Abstract
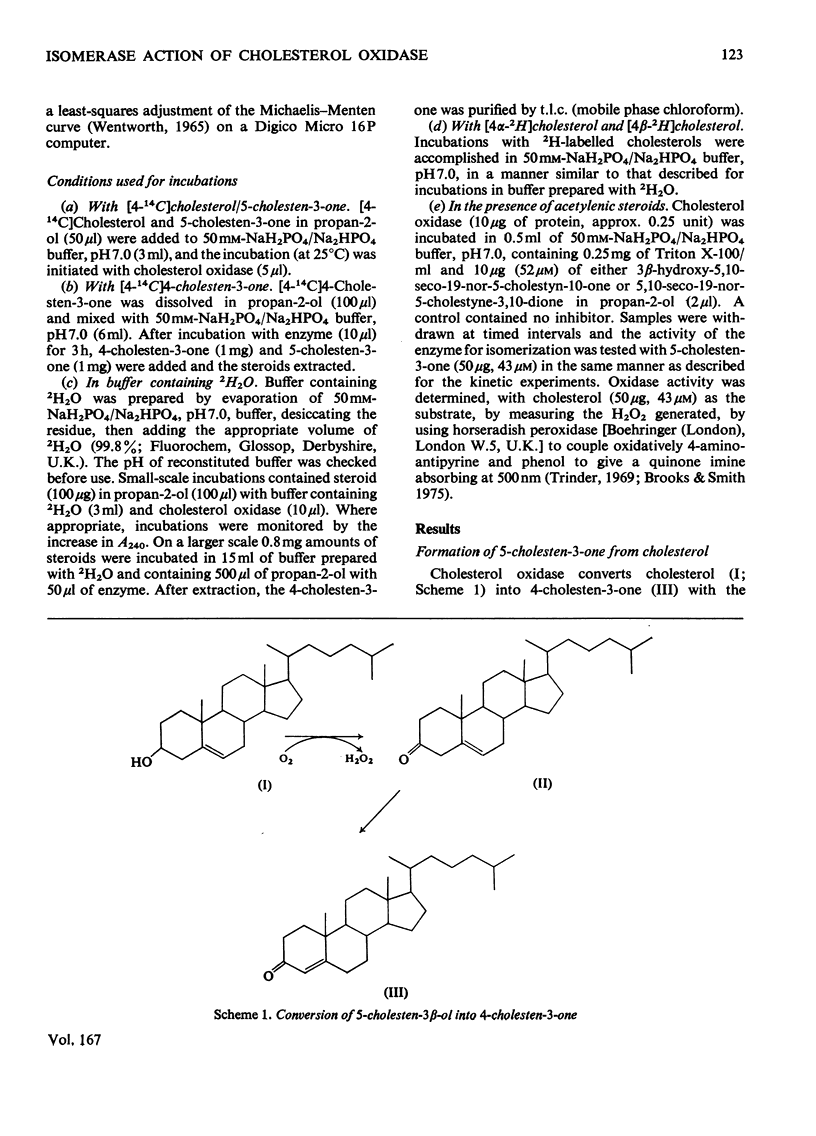
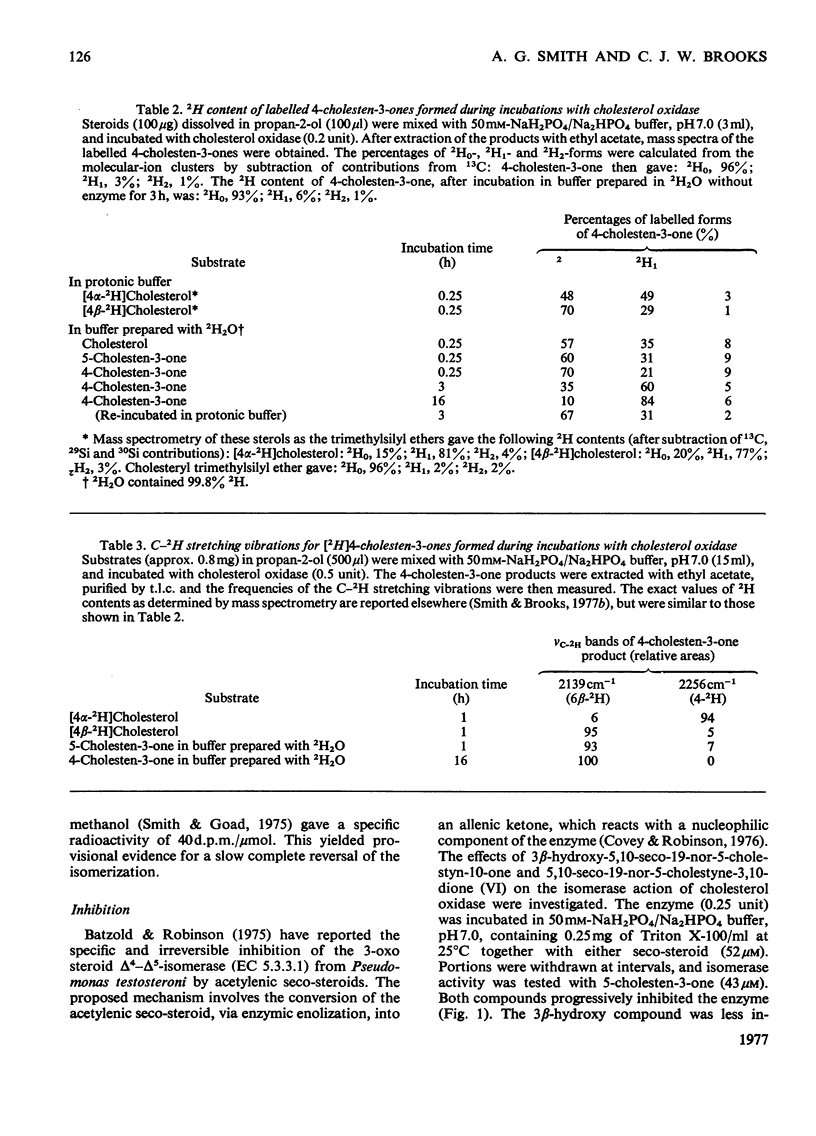
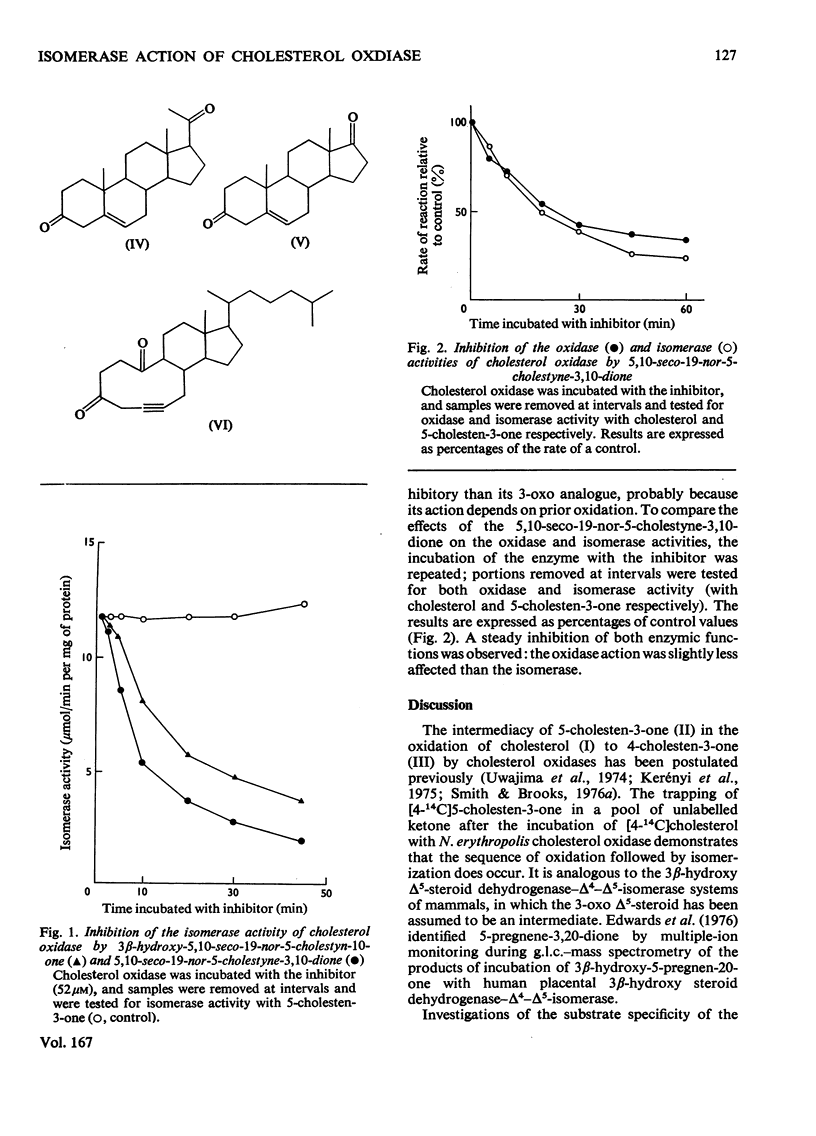
1. 5-Cholesten-3-one was shown to be an intermediate in the conversion of cholesterol into 4-cholesten-3-one by Nocardia cholesterol oxidase. 2. The absence of a C-17 side chain from 5-androstene-3,17-dione slightly increased the Vmax. of the isomerase activity relative to 5-cholesten-3-one (1.7-fold), but greatly increased the Km. 3. Incubations of [4alpha-2H]-and [4beta-2H]-cholesterol with cholesterol oxidase showed that the 4beta-hydrogen atom can be transferred to the 6beta-position. However, incubations of cholesterol, 5-cholesten-3-one and 4-cholesten-3-one with the enzyme in 2H2O led to some incorporation of 2H into the 4-cholesten-3-one products, mostly at position 6beta. 4. Both the isomerase and the oxidase activities of cholesterol oxidase were inhibited by 5,10-seco-19-nor-5-cholestyne-3,10-dione.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzold F. H., Benson A. M., Covey D. F., Robinson C. H., Talalay P. The delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase reaction: catalytic mechanism, specificity and inhibition. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1976;14:243–267. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(76)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzold F. H., Robinson C. H. Letter: Irreversible inhibition of delta-5-3-ketosteroid isomerase by 5,10-secosteroids. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Apr 30;97(9):2576–2578. doi: 10.1021/ja00842a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzold F. H., Robinson C. H. Synthesis of beta,gamma-acetylenic 3-oxo steroids of the 5,10-seco series. J Org Chem. 1976 Jan 23;41(2):313–317. doi: 10.1021/jo00864a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. J., Smith A. G. Cholesterol oxidase. Further studies of substrate specificity in relation to the analytical characterisation of steroids. J Chromatogr. 1975 Oct 29;112:499–511. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99979-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey D. F., Robinson C. H. Letter: Conjugated allenic 3-oxo-5,10-secosteroids. Irreversible inhibitors of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Aug 4;98(16):5038–5040. doi: 10.1021/ja00432a067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. P., O'Conner J. L., Bransome E. D., Jr, Braselton W. E., Jr Human placental 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: delta5-isomerase. Demonstration of an intermediate in the conversion of 3beta-hydroxypregn-5-en-20-one to pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford H. C., Engel L. L. Purification and properties of the delta 5-3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-isomerase system of sheep adrenal cortical microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1363–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda H., Kawakami Y., Nakamura S. A method to screen anticholesterol substances produced by microbes and a new cholesterol oxidase produced by Streptomyces violascens. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1973 Sep;21(9):2057–2060. doi: 10.1248/cpb.21.2057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmkamp G. M., Jr, Brock D. J., Bloch K. Beta-hydroxydecanoly thioester dehydrase. Specificity of substrates and acetylenic inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3229–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerényi G., Szentirmai A., Natonek M. Properties of delta5-3beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase isolated from Streptomyces griseocarneus. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1975;22(4):487–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murota S., Fenselau C. C., Talalay P. Partial purification of a beef adrenal delta-5-3-ketosteroid isomerase and studies of its mechanism of action. Steroids. 1971 Jan;17(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(71)80113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L., Koritz S. B. Studies on the mechanism of action of the delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase from rat adrenal small particles. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3400–3405. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peynet J., Canal J., Delattre J., Rousselet F., Girard M. L. Etude de la spécificité d'action de la cholestérol oxygène oxydoréductase sur certains stérols et substances apparentées. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1976;34(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond W. Preparation and properties of a cholesterol oxidase from Nocardia sp. and its application to the enzymatic assay of total cholesterol in serum. Clin Chem. 1973 Dec;19(12):1350–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Brooks C. J. Cholesterol oxidases: properties and applications. J Steroid Biochem. 1976 Sep;7(9):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(76)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Brooks C. J. Mass spectra of delta 4- and 5 alpha-3-ketosteroids formed during the oxidation of some 3 beta-hydroxysteroids by cholesterol oxidase. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1976 Apr;3(2):81–87. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Brooks C. J. Studies of the substrate specificity of cholesterol oxidase from Nocardia erythropolis in the oxidation of 3-hydroxy steroids. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):675–677. doi: 10.1042/bst0030675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Brooks C. J. The mechanism of the isomerization of Cholest-5-en-3-one to cholest-4-en-3-one by cholesterol oxidase [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(4):1088–1090. doi: 10.1042/bst0051088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Gilbert J. D., Harland W. A., Brooks C. J. The isolation of cholest-5-ene-3beta,26-diol from human brain. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):793–795. doi: 10.1042/bj1390793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Goad L. J. The conversion of cholest-5-en-3beta-ol into cholest-7-en-3beta-ol by the echinoderms Asterias rubens and Solaster papposus. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj1460035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Kagawa M., Nakamura S. Some enzymatic properties of 3beta-hydroxysteroid oxidase produced by Streptomyces violascens. J Biochem. 1976 May;79(5):903–915. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG S. F., KAWAHARA F. S., TALALAY P. The mechanism of the delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase reaction: absorption and fluorescence spectra of enzyme-steroid complexes. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:576–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. G., Engel L. L. Reversibility of steroid delta-isomerase. 3. The soluble enzyme of Pseudomonas testosteroni. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3154–3157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. G., Engel L. L. Reversibility of steroid delta-isomerase. II. The reaction sequence in the conversion of androst-4-ene-3,17-dione to 3-beta-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one by sheep adrenal microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3147–3153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wortberg B. Zur Spezifität der "Cholesterinoxydase" für die enzymatische Cholesterinbestimmung. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch. 1975 Jun 20;157(6):333–338. doi: 10.1007/BF01140487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


