Abstract
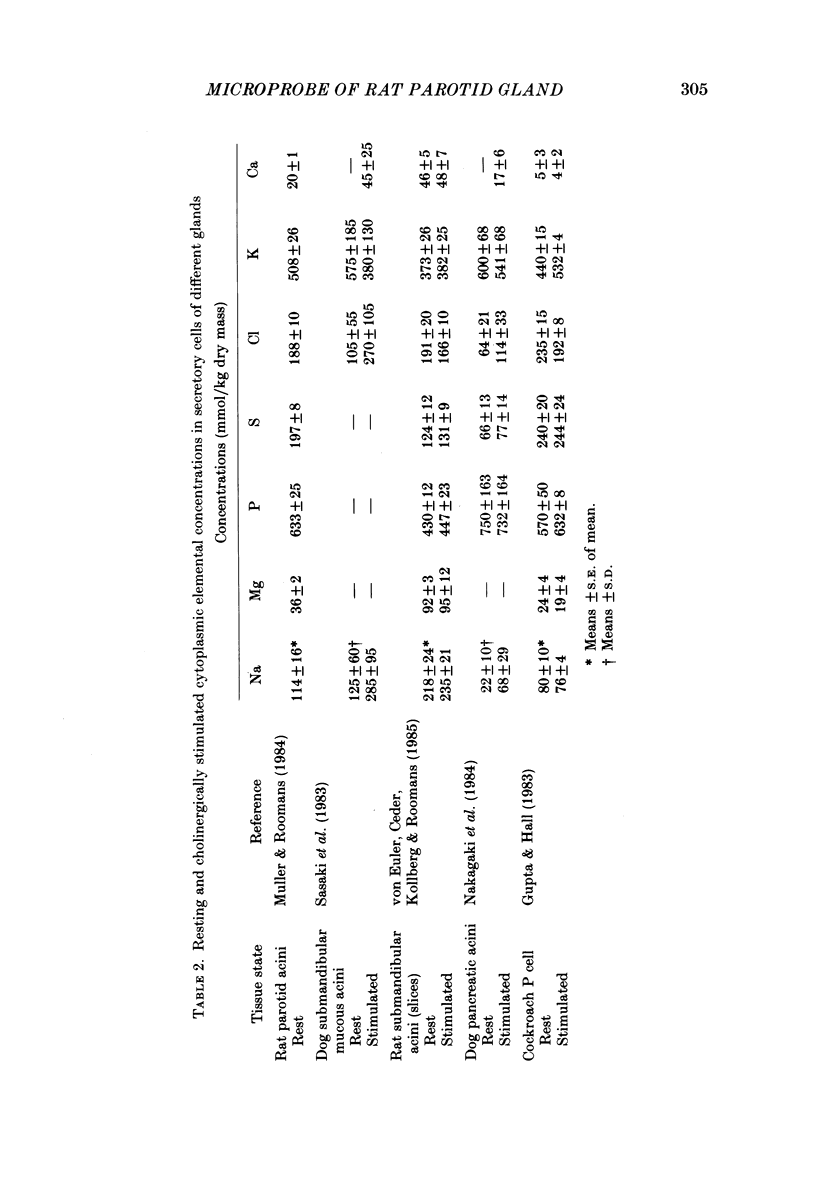
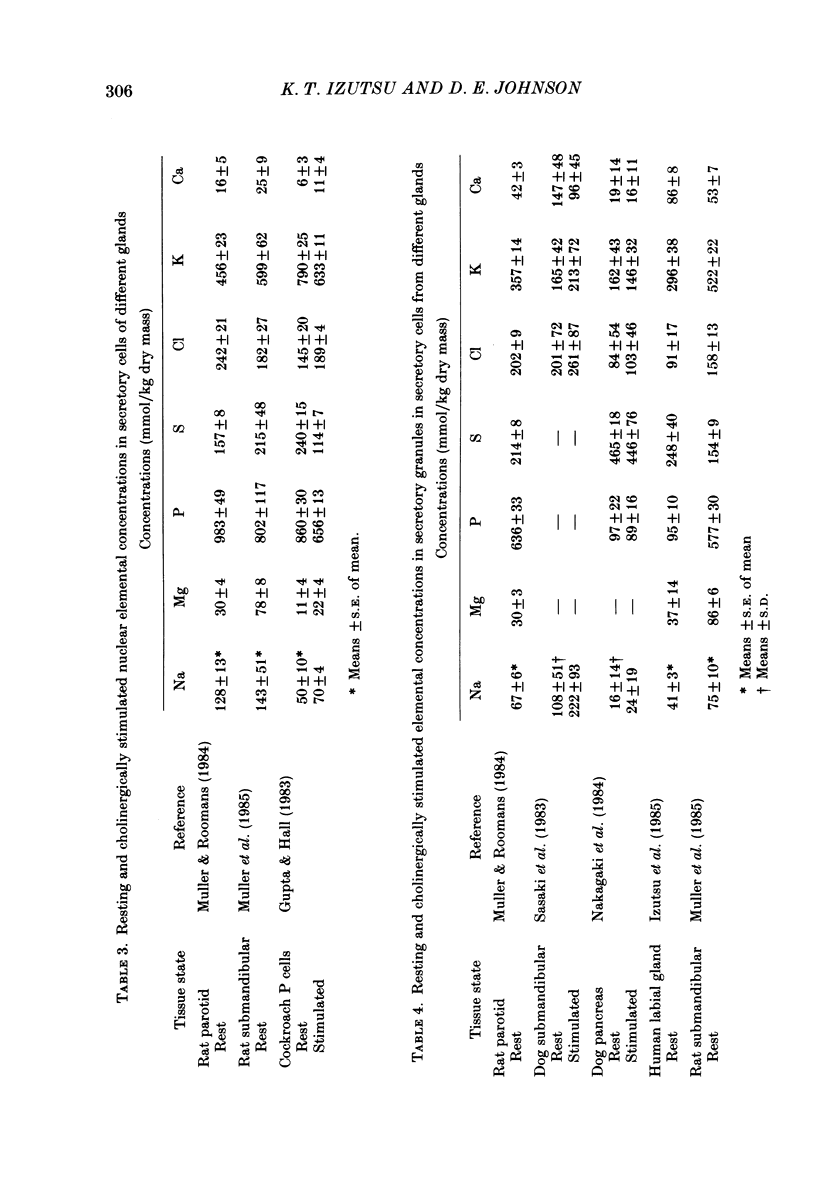
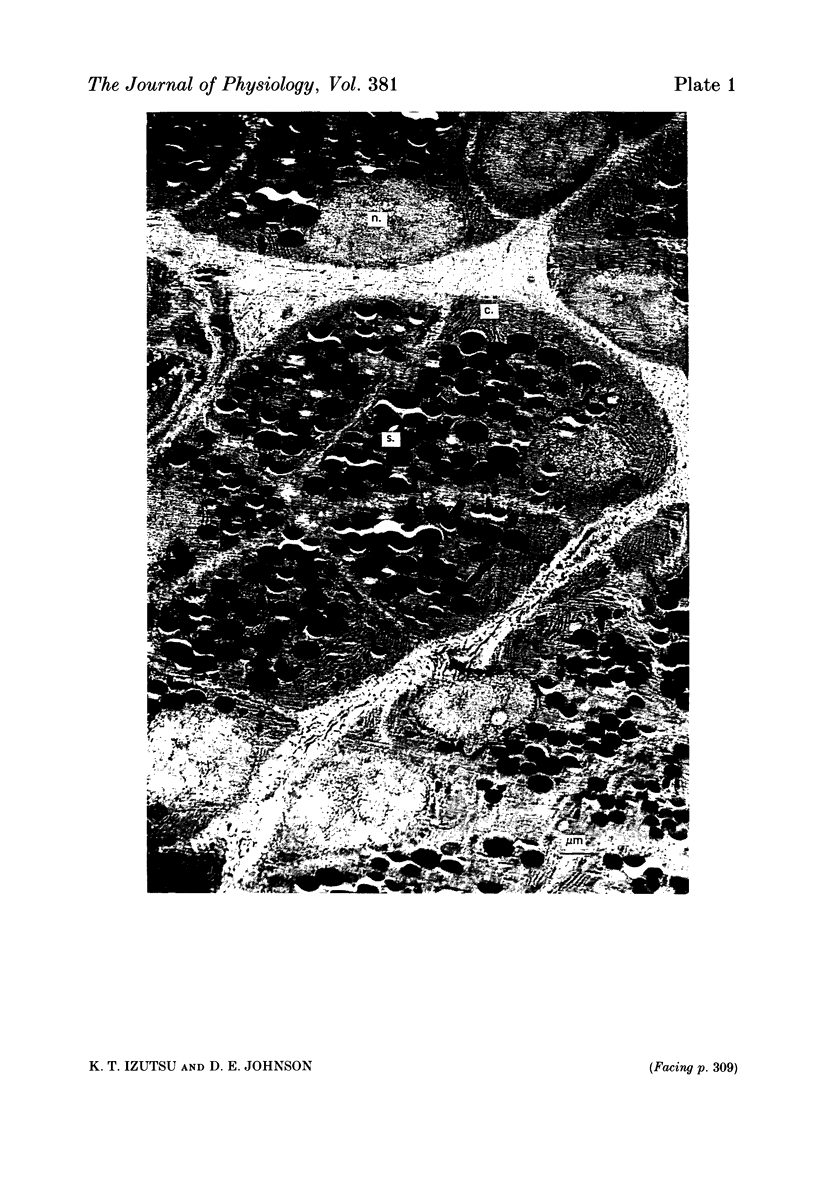
1. Quantitative electron microprobe analysis was used to measure elemental dry weight concentrations in cytoplasm, secretory granules and nuclei of resting and pilocarpine-stimulated rat parotid gland acinar cells. 2. Secretory granules in resting cells had lower concentrations of Na, Mg, P, Cl and K, and higher concentrations of S and Ca than cytoplasm or nuclei. Nuclei in resting cells had lower S and higher K concentrations than cytoplasm. 3. Three major pilocarpine-related changes were found: (i) cytoplasmic dry weight concentrations of Na and Ca increased and the concentration of K decreased, (ii) the nuclear concentration of Na increased while that of K decreased and (iii) the concentrations of Na and Cl increased in secretory granules. 4. These results indicate that the nuclear, and cytoplasmic compartments have different mechanisms for regulating their elemental concentrations relative to the secretory granules. 5. The present results are largely consistent with X-ray microanalysis results from the pilocarpine-stimulated dog submandibular gland.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg N. B., Austin B. P. Intracellular transport of sulfated macromolecules in parotid acinar cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jan 26;165(2):215–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00226660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M. Potassium activities in epithelia. Fed Proc. 1980 Sep;39(11):2865–2870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta B. L., Hall T. A. Ionic distribution in dopamine-stimulated NaCl fluid-secreting cockroach salivary glands. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):R176–R186. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.2.R176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izutsu K., Johnson D., Schubert M., Wang E., Ramsey B., Tamarin A., Truelove E., Ensign W., Young M. Electron microprobe analysis of human labial gland secretory granules in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1951–1956. doi: 10.1172/JCI111911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Johnson R. T., Gupta B. L., Hall T. A. The quantitative measurement of electrolyte elements in nuclei of maturing erythrocytes of chick embryo using electron-probe X-ray microanalysis. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:67–85. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. R., Quissell D. O. Potassium release from the rat submaxillary gland in vitro. II. Induction by parasympathomimetic secretagogues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Dec;199(3):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. M., Grundin T. G., Roomans G. M. Effects of reserpine and isoproterenol on elemental distribution in submandibular gland of rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Apr;123(4):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. M., Roomans G. M. X-ray microanalysis of the rat parotid gland after chronic sympathectomimetic stimulation. Exp Mol Pathol. 1984 Dec;41(3):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(84)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagaki I., Sasaki S., Shiguma M., Imai Y. Distribution of elements in the pancreatic exocrine cells determined by electron probe X-ray microanalysis. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Aug;401(4):340–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00584333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty J., Stark R. J., Crane S. J., Brugge K. L. Changes in cytosolic calcium during cholinergic and adrenergic stimulation of the parotid salivary gland. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Aug;398(3):241–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00657159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen J. H., Bledsoe S. W. Salivary gland K+ transport: in vivo studies with K+-specific microelectrodes. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E79–E83. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen J. H., Oakley B., 2nd Intracellular potassium ion activity in resting and stimulated mouse pancreas and submandibular gland. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Mar 26;204(1154):99–104. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Parod R. J. Calcium-mediated effects of carbachol on cation pumping and Na uptake in rat parotid gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 May;205(2):449–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quissell D. O. Secretory response of dispersed rat submandibular cells. I. Potassium release. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):C90–C98. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.238.3.C90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggio H. A., Palade G. E. Sulfated compounds in the zymogen granules of the guinea pig pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):288–314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. C., Izutsu K. T., Truelove E. L., Menard T. W., Anderson M. W., Morton T. H., Siegel I. A. Rat parotid gland pathophysiology following 137Cs irradiation. Radiat Res. 1982 May;90(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roomans G. M., Wei X., Ceder O., Kollberg H. The reserpinized rat in the study of cystic fibrosis: x-ray microanalysis of submandibular gland and pancreas. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1982 Jul-Sep;3(3):285–293. doi: 10.3109/01913128209016654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEYER L. H., SCHNEYER C. A. Electrolyte and inulin spaces of rat salivary glands and pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1960 Oct;199:649–652. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.4.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Nakagaki I., Mori H., Imai Y. Intracellular calcium store and transport of elements in acinar cells of the salivary gland determined by electron probe X-ray microanalysis. Jpn J Physiol. 1983;33(1):69–83. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.33.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneyer C. A., Hall H. D. Comparison of rat salivas evoked by auriculo-temporal and pilocarpine stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):484–488. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneyer L. H., Young J. A., Schneyer C. A. Salivary secretion of electrolytes. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):720–777. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Quantitative electron probe microanalysis of biological thin sections: methods and validity. Ultramicroscopy. 1976 Sep-Oct;1(4):317–339. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(76)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Shuman H. Electron probe analysis of vascular smooth muscle. Composition of mitochondria, nuclei, and cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):316–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Schramm M. Calcium and the exportable protein in rat parotid gland. Parallel subcellular distribution and concomitant secretion. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler A. M., Ceder O., Kollberg H., Roomans G. M. Effect of chronic treatment with cystic fibrosis fibroblast medium on rat submandibular gland acinar cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Aug;43(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]