Abstract
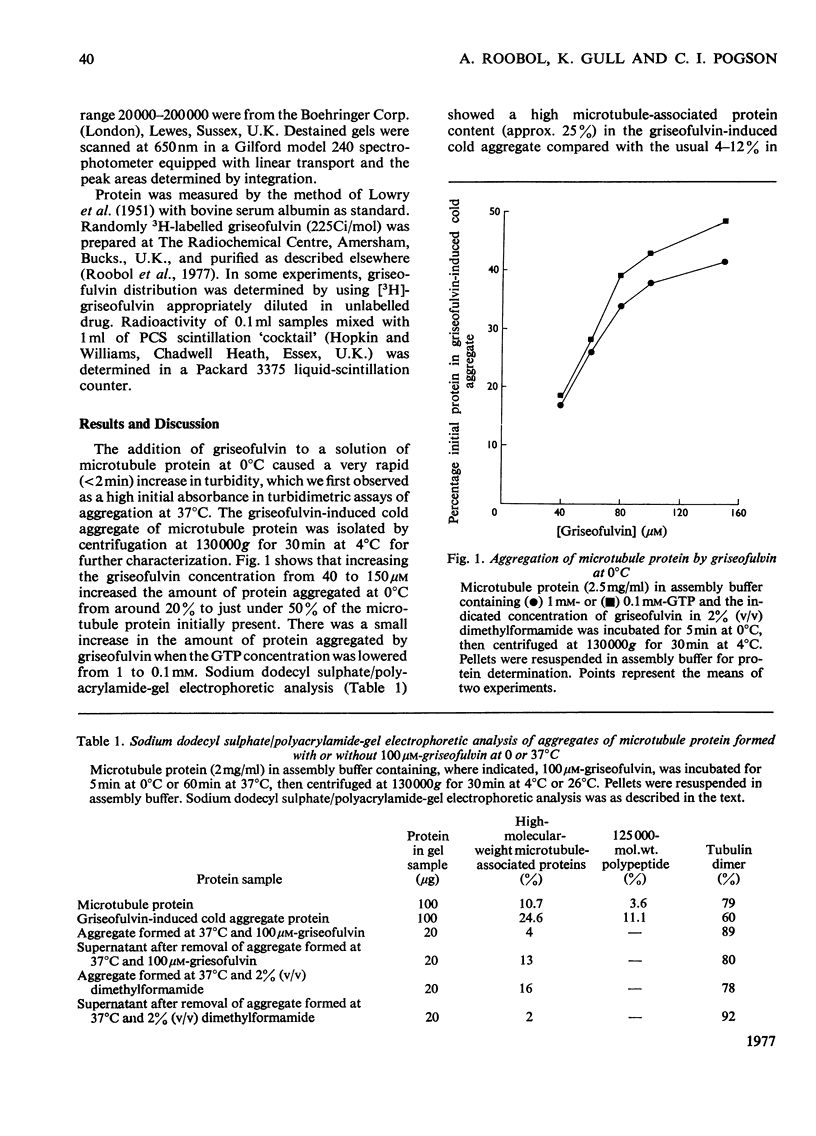
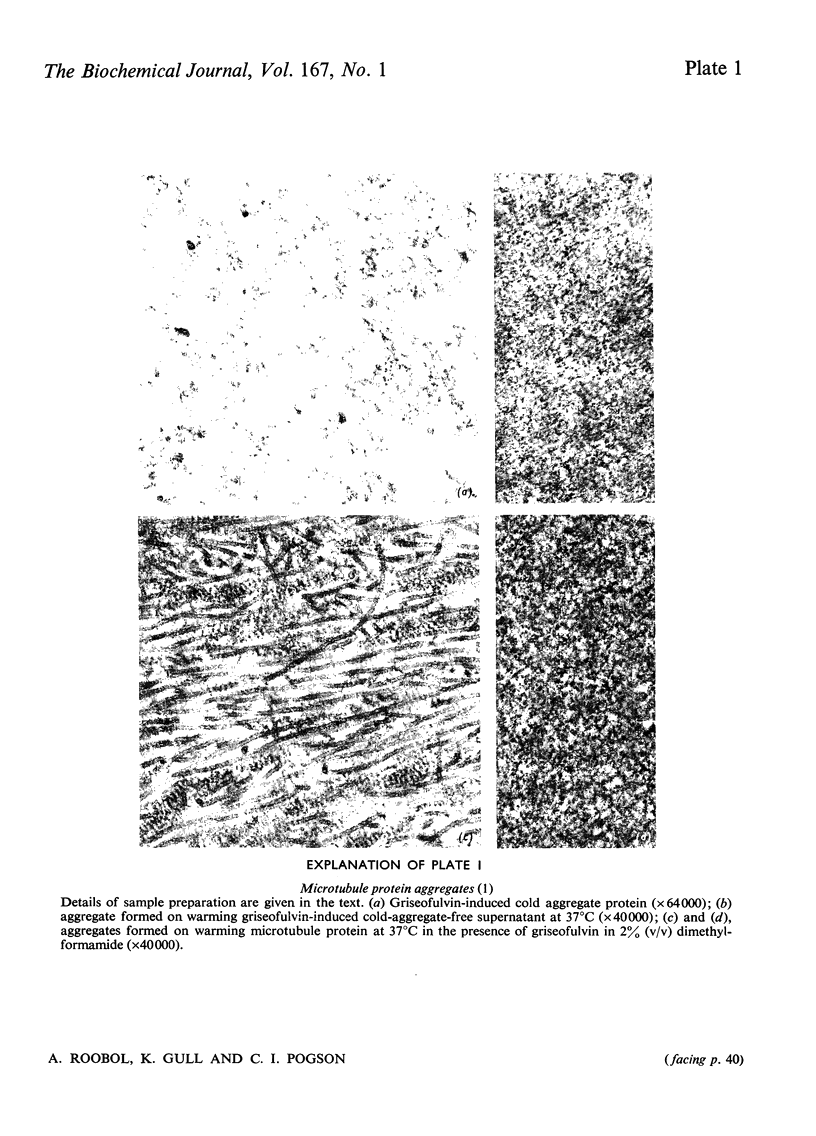
Griseofulvin (7-chloro-2',4,6-trimethoxy-6'-methylspiro[benzofuran-2(3H),1'-[2]cyclohexene]-3,4'-dione) induces aggregation of microtubule protein at 0 degrees C. This aggregate contains approx. 90% of the microtubule-associated proteins originally present in the microtubule protein. The supernatant obtained after removal of the griseofulvin-induced aggregate does not form microtubules on warming at 37 degrees C. Addition of the griseofulvin-aggregated protein to this supernatant and warming to 37 degrees C gives rise to a limited amount of microtubule assembly. The possible involvement of griseofulvin-induced aggregation of microtubule protein at 0 degrees C in the inhibition by griseofulvin of microtubule assembly in vitro is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensch K. G., Malawista S. E. Microtubular crystals in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):95–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Marantz R., Wisniewski H., Shelanski M. Induction in vitro of microtubular crystals by vinca alkaloids. Science. 1969 Aug 1;165(3892):495–496. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3892.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloodgood R. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Initiation of brain tubulin assembly by a high molecular weight flagellar protein factor. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):322–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Marcum J. M., Olmsted J. B., Murphy D. B., Johnson K. A. Purification of tubulin and associated high molecular weight proteins from porcine brain and characterization of microtubule assembly in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:107–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. Vinblastine and microtubules. II. Characterization of two protein subunits from the isolated crystals. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Cantor C. R., Shelanski M. L. Turbidimetric studies of the in vitro assembly and disassembly of porcine neurotubules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):737–755. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskin F., Kramer S. B., Cantor C. R., Adelstein R., Shelanski M. L. A dynein-like protein associated with neurotubules. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 1;40(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Gull K., Pogson C. I. Inhibition by griseofulvin of microtubule assembly in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):248–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80539-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roobol A., Gull K., Pogson I. Evidence that griseofulvin binds to a microtubule associated protein. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Microtubule-associated proteins and the stimulation of tubulin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4497–4505. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventilla M., Cantor C. R., Shelanski M. L. Some features of the vinblastine-induced assembly of porcine tubulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warfield R. K., Bouck G. B. Microtubule-macrotubule transitions: intermediates after exposure to the mitotic inhibitor vinblastine. Science. 1974 Dec 27;186(4170):1219–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4170.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Wehland J., Herzog W. Griseofulvin interacts with microtubules both in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]