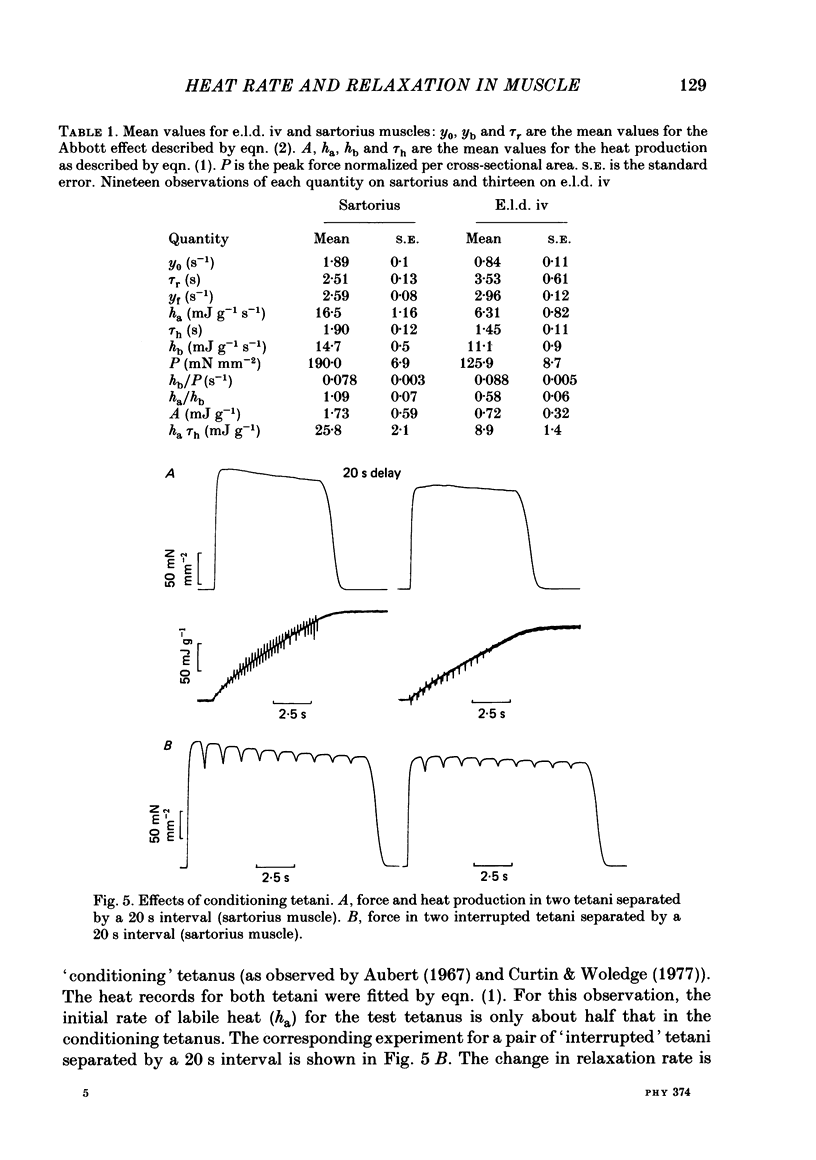
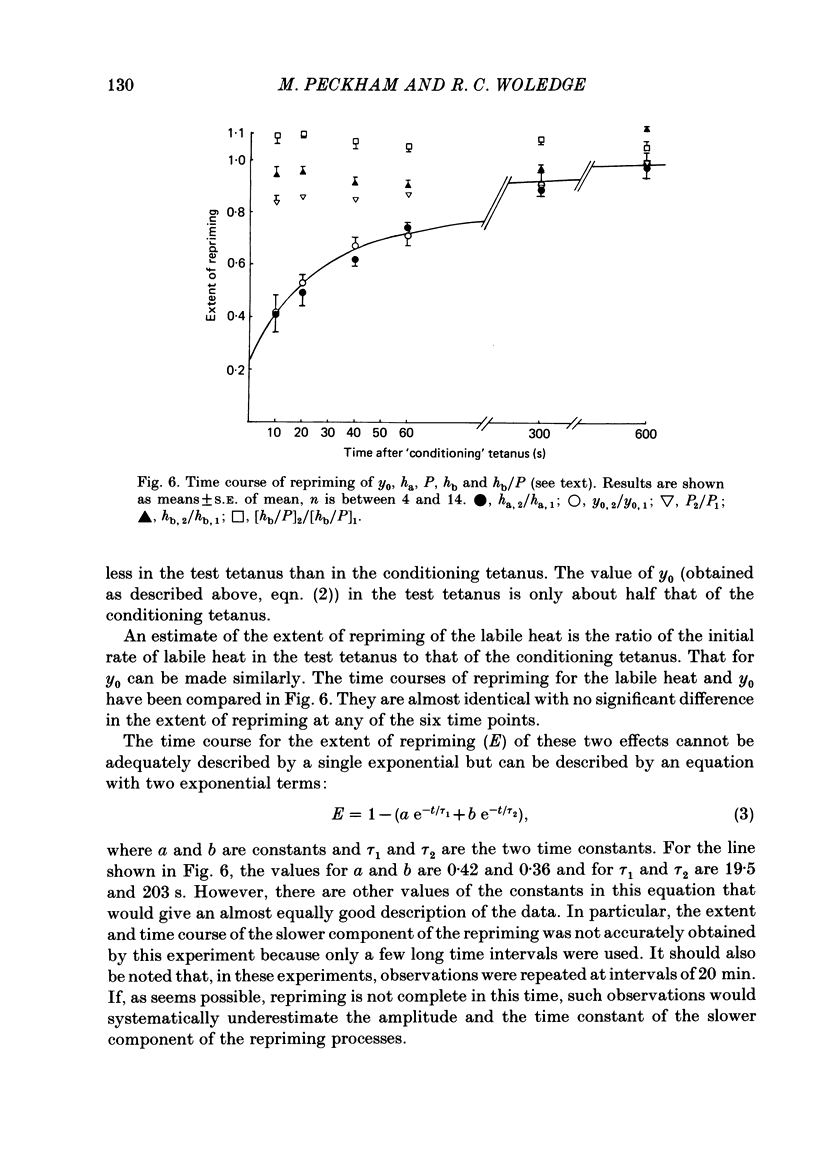
Observations were made of the labile heat and the progressive slowing of relaxation as a function of tetanus duration (Abbott effect) during isometric tetani of frog extensor longus digiti IV (e.l.d. iv) and sartorius muscle. Both the labile heat and slowing of relaxation are less marked in e.l.d. iv than in sartorius muscle. Both effects are depressed to the same extent in the second of two closely spaced tetani in sartorius muscle. The repriming of both effects follows the same time course in sartorius muscle. The hypothesis is discussed that both effects result from binding of calcium to parvalbumin during a tetanus, and that their repriming is due to the removal of calcium from parvalbumin by the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT B. C. The heat production associated with the maintenance of a prolonged contraction and the extra heat produced during large shortening. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):438–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. A comparison of the energy balance in two successive isometric tetani of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):455–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. Chemical change and energy production during contraction of frog muscle: how are their time courses related? J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:353–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. Energy changes and muscular contraction. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jul;58(3):690–761. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.3.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The structures of fast and slow muscle fibres in the frog. J Anat. 1958 Oct;92(4):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M. Relaxation of vertebrate skeletal muscle. A synthesis of the biochemical and physiological approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 3;811(2):97–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(85)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin-rey C., Gerday C. Parvalbumins from frog skeletal muscle (Rana temporaria L.). Isolation and characterization. Structural modifications associated with calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsher E., Kean C. J. Skeletal muscle energetics and metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:93–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell B. R., Kretzschmar M., Woledge R. C. Length and tension transducers. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):10P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar K. M., Wilkie D. R. The use of the Peltier effect for simple and accurate calibration of thermoelectric devices. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Aug 19;190(1100):315–321. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulieri L. A., Luhr G., Trefry J., Alpert N. R. Metal-film thermopiles for use with rabbit right ventricular papillary muscles. Am J Physiol. 1977 Nov;233(5):C146–C156. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.233.5.C146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Gonzalez-Serratos H. G., Shuman H., McClellan G., Somlyo A. P. Calcium release and ionic changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of tetanized muscle: an electron-probe study. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):577–594. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


