Abstract
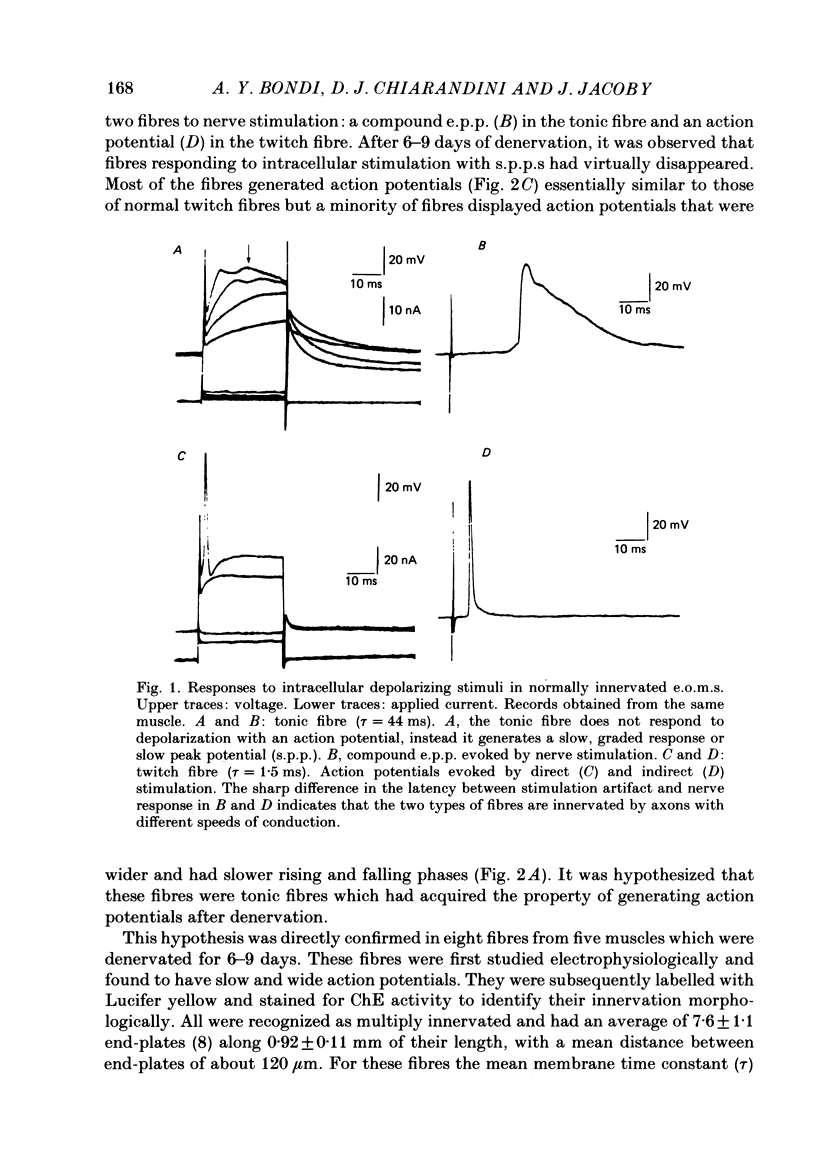
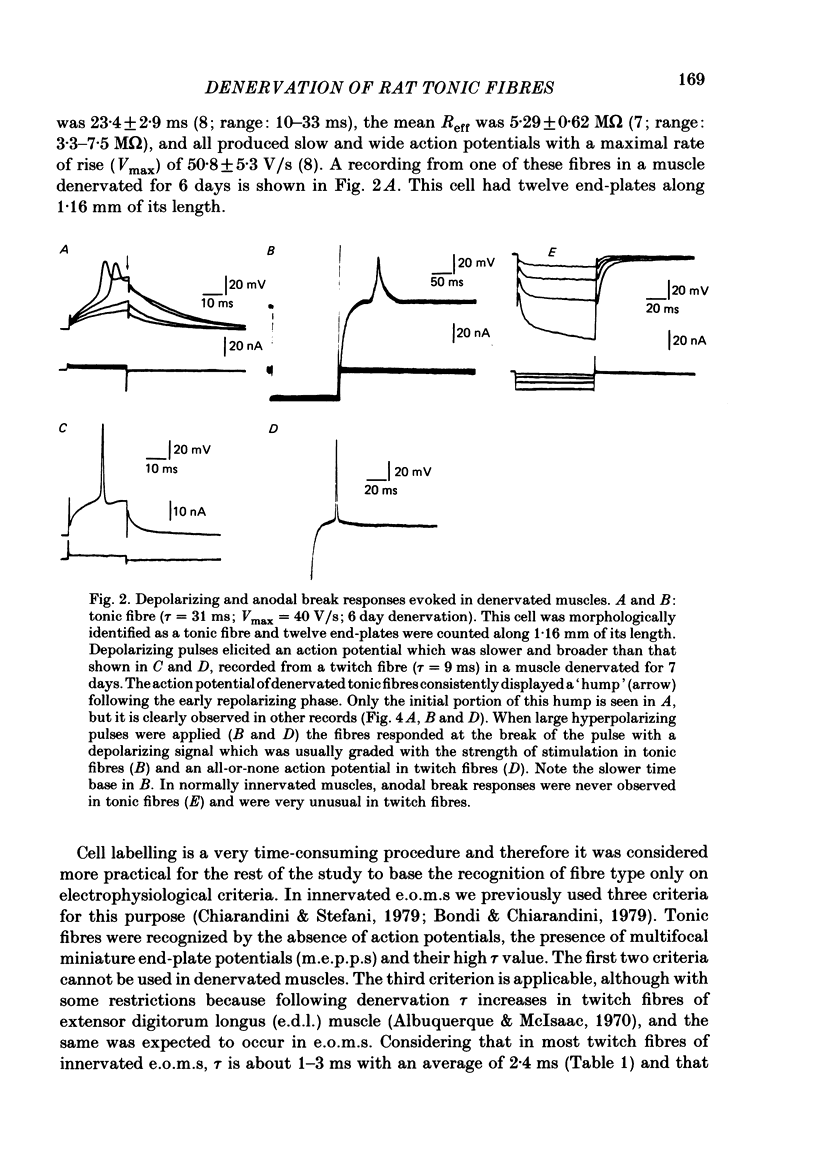
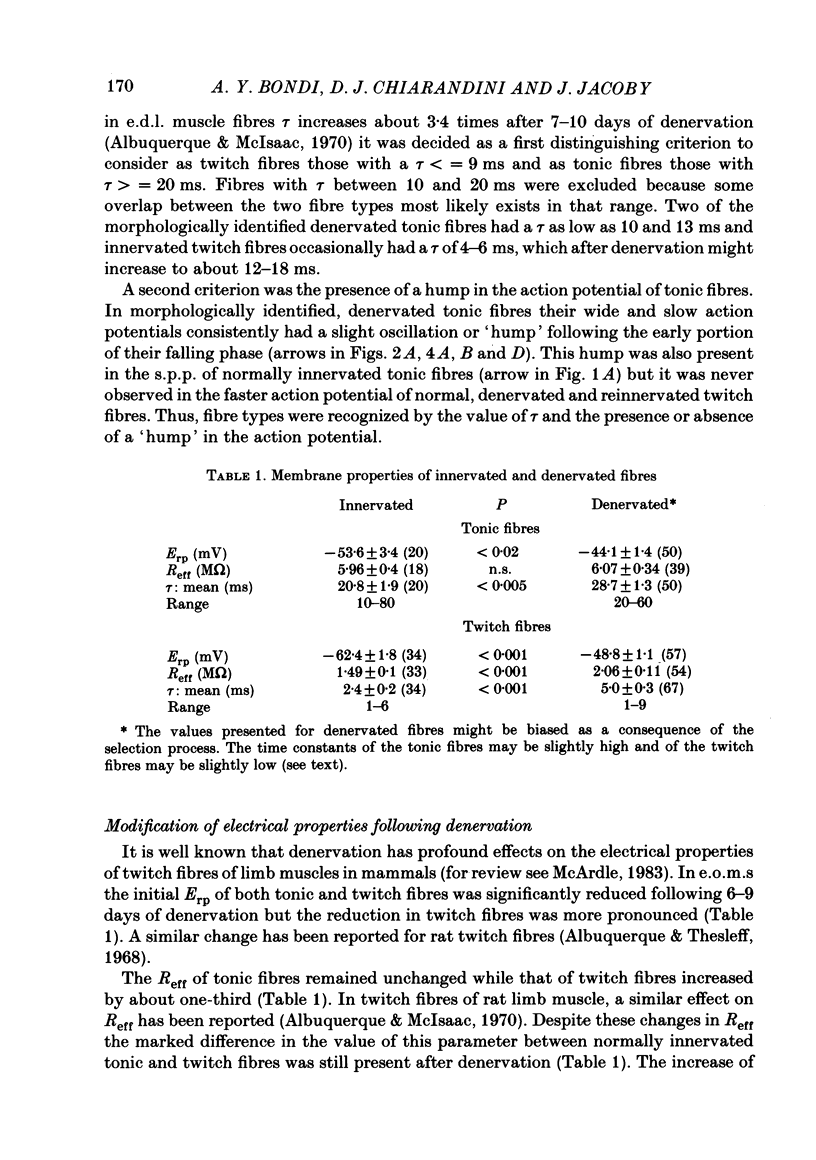
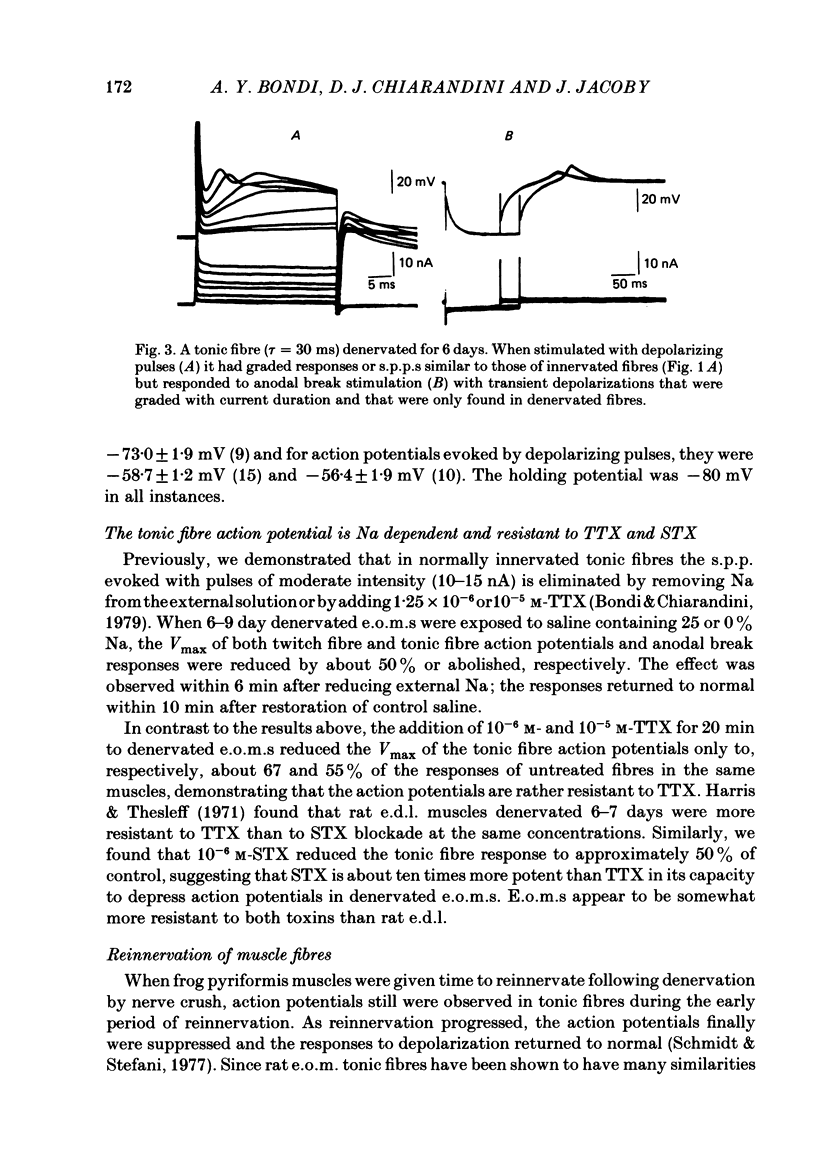
The effects of denervation by nerve section on the electrical properties of tonic and twitch fibres of rat extraocular muscles were examined. Normally innervated tonic fibres lack action potentials. Upon direct stimulation they generate graded, voltage-dependent responses or slow peak potentials (s.p.p.s). However, one week after denervation the s.p.p.s are transformed into action potentials which are slower and broader than those of twitch fibres. The action potentials are Na dependent and partially resistant to blockade with 10(-5) M-tetrodotoxin and 10(-6) M-saxitoxin. Changing the holding potential of the fibres from -80 mV to more negative levels increases the maximal rate of rise of the action potential. This effect is not observed on the s.p.p.s of normally innervated fibres. Following denervation the resting potential of tonic and twitch fibres becomes about 10-15 mV less negative. In denervated muscles stimulation with pulses of hyperpolarizing current evokes graded responses in tonic fibres and action potentials in twitch fibres. In normally innervated muscles, these anodal break responses are never observed in tonic fibres and are very rare in twitch fibres. By two weeks after nerve section, reinnervation is present. The action potentials of tonic fibres are still present but stronger stimulation is needed to evoke anodal break responses. By three weeks, direct stimulation of tonic fibres evokes normal s.p.p.s in about 25% of the studied fibres and action potentials in the rest. By four weeks, most tonic fibres have lost the action potential but small anodal break responses can be evoked in most. It is suggested that following denervation a new population of Na channels appears in tonic fibres. The properties of these channels are different from those of the channels normally present in innervated tonic fibres but they are in some ways similar to those of the channels which appear in twitch fibres following denervation.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., McIsaac R. J. Fast and slow mammalian muscles after denervation. Exp Neurol. 1970 Jan;26(1):183–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Thesleff S. A comparative study of membrane properties of innervated and chronically denervated fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Aug;73(4):471–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1968.tb10886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Lateral distribution of sodium and potassium channels in frog skeletal muscle: measurements with a patch-clamp technique. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:261–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE W., GINSBORG B. L. The electrical properties of the slow muscle fibre membrane. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):586–598. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bay C. M., Strichartz G. R. Saxitoxin binding to sodium channels of rat skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:89–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondi A. Y., Chiarandini D. J. Ionic basis for electrical properties of tonic fibres in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:273–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondi A. Y., Chiarandini D. J. Morphologic and electrophysiologic identification of multiply innervated fibers in rat extraocular muscles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1983 Apr;24(4):516–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmignoto G., Finesso M., Siliprandi R., Gorio A. Muscle reinnervation--I. Restoration of transmitter release mechanisms. Neuroscience. 1983 Mar;8(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J. Activation of two types of fibres in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):199–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Davidowitz J. Structure and function of extraocular muscle fibers. Curr Top Eye Res. 1979;1:91–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarandini D. J., Stefani E. Electrophysiological identification of two types of fibres in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):453–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A., PILAR G. SLOW FIBRES IN THE EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:780–798. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Studies on tetrodotoxin resistant action potentials in denervated skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Nov;83(3):382–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Small-nerve junctional potentials; the distribution of small motor nerves to frog skeletal muscle, and the membrane characteristics of the fibres they innervate. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):289–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. W., Ward M. R. Anode break excitation in denervated rat skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):413–420. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle J. J. Molecular aspects of the trophic influence of nerve on muscle. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;21(3):135–198. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Induction of the action potential mechanism in slow muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):737–754. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS J. G. The electrical properties of denervated skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Jan 27;131(1):1–12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappone P. A. Voltage-clamp experiments in normal and denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:377–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins N. Cation movements in normal and short-term denervated rat fast twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):605–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Stefani E. Action potentials in slow muscle fibres of the frog during regeneration of motor nerves. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):507–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Steinbach A. B. Resting potential and electrical properties of frog slow muscle fibres. Effect of different external solutions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):383–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


