Abstract
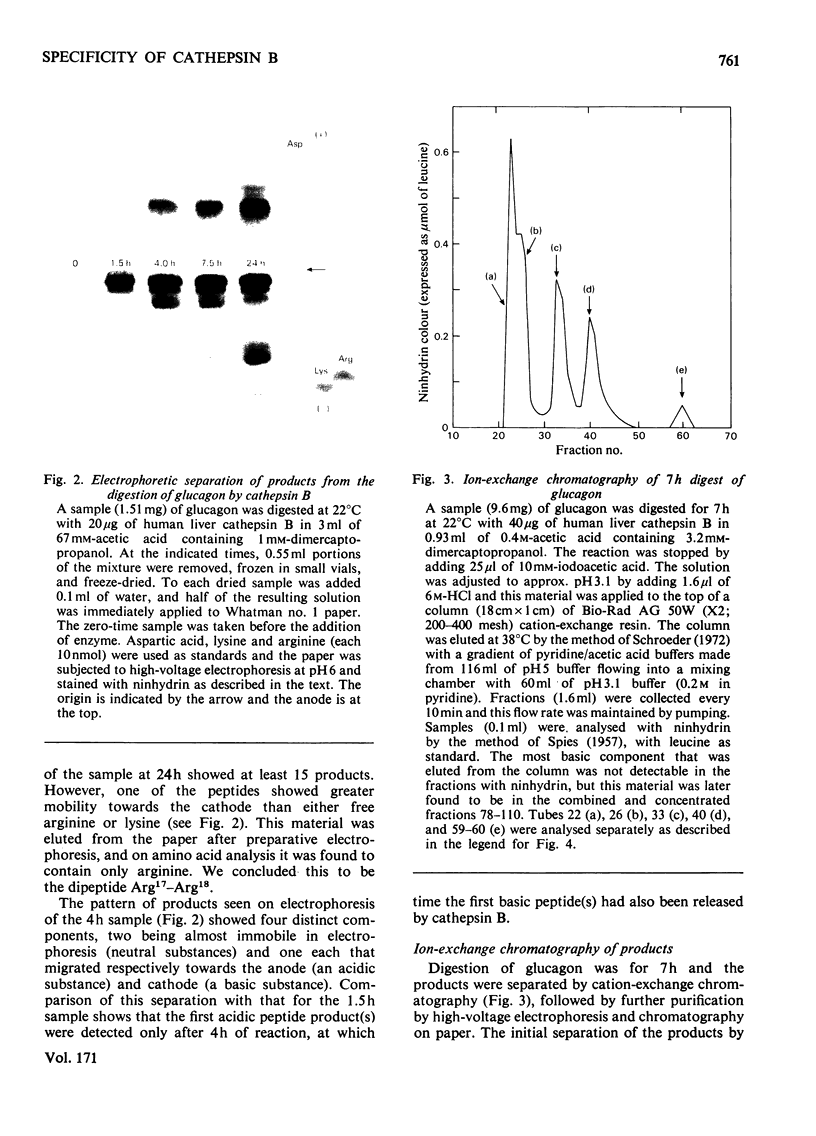
The manner in which human liver cathepsin B (EC 3.4.22.1) digests glucagon was determined. After reaction of the proteinase with the substrate for 24h, more than 15 products were formed. During the first 7 h of reaction, eight products were formed; seven of these were dipeptides that originated from the C-terminal portion of the glucagon molecule, whereas the eighth peptide was the remaining large fragment of the hormone, consisting of residues 1-19. Measurement of the rate of formation of the products showed that cathepsin B degraded glucagon by a sequential cleavage of dipeptides from the C-terminal end of the molecule. Cathepsin B from both rat liver and bovine spleen was shown to hydrolyse glucagon by the same mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afroz H., Otto K., Müller R., Fuhge P. On the specificity of bovine spleen cathepsin B2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):503–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):280–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. An improved color reagent for use in Barrett's assay of Cathepsin B. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):809–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1310809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh M. C., Barrett A. J., Lazarus G. S. Cathepsin B1. A lysosomal enzyme that degrades native collagen. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):387–398. doi: 10.1042/bj1370387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. The conformation of glucagon: predictions and consequences. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2536–2541. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):143–144. doi: 10.1042/bj1370143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Lysosomal enzymes as agents of turnover of soluble cytoplasmic proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 1;58(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmazeaud M. J. Contribution à l'étude de la spécificité de la papaïne: hydrolyse du glucagon. Biochimie. 1972;54(9):1109–1114. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. The purification of bovine cathepsin B1 and its mode of action on bovine collagens. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):547–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1370547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Niall H. D., Jacobs J. W., Keutmann H. T., Potts J. T., Jr, Cohn D. V. The N-terminal amino-acid sequence of bovine proparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):653–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopgood M. F., Clark M. G., Ballard F. J. Inhibition of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):399–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1640399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman W., Lanting L., Doddema H. J., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. Role of individual cathepsins in lysosomal protein digestion as tested by specific inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P., Broghammer U. Intrazellulärer Proteinabbau. VII. Kathepsin L und H: Zwei neue Proteinasen aus Rattenleberlysosomen. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1976;35(3-4):285–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P. Cathepsin L. A new proteinase from rat-liver lysosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda K. Studies on cathepsins of rat liver lysosomes. III. Hydrolysis of peptides, and inactivation of angiotensin and bradykinin by cathepsin A. J Biochem. 1976 Oct;80(4):659–669. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Ellis S. On the substrate specificity of cathepsins B1 and B2 including a new fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin B1. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1269–1276. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. I., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T., Prior D. Cathepsins BI and D. Action on human cartilage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penke B., Ferenczi R., Kovács K. A new acid hydrolysis method for determining tryptophan in peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Barrett A. J. The degradation of cartilage proteoglycans by tissue proteinases. Proteoglycan structure and its susceptibility to proteolysis. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):629–637. doi: 10.1042/bj1670629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Geller D. M. The structure of rat proalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3409–3413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUB A., SINN L., BEHRENS O. K. Purification and crystallization of glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jun;214(2):619–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W., Bird J. W. Degradation of myofibrillar proteins by cathepsins B and D. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):811–820. doi: 10.1042/bj1670811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaron A., Mlynar D., Berger A. A dipeptidocarboxypeptidase from E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):897–902. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90577-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]