Abstract
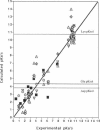
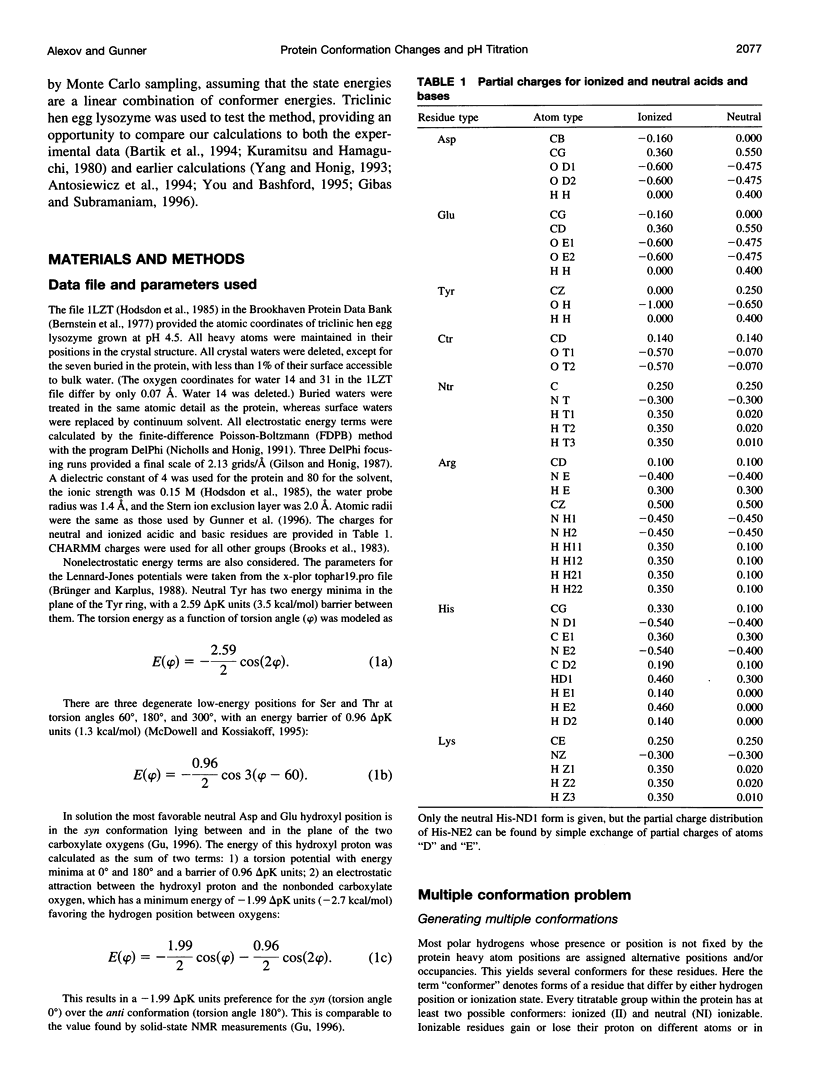
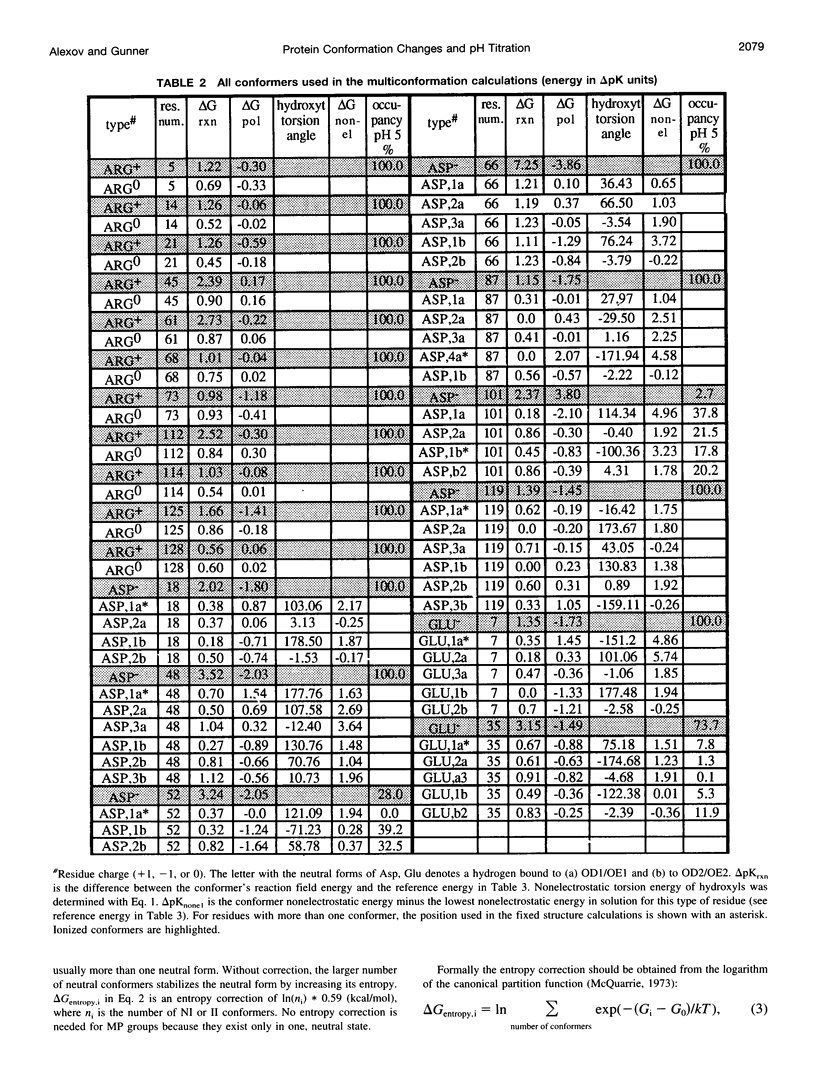
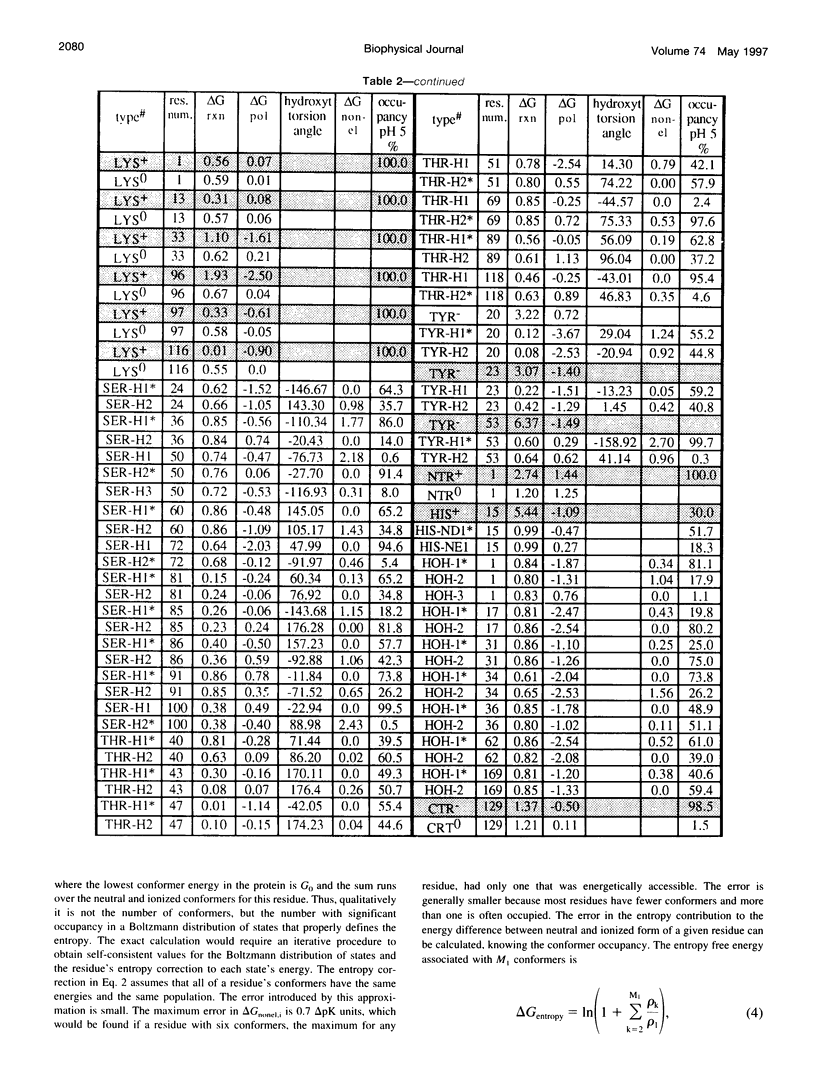
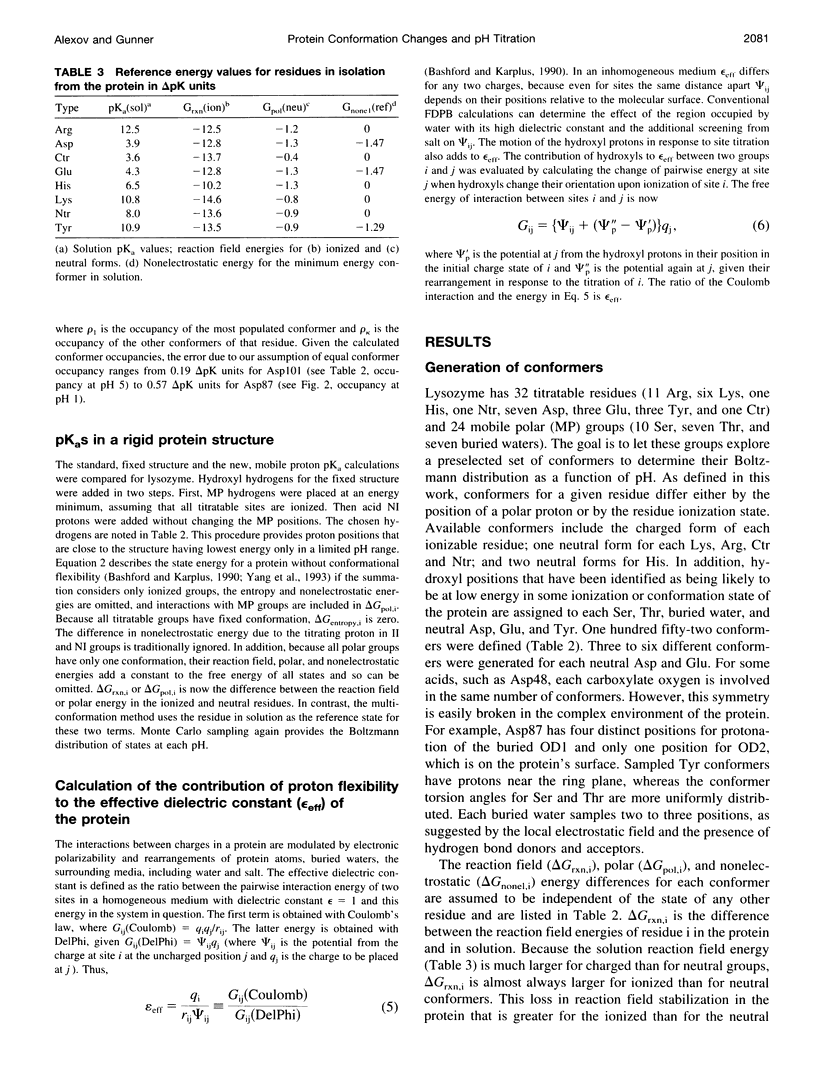
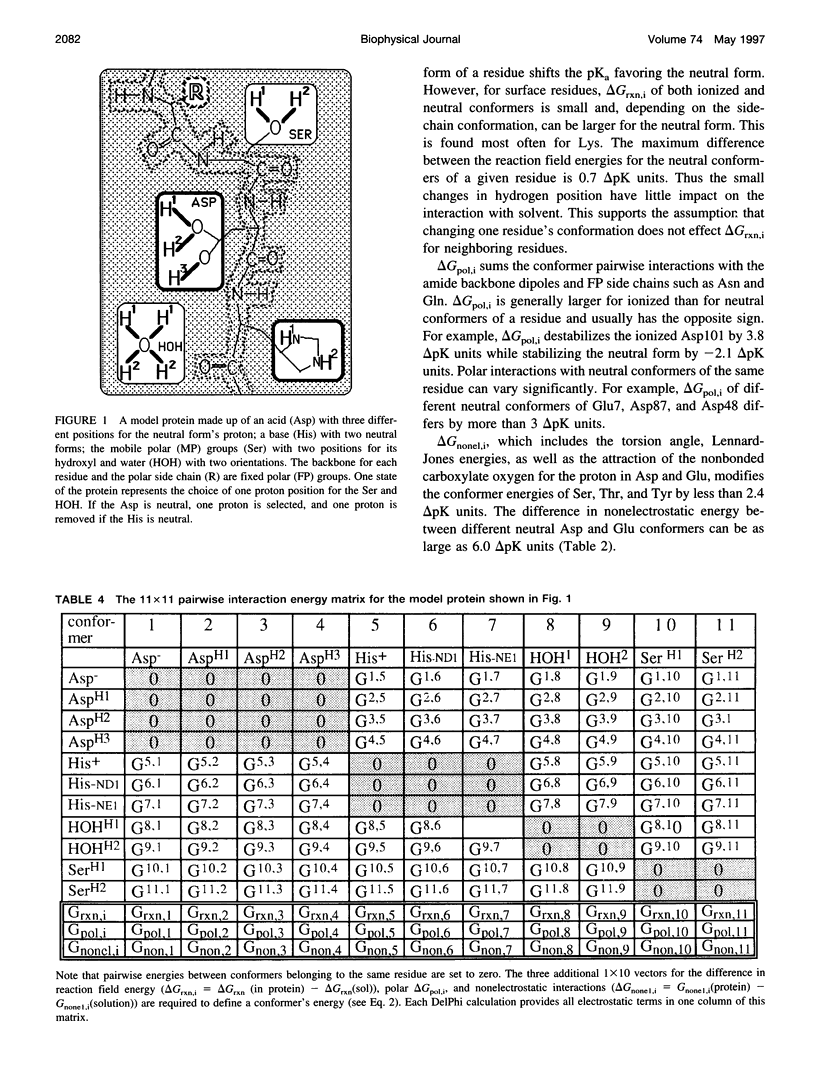
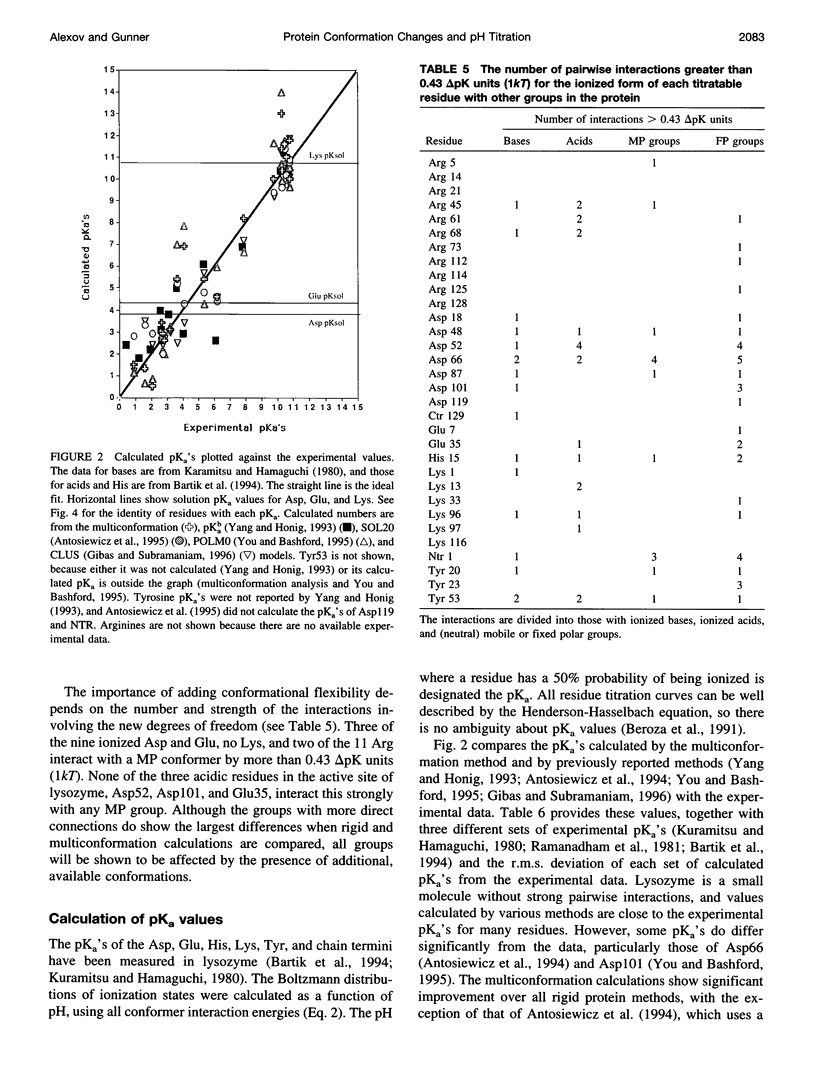
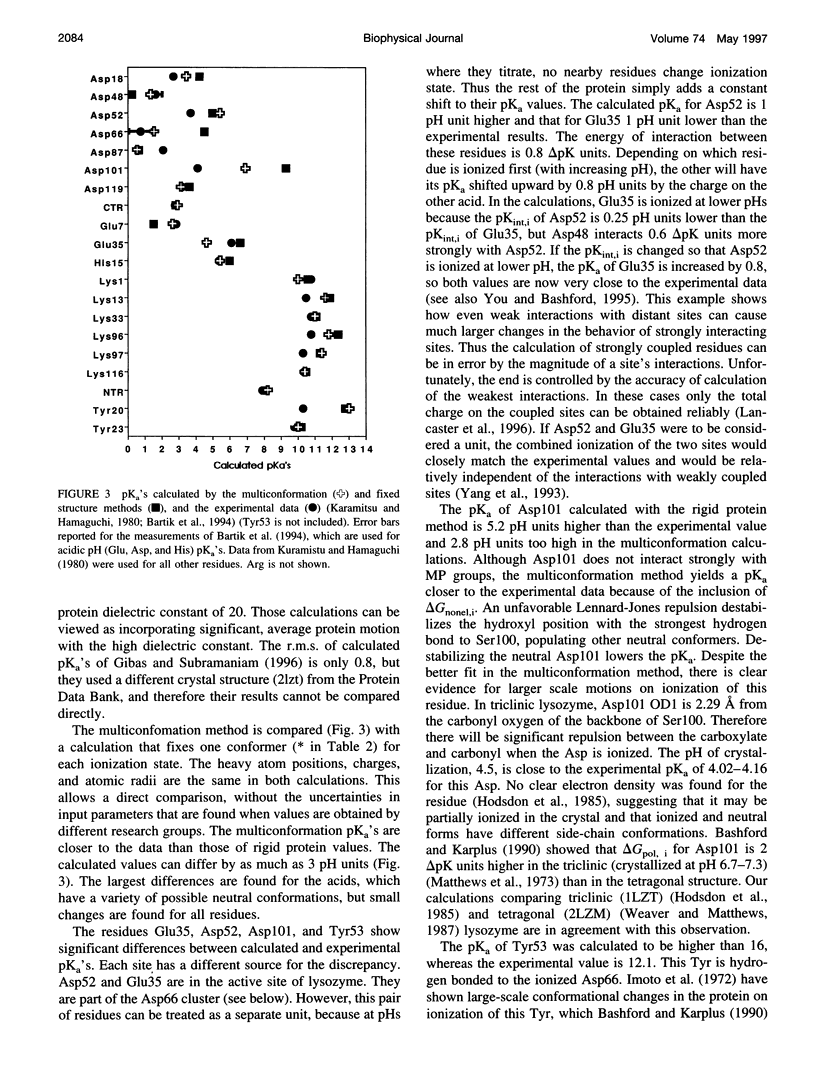
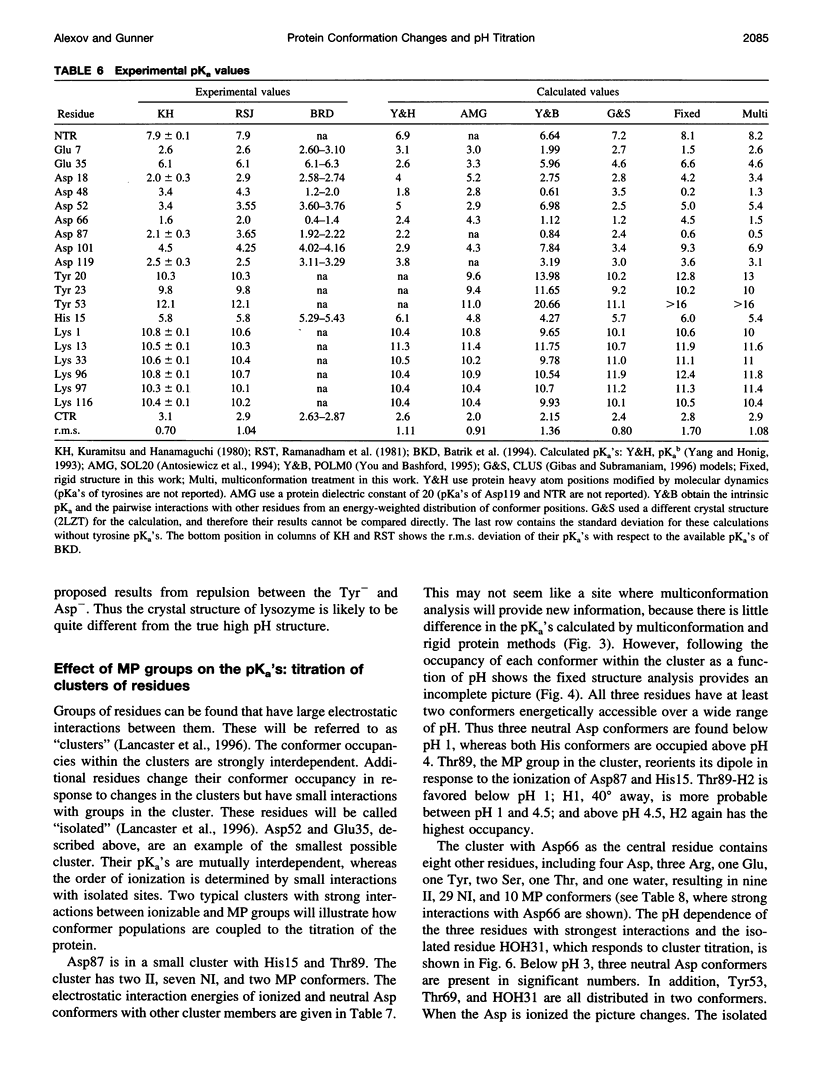
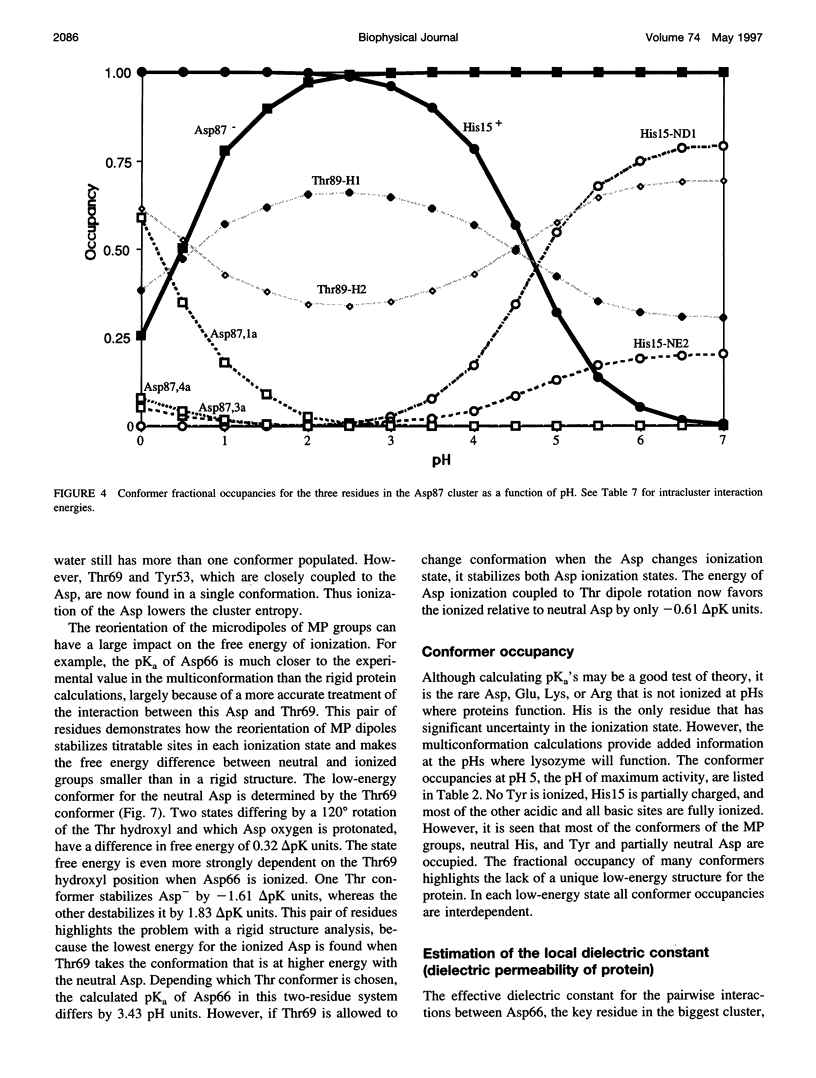
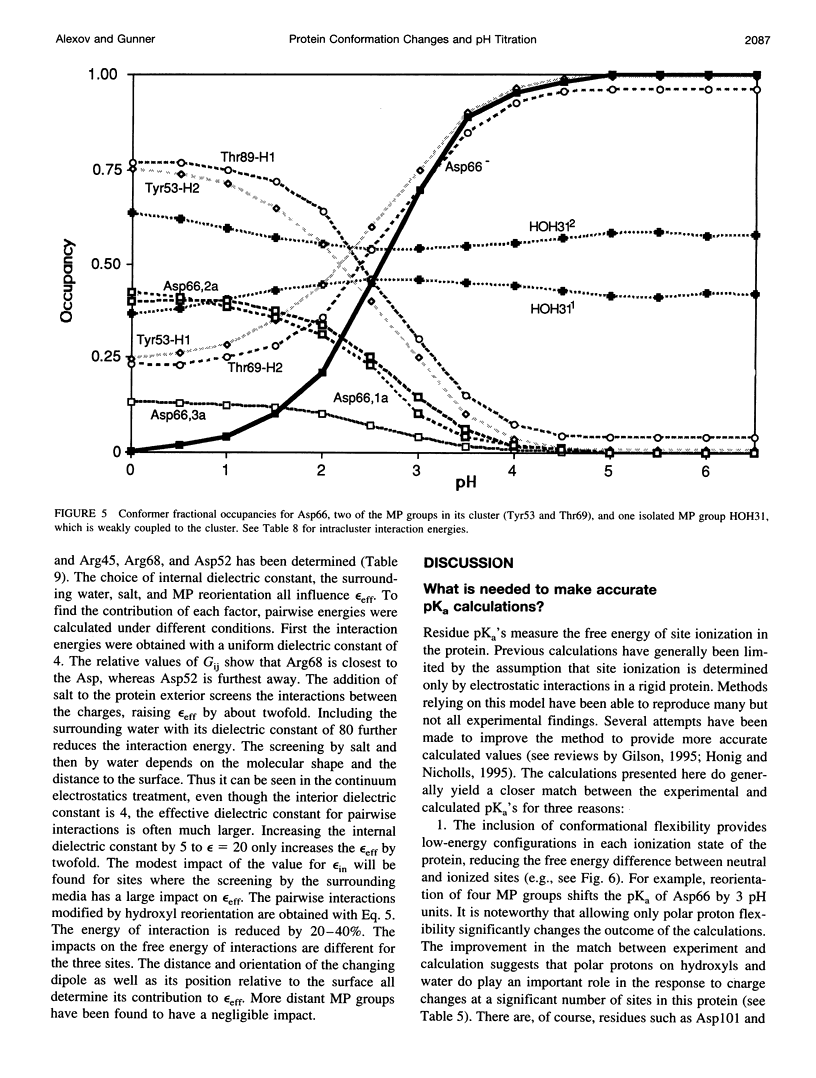
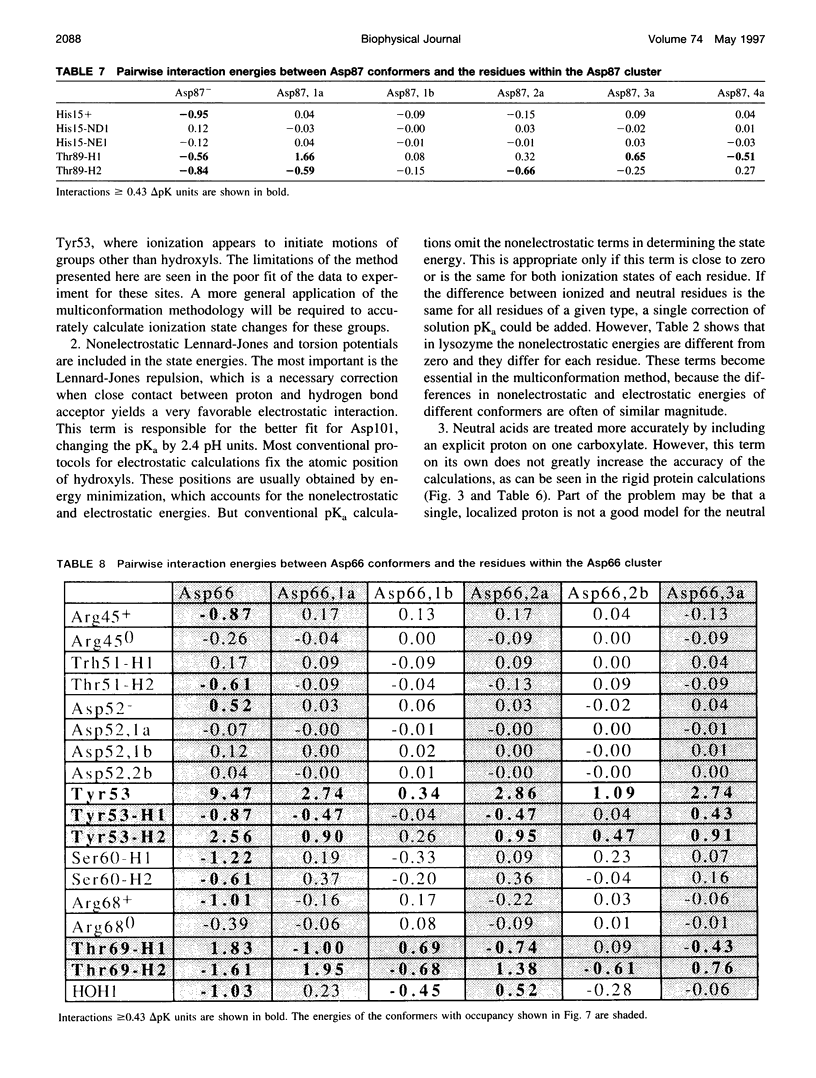
A method for combining calculations of residue pKa's with changes in the position of polar hydrogens has been developed. The Boltzmann distributions of proton positions in hydroxyls and neutral titratable residues are found in the same Monte Carlo sampling procedure that determines the amino acid ionization states at each pH. Electrostatic, Lennard-Jones potentials, and torsion angle energies are considered at each proton position. Many acidic and basic residues are found to have significant electrostatic interactions with either a water- or hydroxyl-containing side chain. Protonation state changes are coupled to reorientation of the neighboring hydroxyl dipoles, resulting in smaller free energy differences between neutral and ionized residues than when the protein is held rigid. Multiconformation pH titration gives better agreement with the experimental pKa's for triclinic hen egg lysozyme than conventional rigid protein calculations. The hydroxyl motion significantly increases the protein dielectric response, making it sensitive to the composition of the local protein structure. More than one conformer per residue is often found at a given pH, providing information about the distribution of low-energy lysozyme structures.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antosiewicz J., McCammon J. A., Gilson M. K. Prediction of pH-dependent properties of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 6;238(3):415–436. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antosiewicz J., McCammon J. A., Gilson M. K. The determinants of pKas in proteins. Biochemistry. 1996 Jun 18;35(24):7819–7833. doi: 10.1021/bi9601565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antosiewicz J., McCammon J. A., Wlodek S. T., Gilson M. K. Simulation of charge-mutant acetylcholinesterases. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 4;34(13):4211–4219. doi: 10.1021/bi00013a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N., Hubbard R. E. Hydrogen bonding in globular proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(2):97–179. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartik K., Redfield C., Dobson C. M. Measurement of the individual pKa values of acidic residues of hen and turkey lysozymes by two-dimensional 1H NMR. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80900-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Karplus M. pKa's of ionizable groups in proteins: atomic detail from a continuum electrostatic model. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10219–10225. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beroza P., Fredkin D. R., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. Protonation of interacting residues in a protein by a Monte Carlo method: application to lysozyme and the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5804–5808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone S., Pethig R. Dielectric studies of the binding of water to lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):571–575. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Karplus M. Polar hydrogen positions in proteins: empirical energy placement and neutron diffraction comparison. Proteins. 1988;4(2):148–156. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender R., Deng H. Nonresonance Raman difference spectroscopy: a general probe of protein structure, ligand binding, enzymatic catalysis, and the structures of other biomacromolecules. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:215–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibas C. J., Subramaniam S. Explicit solvent models in protein pKa calculations. Biophys J. 1996 Jul;71(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79209-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat J. F., Go N. Normal mode analysis of human lysozyme: study of the relative motion of the two domains and characterization of the harmonic motion. Proteins. 1990;8(3):258–279. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. Calculation of electrostatic potentials in an enzyme active site. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):84–86. doi: 10.1038/330084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. The dielectric constant of a folded protein. Biopolymers. 1986 Nov;25(11):2097–2119. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. Calculation of the total electrostatic energy of a macromolecular system: solvation energies, binding energies, and conformational analysis. Proteins. 1988;4(1):7–18. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K. Multiple-site titration and molecular modeling: two rapid methods for computing energies and forces for ionizable groups in proteins. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):266–282. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Rashin A., Fine R., Honig B. On the calculation of electrostatic interactions in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):503–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K. Theory of electrostatic interactions in macromolecules. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995 Apr;5(2):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(95)80079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunner M. R., Honig B. Electrostatic control of midpoint potentials in the cytochrome subunit of the Rhodopseudomonas viridis reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9151–9155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C. Treatment of electrostatic effects in macromolecular modeling. Proteins. 1989;5(1):78–92. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. A., Stenkamp R. E. Structures of met and azidomet hemerythrin at 1.66 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):723–737. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90113-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Nicholls A. Classical electrostatics in biology and chemistry. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1144–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.7761829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossiakoff A. A., Shpungin J., Sintchak M. D. Hydroxyl hydrogen conformations in trypsin determined by the neutron diffraction solvent difference map method: relative importance of steric and electrostatic factors in defining hydrogen-bonding geometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4468–4472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossiakoff A. A., Ultsch M., White S., Eigenbrot C. Neutron structure of subtilisin BPN': effects of chemical environment on hydrogen-bonding geometries and the pattern of hydrogen-deuterium exchange in secondary structure elements. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1211–1221. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Hamaguchi K. Analysis of the acid-base titration curve of hen lysozyme. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1215–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster C. R., Michel H., Honig B., Gunner M. R. Calculated coupling of electron and proton transfer in the photosynthetic reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biophys J. 1996 Jun;70(6):2469–2492. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79820-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Dahlquist F. W., Maynard A. Y. Letter: crystallographic data fro lysoxyme from bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):575–576. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90478-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell R. S., Kossiakoff A. A. A comparison of neutron diffraction and molecular dynamics structures: hydroxyl group and water molecule orientations in trypsin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jul 21;250(4):553–570. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. E., Vásquez J. R., Craik C. S., Yang A. S., Honig B., Fletterick R. J. Perturbing the polar environment of Asp102 in trypsin: consequences of replacing conserved Ser214. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3059–3064. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberoi H., Allewell N. M. Multigrid solution of the nonlinear Poisson-Boltzmann equation and calculation of titration curves. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81032-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Science. 1978 Sep 29;201(4362):1187–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.694508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll D. R., Vorobjev Y. N., Liwo A., Vila J. A., Scheraga H. A. Coupling between folding and ionization equilibria: effects of pH on the conformational preferences of polypeptides. J Mol Biol. 1996 Dec 13;264(4):770–783. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson T., Perahia D., Brünger A. T. Microscopic theory of the dielectric properties of proteins. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):670–690. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82282-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Schwan H. P. Dielectric dispersion of crystalline powders of amino acids, peptides, and proteins. J Phys Chem. 1965 Dec;69(12):4176–4182. doi: 10.1021/j100782a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turano P., Ferrer J. C., Cheesman M. R., Thomson A. J., Banci L., Bertini I., Mauk A. G. pH, electrolyte, and substrate-linked variation in active site structure of the Trp51Ala variant of cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 24;34(42):13895–13905. doi: 10.1021/bi00042a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varadarajan R., Lambright D. G., Boxer S. G. Electrostatic interactions in wild-type and mutant recombinant human myoglobins. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3771–3781. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Russell S. T. Calculations of electrostatic interactions in biological systems and in solutions. Q Rev Biophys. 1984 Aug;17(3):283–422. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwicker J., Watson H. C. Calculation of the electric potential in the active site cleft due to alpha-helix dipoles. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. H., Matthews B. W. Structure of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme refined at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Gunner M. R., Sampogna R., Sharp K., Honig B. On the calculation of pKas in proteins. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):252–265. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. Free energy determinants of secondary structure formation: I. alpha-Helices. J Mol Biol. 1995 Sep 22;252(3):351–365. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. On the pH dependence of protein stability. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):459–474. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. Structural origins of pH and ionic strength effects on protein stability. Acid denaturation of sperm whale apomyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):602–614. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You T. J., Bashford D. Conformation and hydrogen ion titration of proteins: a continuum electrostatic model with conformational flexibility. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1721–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80042-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zauhar R. J., Morgan R. S. A new method for computing the macromolecular electric potential. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90399-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]