Abstract
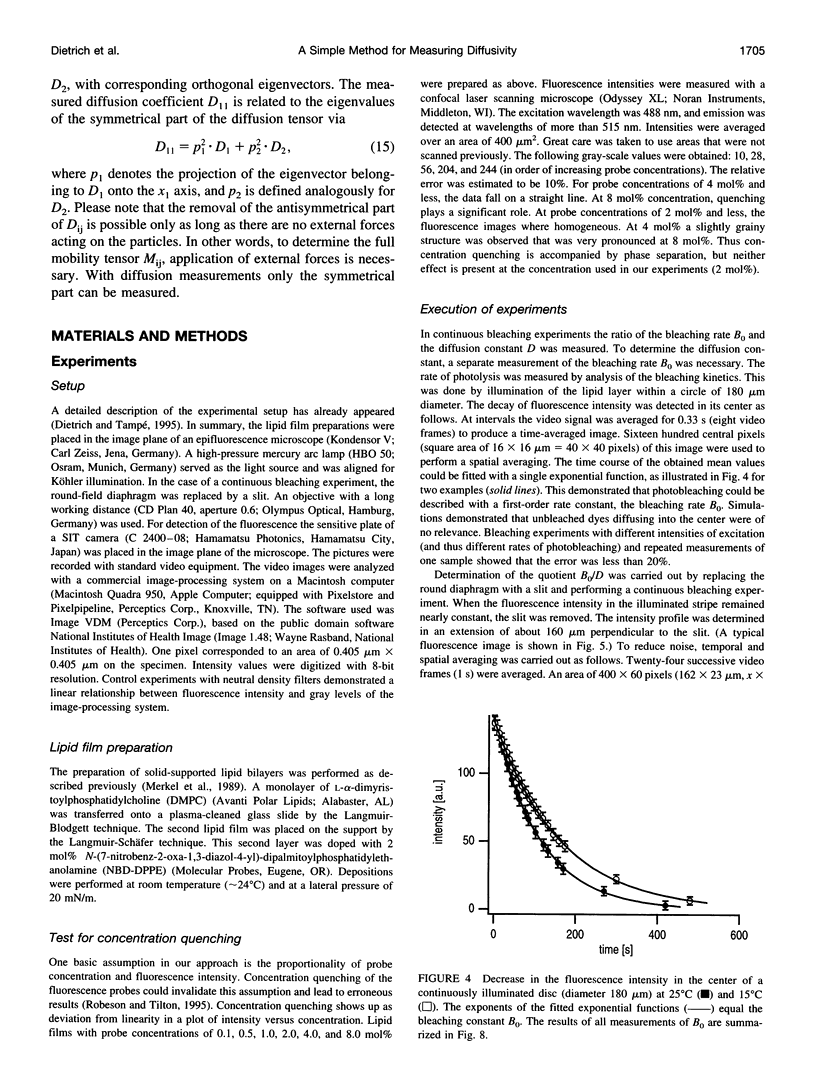
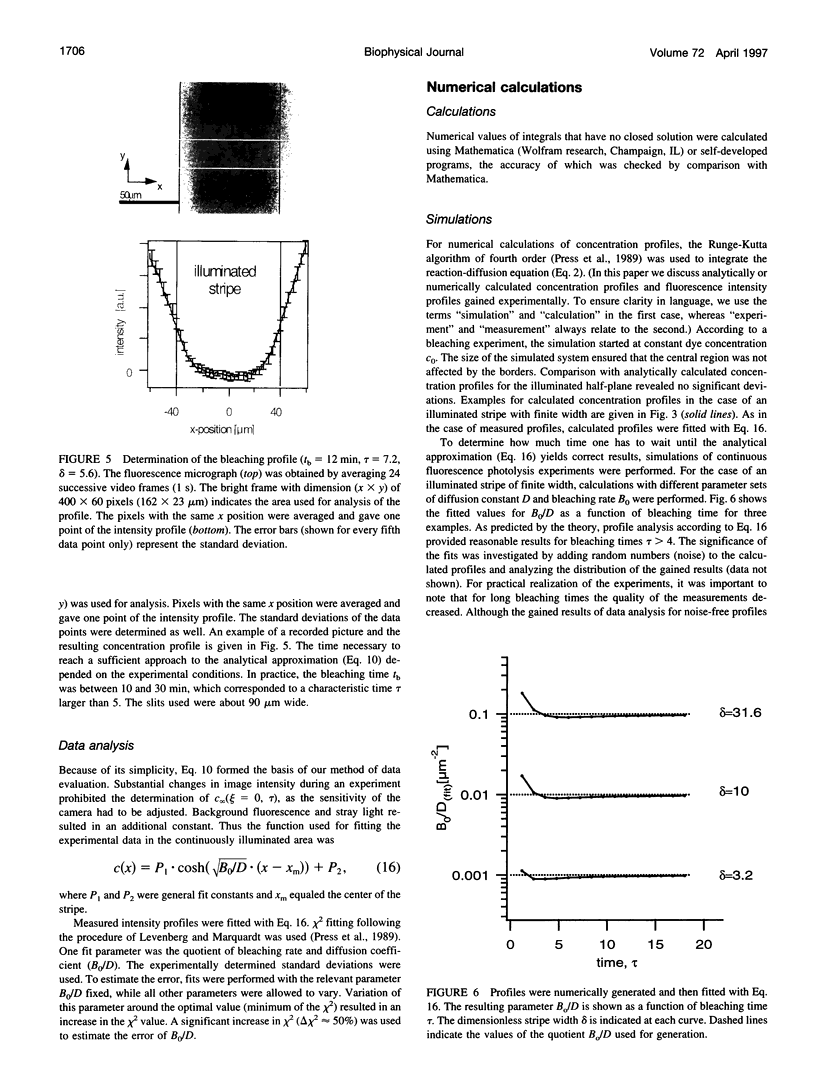
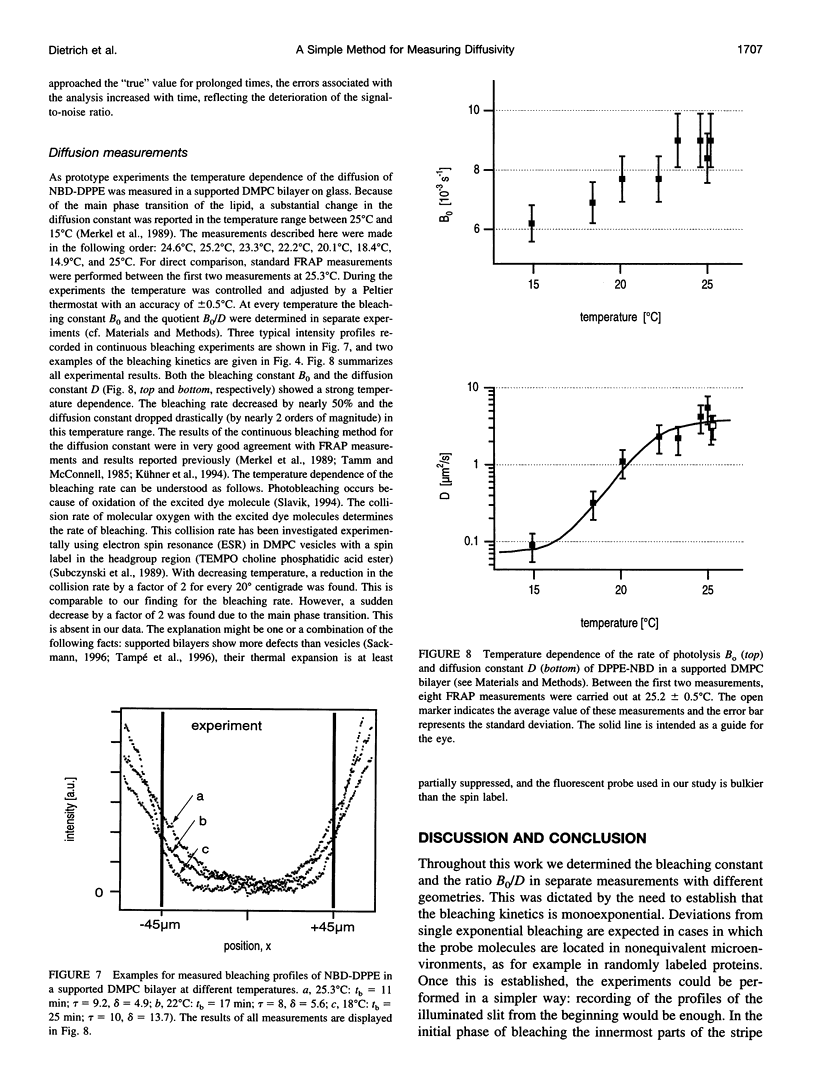
The lateral diffusion of fluorescence-labeled amphiphilic tracer molecules dissolved within a two-dimensional matrix of lipids was measured by continuous illumination of an elongated rectangular region. The resulting spatial concentration profile of unbleached tracer molecules was observed with a standard epifluorescence microscope and analyzed with digital image-processing techniques. These concentration profiles are governed by the mobility of the tracers, their rate of photolysis, and the geometry of the illuminated area. For the case of a long and narrow illuminated stripe, a mathematical analysis of the process is given. After prolonged exposure, the concentration profile can be approximated by a simple analytical function. This fact was used to measure the quotient of the rate of photolysis, and the diffusion constant of the fluorescent probe. With an additional measurement of the rate of photolysis, the mobility of the tracer was determined. As prototype experiments we studied the temperature dependence of the lateral diffusion of N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)-dipalmitoylphosphatidyl++ + ethanolamine in glass-supported bilayers of L-alpha-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine. Because of its simple experimental setup, this technique represents a very useful method of determining the lateral diffusion of fluorescence-labeled membrane molecules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrisch A., Dietrich C., Noegel A. A., Schleicher M., Sackmann E. The actin-binding protein hisactophilin binds in vitro to partially charged membranes and mediates actin coupling to membranes. Biochemistry. 1995 Nov 21;34(46):15182–15190. doi: 10.1021/bi00046a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Rotational and lateral diffusion of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):289–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich C., Tampé R. Charge determination of membrane molecules in polymer-supported lipid layers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Sep 13;1238(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00129-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Sheets E. D., Simson R. Revisiting the fluid mosaic model of membranes. Science. 1995 Jun 9;268(5216):1441–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.7770769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühner M., Tampé R., Sackmann E. Lipid mono- and bilayer supported on polymer films: composite polymer-lipid films on solid substrates. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80472-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhwald H. Phospholipid and phospholipid-protein monolayers at the air/water interface. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1990;41:441–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.41.100190.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nollert P., Kiefer H., Jähnig F. Lipid vesicle adsorption versus formation of planar bilayers on solid surfaces. Biophys J. 1995 Oct;69(4):1447–1455. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80014-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Beck K. Translational diffusion in phospholipid monolayers measured by fluorescence microphotolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7183–7187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Brünger A., Schulten K. Continuous fluorescence microphotolysis: A sensitive method for study of diffusion processes in single cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):962–966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robeson J. L., Tilton R. D. Effect of concentration quenching on fluorescence recovery after photobleaching measurements. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80397-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann E. Supported membranes: scientific and practical applications. Science. 1996 Jan 5;271(5245):43–48. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5245.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Determination of molecular motion in membranes using periodic pattern photobleaching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2759–2763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subczynski W. K., Hyde J. S., Kusumi A. Oxygen permeability of phosphatidylcholine--cholesterol membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm L. K., McConnell H. M. Supported phospholipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1985 Jan;47(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83882-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Burghardt T. P., Axelrod D. Measuring surface dynamics of biomolecules by total internal reflection fluorescence with photobleaching recovery or correlation spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):435–454. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84905-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Clegg R. M., Hallmann D. Translational diffusion of lipids in liquid crystalline phase phosphatidylcholine multibilayers. A comparison of experiment with theory. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):781–786. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedekind P., Kubitscheck U., Peters R. Scanning microphotolysis: a new photobleaching technique based on fast intensity modulation of a scanned laser beam and confocal imaging. J Microsc. 1994 Oct;176(Pt 1):23–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1994.tb03496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]