Abstract
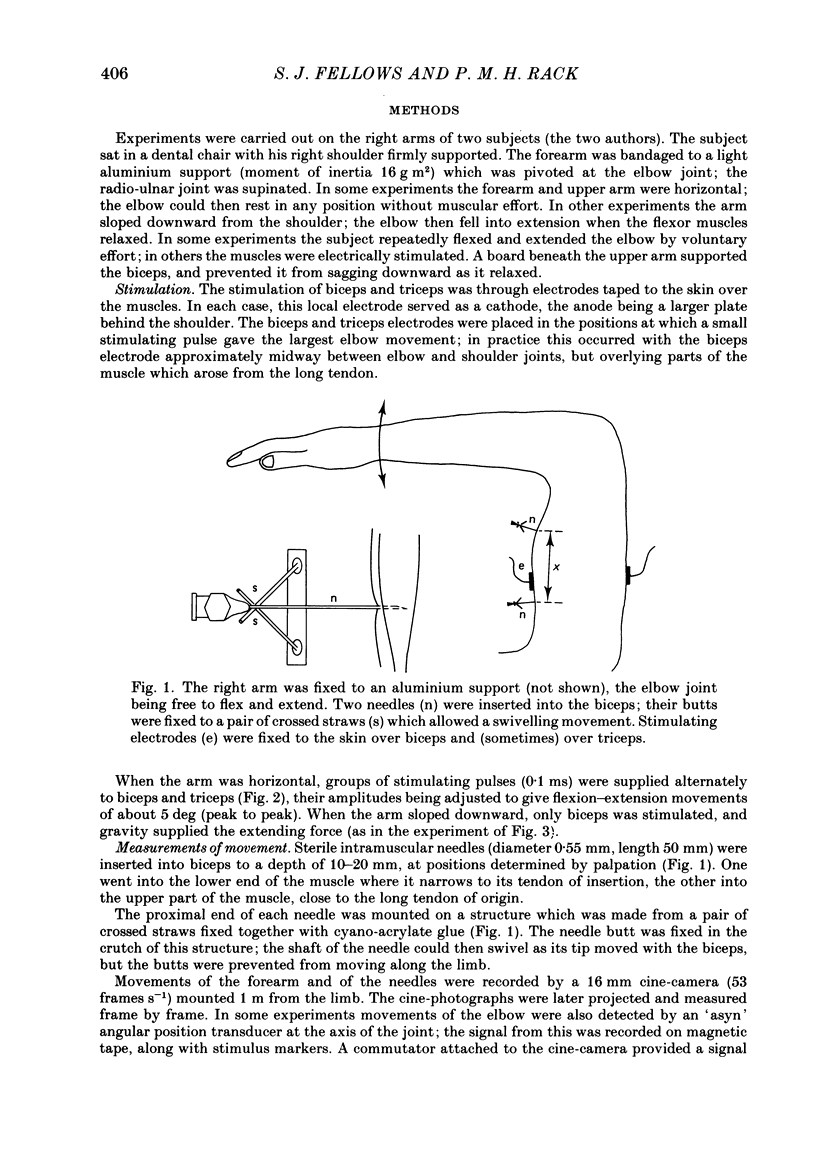
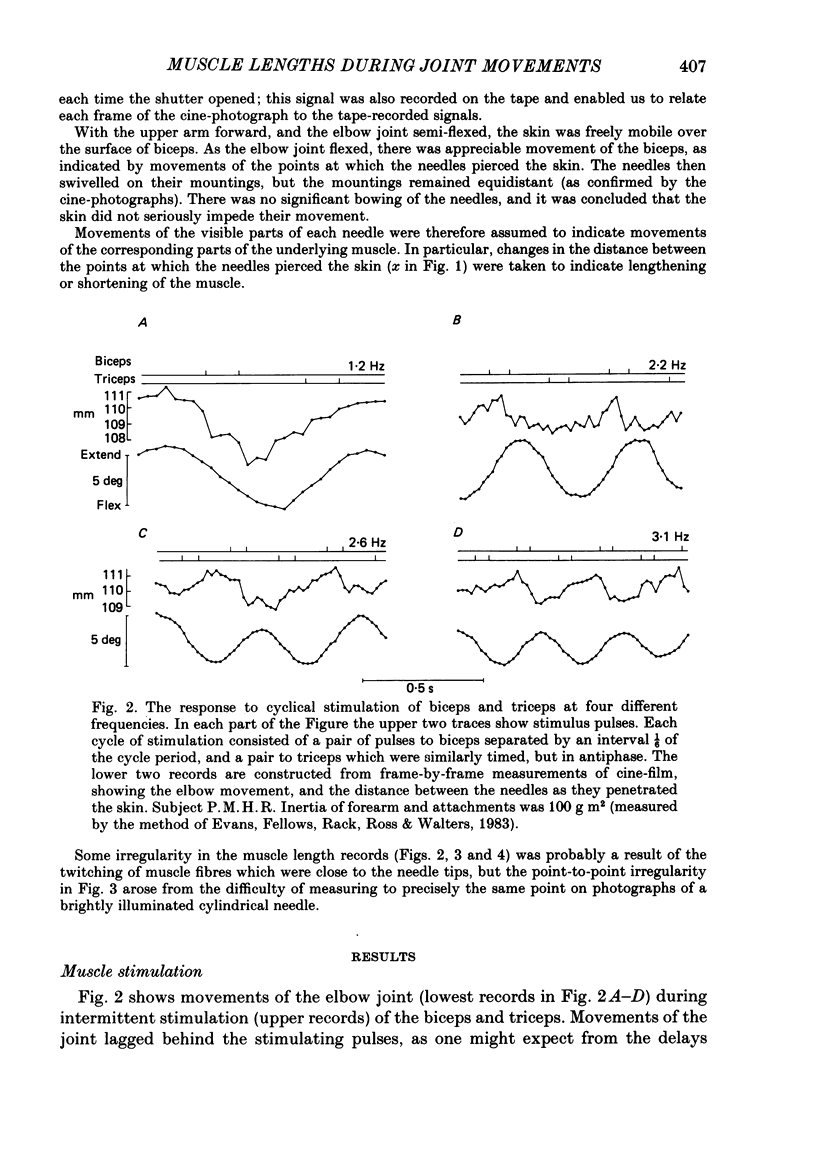
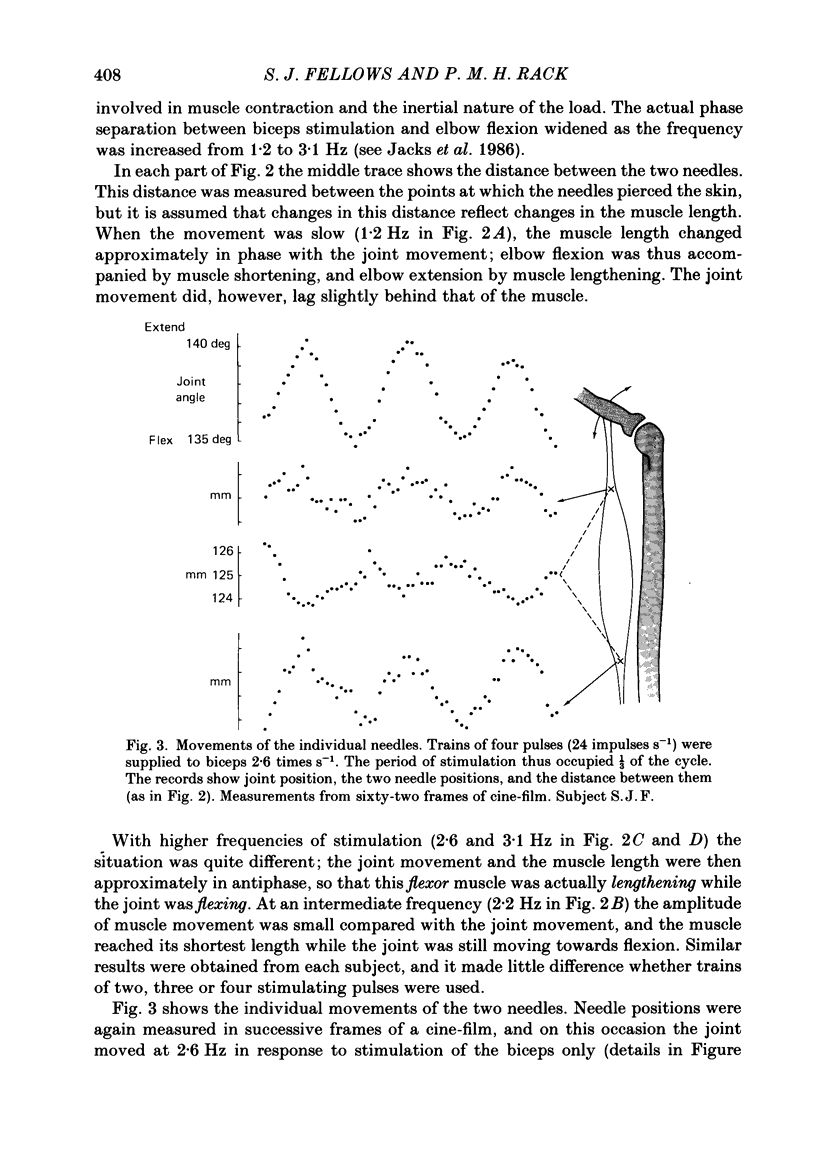
1. Needles inserted into the biceps move with the muscle as the elbow flexes or extends. Pairs of needles were used to indicate changes in length of the muscle fibres. 2. During low-frequency flexion-extension movements the biceps lengthened as the joint extended. 3. When, however, joint movements at greater than 2.2 Hz were maintained by external electrical stimulation of triceps and the long head of biceps, or of biceps alone, the biceps lengthened and shortened in antiphase to the joint movement. The elastic properties of the biceps tendons then combined with the mass of the forearm as a spring-mass system whose natural frequency was about 2.2 Hz. 4. No such phase reversal appeared during voluntary elbow movements at frequencies up to 5 Hz. It was concluded that the combined tendons of biceps, brachialis and brachioradialis made a much less compliant muscle-to-bone coupling. 5. The results are discussed in relation to possible tremor mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd C. A., Shennan D. B. Human placental sulphate transport: studies on chorionic trophoblast brush border membrane vesicles. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:15–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant J., Keller A., Baer E., Litt M., Arridge R. G. Collagen; ultrastructure and its relation to mechanical properties as a function of ageing. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Mar 14;180(1060):293–315. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. M., Fellows S. J., Rack P. M., Ross H. F., Walters D. K. Response of the normal human ankle joint to imposed sinusoidal movements. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:483–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ker R. F. Dynamic tensile properties of the plantaris tendon of sheep (Ovis aries). J Exp Biol. 1981 Aug;93:283–302. doi: 10.1242/jeb.93.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]