Abstract
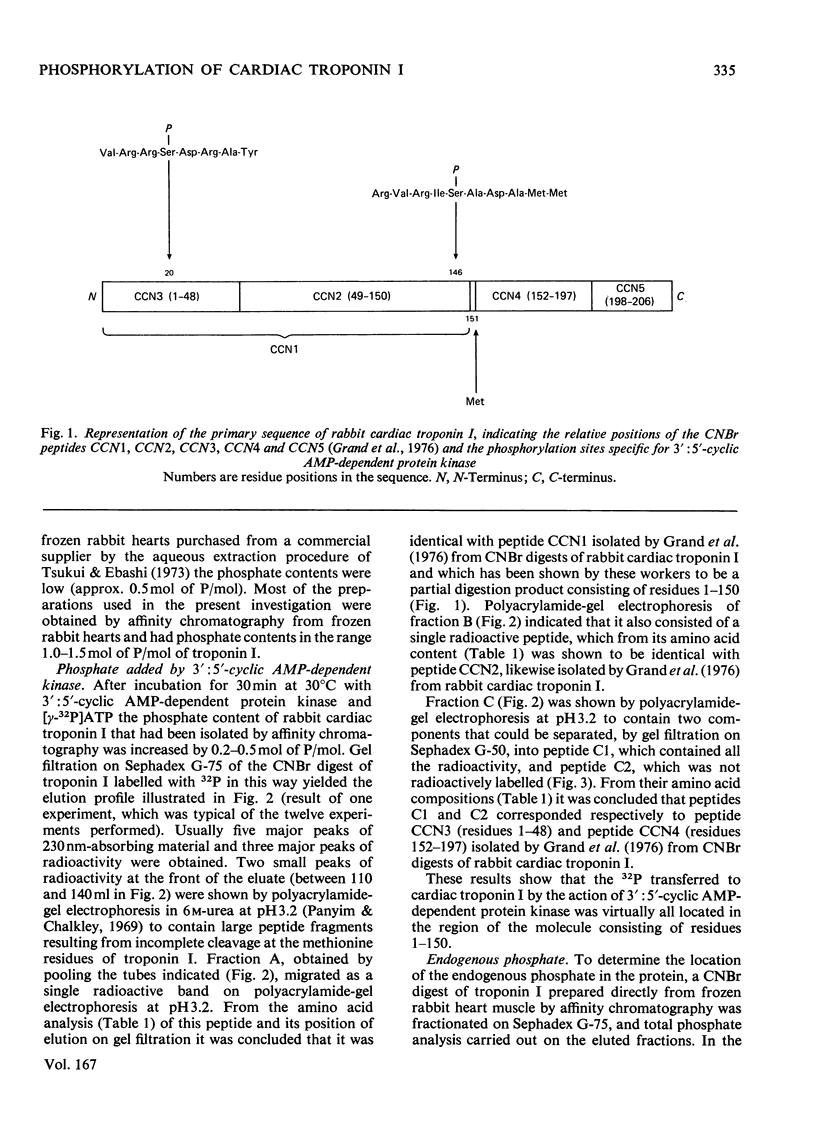
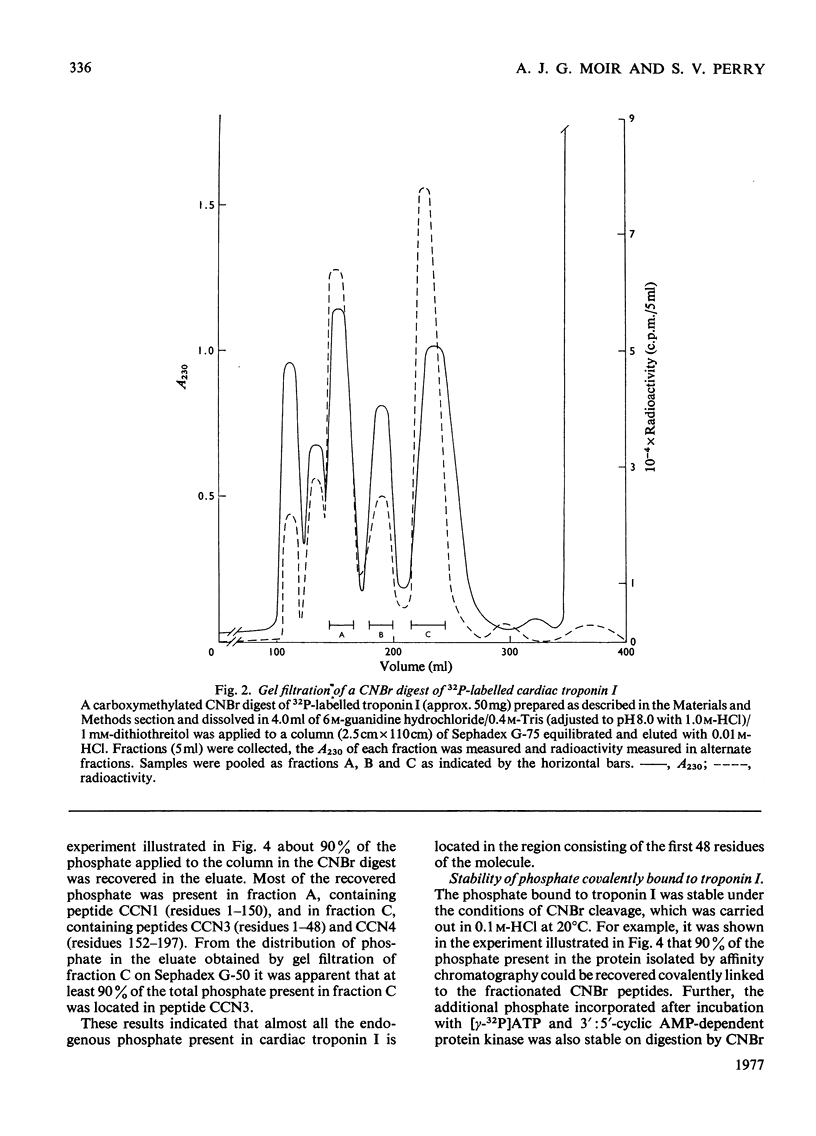
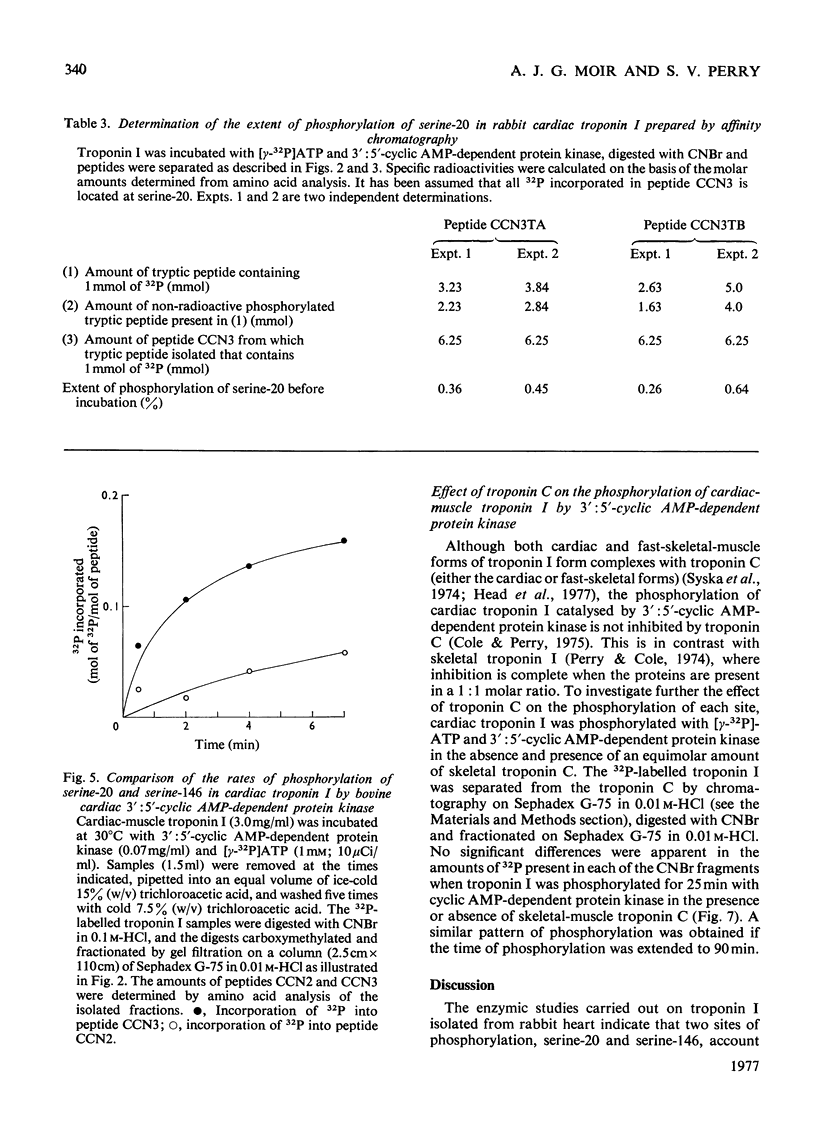
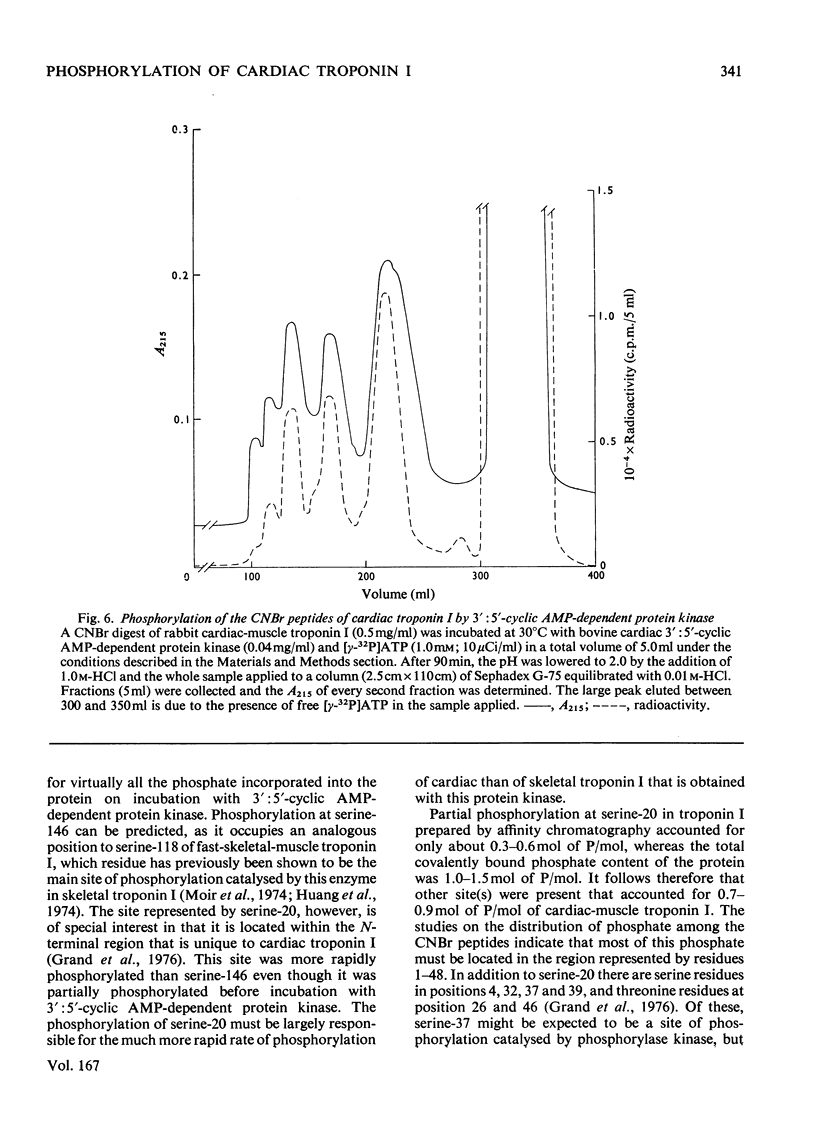
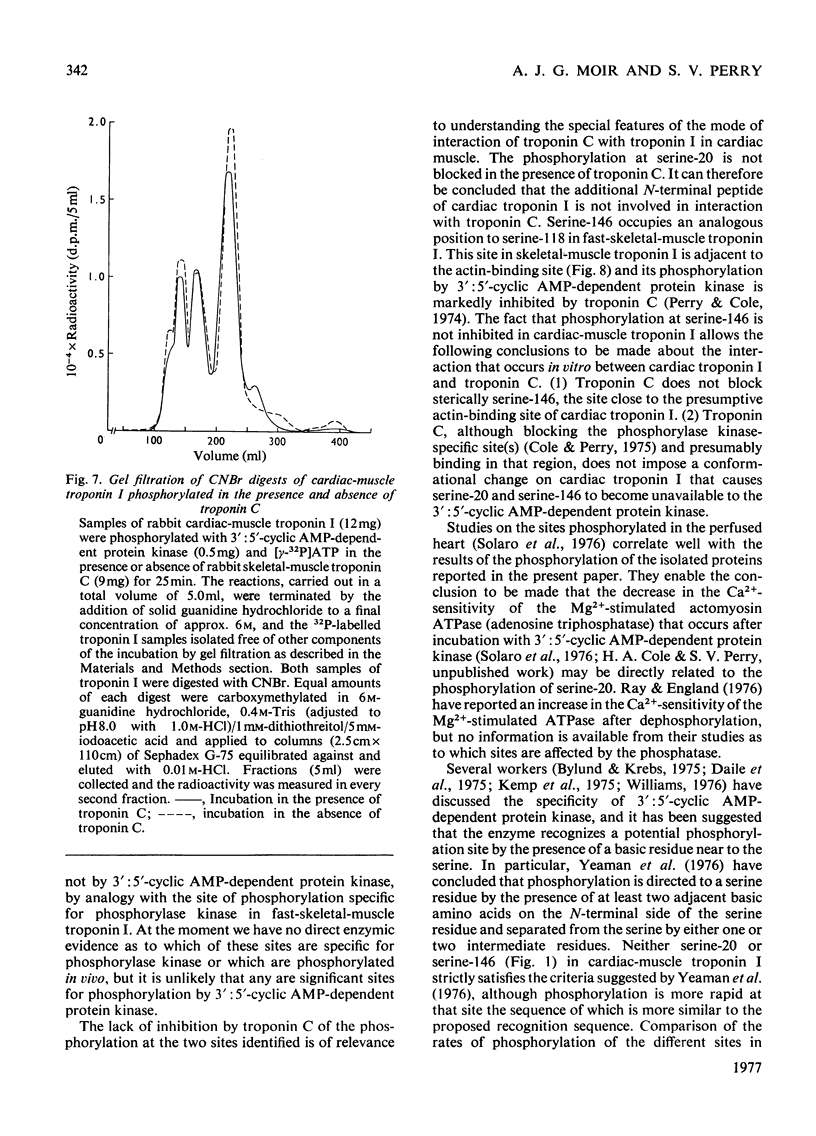
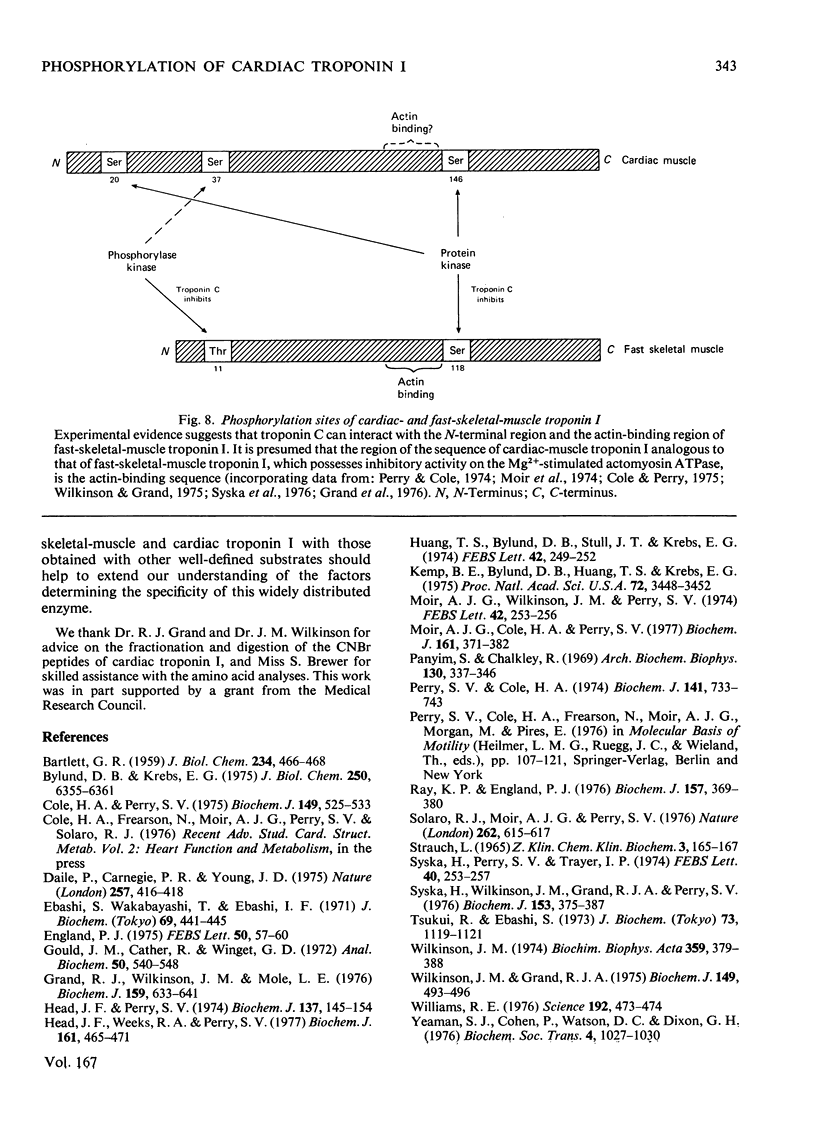
1. Troponin I prepared from rabbit hearts contains 1.0-1.5 mol of P/mol when isolated by affinity chromatography. Most of the covalently bound phosphate is located in residues 1-48 of the molecule. 2. 3':5'-Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase catalyses phosphorylation at serine-20 and serine-146. Serine-20 is more rapidly phosphorylated than serine-146. 3. In troponin I prepared from frozen hearts by affinity chromatography about 0.3-0.5 mol of P/mol is associated with serine-20 and 0.8-1.0 mol of P/mol with other site(s) in residues 1-48 of the molecule. 4. Phosphorylation at serine-20 and servine-146 is not significantly inhibited by troponin C. 5. The mechansim of the interaction of troponin C with cardiac troponin I is discussed in the light of these results.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Krebs E. G. Effect of denaturation on the susceptibility of proteins to enzymic phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6355–6361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation of troponin I from cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1490525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daile P., Carnegie P. R., Young J. D. Synthetic substrate for cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):416–418. doi: 10.1038/257416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Wakabayashi T., Ebashi F. Troponin and its components. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):441–445. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Correlation between contraction and phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin in perfused rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cather R., Winget G. D. Advantages of the use of Cerenkov vounting for determination of P 32 in photophosphorylation research. Anal Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(2):540–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Wilkinson J. M. The amino acid sequence of rabbit cardiac troponin I. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):633–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1590633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Perry S. V. The interaction of the calcium-binding protein (troponin C) with bivalent cations and the inhibitory protein (troponin I). Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):145–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1370145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. S., Bylund D. B., Stull J. T., Krebs E. G. The amino acid sequences of the phosphorylated sites in troponin-I from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80738-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Bylund D. B., Huang T. S., Krebs E. G. Substrate specificity of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation sites of troponin T from white skeletal muscle and the effects of interaction with troponin C on their phosphorylation by phosphorylase kinase. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):371–382. doi: 10.1042/bj1610371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation sites of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80739-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray K. P., England P. J. The identification and properties of phosphatases in skeletal muscle with activity towards the inhibitory subunit of troponin, and their relationship to other phosphoprotein phosphatases. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):369–380. doi: 10.1042/bj1570369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Moir A. J., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of troponin I and the inotropic effect of adrenaline in the perfused rabbit heart. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):615–617. doi: 10.1038/262615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Perry S. V., Trayer I. P. A new method of preparation of troponin I (inhibitory protein) using affinity chromatography. Evidence for three different forms of troponin I in striated muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 Apr 1;40(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syska H., Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):375–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1530375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukui R., Ebashi S. Cardiac troponin. J Biochem. 1973 May;73(5):1119–1121. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Grand R. J. The amino acid sequence of troponin I from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):493–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. The preparation and properties of the components of troponin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. E. Phosphorylated sites in substrates of intracellular protein kinases: a common feature in amino acid sequences. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):473–474. doi: 10.1126/science.1257781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Cohen P. The specificity of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(6):1027–1030. doi: 10.1042/bst0041027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


