Abstract
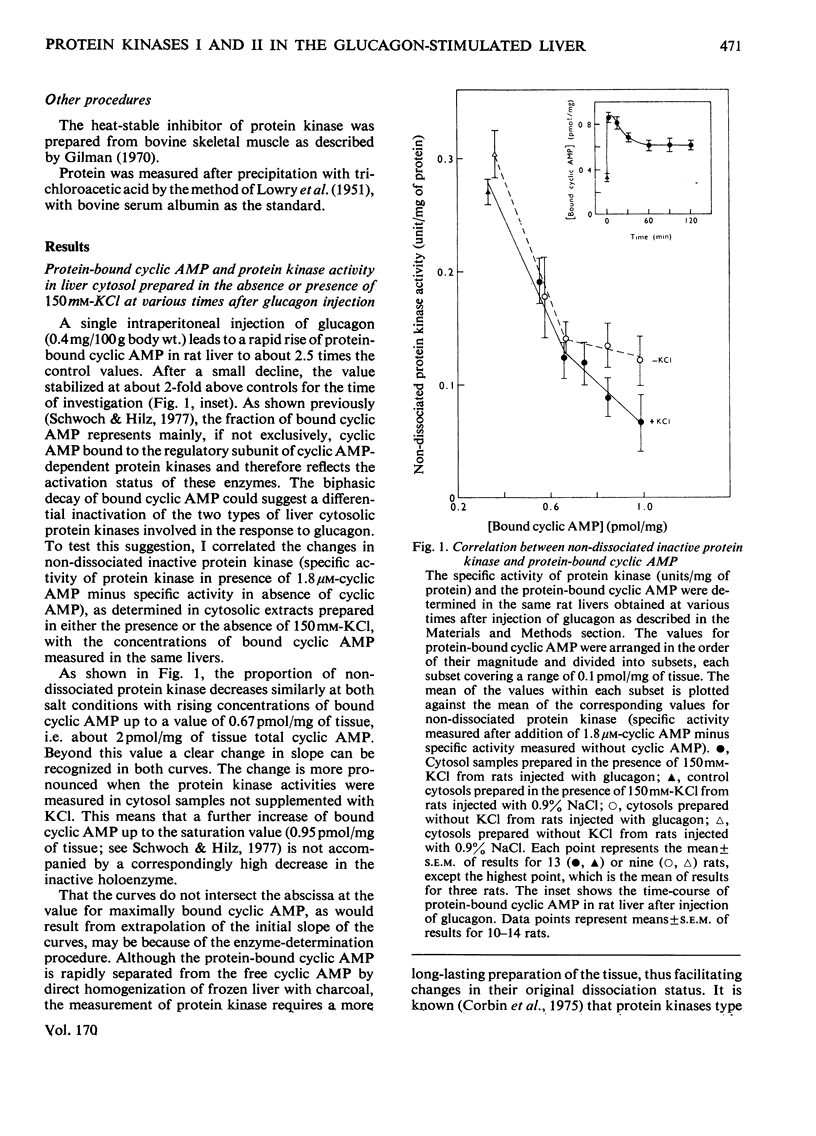
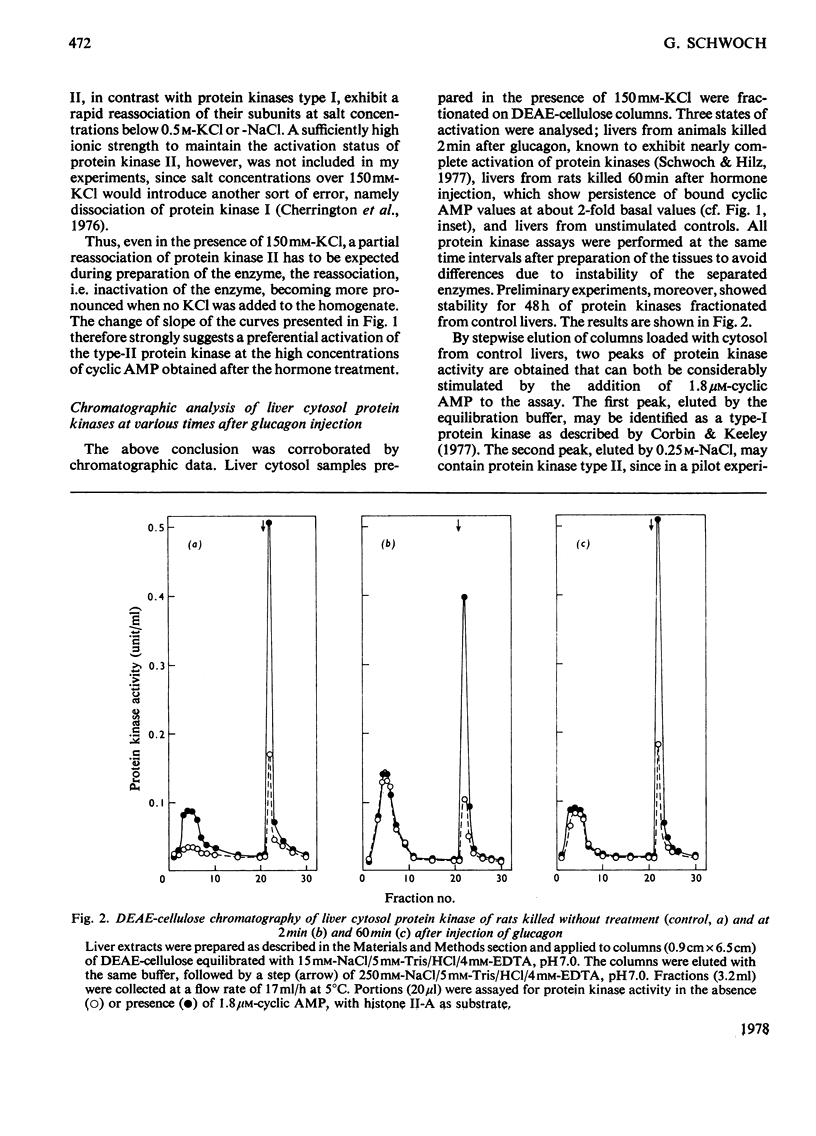
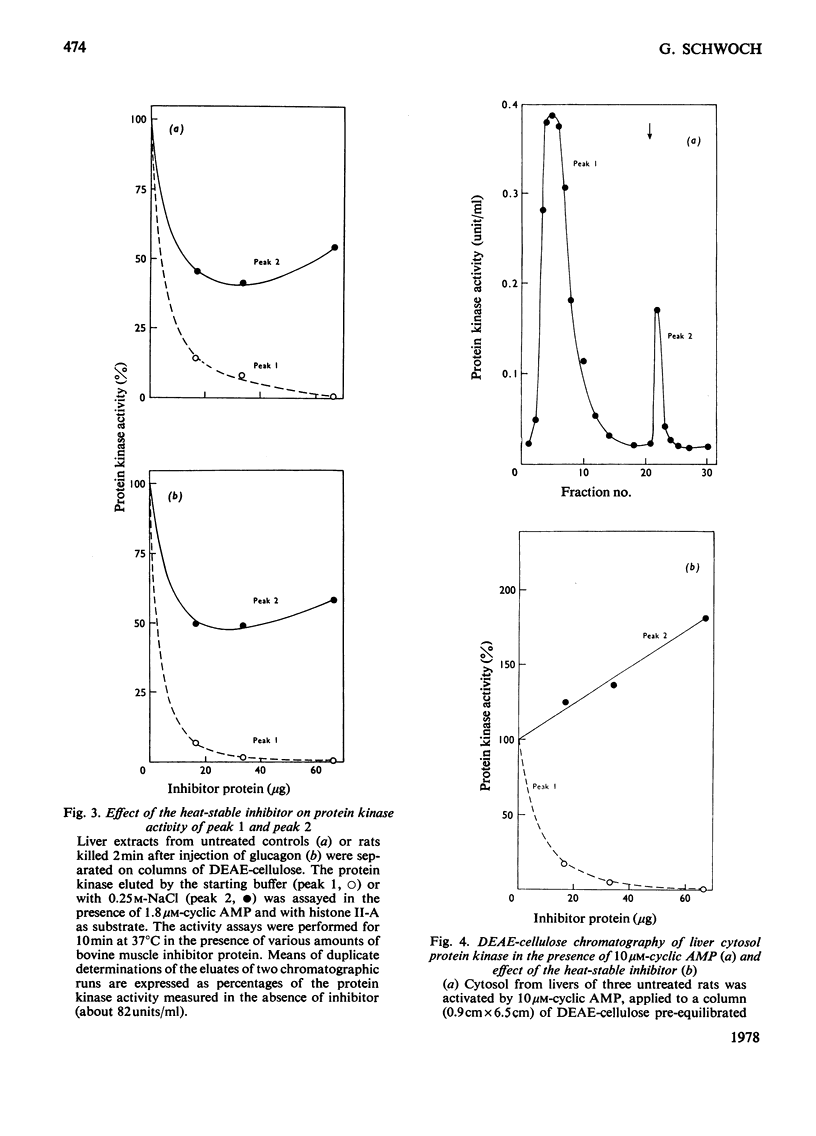
The protein-bound cyclic AMP and the activity of cytosolic protein kinases in the presence and absence of cyclic AMP were determined in rat liver up to 2h after injection of glucagon. On the basis of the different salt-sensitivities of the activated cyclic AMP-dependent proteinkinases I and II, an activation of protein kinase II restricted to the high cyclic AMP concentrations present in the first 30 min after hormone injection was found. Essentially the same result was obtained by chromatographic analysis on DEAE-cellulose of liver cytosol from untreated rats and from rats killed at 2 and 60 min after glucagon injection. Protein kinase II activation was only detected at 2 min after injection. In contrast, the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase I was found to be nearly totally activated at 2 min and to be still almost as active at 60 min after the hormone stimulus, whereas the amount of bound cyclic AMP and the activation of total cytosolic protein kinases had fallen to two-thirds of their maximal values during this time period. A third cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase, which co-chromatographed with protein kinase type II, could be clearly distinguished from the two cyclic AMP-dependent kinases by use of the heat-stable inhibitor from bovine muscle, which totally inhibited the cyclic AMP-dependent enzymes, but stimulated the cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaum M. J., Fain J. N. Activation of protein kinase and glycogen phosphorylase in isolated rat liver cells by glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):528–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Kon C. An improved protein binding assay for cyclic AMP. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Ekins R. P., Albano J. D. Saturation assay for cyclic AMP using endogenous binding protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;2:25–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Chubb J. M., Huxtable R. J., Russell D. H. Increase in type I adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase during isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):694–702. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Hayes J. S., Brendel K., Russell D. H. Correlation between cAMP, activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase(s), and rate of glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Life Sci. 1976 Aug 1;19(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Walsh D. A. Multiple forms of hepatic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 14;10(19):3614–3621. doi: 10.1021/bi00795a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Assimacopoulos F. D., Harper S. C., Corbin J. D., Park C. R., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-andrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. II. Investigation of the roles of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in the actions of phenylephrine in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5209–5218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Exton J. H. Studies on the role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the actions of glucagon and catecholamines on liver glycogen metabolism. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1351–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L. Characterization and regulation of heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):910–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Reimann E. M. Assay of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Gerner E. W., Russell D. H. Cell cycle-specific activity of type I and type II cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3313–3319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly T. E., Jr, Kuo J. F., Reyes P. L., Liu Y. P., Greengard P. Protein kinase modulator from lobster tail muscle. I. Stimulatory and inhibitory effects of the modulator on the phosphorylation of substrate proteins by guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):190–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eil C., Wool I. G. Phosphorylation of rat liver ribosomal subunits: partial purification of two cyclic AMP activated protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K. Absence of high-affinity adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate binding sites from the cytosol of three hepatic-derived cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Comparison of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rabbit skeletal and bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7795–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Concentrations of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in various tissues. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1441–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keely S. L., Jr, Corbin J. D., Park C. R. On the question of translocation of heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1501–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzel V., Kübler D. Single step purification of the catalytic subunit(s) of cyclic 3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase(s) from rat muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumon A., Nishiyama K., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Multiplicity of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rat liver and mode of action of nucleoside 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3726–3735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F. Divergent actions of protein kinase modulator in regulating mammalian cyclic GMP-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Metabolism. 1975 Mar;24(3):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Radloff D., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Testicular protein kinases. Characterization of multiple forms and ontogeny. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):914–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauk G. L., Reddy W. J. Evaluation of the liver adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response to glucagon. Diabetes. 1971 Mar;20(3):129–133. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.3.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Aldao R., Rosen O. M. Dissociation and reassociation of the phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of adenosine 3':5' -monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3375–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J. Reversible autophosphorylation of a cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7788–7794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., De Visscher M. Artifactual stimulation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity by the heat-stable protein kinase "inhibitor". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1423–1429. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hilz H. Protein-bound adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in liver of glucagon-treated rats. Determination of half-maximal binding in vivo and correlation with protein kinase activation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Doskeland S. O. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependence of protein kinase isoenzymes from mouse liver. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):117–126. doi: 10.1042/bj1570117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H., Kumon A., Nishiyama K., Takeda M., Nishizuka Y. Characterization of two adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1560–1566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H., Nishiyama K., Shimomura R., Nishizuka Y. Comparison of catalytic units of muscle and liver adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):856–862. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


