Abstract
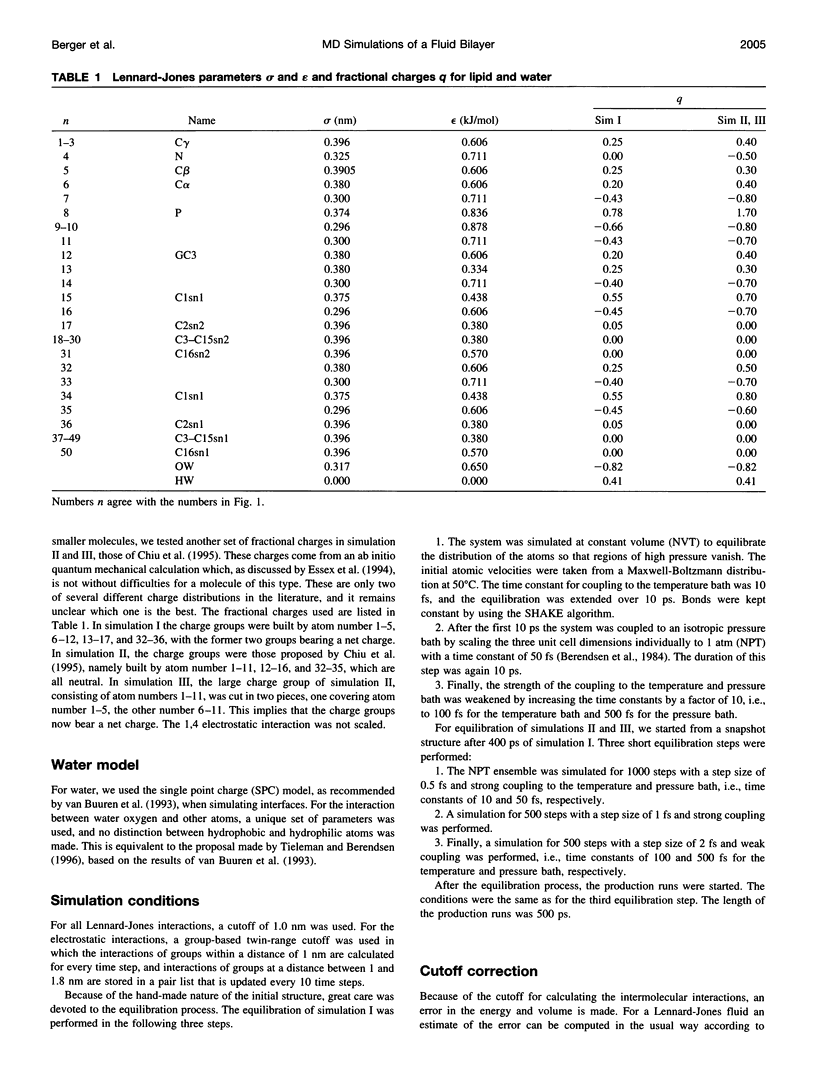
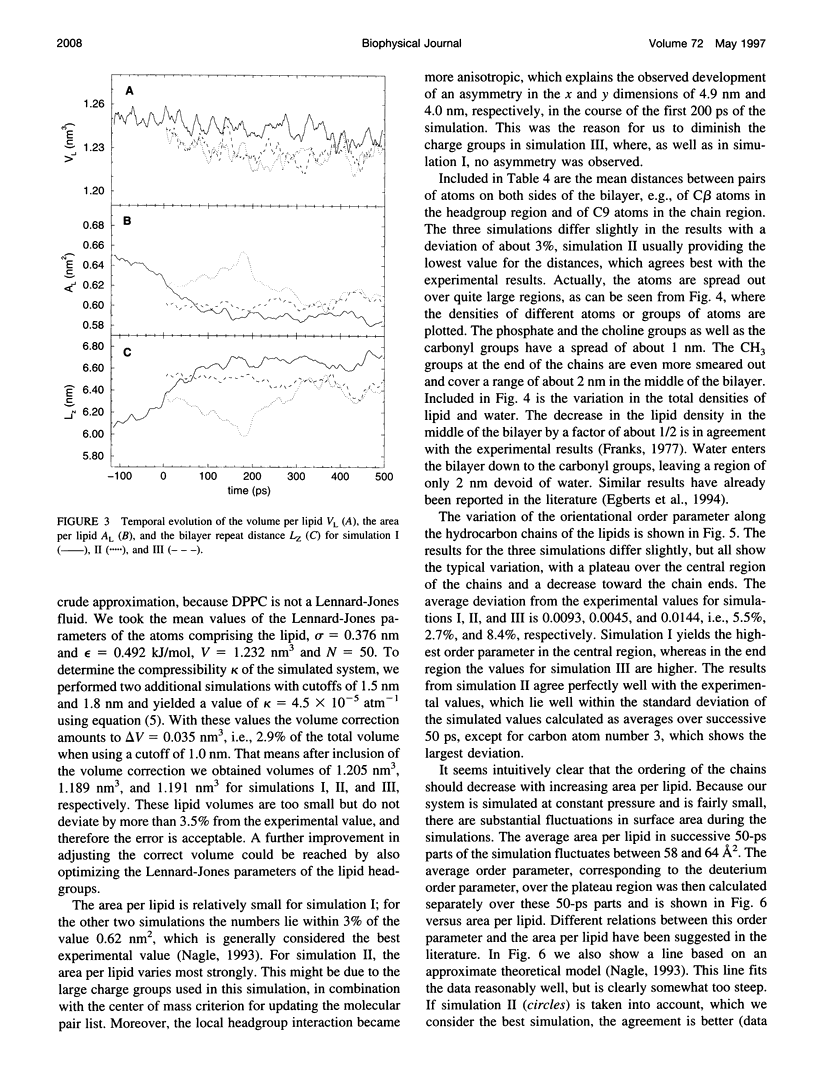
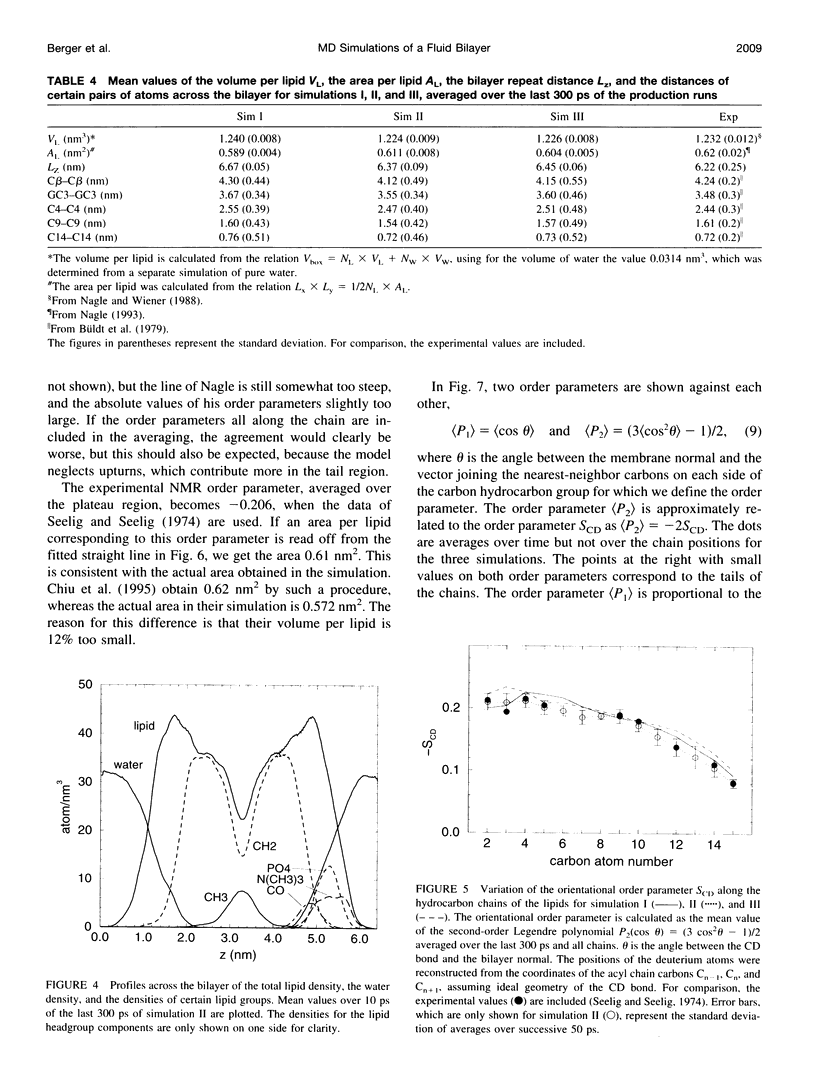
Molecular dynamics simulations of 500 ps were performed on a system consisting of a bilayer of 64 molecules of the lipid dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and 23 water molecules per lipid at an isotropic pressure of 1 atm and 50 degrees C. Special attention was devoted to reproduce the correct density of the lipid, because this quantity is known experimentally with a precision better than 1%. For this purpose, the Lennard-Jones parameters of the hydrocarbon chains were adjusted by simulating a system consisting of 128 pentadecane molecules and varying the Lennard-Jones parameters until the experimental density and heat of vaporization were obtained. With these parameters the lipid density resulted in perfect agreement with the experimental density. The orientational order parameter of the hydrocarbon chains agreed perfectly well with the experimental values, which, because of its correlation with the area per lipid, makes it possible to give a proper estimate of the area per lipid of 0.61 +/- 0.01 nm2.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassolino-Klimas D., Alper H. E., Stouch T. R. Solute diffusion in lipid bilayer membranes: an atomic level study by molecular dynamics simulation. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12624–12637. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Clark M., Balaji V., Subramaniam S., Scott H. L., Jakobsson E. Incorporation of surface tension into molecular dynamics simulation of an interface: a fluid phase lipid bilayer membrane. Biophys J. 1995 Oct;69(4):1230–1245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80005-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Young L. R., Dill K. A. Solute partitioning into lipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5281–5289. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egberts E., Marrink S. J., Berendsen H. J. Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid membrane. Eur Biophys J. 1994;22(6):423–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00180163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essex J. W., Hann M. M., Richards W. G. Molecular dynamics simulation of a hydrated phospholipid bilayer. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 May 28;344(1309):239–260. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P. Structural analysis of hydrated egg lecithin and cholesterol bilayers. I. X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):345–358. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Ruston D., Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Fuller N. Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1213–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81931-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig C. R., Reddy Y. S. Calcium, tropomyosin, and actomyosin as controls of calcium binding by troponin. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct Metab. 1975;8:233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P., Perez J. J., Loew G. H. Molecular dynamics simulations of phospholipid bilayers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Apr;11(5):927–956. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. What is the surface tension of a lipid bilayer membrane? Biophys J. 1996 Sep;71(3):1348–1349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79336-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. A., Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer thickness varies linearly with acyl chain length in fluid phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Area/lipid of bilayers from NMR. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1476–1481. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81514-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Structure of fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. J., Richards W. G., Thomas P. J., Hann M. M. Head group and chain behavior in biological membranes: a molecular dynamics computer simulation. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2345–2354. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80720-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu K., Tobias D. J., Klein M. L. Constant pressure and temperature molecular dynamics simulation of a fully hydrated liquid crystal phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biophys J. 1995 Dec;69(6):2558–2562. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80126-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Zhang Y., Hardy B. J., Pastor R. W. Molecular dynamics simulations of a lipid bilayer and of hexadecane: an investigation of membrane fluidity. Science. 1993 Oct 8;262(5131):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.8211140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



