Abstract
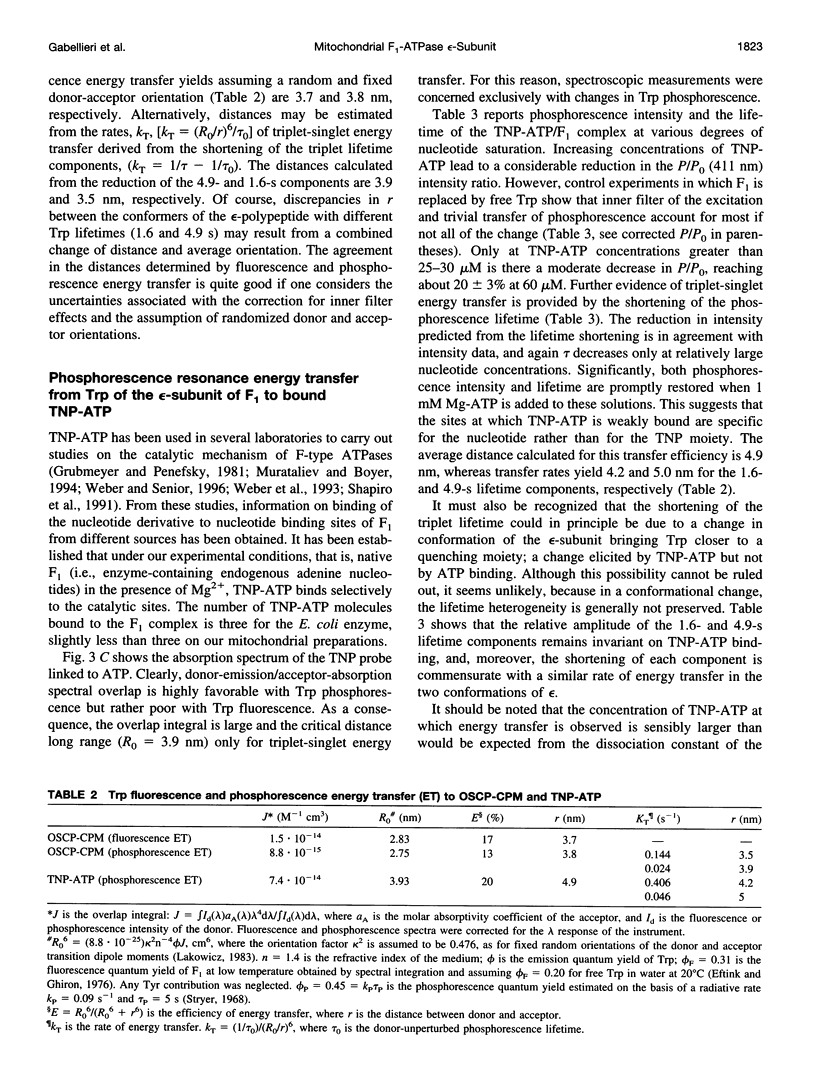
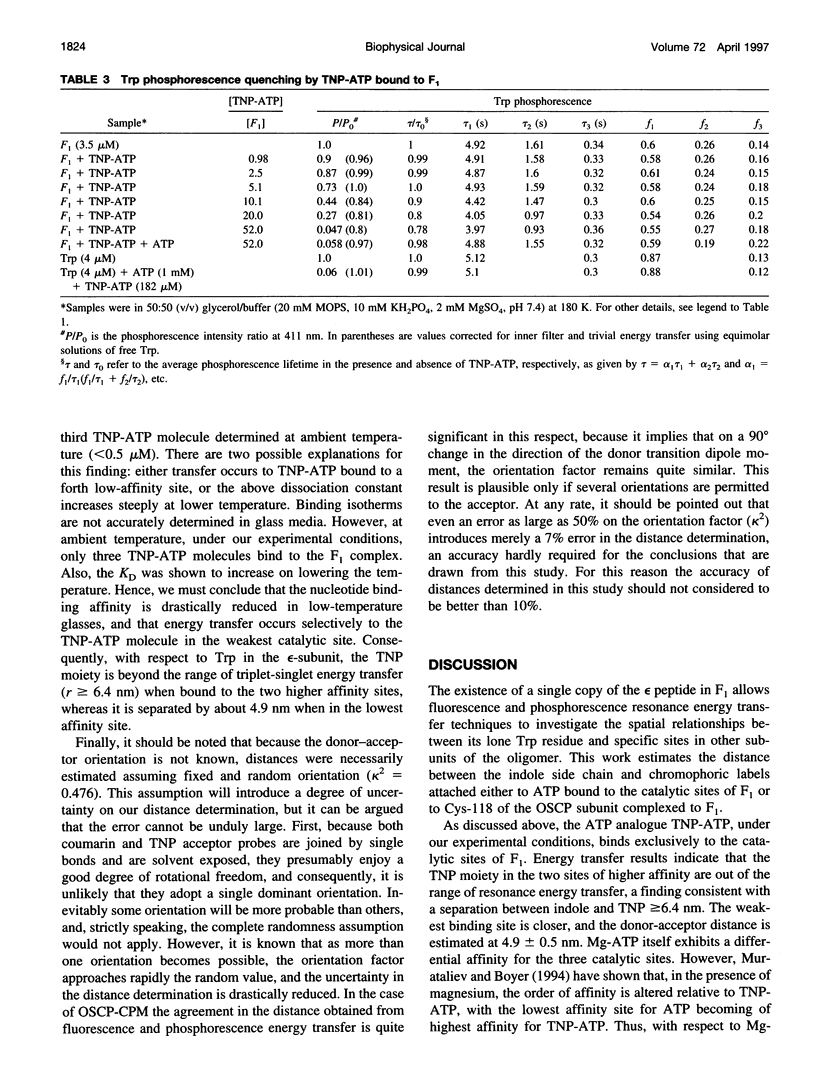
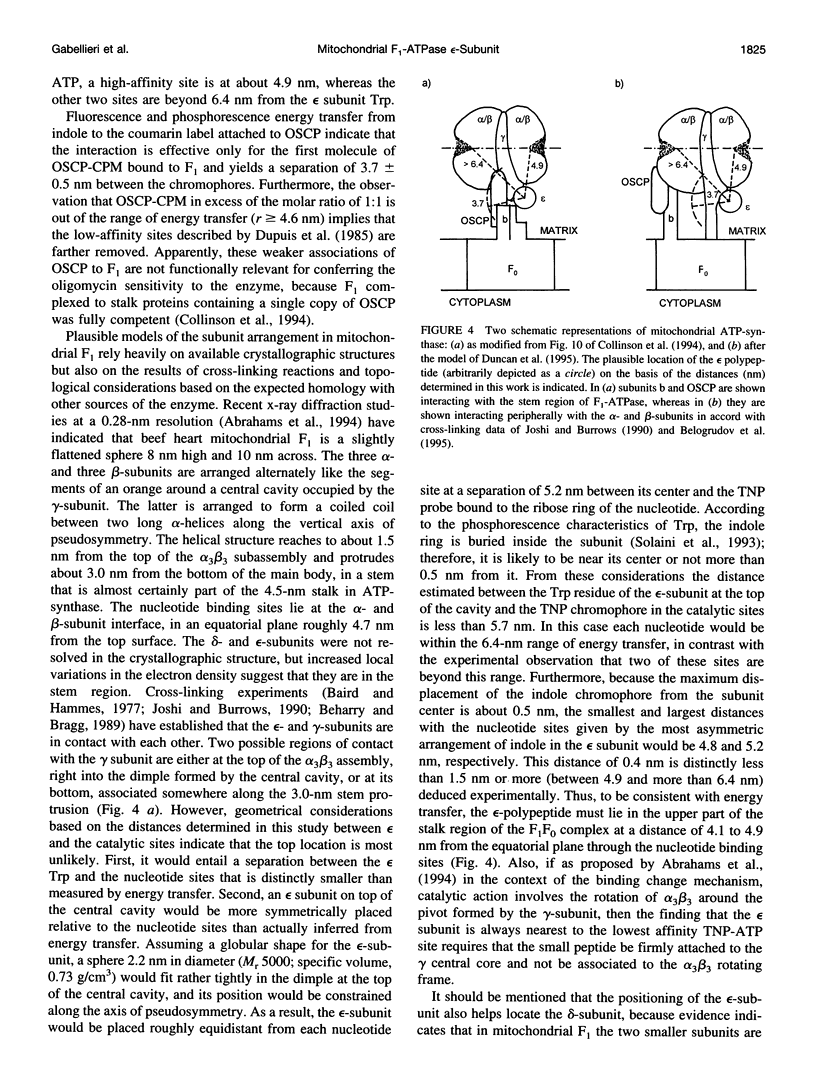
Phosphorescence and fluorescence energy transfer measurements have been used to locate the epsilon-subunit within the know structural frame of the mitochondrial soluble part of F-type H(+)-ATPase complex (F1). The fluorescence probe 2'-O-(trinitrophenyl)adenosine-5'-triphosphate was bound to the nucleotide binding sites of the enzyme, whereas the probe 7-diethylamino-3'-(4'-maleimidylphenyl)-4-methylcoumarin was attached to the single sulfhydryl residue of isolated oligomycin sensitivity-conferring protein (OSCP), which was then reconstituted with F1. Fluorescence and phosphorescence resonance energy transfer yields from the lone tryptophan residue of F1 present in the epsilon-polypeptide and the fluorescence labels attached to the F1 complex established that tryptophan is separated by 3.7 nm from Cys-118 of OSCP in the reconstituted OSCP-F1 complex, by 4.9 nm from its closest catalytic site and by more than 6.4 nm from the two other catalytic sites, including the lowest affinity ATP site. These separations together with the crystallographic coordinates of the F1 complex (Abrahams, J.P., A. G. W. Leslie, R. Lutter, and J.E. Walker. 1994. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 370:621-628) place the epsilon-subunit in the stem region of the F1 molecule in a unique asymmetrical position relative to the catalytic sites of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF
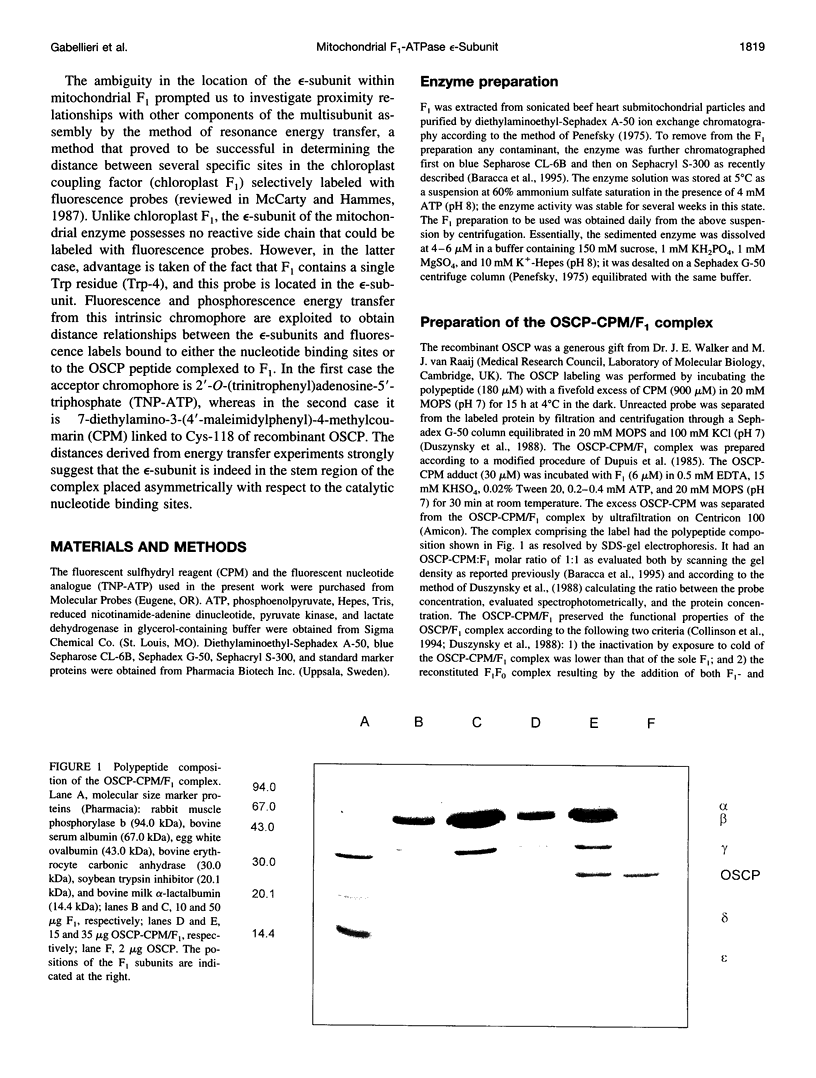

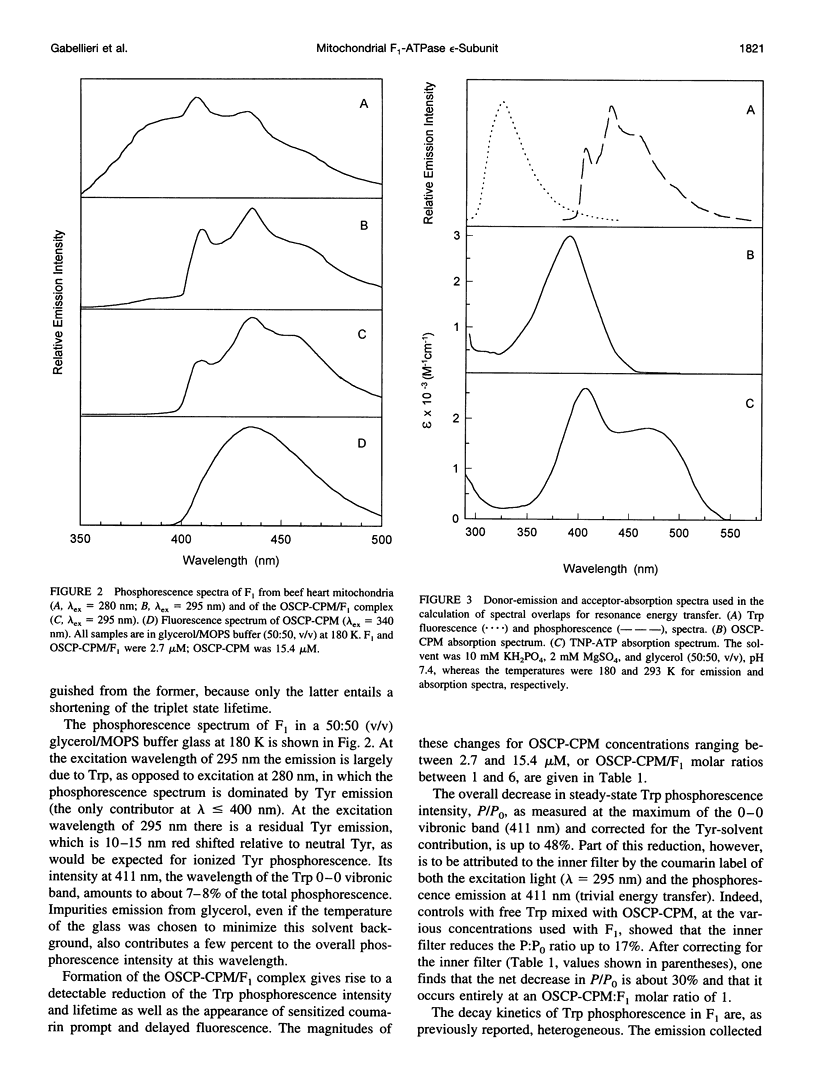
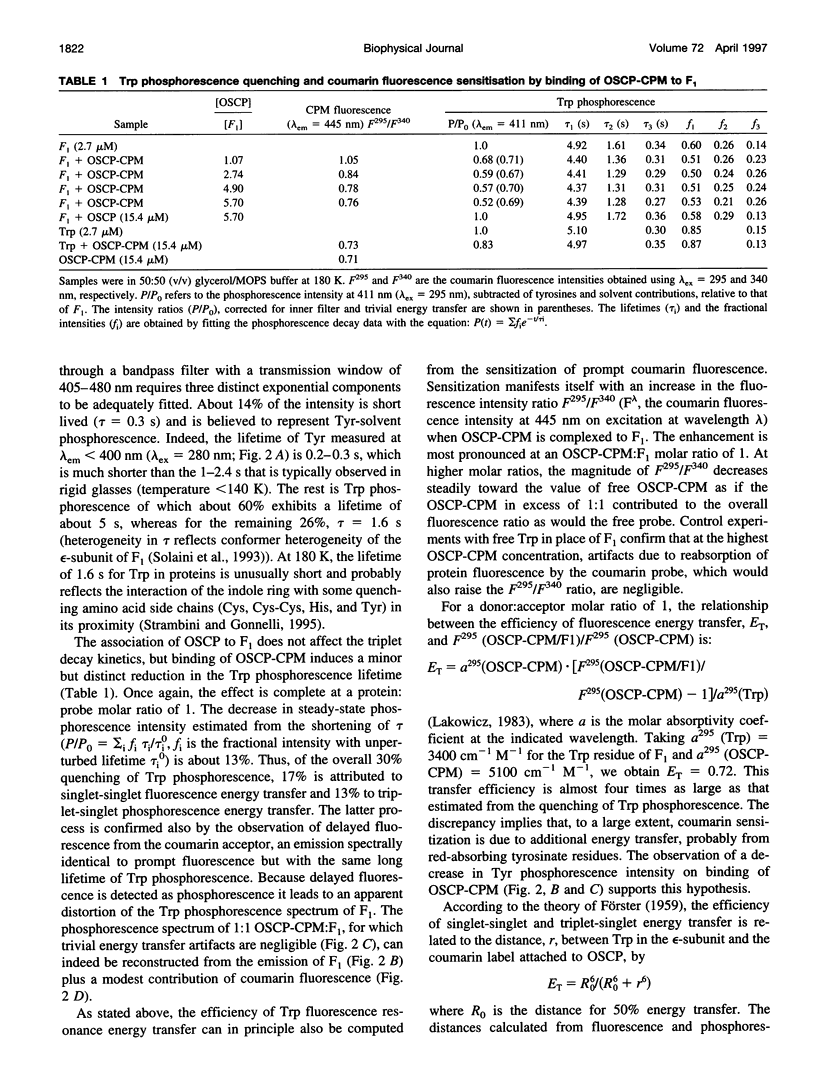


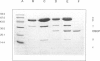
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams J. P., Leslie A. G., Lutter R., Walker J. E. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):621–628. doi: 10.1038/370621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams J. P., Lutter R., Todd R. J., van Raaij M. J., Leslie A. G., Walker J. E. Inherent asymmetry of the structure of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria at 6.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1775–1780. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird B. A., Hammes G. G. Chemical cross-linking studies of beef heart mitochondrial coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4743–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baracca A., Gabellieri E., Barogi S., Solaini G. Conformational changes of the mitochondrial F1-ATPase epsilon-subunit induced by nucleotide binding as observed by phosphorescence spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21845–21851. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beharry S., Bragg P. D. Conformational change in beef-heart mitochondrial F1 ATPase to ATP synthesis mode induced by dimethylsulfoxide and ATP revealed by sulfhydryl group labeling. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80975-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belogrudov G. I., Tomich J. M., Hatefi Y. ATP synthase complex. Proximities of subunits in bovine submitochondrial particles. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 3;270(5):2053–2060. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.5.2053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchet M., Ysern X., Hullihen J., Pedersen P. L., Amzel L. M. Mitochondrial ATP synthase. Quaternary structure of the F1 moiety at 3.6 A determined by x-ray diffraction analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21197–21201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D. A perspective of the binding change mechanism for ATP synthesis. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2164–2178. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2526771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D. The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase--some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 8;1140(3):215–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90063-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A. F1-ATPase in a spin. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Oct;1(10):660–663. doi: 10.1038/nsb1094-660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioni P., Strambini G. B. Dynamical structure of glutamate dehydrogenase as monitored by tryptophan phosphorescence. Signal transmission following binding of allosteric effectors. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson I. R., van Raaij M. J., Runswick M. J., Fearnley I. M., Skehel J. M., Orriss G. L., Miroux B., Walker J. E. ATP synthase from bovine heart mitochondria. In vitro assembly of a stalk complex in the presence of F1-ATPase and in its absence. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 30;242(4):408–421. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Nalin C. M. Adenine nucleotide binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Evidence for three exchangeable sites that are distinct from three noncatalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2874–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan T. M., Bulygin V. V., Zhou Y., Hutcheon M. L., Cross R. L. Rotation of subunits during catalysis by Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 21;92(24):10964–10968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.10964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis A., Lunardi J., Issartel J. P., Vignais P. V. Interactions between the oligomycin sensitivity conferring protein (OSCP) and beef heart mitochondrial F1-ATPase. 2. Identification of the interacting F1 subunits by cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):734–739. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duszynski J., Dupuis A., Lux B., Vignais P. V. Spectral properties of fluorescent derivatives of the oligomycin sensitivity conferring protein and analysis of their interaction with the F1 and F0 sectors of the mitochondrial ATPase complex. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6288–6296. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A. Exposure of tryptophanyl residues in proteins. Quantitative determination by fluorescence quenching studies. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):672–680. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNANDEZ-MORAN H. Cell-membrane ultrastructure. Low-temperature electron microsopy and x-ray diffraction studies of lipoprotein components in lamellar systems. Circulation. 1962 Nov;26:1039–1065. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.26.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galley W. C., Stryer L. Triplet-singlet energy transfer in proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):1831–1838. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser M. J., Myers J. A., Boyer P. D. Catalytic site cooperativity of beef heart mitochondrial F1 adenosine triphosphatase. Correlations of initial velocity, bound intermediate, and oxygen exchange measurements with an alternating three-site model. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12030–12038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S. The presence of two hydrolytic sites on beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3718–3727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issartel J. P., Lunardi J., Vignais P. V. Characterization of exchangeable and nonexchangeable bound adenine nucleotides in F1-ATPase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):895–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi S., Burrows R. ATP synthase complex from bovine heart mitochondria. Subunit arrangement as revealed by nearest neighbor analysis and susceptibility to trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14518–14525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muneyuki E., Hisabori T., Allison W. S., Jault J. M., Sasayama T., Yoshida M. Catalytic cooperativity of beef heart mitochondrial F1-ATPase revealed by using 2',3'-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-ATP as a substrate; an indication of mutually activating catalytic sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Nov 1;1188(1-2):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(94)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murataliev M. B., Boyer P. D. Interaction of mitochondrial F1-ATPase with trinitrophenyl derivatives of ATP and ADP. Participation of third catalytic site and role of Mg2+ in enzyme inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15431–15439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orriss G. L., Runswick M. J., Collinson I. R., Miroux B., Fearnley I. M., Skehel J. M., Walker J. E. The delta- and epsilon-subunits of bovine F1-ATPase interact to form a heterodimeric subcomplex. Biochem J. 1996 Mar 1;314(Pt 2):695–700. doi: 10.1042/bj3140695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S., Cross R. L. Structure and mechanism of FoF1-type ATP synthases and ATPases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1991;64:173–214. doi: 10.1002/9780470123102.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penin F., Deléage G., Gagliardi D., Roux B., Gautheron D. C. Interaction between delta and epsilon subunits of F1-ATPase from pig heart mitochondria. Circular dichroism and intrinsic fluorescence of purified and reconstituted delta epsilon complex. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9358–9364. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter M. L., Snyder B., McCarty R. E., Hammes G. G. Binding stoichiometry and structural mapping of the epsilon polypeptide of chloroplast coupling factor 1. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5755–5763. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E. ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jan;68(1):177–231. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. B., Gibson K. D., Scheraga H. A., McCarty R. E. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer mapping of the fourth of six nucleotide-binding sites of chloroplast coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17276–17285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaini G., Baracca A., Parenti Castelli G., Strambini G. B. Tryptophan phosphorescence as a structural probe of mitochondrial F1-ATPase epsilon-subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 15;214(3):729–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strambini G. B., Cioni P., Peracchi A., Mozzarelli A. Characterization of tryptophan and coenzyme luminescence in tryptophan synthase from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7527–7534. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence spectroscopy of proteins. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):526–533. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedge H., Schäfer G. Site-site interaction on mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Functional symmetry of the high-affinity nucleotide binding sites. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Aug;367(8):689–694. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Maclennan D. H., Byington K. H. Studies on the mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase system. 3. Isolation from the oligomycin-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase complex of the factors which bind F-1 and determine oligomycin sensitivity of bound F-1. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1596–1602. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Fearnley I. M., Gay N. J., Gibson B. W., Northrop F. D., Powell S. J., Runswick M. J., Saraste M., Tybulewicz V. L. Primary structure and subunit stoichiometry of F1-ATPase from bovine mitochondria. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):677–701. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Senior A. E. Binding and hydrolysis of TNP-ATP by Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 16;271(7):3474–3477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.7.3474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Wilke-Mounts S., Lee R. S., Grell E., Senior A. E. Specific placement of tryptophan in the catalytic sites of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase provides a direct probe of nucleotide binding: maximal ATP hydrolysis occurs with three sites occupied. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20126–20133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]