Abstract
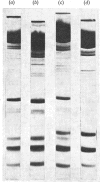
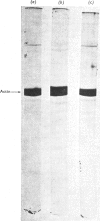
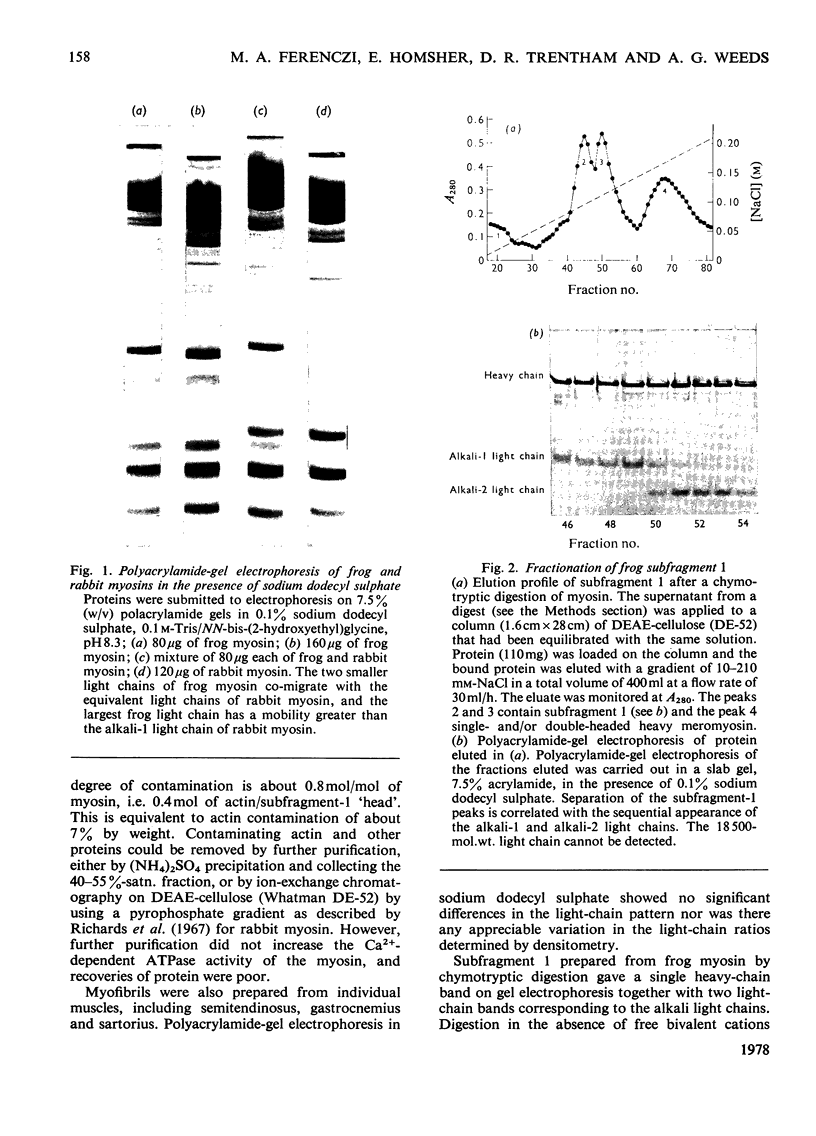
The preparation, structural and steady-state kinetic characteristics of contractile proteins from the leg muscle of frogs Rana temporaria and Rana pipiens are described. Actin and myosin from the two frog species are indistinguishable. The proteins have structural and steady-state kinetic properties similar to those from rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle. Chymotrypsin digestion of frog myosin or myofibrils in the presence of EDTA yields subfragment 1, which is separated by chromatography into two components that are distinguished by their alkali light-chain content.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babul J., Stellwagen E. Measurement of protein concentration with interferences optics. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R. On the location of the divalent metal binding sites and the light chain subunits of vertebrate myosin. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 11;16(1):59–67. doi: 10.1021/bi00620a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R., Trentham D. R. The characterization of myosin-product complexes and of product-release steps during the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase reaction. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):331–349. doi: 10.1042/bj1410331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R., Trentham D. R. The reversibility of adenosine triphosphate cleavage by myosin. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):323–328. doi: 10.1042/bj1330323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Moos C. Actin activation of heavy meromyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Dependence on adenosine triphosphate and actin concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2451–2456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H., Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Complete amino-acid sequence of actin of rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEUER G., MOLNAR F. Studies on the composition and polymerization of actin. Hung Acta Physiol. 1948;1(4-5):150–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A., Homsher E., Simmons R. M., Trentham D. R. Reaction mechanism of the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of frog muscle myosin and subfragment 1. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):165–175. doi: 10.1042/bj1710165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G., Weeds A. G. The amino-acid sequence of the alkali light chains of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):317–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORNALL A. G., BARDAWILL C. J., DAVID M. M. Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem. 1949 Feb;177(2):751–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershman L. C., Stracher A., Dreizen P. Subunit structure of myosin. 3. A proposed model for rabbit skeletal myosin. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 25;244(10):2726–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I. A., Goldspink G. Thermodynamic activation parameters of fish myofibrillar ATPase enzyme and evolutionary adaptations to temperature. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):620–622. doi: 10.1038/257620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Risby D. Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):81–85. doi: 10.1038/234081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. G., Chung C. S., Menzel D. B., Olcott H. S. Chromatography of myosin on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex A-50. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):528–540. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliselfeld L. H., Bárány M. The binding of adenosine triphosphate to myosin. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3206–3213. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliselfeld L. H. Steady-state studies of the actin-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity of myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 12;445(1):234–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J. A., Taylor E. W. Intermediate states of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5813–5817. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Transient phase of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by myosin, heavy meromyosin, and subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):732–739. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. S., Weeds A. G. The magnesium-ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of bovine cardiac Myosin and its subfragment-1. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):301–315. doi: 10.1042/bj1590301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Hartley B. S. Selective purification of the thiol peptides of myosin. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):531–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1070531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G. Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule. II. The light chains of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):701–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. J., Nagy B., Gergely J. Free adenosine diphosphate as an intermediary in the phosphorylation by creatine phosphate of adenosine diphosphate bound to actin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1140–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Taylor E. W. Energetics and mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5818–5826. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]