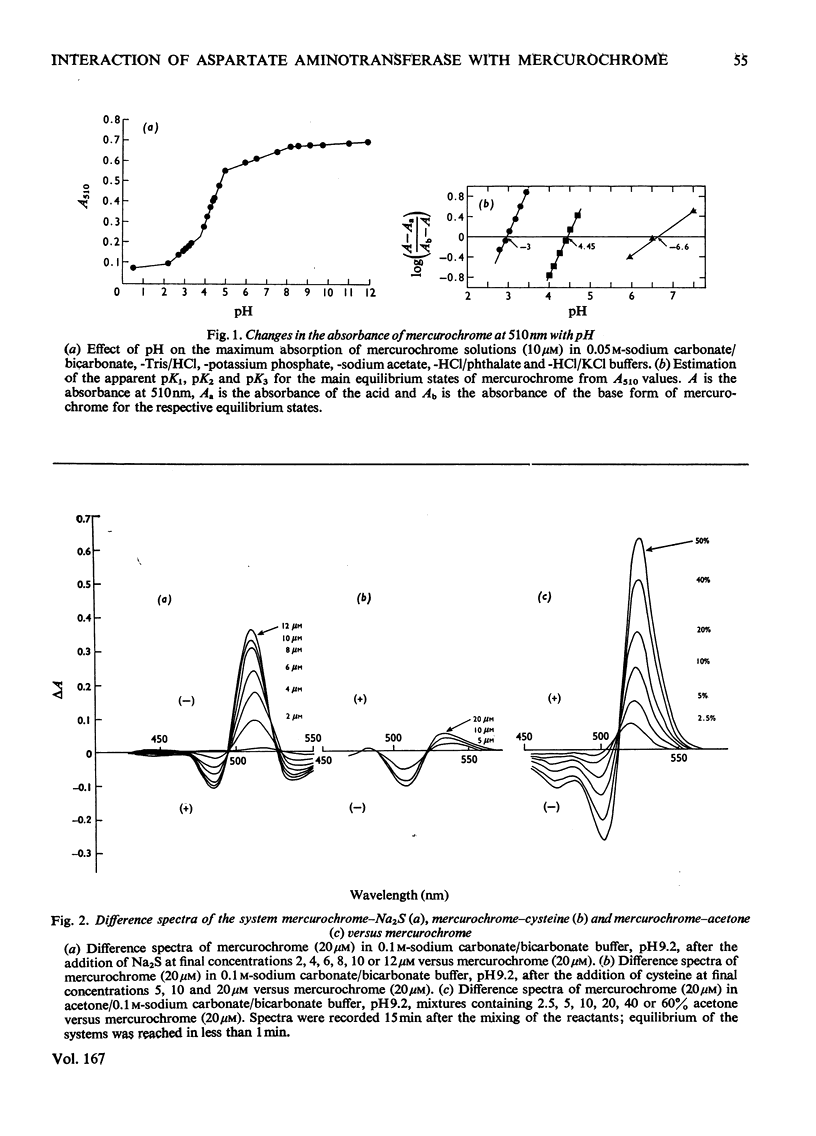
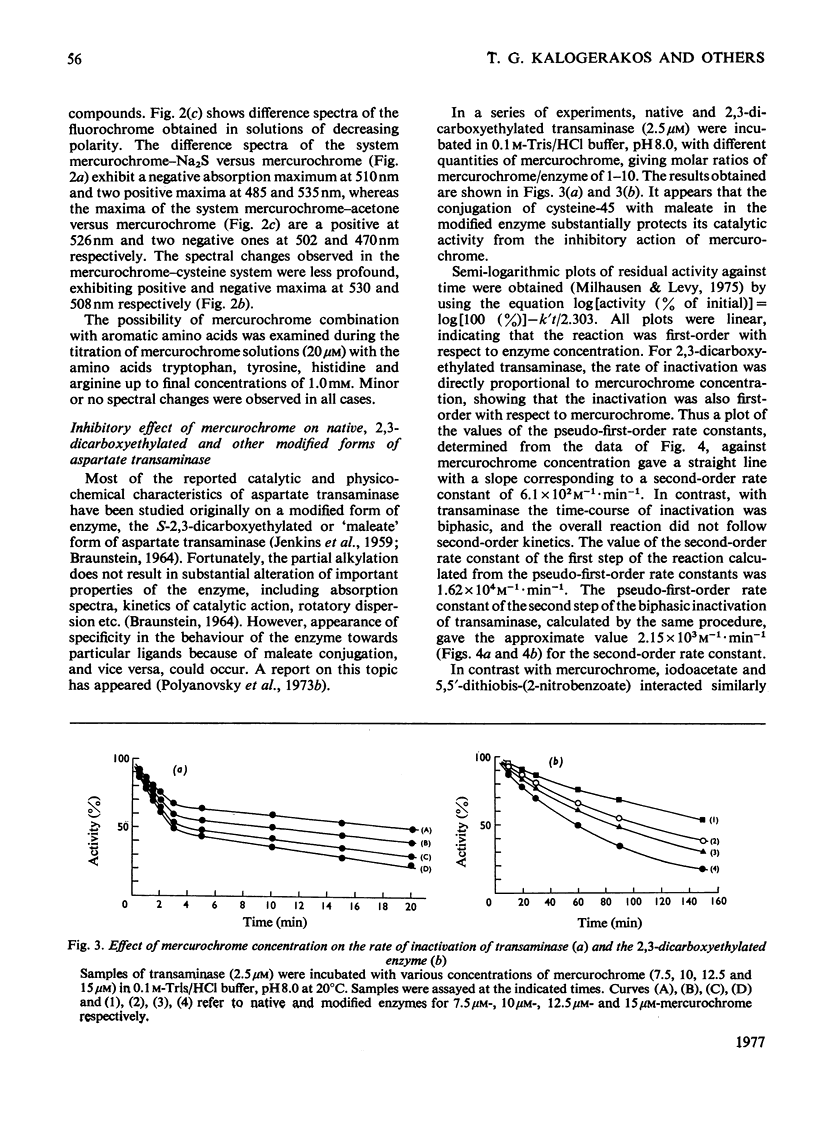
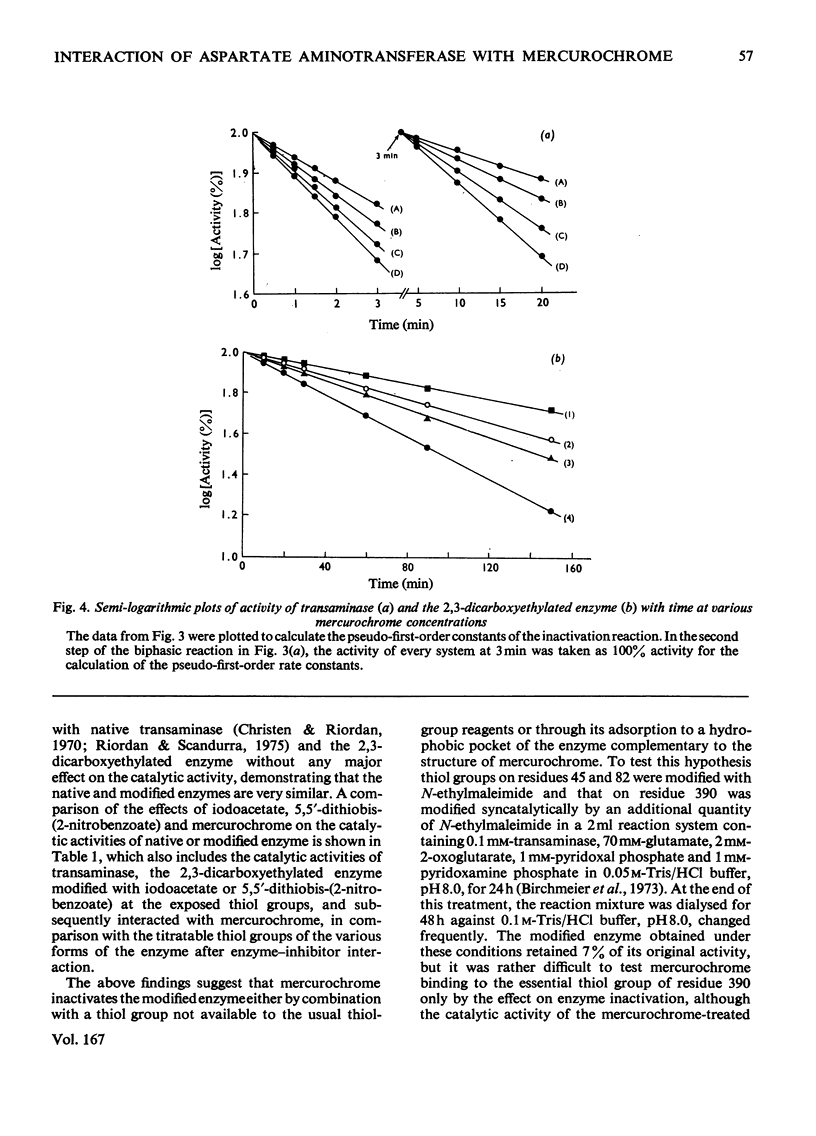
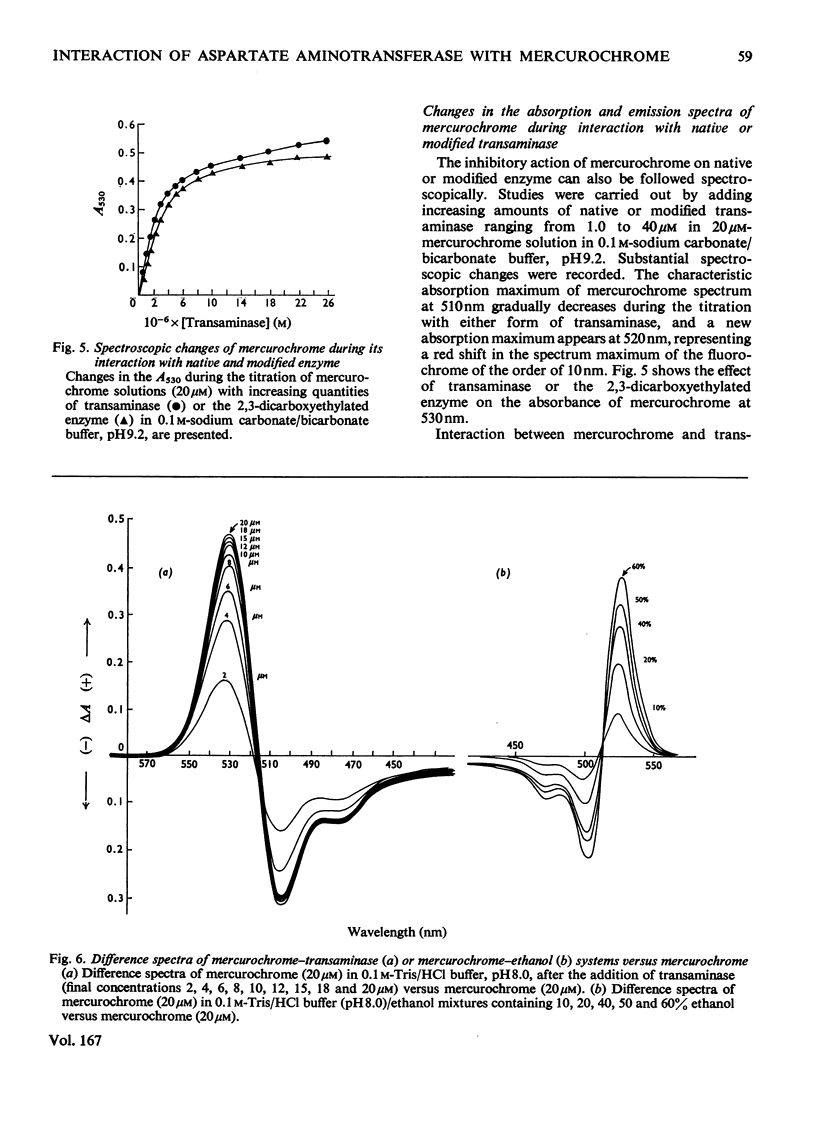
Abstract
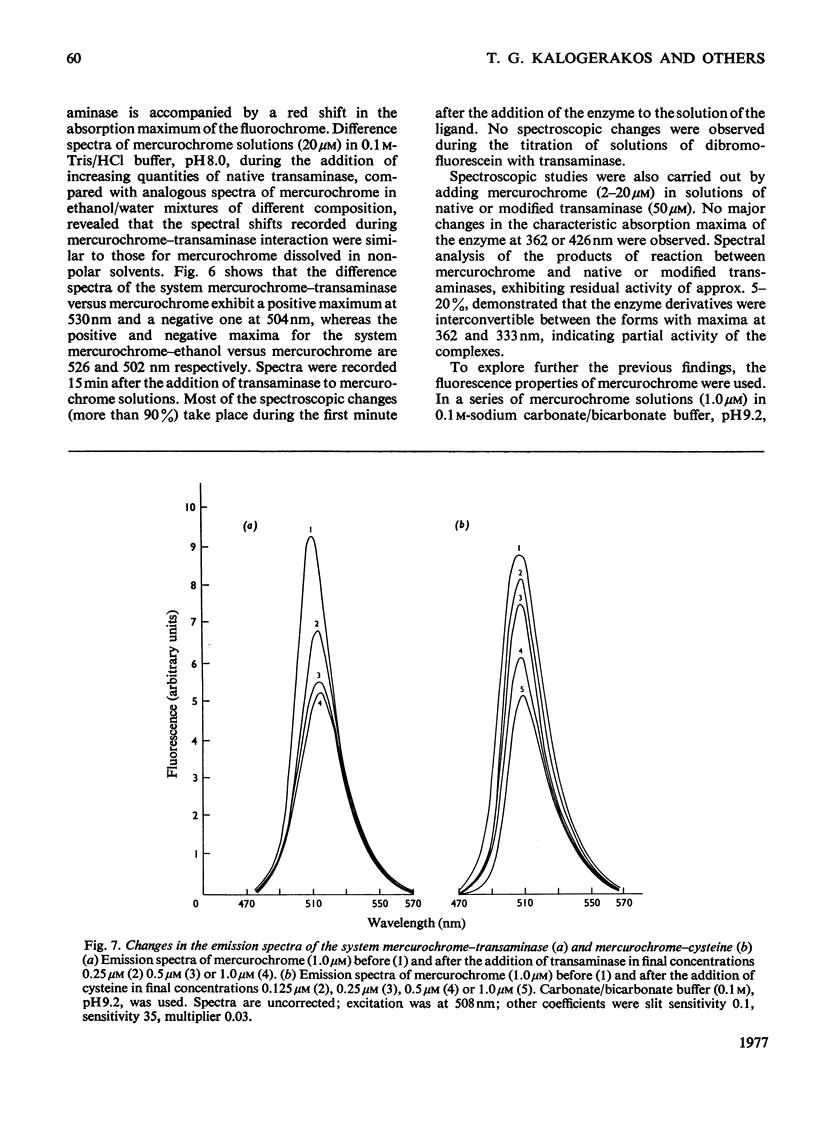
Mercurochrome strongly inhibits aspartate transaminase and 2,3-dicarboxyethylated aspartate transaminase. The native enzyme exhibits a biphasic time-course of inactivation by mercurochrome with second-order rate constants 1.62 x 10(4) M-1 - min-1 and 2.15 x 10(3) M-1 - min-1, whereas the modified enzyme is inactivated more slowly (second-order rate constant 6.1 x 10(2) M-1 - min-1) under the same conditions. The inhibitor inactivates native and modified enzyme in the absence as well as in the presence of substrates. Mercurochrome-transaminase interaction is accompanied by a red shift in the absorption maximum of the fluorochrome of about 10 nm. Difference spectra of the mercurochrome-enzyme system versus mercurochrome, compared with analogous spectra of mercurochrome-ethanol, revealed that the spectral shifts recorded during mercurochrome-transaminase interaction are similar to those that occur when mercurochrome is dissolved in non-polar solvents. Studies of mercurochrome complexes with native or modified transaminase, isolated by chromatography on Sephadex G-25, revealed that native transaminase is able to conjugate with four mercurochrome molecules per molecule, but the modified enzyme is able to conjugate with only two mercurochrome molecules per molecule.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUNSTEIN A. E. BINDING AND REACTIONS OF THE VITAMIN B6 COENZYME IN THE CATALYTIC CENTER OF ASPARTATE TRANSAMINASE. Vitam Horm. 1964;22:451–484. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier W., Wilson K. J., Christen P. Cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase: syncatalytic sulfhydryl group modification. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1751–1759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMMARATA P. S., COHEN P. P. Fractionation and properties of glutamic oxalacetic transaminase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen P., Riordan J. F. Syncatalytic modification of a functional tyrosyl residue in aspartate aminotransferase. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 21;9(15):3025–3034. doi: 10.1021/bi00817a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitropoulos C. G., Oikonomakos N. G., Karni-Katsadima I. A., Kalogerakos T. G., Evangelopoulos A. E. Experimental evidence for a hydrophobic active center of glutamic-aspartic transaminase. Specific interaction of holoenzyme and apoenzyme with two fluorescein derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):537–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES R. C., JENKINS W. T., FISCHER E. H. The site of binding of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate to heart glutamic-aspartic transaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1615–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS W. T., YPHANTIS D. A., SIZER I. W. Glutamic aspartic transaminase. I. Assay, purification, and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karni-Katsadimas I., Dimitropoulos C., Evangelopoulos A. E. Substrate induced changes in the reactivity of the sulfhydryl groups of aspartate transaminase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(1):50–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsiris K. D., Dimitropoulos C. G., Patramanis I. M., Pavlatos M. P., Evangelopoulos A. E. Isolation of antitransaminase antibodies with selective reactivity against transaminase or its tryptic hydrolysate. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May;27(1):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDLEY H. A study of the kinetics of the reaction between thiol compounds and choloracetamide. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:577–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0740577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Slebe J. C., Boettcher B., Relimpio A. M. Fluorine-19 as a covalent active site-directed magnetic resonance probe in aspartate transaminase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1853–1858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Carrion M., Turano C., Riva F., Fasella P. Evidence of a critical histidine residue in soluble aspartic aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1426–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola D. A., Morris J. W., Arquilla E. R. Use of resonance interaction in the study of the chain folding of insulin in solution. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 10;11(21):3860–3874. doi: 10.1021/bi00771a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Levy H. R. Evidence for an essential lysine in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 2;50(2):453–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Egorov C. A., Aldanova N. A., Feigina M. Y., Lipkin V. M., Abdulaev N. G., Grishin E. V., Kiselev A. P., Modyanov N. N., Braunstein A. E. The complete amino acid sequence of cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase from pig heart. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 1;29(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyanovsky O. L., Nosikov V. V., Deyev S. M., Braunstein A. E., Grishin E. V., Ovchinnikov Y. A. Location of exposed and buried cysteine residues in the polypeptide chain of aspartate aminotransferase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyanovsky O. L., Timofeev V. P., Shaduri M. I., Misharin A. Y., Volkenstein M. V. Conformational changes of aspartate aminotransferases in the region of Cys-45 residue observed by means of spin label. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 15;327(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. F., Scandurra R. Essential arginyl residues in aspartate aminotransferases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):417–424. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zufarova R. A., Dedyukina M. M., Memelova L. V., Torchinsky Y. M. Identification of the exposed and buried cysteine residues in the peptide sequence of aspartate aminotransferase from pig heart cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90898-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


